The Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) has long served as the backbone of structured software development. This comprehensive guide on sdlc automation guides development teams through essential stages including planning, design, development, testing, deployment, and maintenance.

Challenges in Traditional SDLC
Traditional software development approaches encounter several significant obstacles:
- Time-Consuming Testing: The testing phase is extraordinarily time-consuming and vulnerable to human error
- Redundant Coding Tasks: Development processes frequently involve repetitive tasks that drain valuable resources and introduce delays
- Complexity Management: Modern applications create bottlenecks that slow innovation and increase costs
- Speed vs. Quality Dilemma: Teams struggle to balance thoroughness with the need for rapid delivery
- Error-Prone Processes: Manual processes, from code reviews to testing procedures, are vulnerable to mistakes
- Resource Allocation Challenges: Project managers lack adequate predictive tools to distribute talent and time effectively
The AI Revolution in Software Development
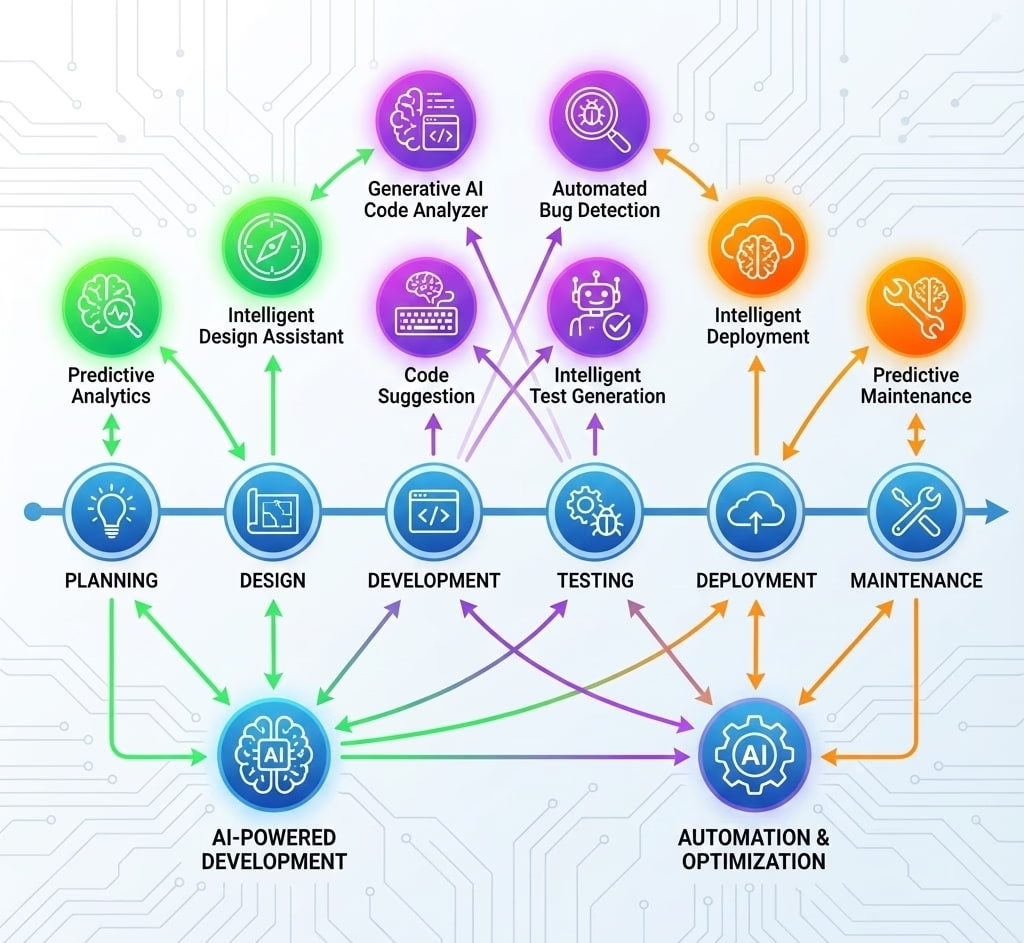
The integration of Artificial Intelligence into the SDLC, in short ai sdlc represents a transformative shift that addresses these fundamental challenges. AI technologies bring unprecedented capabilities to each development phase:
- Driving efficiency across all stages
- Improving accuracy in development and testing
- Enabling a more agile and responsive development process
- Fundamentally reimagining how software is conceived, built, tested, and maintained
AI’s Transformative Role Across SDLC
Automation of Repetitive Tasks
AI excels at handling mundane, repetitive tasks that consume developer time:
- Code Analyzers: Streamline workflows by automating code generation
- Auto-Completion Tools: Speed up coding with intelligent suggestions
- Bug Detection Algorithms: Identify and fix bugs automatically
- Routine Checks: Conduct standard quality assessments without manual intervention
This automation liberates developers to focus on creative problem-solving and architectural innovation rather than mechanical tasks.
