Artificial Intelligence (AI) has evolved beyond static automation and scripted chatbots. One of the most important shifts in recent years is the rise of AI agent systems designed to reason, plan, and take actions toward specific goals by combining large language models, tools, and structured workflows.
Unlike traditional automation, AI agents can interpret context, decide what steps to take next, and coordinate multiple actions across systems while operating within predefined rules and safeguards. This makes them especially valuable for complex tasks such as decision support, workflow orchestration, customer operations, and data-driven automation.
This article explores what AI agents are, how they work, their core features, different types, and how they’re transforming industries around the world.
What Are AI Agents?
AI agents are intelligent software systems that can think, learn, and act autonomously. AI agents make decisions to reach specific goals based on predefined objectives, workflows, and human-configured instructions.
Unlike traditional automation or simple chatbots, AI agents can analyze situations, plan actions, and adapt to changes in real time. They don’t just follow pre-set rules; they reason through problems and choose the best way to complete a task.
For example, a customer service AI agent can handle support requests by identifying the problem, searching for solutions, and even taking actions such as updating records or recommending refunds within predefined rules and approval workflows.
Key Features of AI Agents
AI agents stand out because they can operate independently, adapt to change, and make smart decisions. Below are the key features that define them:
1. Autonomy
AI agents can perform tasks without constant human supervision. Once given a goal, they decide what actions to take and how to achieve the best outcome on their own.
2. Goal-Oriented Behavior
Every AI agent works toward a specific objective. It evaluates its environment, identifies what’s needed, and plans steps to reach that goal efficiently.
3. Perception
Through sensors, data inputs, or connected systems, AI agents can “see” what’s happening around them. They gather and interpret information to understand their environment.
4. Rationality
AI agents make logical, data-driven decisions. They compare possible actions and choose the one most likely to succeed based on their analysis.
5. Proactivity
Rather than waiting for instructions, AI agents take initiative. They anticipate needs, detect opportunities, and act to improve results or prevent problems.
6. Continuous Learning
By analyzing feedback from their actions, AI agents learn what works and what doesn’t. This allows them to improve accuracy and performance over time.
7. Adaptability
AI agents adjust their behavior when conditions change. Whether new data appears or unexpected events happen, they can re-plan and respond effectively.
8. Collaboration
Many AI agents can communicate and work together with humans or other agents. This teamwork helps them solve complex, multi-step tasks faster and more efficiently.

AI Agents vs LLM Agents vs Agentic AI
The terms AI agents, LLM agents, and agentic AI are often used as if they mean the same thing. In reality, they describe different levels of intelligence, flexibility, and system design. Understanding the difference helps teams choose the right approach for automation and AI-driven workflows.
AI Agents
AI agents are systems built to achieve specific goals by observing inputs, making decisions, and taking action. They usually operate within clear rules, predefined workflows, and safety constraints.
They may use traditional machine learning, rules, or language models, but their scope is typically task-focused such as automating processes, optimizing operations, or supporting decisions.
Best for: Structured automation, operational efficiency, and repeatable business tasks.
LLM Agents
LLM agents are a type of AI agent powered by large language models. Instead of only following fixed rules, they can reason through problems, plan steps, use tools or APIs, retrieve information, and adapt their responses based on context.
These agents are especially effective when working with unstructured data like text, documents, or conversations.
Best for: Research, customer support, data analysis, content workflows, and multi-step reasoning tasks.
Agentic AI
Agentic AI is not a single agent; it’s an architecture. It refers to systems where multiple agents, tools, and models work together to handle complex goals.
Agentic AI systems often include orchestration layers, shared memory, monitoring, and human oversight. The focus is on coordination, governance, and scalability, not full autonomy.
Best for: Enterprise-scale systems, complex workflows, and long-running processes that require control and visibility.
Key Differences at a Glance
| Feature | AI Agents | LLM Agents | Agentic AI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Main Role | Execute defined tasks | Reason and act using language | Coordinate multiple agents |
| Intelligence Source | Rules, ML, or LLMs | Large language models | Agents + tools + orchestration |
| Autonomy | Limited and controlled | Moderate and tool-guided | Structured and governed |
| Typical Scope | Single-task automation | Multi-step problem solving | End-to-end intelligent systems |
Most modern systems use all three concepts together. Organizations often start with basic AI agents, enhance them with LLM agents for reasoning, and evolve toward agentic AI architectures as workflows become more complex.
