- What Are AI Agents in Customer Service?
- AI Agents vs Chatbots vs Agentic AI
- How Do AI Agents Work in Customer Service?
- Key Components of AI Agents in Customer Service
- Types of AI Agents in Customer Service
- Role of AI Agents in the Customer Service Process
- How AI Agents Enhance Customer Service
- Use Cases of AI Agents in Customer Service
- Essential Steps to Get Started
- Why AI Agents Are the Future of Customer Service
Customers don’t wait anymore. The moment something goes wrong, an order delay, a billing mistake, a login problem, they expect answers now. Not in an hour. Not tomorrow. Now.
But most support teams are already at their limit. Tickets pile up. Wait times grow. Pressure rises. And every slow response becomes a lost opportunity to keep a customer loyal.
This is why AI agents are changing everything.
AI agents don’t get tired. They don’t miss details. They don’t make customers wait. They step in the moment help is needed, resolving issues, taking action, and guiding customers through problems with speed that humans alone can’t match.
For companies fighting to deliver fast, effortless service, AI agents are no longer an upgrade. They are the breakthrough that finally closes the gap between what customers expect and what teams can realistically deliver.
If your customer experience feels stretched, strained, or stuck, AI agents are the future and the turning point.
What Are AI Agents in Customer Service?
AI agents for customer service are autonomous, AI-powered virtual assistants that can interact with customers and complete tasks on their own. They use technologies like machine learning, natural language processing (NLP), and large language models (LLMs) to understand questions, make decisions, and deliver accurate, real-time responses.
These agents work by analyzing what a customer says, pulling the right information from CRM or help desk systems, and carrying out routine processes. This includes answering common questions, handling issues like password resets or order tracking, sorting and routing tickets, and escalating complex cases to human agents when needed. They also learn from each interaction, which helps them become more accurate and efficient over time.

AI agents provide 24/7 support, fast issue resolution, and consistent answers across all channels. They can personalize support by remembering past conversations, building simple customer profiles, and anticipating needs. Many can also communicate in multiple languages and automate repetitive workflows, allowing human support teams to focus on more complex or sensitive tasks.
Overall, AI agents turn customer service into a more proactive, scalable, and data-driven operation. They help improve customer satisfaction, reduce operational costs, and support business growth.
AI Agents vs Chatbots vs Agentic AI
Here is a comparison of AI Agents, Chatbots, and Agentic AI:
| Feature | Chatbots | AI Agents | Agentic AI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Autonomy | Respond to predefined queries; reactive | Autonomous in task execution; proactive | Full autonomy with goal-setting, planning, and adaptive learning |
| Complexity | Simple to moderate; scripted or LLM-based | Complex; handles multi-step tasks and workflows | Highly complex; manages goals, sub-tasks, and adapts dynamically |
| Conversational Ability | Limited, rule-based, or NLP-enhanced | Human-like, context-aware conversations | Advanced reasoning with multi-modal inputs and cognitive memory |
| Decision-Making | Minimal; mostly responses to queries | Medium: can make decisions linked to tasks | Advanced strategic planning, prioritization, and real-time adaptation |
| Learning Capability | Little to no; static or periodic updates | Continuous learning from interactions | Learns and evolves continuously from past and current contexts |
| Integration | Limited backend integration | Integrates deeply with CRM, ticketing, and knowledge bases | Extends AI agents’ integration with broader environments and data sources |
| Task Scope | Basic FAQs, simple transactions | End-to-end support workflows, escalation, and analysis | Full workflow automation with reasoning, multimodal input handling |
| Proactivity | No | Yes, initiates actions based on goals | Yes, dynamically sets and adjusts goals and plans |
| Use Cases | Simple customer service queries | Complex customer service, sales, and process automation | Enterprise-level problem-solving, autonomous decision systems |
| Maturity & Stability | Mature and widely used | Growing adoption; medium maturity | Emerging and experimental; considered the next frontier |
How Do AI Agents Work in Customer Service?
AI agents work by following a structured, goal-driven workflow that allows them to understand requests, plan actions, access systems, and resolve customer issues with minimal human intervention. Their behavior is driven by a combination of reasoning, knowledge retrieval, data access, and action execution across integrated tools.
