- Key Insights Overview
- What is API Development?
- How Does an API Work
- How to Develop an API
- Why APIs Matter to Developers and Businesses
- How Do You Test and Maintain APIs
- How to Scale APIs for Global Applications
- What is the Best Practices of API Security
- How Much Does It Cost to Build an API
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
If you’re building anything online today, whether it’s a mobile app, website, or enterprise software, you’re likely using or creating APIs. API is what makes it possible for different software systems to communicate and work together. Without APIs, the world of interconnected apps, services, and platforms we know today simply wouldn’t exist.
But the API development process can be tricky. From designing APIs to securing them and getting them ready for deployment, there’s a lot to consider. And with so many different tools and frameworks available, where do you even begin?
Don’t worry, this guide will help you navigate each step of the API development process. Whether you’re new to the world of APIs or looking to improve your current skills, we’ve got you covered. By the end of this article, you’ll have a clear understanding of how to design, build, and deploy APIs that are secure, efficient, and ready to grow with your project.
Key Insights Overview
| Topic | Key Insights |
|---|---|
| What is API Development? | API development refers to the process of designing and building Application Programming Interfaces that allow different software systems to communicate and exchange data. |
| API Types | Common API types include REST, SOAP, GraphQL, and WebSockets. Each has its own strengths, depending on the application and technical requirements. |
| Tools & Frameworks | Popular tools for API development include Postman for testing, Swagger for documentation, and frameworks like Node.js and Spring Boot for building APIs. |
| Best Practices for API Design | Follow RESTful principles, keep endpoints simple, ensure good documentation, and implement version control and error handling. |
| API Security | Authentication via OAuth or JWT, rate limiting, and secure data transmission are crucial to ensuring your API is safe and protected. |
What is API Development?
API development involves creating APIs that enable different software systems to communicate and exchange data seamlessly. It encompasses the design, creation, testing, and maintenance of APIs that serve as the bridge between applications, devices, and data sources.
For example, when you use a mobile app to check the weather, the app sends a request to a weather API, which in turn fetches the relevant data from a server and sends it back to your phone for display.
The Role of APIs in Software Development
APIs are critical to modern software development because they:
- Allow applications to communicate with one another, even if they are built with different programming languages.
- Enable third-party services to integrate with your system, such as payment gateways (Stripe, PayPal) or social media logins (Facebook, Google).
- Simplify the development process by allowing developers to focus on core functionality while leveraging existing services through APIs.
Why Is API Development Important?
- Enhancing Functionality: APIs allow developers to extend the functionality of their software by integrating third-party services.
- Enabling Innovation: APIs enable businesses to innovate and create new services by leveraging existing technologies.
- Business Growth: APIs provide new revenue opportunities, such as creating an API marketplace or offering access to your data for external partners.
How Does an API Work?
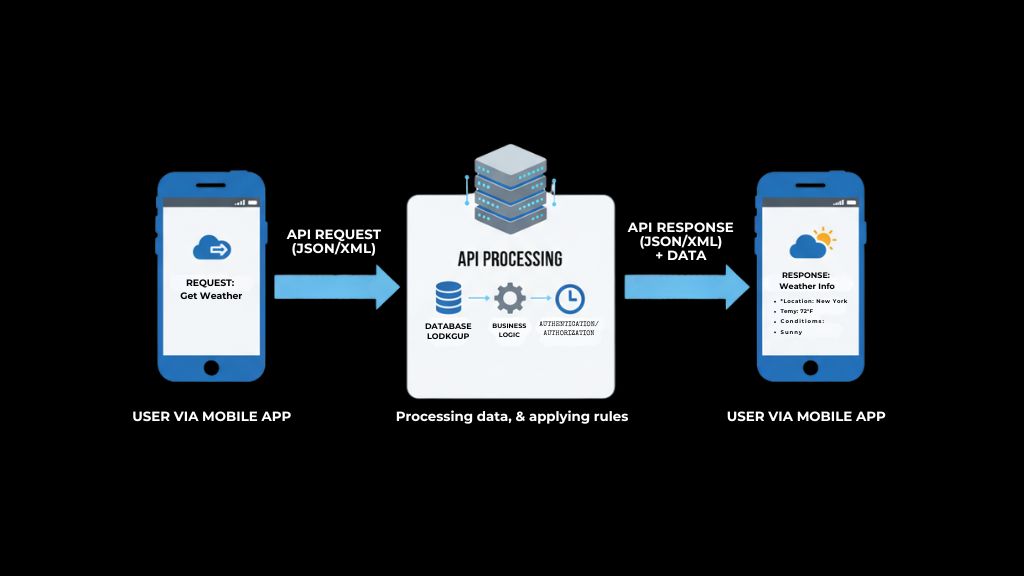
APIs enable communication between different software applications, allowing them to exchange data and functionality. The process follows a request-response model, where one system sends a request to another, and the receiving system sends back a response.