This layered approach allows businesses to gain flexibility and intelligence without losing control, safety, or accountability.
Types of AI Agents
AI agents come in several types, each with its own way of thinking, acting, and learning. These types range from simple rule-based systems to advanced learning agents capable of reasoning and adaptation.
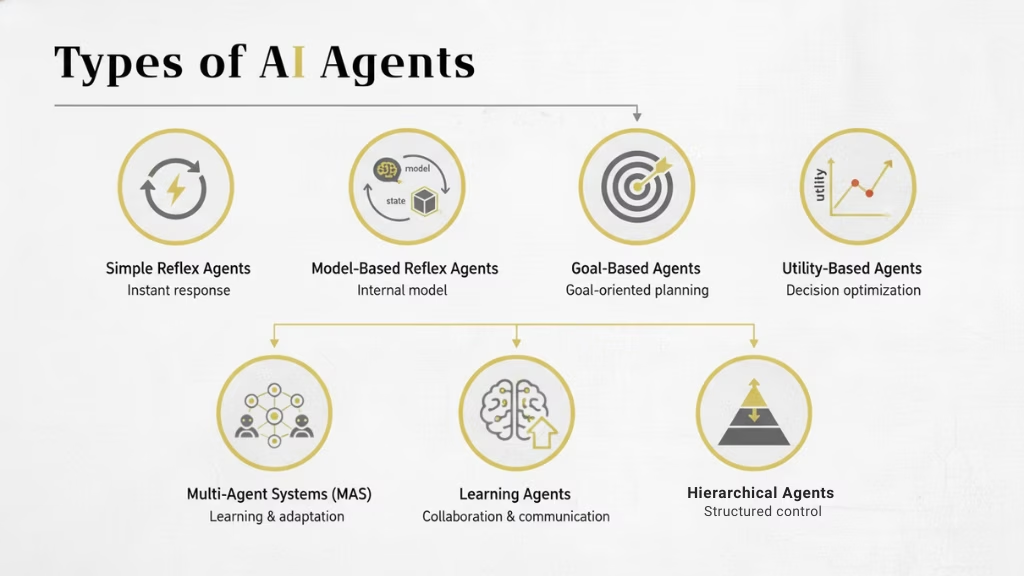
1. Simple Reflex Agents
Simple Reflex Agents follow a basic set of “if–then” rules to react instantly to changes in their environment. They don’t store any history or learn from past actions.
Example: A thermostat that turns on heating when the temperature drops below a set level. These agents are fast and efficient for simple tasks but struggle with complex or unpredictable situations.
2. Model-Based Reflex Agents
Model-Based Reflex Agents use an internal model of the environment to make better decisions. They track information about what has happened before, allowing them to work in partially observable environments.
Example: A robot vacuum that maps a room to remember which areas it has already cleaned.
3. Goal-Based Agents
Goal-Based Agents think ahead and plan actions to achieve specific goals. They evaluate different possibilities and choose the best path toward their target.
Example: A self-driving car that plans the safest and fastest route to its destination.
4. Utility-Based Agents
Utility-Based Agents aim to achieve the best possible outcome rather than just meeting a goal. They assign a value, or “utility,” to each possible action and pick the one with the highest benefit.
Example: A ride-hailing app’s AI that chooses routes balancing wait time, cost, and comfort.
5. Learning Agents
Learning Agents can improve their performance over time by learning from experience. They analyze feedback, detect what worked or failed, and adapt their strategies to perform better.
Example: A recommendation engine that refines its suggestions based on user behavior and feedback.
6. Multi-Agent Systems (MAS)
In many real-world applications, multiple agents operate together in what’s called a Multi-Agent System (MAS). Each agent functions independently but can collaborate or compete with others to complete shared tasks.
a. Cooperative MAS
Agents work together toward a shared goal.
Example: Robots in a warehouse coordinate to move packages efficiently.
b. Competitive MAS
Agents compete with one another to get the best results.