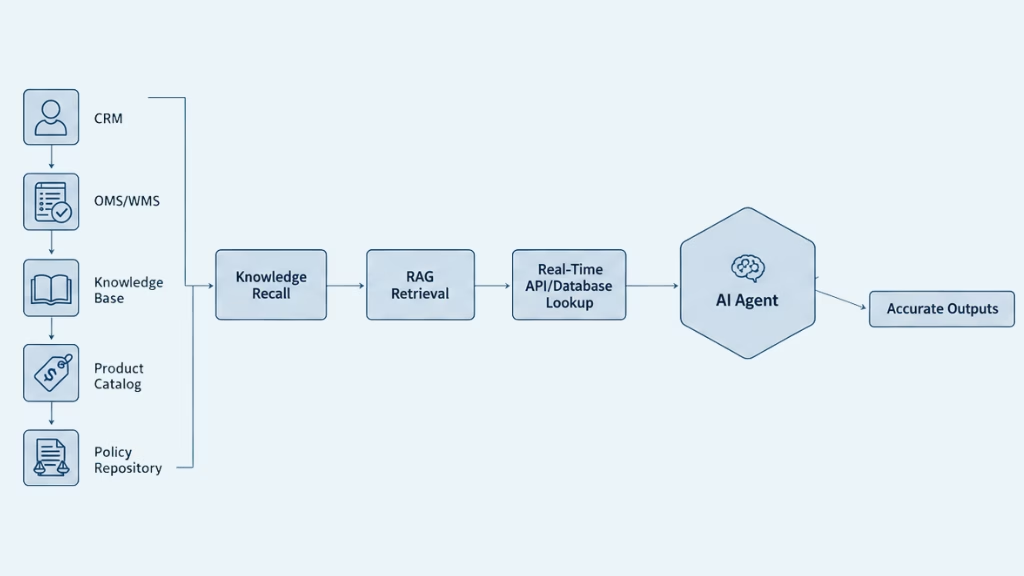
Below is a more complete, enterprise-level breakdown.
1. Understanding the Goal
Every interaction starts with a goal. The agent identifies what the customer wants by analyzing their message and extracting intent, entities, and context.
Examples of customer goals:
- “I want to return my order.”
- “My payment failed.”
- “Update my delivery address.”
- “Why is my subscription paused?”
Once the goal is clear, the agent breaks it down into subtasks, such as:
- Retrieve customer account
- Check order status
- Validate eligibility (refund window, subscription rules, etc.)
- Retrieve relevant policy
- Generate explanation
- Execute action (refund, update, escalate)
This task decomposition allows the AI agent to reason and act step-by-step instead of giving generic responses.
2. Acquiring Information
AI agents depend on accurate data. To complete their tasks, they pull information from internal systems such as:
Internal data sources:
- CRM (customer profile, purchase history, subscription status)
- OMS/WMS (order management, shipping updates, tracking details)
- Billing and payment gateway logs
- Knowledge base articles
- Product catalog and specs
- Policy repositories
Retrieval capabilities include:
- Knowledge recall: retrieving predefined answers from KB and FAQs
- RAG: retrieving relevant content during the LLM generation
- Database/API lookups: real-time data (e.g., “Order #51402 shipped via UPS yesterday”)
This ensures the agent doesn’t rely solely on the LLM’s “memory,” but on verified internal data.
3. Planning & Decision-Making
After collecting information, the agent generates a plan to resolve the issue. This involves:
- Selecting actions
- Setting the correct order of execution
- Checking dependencies (e.g., “Is this order refundable?”)
- Validating rules and constraints
- Determining whether human review is required
Planning is where AI agents outperform traditional chatbots; they can reason about the next steps instead of following fixed scripts.
4. Executing Tasks (Action Layer)
Once the plan is defined, the agent executes actions via secure system integrations.
Common actions include:
- Creating or updating support tickets
- Processing refunds or exchanges
- Modifying customer details
- Reordering products
- Resetting account access
- Scheduling appointments
- Generating documents (invoices, confirmations, return labels)
Action execution methods:
- API calls
- CRM workflows
- Integrations with order or billing systems
- Webhooks
- Multi-agent handoffs (e.g., separate billing agent, logistics agent)
Each completed task updates the agent’s working memory and reduces the remaining sub-goals.
5. Generating a Final Response
Once actions are executed, the AI summarizes the outcome clearly and professionally.
A strong AI agent will:
- Explain what was done
- Include next steps if needed
- Provide relevant links (tracking page, invoice, policy)
- Maintain brand tone and clarity
Response examples:
- “Your refund has been issued. It will reach your account in 3–5 business days.”