Predictive Analytics for Proactive Management
AI-based tools leverage historical data and pattern recognition to forecast issues before they materialize:
- Predict potential bottlenecks in the development process
- Identify resource allocation problems early
- Forecast likely delays and their causes
- Alert teams to emerging issues proactively
This transforms project management from reactive firefighting to proactive optimization.
Data-Driven Decision Making
AI empowers intelligent decision-making throughout the development lifecycle:
- Resource Allocation: Efficiently distribute team members and resources
- Tool Selection: Identify optimal tools and technologies for specific projects
- Risk Management: Manage risks with greater precision using data insights
- Pattern Detection: Surface insights from vast datasets that humans cannot detect manually
The Six Phases of an AI-Driven SDLC
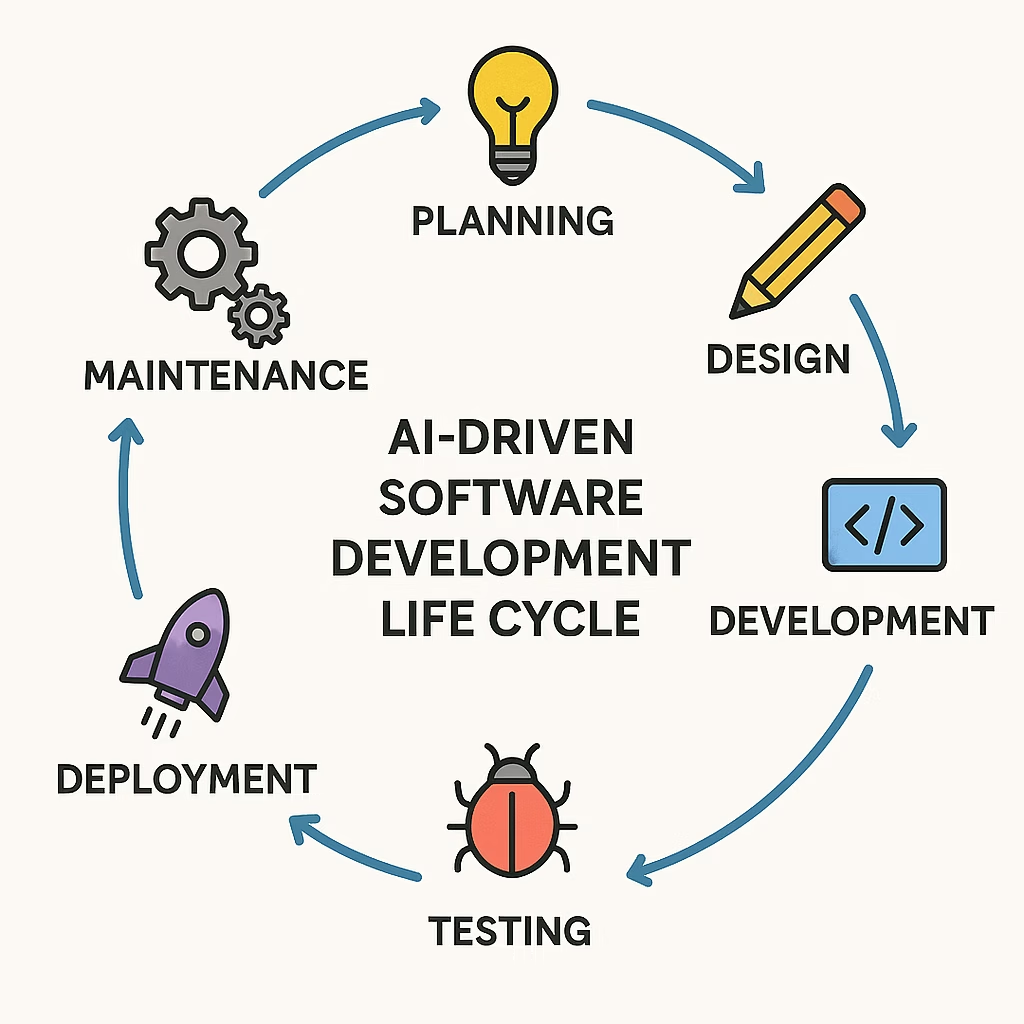
Phase 1: Planning – Foundation with Foresight
The planning phase sets the trajectory for the entire project. AI dramatically enhances its accuracy and reliability through:
AI-Enhanced Planning:
- Machine learning models analyze historical data from similar projects
- Create realistic timelines based on past successes and failures
- Predict project complexity with remarkable accuracy
Intelligent Risk Management:
- Identify potential risks early by analyzing project parameters
- Evaluate market conditions and external factors
- Consider emerging technologies and competitor behavior
- Enable teams to develop mitigation strategies before risks materialize
Optimized Resource Allocation:
- Analyze historical performance data and team expertise
- Match technical skill sets with project requirements
- Suggest optimal resource allocation strategies
- Ensure the right people are assigned to appropriate tasks
- Maximize productivity while minimizing waste
Phase 2: Design – Intelligent Architecture
The design phase benefits enormously from AI’s analytical and generative capabilities:
AI for Design Optimization:
- Generative design algorithms optimize user interfaces
- System architectures become more efficient
- Designs align with user expectations
- Technical debt is minimized from the outset
Automated Prototyping:
- AI assists in rapid prototype creation of user interfaces and features
- Dramatically shortens the design iteration cycle
- Enables more experimentation through faster feedback loops
- Results in better-designed products
Phase 3: Development – Augmented Coding
Development represents perhaps the most visible transformation in the AI-driven SDLC.