Example: AI trading bots competing to buy or sell assets at the best price.
c. Mixed MAS
Agents both cooperate and compete depending on the situation.
Example: AI players in a game may team up within groups but compete against rival teams.
7. Hierarchical Agents
Hierarchical Agents follow a layered structure where top-level agents handle planning and decision-making, while lower-level agents perform actions. This structure helps manage complex tasks efficiently.
Example: In a smart factory, a top-level agent plans production schedules, while lower-level agents control the machinery.
Architecture of AI Agents
The architecture of an AI agent defines how it thinks, learns, and acts. It is made up of several modules that work together to help the agent sense its environment, make decisions, and take action. Each module plays a specific role in ensuring the agent operates effectively and intelligently.
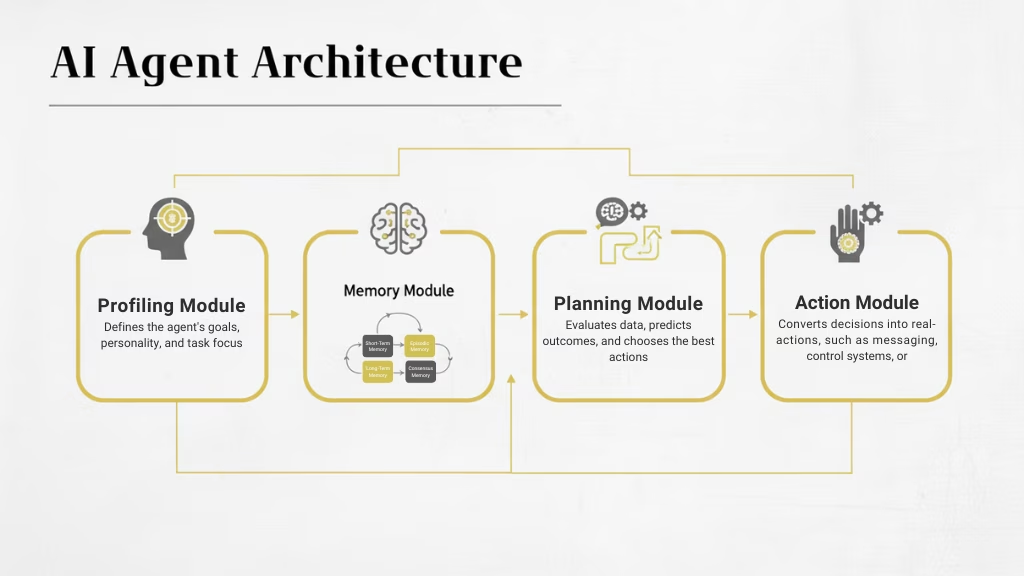
1. Profiling Module
The Profiling Module helps the agent understand its purpose, personality, and behavioral style. It defines who the agent is, including its goals, tone of communication, and the type of tasks it should perform. This module ensures that the agent’s actions stay aligned with its role and objectives.
2. Memory Module
The Memory Module allows the agent to remember information from past interactions and use it in the future. It includes different types of memory that work together:
- Short-Term Memory: Stores recent information for immediate tasks, such as a user’s latest question or command.
- Long-Term Memory: Keeps important data and experiences that help the agent improve performance over time.
- Episodic Memory: Records specific events or interactions, allowing the agent to recall past situations when needed.
- Shared Memory: Enables multiple agents to access common data stores or context, supporting coordination and consistent behavior.
3. Planning Module
The Planning Module helps the agent reason, plan, and make decisions. It evaluates available data, predicts possible outcomes, and selects the best series of actions to achieve its goals. This module gives the agent the ability to think ahead and handle complex, multi-step problems effectively.
4. Action Module
The Action Module executes the agent’s chosen tasks. It converts decisions into real actions such as sending messages, updating databases, triggering alerts, or controlling devices. This is where planning turns into real-world impact, making the agent capable of interacting with systems, humans, or the environment.
How Does an AI Agent Work?
AI agents work by combining goal-setting, information processing, and intelligent action to complete complex tasks automatically. Their workflow follows a simple but powerful cycle that allows them to operate independently and improve over time.