- “Your delivery address has been updated. Here is your new tracking link.”
6. Reviewing Results & Learning
AI agents improve over time through:
- User feedback (“This didn’t help”)
- Human agent corrections
- System logs
- Updated knowledge sources
- Pattern recognition across conversations
This creates a continuous learning loop, reducing errors and improving performance.
Key Components of AI Agents in Customer Service
AI agents depend on several core components that enable them to understand customers, make decisions, and complete tasks across support systems. Together, these components form the foundation of an agent’s intelligence, accuracy, and reliability in real-world service environments.

1. Language Understanding (NLU + LLM)
At the center of every AI agent is the ability to understand natural language. This includes identifying intent, extracting important details, and interpreting the customer’s message even when it is unclear or incomplete. This capability ensures that the agent responds with accuracy and relevance.
2. Reasoning and Decision-Making Engine
Once the agent understands the request, it uses a reasoning engine to determine the best next step. This could involve planning a sequence of actions, selecting the right workflow, or deciding whether the issue requires human escalation. This is what allows AI agents to handle more than simple questions.
3. Knowledge Retrieval / RAG System
AI agents depend on accurate information. They access this information through a retrieval system that connects to help center articles, product documentation, policies, and internal knowledge bases. Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) or search-based retrieval ensures the agent provides precise, up-to-date answers instead of relying on guesswork.
4. Action Execution Layer (APIs, Tools, and Workflows)
This is the component that transforms an AI model into a true “agent.” Through APIs and integrations, the agent can take real actions such as updating orders, processing refunds, modifying accounts, or creating support tickets. This allows the agent to resolve issues instead of simply explaining them.
5. Context Memory and Conversation State
AI agents maintain context throughout the interaction. They track what the customer has already shared, remember previous steps in the conversation, and avoid repeating questions. This reduces friction and creates a more natural, efficient experience.
6. Safety, Compliance, and Guardrails
Enterprise use requires strict safety controls. AI agents follow business rules, enforce policy boundaries, protect sensitive data, and avoid unauthorized actions. Guardrails help prevent errors, contain risks, and ensure the agent operates within approved limits.
7. Monitoring, Analytics, and Continuous Improvement
After deployment, the agent’s performance is monitored through analytics and quality review tools. Teams can see success rates, identify failure patterns, refine workflows, and update knowledge sources. This continuous improvement cycle keeps the agent accurate and effective over time.
These components allow AI agents to function as reliable digital workers capable of understanding, deciding, acting, and improving at scale.
Types of AI Agents in Customer Service
AI agents take on different roles within the customer service ecosystem. Each type is designed to support a specific part of the customer journey or internal workflow. Together, they create a flexible, scalable service operation that can respond quickly and consistently across channels.
1. Customer Interaction Agents
Customer-facing conversational systems are designed to manage inquiries across digital channels.
Channels include:
- SMS
- Web chat
- In-app messaging
- Social messaging apps
- Email automation
Function:
Resolve inquiries, provide guided assistance, and execute actions directly from the conversation interface.
2. Intelligent Voice Interaction Agents
AI-powered voice systems capable of handling phone-based interactions.

Capabilities:
- Speech recognition
- Natural language understanding
- Voice response generation
- Call routing and task execution
Function:
Reduce wait times, streamline call flows, and automate high-volume voice requests.
3. Workflow Execution Agents
Back-end agents are designed to execute operational tasks with precision.
Examples:
- Order lookups
- Account updates
- Refund initiation
- Appointment scheduling
- Subscription modifications
Function:
Act as digital workers who complete structured or semi-structured tasks across systems of record.
4. Agent Assist & Decision Support Agents
Internal-facing AI that supports human agents in real time.
Capabilities:
- Suggesting replies
- Summarizing conversations
- Searching internal knowledge
- Identifying next best actions
- Auto-populating case fields
Function:
Enhance agent accuracy and reduce handling time in contact centers.
5. Knowledge Intelligence Agents
Agents responsible for curating, managing, and retrieving organizational knowledge.
Capabilities:
- Real-time knowledge retrieval
- Document analysis
- Article improvement
- Policy interpretation
- Detecting outdated or conflicting information
Function:
Ensure that agents, both human and AI, rely on authoritative, up-to-date knowledge.
6. Governance, Policy, and Compliance Agents
Oversight agents that evaluate AI decisions and enforce operational and regulatory policies.