Automated Code Generation:
- AI-powered tools like GitHub Copilot and Tabnine offer intelligent auto-completion
- Generate entire functions based on natural language descriptions
- Developers describe intentions in plain language
- AI translates descriptions into working code
- Development velocity is greatly accelerated
AI-Powered Code Reviews:
- AI systems conduct continuous code reviews during development
- Scan for common errors and security vulnerabilities
- Check adherence to best practices and coding standards
- Provide real-time feedback to developers
- Ensure high-quality code output
- Catch issues before they propagate through the system
Phase 4: Testing – Comprehensive and Intelligent
Testing traditionally consumes substantial time and resources, but AI transforms it into a faster, more thorough process.
AI-Powered Automated Testing:
- Handle regression testing, unit testing, and functional testing with minimal human intervention
- Simulate various user interactions automatically
- Identify edge cases that humans might overlook
- Dramatically reduce manual effort required
Predictive Testing Strategies:
- AI predicts which code sections are most likely to fail
- Analysis based on historical patterns and code complexity
- Testing efforts focus on high-risk areas
- Maximize efficiency of quality assurance resources
Pattern-Based Bug Detection:
- Machine learning algorithms learn from previously detected bugs
- Identify patterns and signatures of common issues
- Automatically detect similar problems in new code
- Catch bugs before they reach production
- Improve detection accuracy over time with each project
Phase 5: Deployment – Strategic Release Management
Deployment strategies become significantly more sophisticated with AI assistance.
AI-Optimized Deployment:
- Predict optimal deployment windows based on usage patterns
- Analyze system load and historical data
- Reduce downtime through intelligent timing
- Increase deployment success rates
- Minimize negative impact on users
Enhanced CI/CD Pipelines:
- AI predicts the likelihood of build failures before they occur
- Automatically triggers rollbacks when issues are detected
- Ensures smoother, faster deployments
- Reduces stress and risk associated with releasing new versions
Phase 6: Maintenance – Proactive System Care
Maintenance shifts from reactive problem-solving to proactive system optimization.
Predictive Maintenance:
- AI models analyze usage patterns and system performance
- Review historical maintenance data
- Predict which components are likely to require attention
- Allow developers to address issues before they cause significant problems
- Prevent user impact through proactive intervention
Real-Time Monitoring and Resolution:
- AI continuously monitors software systems in production
- Watch for performance degradation
- Detect security vulnerabilities
- Identify service interruptions
- Often detect and resolve issues automatically
- Sometimes fix problems before users notice
- Ensure system reliability and user satisfaction
The Compelling Benefits of AI-Driven SDLC
Dramatically Increased Efficiency
The cumulative effect of AI automation across all phases produces dramatic improvements:
- Automation of repetitive tasks frees developers for higher-level work
- Teams focus on problem-solving, architectural decisions, and innovation
- Accomplish more with the same resources
- Complete work faster with fewer resources
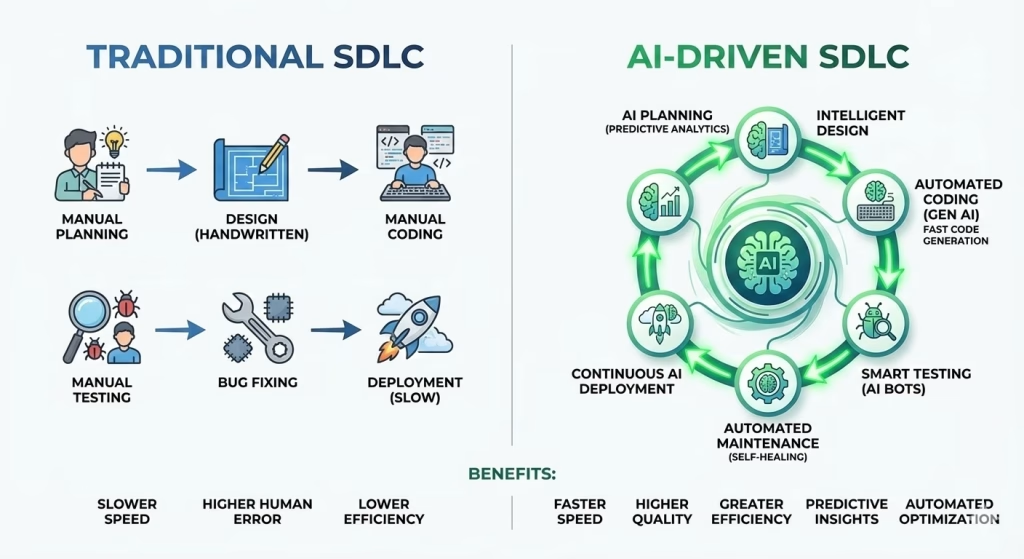
Superior Code Quality
AI-driven code review and testing deliver measurably better outcomes:
- Fewer bugs in production code
- Higher application performance
- More secure applications
- Consistent AI analysis catches issues human reviewers might miss
- Software becomes more reliable, maintainable, and secure
Accelerated Time to Market
AI-driven SDLC delivers significant speed advantages:
- Predictive models optimize planning phases
- AI-assisted development speeds coding
- Enhanced testing catches issues faster
- Intelligent deployment reduces release risk
- Products reach the market faster without sacrificing quality
Continuous Learning and Improvement
Unlike static processes, AI systems evolve with every project:
- Prediction accuracy improves over time
- Bug detection becomes more sophisticated
- Decision-making recommendations grow more nuanced
- Each project makes the next one better
- Creates a virtuous cycle of continuous improvement
The Future: Toward Autonomous Development
The trajectory of AI in software development points toward even more profound transformations:
- Boundaries between AI and human developers continue to blur
- AI takes on increasingly sophisticated tasks
- Future may see fully autonomous development cycles for certain projects
- AI could handle everything from requirements analysis through deployment and maintenance
The Evolving Role of Developers:
Developers won’t become obsolete – they’ll evolve:
- Focus on higher-level strategy and innovation
- Concentrate on creative aspects AI cannot replicate
- Become orchestrators and architects
- Define what should be built and why
- Let AI handle much of the how
Future Capabilities:
As AI capabilities advance:
- Development cycles become faster, more efficient, and more reliable
- Software is built better and deployed faster
- Maintenance becomes more effective
- The AI-driven SDLC represents a fundamental reimagining of software creation
Conclusion
The integration of AI into the Software Development Life Cycle addresses critical limitations of traditional approaches while unlocking new possibilities for innovation.
Key Transformations:
- Intelligent planning with predictive capabilities
- Design optimization through AI algorithms
- Automated development with code generation
- Comprehensive AI-powered testing
- Strategic deployment timing
- Proactive maintenance strategies
Competitive Advantages:
- Faster delivery of products and features
- Higher quality outputs
- More efficient resource utilization
- Continuous improvement over time
Organizations that embrace AI-driven SDLC gain significant competitive advantages. As AI technologies continue to evolve, these advantages will only grow more pronounced. The future of software development is not just faster or cheaper – it’s fundamentally smarter, more responsive, and more capable of delivering the sophisticated solutions that modern challenges demand.
How could ai help optimize software performance during the sdlc?
AI optimizes software performance across the SDLC by predicting bottlenecks early, generating performance test cases, analyzing logs and traces, detecting inefficient code paths, and recommending fixes. It improves speed, scalability, and reliability through automated profiling, anomaly detection, and continuous performance monitoring in CI/CD.
What are the benefits of ai in software development?
AI improves software development by speeding up coding, reducing bugs, and automating testing and reviews. It boosts developer productivity with code suggestions, faster debugging, smarter documentation, and better planning, while improving software quality through early defect detection, security scanning, and continuous monitoring.
How to use ai in software development?
Use AI in software development to generate and refactor code, write unit tests, review pull requests, detect bugs and security issues, analyze logs, and automate documentation. Integrate AI into IDEs and CI/CD pipelines for continuous code quality checks, faster debugging, and performance monitoring.
What are the risks of ai in software development?
Risks of AI in software development include insecure or incorrect code suggestions, hidden bugs, license or copyright issues, data leakage from sensitive prompts, and over-reliance that weakens developer review. Teams should use human validation, secure tooling, coding standards, and privacy controls to reduce risk.
What is the meaning of ai sdlc?
AI SDLC means using artificial intelligence across the software development lifecycle to plan, build, test, deploy, and maintain software faster and with higher quality. It includes AI for coding, automated testing, defect detection, performance optimization, security scanning, and monitoring.
This page was last edited on 29 January 2026, at 2:49 pm
Contact Us Now

Contact Us Now
Start a conversation with our team to solve complex challenges and move forward with confidence.