1. Setting the Goal
Every AI agent begins with a clear purpose or goal. It determines what needs to be achieved, whether that’s solving a problem, providing information, or completing a process. This goal guides every decision the agent makes throughout the task.
2. Gathering and Understanding Information
Once the goal is defined, the agent collects relevant information from its environment. It might use data from sensors, databases, user inputs, or external tools. The agent then processes and interprets this data to understand the current situation and decide what actions to take next.
3. Planning and Taking Action
With the information analyzed, the agent creates a plan and executes actions to reach its goal. These actions can include running commands, sending messages, updating systems, or even interacting with other agents. As it acts, the agent monitors outcomes and adjusts its behavior if necessary.
4. Learning and Improving
After completing each task, the agent reviews the results and learns from experience. It identifies what worked well and what didn’t, allowing it to perform better in the future. This feedback loop of action and learning helps AI agents become more accurate, efficient, and adaptive over time.
Benefits of AI Agents
AI agents bring powerful advantages to businesses and organizations by combining automation, intelligence, and adaptability. They help streamline operations, boost performance, and create more personalized user experiences.
1. Improved Productivity
AI agents can handle repetitive or time-consuming tasks quickly and accurately. By automating processes such as data entry, customer support, and analysis, they free up human employees to focus on creative and strategic work.
2. Reduced Costs
By automating daily operations and minimizing human errors, AI agents help organizations cut operational costs. They also predict issues early, like equipment failure or process inefficiencies, which saves money on repairs and downtime.
3. Informed Decision-Making
AI agents can process large amounts of data and deliver real-time insights. They help leaders make smarter, faster decisions by identifying patterns, trends, and opportunities that humans might miss.
4. Improved Customer Experience
AI agents offer personalized and consistent support around the clock. They respond instantly, learn from each interaction, and adapt to user preferences, creating smoother, more satisfying customer experiences.
Limitations of AI Agents
While AI agents offer many advantages, they also face certain challenges and limitations. Understanding these helps organizations plan better, manage risks, and use AI responsibly.
1. Data Privacy Concerns
AI agents rely on large amounts of data to learn and make decisions. If this data isn’t protected properly, it can lead to privacy risks and data breaches. Organizations must ensure that user information is handled securely and follows data protection laws like GDPR or HIPAA.
2. Ethical Challenges
AI agents sometimes make decisions that are hard to explain or may show bias if trained on unfair data. This creates ethical concerns around transparency, fairness, and accountability. Clear rules and human oversight are needed to ensure AI systems act responsibly.
3. Technical Complexities
Building, training, and maintaining AI agents requires advanced technical expertise. Integration with existing systems can be difficult, and agents may struggle when faced with unexpected situations or poor-quality data.
4. Limited Compute Resources
AI agents, especially those using large models, need significant computing power to run efficiently. This can lead to high costs and slower performance if resources are limited, particularly in smaller organizations.
Use Cases of AI Agents
AI agents are being used across many industries to automate complex tasks, improve accuracy, and make smarter decisions. They help businesses work faster, save costs, and provide better services. Below are some key areas where AI agents are making a real difference.
1. Financial Services
a. Personalized Client Service
AI agents can analyze client portfolios, spending habits, and financial goals to provide personalized recommendations. They assist customers with investment planning, credit management, and real-time support, improving both satisfaction and loyalty.
b. Enhanced Meeting Preparation
Financial advisors use AI agents to summarize client data, market trends, and key discussion points before meetings. This saves time and ensures every interaction is informed and productive.
2. Manufacturing & Operations
a. Predictive Maintenance and Production Optimization
AI agents continuously monitor machinery and production systems to predict failures before they happen. They also adjust schedules and processes for maximum efficiency, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
b. Sales Agreement Analysis
Agents can scan and analyze thousands of sales contracts, identifying risks, inconsistencies, or missed opportunities automatically.
c. Optimized Inventory Management
By studying demand trends and supply data, AI agents ensure that inventory levels stay balanced, preventing both shortages and overstocking.
3. Retail & Marketing
a. Automated Promotional Content Generation
AI agents can generate marketing materials, social media posts, and personalized product recommendations based on customer behavior and preferences. This allows companies to scale marketing efforts while keeping content relevant and engaging.