Capabilities:
- Monitoring interactions for policy compliance
- Detecting sensitive data exposure
- Enforcing business rules
- Validating high-risk actions
- Providing corrective guidance to other agents
Function:
Establish guardrails and operational assurance for enterprise-scale deployments.
7. Orchestration & Coordination Agents
Meta-agents are responsible for planning, routing, and coordinating work across specialized agents.
Capabilities:
- Intent classification
- Task routing
- Multi-agent workflow coordination
- Prioritization logic
- Resource allocation across digital and human workers
Function:
Ensure the right agent or human handles each task, creating a seamless, end-to-end customer experience.
Role of AI Agents in the Customer Service Process
AI agents play a role across the entire customer service journey, not just at the point of contact. Their value comes from their ability to support customers, assist human agents, and automate operational tasks that previously required manual effort. This creates a smoother, faster, and more consistent experience for customers while reducing pressure on support teams.
Below are the core roles AI agents fulfill within the customer service process:
1. First-Line Support and Inquiry Handling
AI agents often act as the first point of contact. They can greet customers, understand their requests, and resolve many issues instantly. This reduces wait times and prevents backlogs from forming in high-volume periods.
2. Intelligent Routing and Prioritization
When a request requires human attention, AI agents can classify the issue, assess urgency, and route it to the right team. They help ensure that complex, high-value, or sensitive cases reach the proper support agent without delay.
3. Automated Task Execution
Many customer service requests involve predictable workflows. AI agents can complete these tasks without human involvement, such as:
- Checking delivery status
- Modifying account details
- Processing cancellations or refunds
- Resetting passwords
Automating these actions reduces repetitive work and speeds up resolutions.

4. Real-Time Assistance for Human Agents
For support teams, AI agents act as a co-pilot. They can:
- Suggest accurate responses
- Surface relevant knowledge
- Summarize conversations
- Highlight customer history
- Recommend next best actions
This improves accuracy, shortens handle times, and helps new agents get up to speed faster.
5. Continuous Customer Engagement
AI agents maintain ongoing interactions throughout the service process, such as:
- Sending proactive updates
- Following up on open cases
- Requesting feedback
- Providing status notifications
This ensures customers stay informed without requiring manual outreach.
6. Consistency and Compliance Enforcement
AI agents ensure every interaction follows company guidelines and policy rules. They deliver consistent messaging, reduce human error, and apply compliance checks automatically during action-driven tasks.
7. Operational Insights and Improvement
AI agents track trends across interactions, common issues, bottlenecks, sentiment patterns, and knowledge gaps. This data helps service leaders improve processes, update resources, and increase overall efficiency.
AI agents don’t replace the customer service processes; they strengthen it. By supporting customers, elevating human agents, and reducing operational effort, they create a balanced, high-performing service ecosystem.
How AI Agents Enhance Customer Service
AI agents enhance customer service by introducing an operational model that blends automation, intelligence, and real-time decision-making across every stage of the support lifecycle. Their impact is not limited to faster responses; they fundamentally change how organizations deliver service, manage resources, and scale operations.
Below is a deeper look at the ways AI agents create measurable improvement across customer experience, workforce efficiency, and business performance.
1. Accelerating Response and Resolution Times
AI agents eliminate delays by responding the moment a customer reaches out.
They can:
- Interpret questions instantly
- Retrieve relevant information without searching manually
- Execute actions (e.g., check order status or update account details) within seconds
For high-volume operations, shaving even 30–60 seconds per interaction creates a meaningful reduction in wait times. At scale, this leads to:
- Lower Average Handle Time (AHT)
- Higher First Contact Resolution (FCR)
- Reduced ticket queues
Speed becomes a competitive advantage instead of a persistent challenge.
2. Reducing Operational Load on Human Agents
Most customer service interactions involve a shortlist of repetitive tasks: order tracking, account updates, basic troubleshooting, and billing questions.
AI agents absorb much of this workload, allowing human agents to focus on:
- Complex issues that require empathy or deep product knowledge
- High-value customers
- Sensitive requests
- Escalations that directly impact retention
The result is a more balanced, less-stressed support team and a clearer division of work between automation and human expertise.
3. Ensuring Consistency and Compliance Across All Interactions
Human responses naturally vary based on experience, memory, and interpretation.
AI agents eliminate this variability by:
- Referencing unified knowledge bases
- Applying policies the same way each time
- Following standardized workflows
- Avoiding omissions or incorrect steps
This ensures the organization delivers consistent, policy-aligned service across every channel and time zone, even during high-volume periods or staffing shortages.
4. Strengthening Self-Service as a Primary Support Channel
Self-service succeeds only when customers can actually resolve their issues without friction.
AI agents improve the self-service channel by:
- Understanding natural conversational language
- Guiding users step-by-step through tasks
- Handling actions that typical FAQs cannot perform
- Personalizing the experience based on customer context
This reduces reliance on live support, lowers cost-to-serve, and increases satisfaction for customers who prefer quick, interaction-free solutions.
5. Providing 24/7, Always-On Customer Support
Customers expect help on their schedule, not during business hours.
AI agents provide:
- Full availability during nights, weekends, and holidays
- Stable service levels regardless of staffing
- Smooth coverage across regions and languages
- Zero wait time, even during peak demand
This provides global continuity without adding headcount or increasing costs.
6. Improving Routing, Prioritization, and Issue Classification
AI agents can analyze context and sentiment to determine:
- Urgency level
- Intent type
- Required skills or department
- Customer history or past issues
This ensures the right cases reach the right people. Misrouted inquiries, one of the highest hidden costs in customer service, are drastically reduced.
7. Delivering Personalization at Scale
AI agents use available data (previous tickets, purchase history, preferences) to adapt responses and recommendations.
Examples include:
- Recognizing returning customers
- Adjusting troubleshooting steps based on the device or plan
- Recommending relevant articles or products
- Tailoring actions based on prior interactions
This moves customer service from transactional to personalized without increasing the workload on human teams.
8. Enabling Seamless Escalation to Human Agents
Not all interactions can or should be automated.
When escalation is needed, AI agents:
- Transfer full context
- Summarize the conversation
- Highlight key details and actions taken
- Reduce repetitive questioning for the customer
This prevents “starting over,” which is one of the top drivers of frustration in customer service.
9. Enhancing Scalability During Peak and Unpredictable Demand
Seasonal spikes, product launches, and unexpected surges can overwhelm support teams.
AI agents scale instantly, giving organizations:
- Surge capacity without temporary hires
- Stable service levels
- Predictable cost structures
- Resilience to sudden volume changes
This protects both customer experience and operational performance during critical periods.
10. Generating Operational Insights and Improvement Opportunities
AI agents record detailed patterns from customer interactions.
Leaders gain visibility into:
- Repeated failure points
- High-contact issues
- Gaps in product knowledge or documentation
- Sentiment trends
- Process bottlenecks
- Automation opportunities
These insights inform product decisions, coaching, training, and documentation updates, allowing the organization to continuously refine its service model.
11. Lowering Cost-to-Serve Without Compromising Quality
AI agents reduce the volume of manual tasks and the number of inquiries requiring human intervention.
This leads to:
- Lower staffing costs
- Reduced overtime
- Fewer escalations
- Higher agent productivity
- Better ticket containment
Instead of adding more people to match rising volume, companies can handle more interactions without expanding headcount.
12. Improving Customer Satisfaction Through Predictability and Clarity
When customers receive immediate, accurate, and consistent help, satisfaction rises. AI agents excel at delivering predictable experiences, something customers value highly.
They can also:
- Provide proactive updates
- Remind customers about ongoing cases
- Follow up after resolutions
This creates a service journey that feels reliable and attentive.
Together, these enhancements make AI agents a strategic asset, not just a customer service tool, but an enabler of better operations, better customer experiences, and better resource management across the organization.
Use Cases of AI Agents in Customer Service
AI agents are now integrated into a wide range of customer service operations. Their ability to understand requests, execute tasks, and maintain context makes them effective across both simple and complex service scenarios. Below are the most common and high-impact use cases across industries.