4. Automotive
a. Vehicle Performance Monitoring and Proactive Maintenance
Modern vehicles use AI agents to track performance data and detect early signs of mechanical issues. They can alert drivers or schedule maintenance automatically, improving safety and reliability.
b. Dealership Commerce and Promotions
Dealerships use AI agents to manage promotions, analyze customer trends, and personalize offers, creating a smoother buying experience.
5. Healthcare
a. Personalized Patient Services
AI agents assist patients with scheduling, medication reminders, and personalized health recommendations. They help reduce wait times and improve patient satisfaction.
b. Clinical Trial Matching and Provider Network Optimization
AI agents analyze patient data and medical records to match candidates with suitable clinical trials. They also optimize provider networks to ensure efficient use of healthcare resources.
Best Practices for Deploying Generative AI Agents
Deploying AI agents successfully requires careful planning and responsible management. Following best practices ensures that these systems work effectively, stay secure, and deliver real business value.
1. Define Clear Objectives
Start by setting specific goals for what the AI agent should achieve. Clear objectives help guide design decisions, measure success, and prevent wasted effort on unnecessary features.
2. Assess and Prepare Your Data
AI agents depend on accurate and well-structured data. Before deployment, review your data sources, clean up errors, and remove bias to improve the quality of training and results.
3. Choose the Right AI Agent Type
Select the type of agent that best fits your use case, for example, a goal-based agent for planning tasks or a learning agent for systems that need to adapt over time.
4. Integrate with Existing Systems
Make sure your AI agent works smoothly with your company’s current tools, APIs, and databases. Seamless integration helps maintain workflow consistency and prevents data silos.
5. Focus on User Experience
Design your AI agent to be user-friendly and reliable. Use natural language interfaces, clear communication, and a consistent persona to build trust and engagement with users.
6. Monitor and Optimize
After deployment, continuously track the agent’s performance. Collect feedback, measure key metrics, and update models to keep the system accurate and efficient.
7. Plan for Human Oversight
Even the smartest AI agents need human supervision. Include humans in the loop for critical decisions, ethical reviews, and conflict resolution to maintain control and accountability.
8. Ensure Data Privacy and Security
Protect user information with strong data governance policies. Encrypt sensitive data, limit access, and regularly audit your systems to reduce privacy risks and ensure compliance with regulations.
Real Example of a Company Working with AI Agents
Several leading companies are already using AI agents to transform their operations, enhance customer experiences, and boost productivity. One notable example is Uber.
Uber’s Financial Data Agent: Finch
Uber has developed a powerful AI agent named Finch, designed to simplify and speed up financial data analysis across the company. Finch acts as a conversational AI agent that allows financial analysts to access complex data instantly through simple messages in Slack.
Instead of writing long and complex SQL queries, analysts can now ask questions in plain language. Finch automatically converts those questions into structured data queries, retrieves the information, and presents the results directly within Slack. This saves time, reduces manual effort, and ensures quick access to accurate financial insights.
Finch operates through a multi-agent system architecture. When a team member submits a question, a Supervisor Agent determines which sub-agent should handle it for example, the SQL Writer Agent, which constructs and runs the necessary database queries. Other agents manage metadata indexing, data formatting, and real-time progress updates, ensuring a smooth and efficient workflow from start to finish.
To ensure accuracy and reliability, Uber follows a strict testing process. This includes agent accuracy testing, which compares responses against verified “golden” results, supervisor routing validation to confirm that each request is handled by the correct tool, and end-to-end system testing to guarantee dependable performance. Uber also performs regression testing to detect and fix performance drifts before updates are released.
By combining automation, reasoning, and collaboration between multiple AI agents, Uber’s Finch system shows how agentic AI can transform business operations, turning slow, manual data processes into fast, intelligent, and seamless interactions.
The Future of AI Agents
The future of AI agents looks incredibly promising. As technology continues to evolve, these intelligent systems will become more autonomous, adaptable, and integrated into everyday life.
In the coming years, AI agents are expected to move beyond simple automation and act as collaborative digital partners capable of reasoning, learning, and working alongside humans across industries. They will manage complex workflows, make faster data-driven decisions, and even predict challenges before they occur.