| Use Case | What the AI Agent Does |
|---|---|
| Order Tracking & Status Updates | Looks up order details, delivery progress, and shipping status and resolves related questions such as delays or missing packages. |
| Returns, Refunds & Exchanges | Initiates return workflows, processes refunds based on policy, and guides customers through exchange options. |
| Account Management & Profile Updates | Handles password resets, profile changes, billing updates, subscription changes, and account-level tasks. |
| Troubleshooting & Technical Support | Provides step-by-step instructions, runs diagnostic checks, gathers information, or escalates when needed. |
| Appointment Scheduling & Reservations | Books, cancels, or reschedules appointments by checking real-time availability in backend systems. |
| Billing & Payment Support | Explains charges, retrieves invoices, resolves payment issues, updates payment methods, and verifies billing information. |
| Product Discovery & Recommendations | Helps customers find products, compare options, and receive personalized recommendations. |
| Case Creation & Ticket Management | Creates support tickets with full context, categorizes issues, and routes them to the correct team. |
| Policy & Information Queries | Provides accurate answers about warranties, shipping rules, return windows, or service availability from verified sources. |
| Proactive Notifications & Updates | Sends follow-ups, delivery updates, reminders, and status changes without manual involvement. |
| Sentiment Detection & Smart Escalation | Identifies frustration or urgency and escalates cases to human agents with proper context. |
| Internal Support for Agents | Summarizes conversations, retrieves documents, drafts responses, and suggests next steps for human representatives. |
Essential Steps to Get Started
Implementing AI agents in customer service requires a structured approach. When done correctly, organizations can move from exploration to meaningful automation in a clear, predictable way. The following steps outline how to prepare, build, deploy, and scale AI agents with confidence.
1. Define Scope and Objectives
Start by identifying the goals you want to achieve. This may include reducing response times, increasing self-service rates, lowering operational costs, or improving customer satisfaction.
Next, determine which customer journeys or tasks should be automated first, focusing on high-volume, repetitive, and rule-based interactions.
2. Select the Right AI Technology and Models
Choose AI technology that aligns with your business needs and infrastructure. Consider:
- Language model quality
- Ability to integrate with your existing systems
- Support for multi-channel interactions
- Security and compliance requirements
- Scalability and performance
Selecting the right platform ensures your AI agent can deliver reliable results from day one.
3. Collect and Organize Data
AI agents rely on well-structured knowledge. Assemble the core resources they will use, such as:
- Help center content
- Product or service documentation
- Policy and compliance guidelines
- Internal playbooks or SOPs
- Past customer interactions
Clean, centralized information improves agent accuracy and reduces errors.
4. Design the Agent Architecture and Workflows
Define how the AI agent will operate within your customer service environment. This includes:
- Mapping the workflows it will automate
- Setting rules for what the agent can and cannot do
- Configuring integrations with CRM, ticketing, or order systems
- Establishing safe action boundaries (refund limits, authorization checks, etc.)
A clear architecture ensures the agent behaves consistently and securely.
5. Build, Test, and Validate
Be thorough during testing. Evaluate performance on:
- Accuracy of responses
- Ability to complete tasks
- Handling of edge cases
- Tone and clarity of communication
- Compliance with safety and policy requirements
Testing should cover both scripted scenarios and real-world interactions to confirm the agent can operate reliably.
6. Deploy Gradually and Monitor
Introduce the AI agent in controlled phases. Many organizations start with a small percentage of traffic and expand as confidence grows.
Track key indicators such as:
- Resolution rate
- Containment rate
- Customer satisfaction
- Escalation trends
- Error types
Continuous monitoring ensures issues are caught early and improvements are made promptly.
7. Improve and Expand Over Time
AI agents get better as they gain exposure to more interactions. Regularly update the knowledge sources, refine workflows, and introduce additional capabilities. Over time, expand the agent’s responsibilities into more channels and customer journeys.
Why AI Agents Are the Future of Customer Service
Customer service is undergoing a fundamental shift. Rising expectations, increased complexity, and nonstop demand have made traditional support models difficult to scale. AI agents address these challenges by enabling faster, more consistent, and more intelligent service at a level that manual teams alone cannot sustain.
Here are the key reasons AI agents are shaping the future of customer service:
1. The Demand for Instant, Always-Available Support
Customers expect immediate answers at any time of day. AI agents meet this demand with 24/7 availability across all channels without the cost or limitations of expanding human staffing.
2. Growing Pressure to Reduce Operational Costs
Support teams face rising workloads and higher expectations while operating under tight budgets. AI agents automate the bulk of repetitive tasks, lowering cost per interaction and enabling teams to do more with fewer resources.
3. Increased Complexity in Customer Interactions
Today’s inquiries involve multiple systems, policies, and steps. AI agents can follow structured workflows, check multiple data sources, and execute actions that traditional chatbots can’t manage.
4. Shift Toward Hyper-Personalized Experiences
Customers expect more than generic responses. AI agents can tailor interactions based on past history, behavior, and preferences, creating a personalized experience at scale.
5. Advancements in Language Models and Agentic AI
Newer AI models can reason, plan, and act. This transforms support from reactive messaging to proactive problem-solving. It also allows AI agents to work as true digital employees, not just automated responders.