Businesses will use AI agents to create smarter, self-optimizing environments, where systems can monitor performance, solve problems, and improve over time through monitored updates, feedback loops, and periodic human review.
At the same time, the rise of AI agents brings new responsibilities. Companies will need to focus on transparency, fairness, and ethical use to ensure that these technologies remain trustworthy and beneficial for everyone.
In short, AI agents represent the next big step in artificial intelligence systems that think, learn, and act independently, helping people and organizations achieve more than ever before.
Conclusion
AI agents are reshaping the way we interact with technology. They go beyond traditional automation by combining intelligence, adaptability, and independent decision-making. From assisting customers and managing complex workflows to predicting outcomes and learning from experience, AI agents are becoming essential tools for modern businesses.
As these systems continue to evolve, their ability to think, plan, and collaborate will only grow stronger. However, success depends on responsible deployment focusing on data privacy, ethical design, and human oversight to maintain trust and transparency.
In the near future, AI agents will not just support human work; they will become reliable digital teammates, helping organizations innovate faster, operate smarter, and deliver better experiences to people everywhere.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What exactly is an AI agent?
An AI agent is an intelligent software program that can observe its environment, make decisions, and take actions to achieve specific goals without needing step-by-step human instructions. It combines reasoning, learning, and automation to operate independently and complete tasks efficiently.
How is an AI agent different from a chatbot or virtual assistant?
While chatbots follow pre-written scripts or respond to keywords, AI agents are more advanced. They can analyze information, plan actions, and adapt to changes in real time. In short, a chatbot reacts, but an AI agent thinks and acts to accomplish objectives on its own.
How do AI agents actually work?
AI agents work through a continuous cycle of perception, reasoning, action, and learning. They start by collecting data from their environment, process it to understand what’s happening, plan what to do next, and then take action. Afterward, they learn from the results, allowing them to perform better over time.
How autonomous are AI agents really?
Most AI agents can operate on their own to a large extent, but they still benefit from human supervision. Fully autonomous agents are rare and typically deployed in controlled, sandboxed, or narrowly scoped environments with strict monitoring. In most real-world applications, humans and agents work together to ensure accuracy, safety, and accountability.
What are some real-world examples of AI agents?
AI agents are already being used in many industries. Mercedes-Benz, for example, has developed the MBUX Virtual Assistant, which allows drivers to interact naturally with their cars using voice commands.
Why do some people say AI agents are overhyped?
Many online discussions, especially on Reddit and Quora, point out that current AI agents often need human setup or monitoring. While they are powerful and flexible, they are not yet capable of full independent reasoning.
What industries benefit most from AI agents?
AI agents are transforming several key industries. In finance, they detect fraud and enhance customer service. In healthcare, they assist with diagnosis and patient care. Manufacturing uses them for predictive maintenance and efficiency improvements. Retail companies rely on agents for personalized marketing, and the automotive sector uses them for performance monitoring and safety features.
Do AI agents need a lot of data to function well?
Yes, AI agents depend heavily on high-quality data to perform effectively. Good data allows them to learn patterns accurately and make better decisions. Poor or biased data can cause incorrect actions or faulty reasoning, so careful data preparation and monitoring are essential.
Will AI agents replace human workers?
AI agents are designed to assist humans, not replace them. They take over repetitive, data-heavy, and time-consuming tasks, allowing people to focus on creative thinking, strategic decisions, and emotional intelligence areas where human abilities remain unmatched.
What challenges do AI agents face today?
AI agents still face limitations such as data privacy risks, ethical concerns, and technical complexity. They can also be expensive to operate due to high computing requirements. Despite these challenges, continuous innovation is making AI agents more transparent, reliable, and accessible.
How can businesses start using AI agents?
Businesses can begin by identifying clear objectives where automation can add value, such as customer support or data analysis. Once goals are defined, organizations should ensure that data systems are clean and integrated.
This page was last edited on 28 December 2025, at 11:13 am
Contact Us Now

Contact Us Now
Start a conversation with our team to solve complex challenges and move forward with confidence.