6. Seamless Collaboration Between Humans and AI
The future is not about replacing human agents. It’s about augmenting them. AI agents handle repetitive work, while human agents focus on empathy, judgment, and complex cases. This creates a hybrid workforce that is more effective than working alone.
7. Proactive Service Will Become Standard
AI agents can detect issues before customers encounter them delivery delays, payment failures, and account risks, and initiate communication automatically. As proactive support becomes the norm, AI will play a central role in anticipating and preventing problems.
8. Data-Driven Improvement Across the Organization
AI agents generate insights from every interaction. These patterns help companies refine products, improve documentation, optimize processes, and enhance service quality over time.
9. Multi-Agent Systems Will Expand Capabilities
Future service operations will rely on specialized agents working together. Routing agents, knowledge agents, action agents, and voice agents will collaborate to manage complex end-to-end workflows.
10. Customer Expectations Will Continue to Rise
As more companies adopt AI agents, customers will grow accustomed to faster, more efficient service. Organizations that do not adapt will fall behind competitors who resolve issues in seconds instead of minutes.
AI agents are not a trend; they are a structural shift in how customer service operates. They offer a scalable, intelligent, and cost-effective way to deliver support that meets modern expectations while preparing organizations for the next generation of customer experience.
Conclusion
AI agents are reshaping what customers expect from service and what teams are capable of delivering. They bring the speed, consistency, and intelligence that modern support demands while reducing the pressure on human agents and lowering operational costs.
As more organizations adopt AI-driven workflows, the gap between traditional support and AI-enhanced service will only grow. Companies that move early will set the standard for fast, effortless, and reliable customer experiences. Those who wait will struggle to keep pace.
If your goal is to create a service operation that can scale, adapt, and perform with precision, AI agents offer the most direct path forward. They are not a future possibility; they are a present advantage.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are AI agents for customer service?
AI agents are software systems powered by artificial intelligence that interact with customers (via chat, email, voice, etc.) and can also perform actions in backend systems such as looking up orders, updating accounts, or creating support tickets to resolve customer issues end-to-end.
How do they differ from traditional chatbots?
Traditional chatbots often rely on scripted responses or rule-based logic and are limited to answering basic FAQs. By contrast, AI agents use natural language understanding (NLU), context awareness, reasoning, and system integrations, enabling them to handle complex requests, execute workflows, and take real actions rather than just returning prewritten text.
Can AI agents handle real customer issues, not just FAQs?
Yes. Modern AI agents are built to handle real-world support tasks such as order tracking, returns/refunds, account updates, billing inquiries, password resets, and even more complex workflows when properly configured.
Do AI agents work 24/7 and across multiple channels?
Yes. One of their major advantages is always-on availability; they can support customers around the clock (including outside working hours and across time zones) and across channels such as chat, email, messenger apps, and voice.
Will AI agents replace human support staff?
Not necessarily the most effective use of AI agents is as a complement to human teams. They handle repetitive, high-volume, or simple tasks, freeing human agents to focus on complex, sensitive, or high-value interactions.
What are the limitations or risks of deploying AI agents?
AI agents aren’t perfect. Risks include: potential misunderstanding of complex or ambiguous customer queries; mistakes or “hallucinations” if internal data or knowledge base is outdated or incomplete; limitations in handling emotionally sensitive or highly nuanced issues; and compliance or data privacy concerns when agents access sensitive systems.
How should a company get started with AI agents for support?
Start by defining clear objectives (e.g., reduce response time, automate returns). Then select technology that fits your systems, gather and clean internal data (knowledge base, product info, workflows), map out which tasks you want the agent to handle, build and test in a controlled environment, and deploy gradually, monitoring performance (resolution rates, escalation rates, customer satisfaction) and iterating as needed.
Will AI agents improve customer satisfaction?
Yes, when implemented properly. Because agents offer instant responses, consistent accuracy, 24/7 availability, and reduced wait times, many companies report improved customer satisfaction and better overall support experience.
Can AI agents handle both simple and complex support tasks together?
With the right design, yes. AI agents can manage routine queries automatically and route or escalate complex or sensitive requests to human agents, ensuring a balance between automation efficiency and human judgment when needed.
This page was last edited on 27 November 2025, at 5:40 pm
Contact Us Now

Contact Us Now
Start a conversation with our team to solve complex challenges and move forward with confidence.