1. The Request-Response Model:
At its core, an API operates through a request-response cycle. Here’s how the process typically works:
- Client Sends a Request:
The client (which could be a user, application, or server) sends a request to an API. This request typically includes the type of operation (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE), specific data, and necessary authentication credentials.
Example: A user accesses a weather app on their phone. The app sends a request to a weather API to retrieve the current weather data for the user’s location. - API Processes the Request:
Once the request is received, the API processes the data and performs the necessary operations. This could include querying a database, accessing another service, or processing data.
Example: The weather API accesses a weather database or service to fetch the latest weather information for the requested location. - API Sends a Response:
After processing the request, the API sends a response back to the client. The response typically includes the requested data or a confirmation of the operation that was completed. It may also include a status code indicating whether the request was successful or if there was an error.
Example: The weather API returns the current temperature, humidity, and weather conditions to the app.
2. Key Components of an API Request:
An API request usually includes several key components:
- Endpoint:
The URL that specifies the resource or service the client is requesting. It typically includes the base URL, followed by the resource path and any query parameters.
Example: https://api.weather.com/v1/forecast?location=NYC - HTTP Method:
The HTTP method defines the action to be performed. The most common methods are:
- GET: Retrieve data from the server.
- POST: Send data to the server (e.g., submitting a form).
- PUT: Update existing data on the server.
- DELETE: Remove data from the server.
Example: A GET request is used to retrieve weather data, while a POST request might be used to submit a new user review.
- Headers:
Headers provide additional information to the API, such as authentication tokens or content types. For example, the Authorization header may be used to pass an API key or OAuth token.
Example: A header might look like: Authorization: Bearer [your_token_here] - Body (for POST/PUT requests):
The body of the request contains the data being sent to the server, typically in JSON format. For example, if a user is submitting a form to update their profile, the request body would contain the user’s updated details.
Example: {“username”: “john_doe”, “email”: “john.doe@example.com”}
3. API Response:
After the API processes the request, it sends back a response. This response contains several important elements:
- Status Code:
The status code is a three-digit number that indicates the outcome of the request. Common status codes include:
- 200 OK: The request was successful.
- 400 Bad Request: There was an error with the request (e.g., missing data).
- 401 Unauthorized: The request was not authenticated properly.
- 404 Not Found: The requested resource could not be found.
- 500 Internal Server Error: An error occurred on the server.
Response Body:
The response body contains the data that the client requested (in formats like JSON or XML) or confirmation that the request was successful. This could include user details, product information, or other requested data.
Example: For a weather API, the response body might look like:
{
"location": "New York",
"temperature": "18°C",
"humidity": "65%",
"forecast": "Partly cloudy"
}- Headers:
Just like the request, the response includes headers with metadata, such as the content type (application/json) and the length of the response body.
4. Example of an API Request and Response:
Here’s a simple example of how an API request and response might work in practice.
Request:
A client (e.g., a mobile app) sends a GET request to the API to retrieve user information.
GET https://api.example.com/users/12345
Authorization: Bearer your_api_token
- Response:
The API processes the request, retrieves the user’s data from the database, and returns it in the response. - The status code would be 200 OK, indicating a successful request.
{
"id": 12345,
"name": "John Doe",
"email": "johndoe@example.com",
"joined": "2020-01-15"
}How to Develop an API
Developing an API is an essential step in enabling communication between different software systems, allowing them to exchange data and functionality. The process involves several stages, from planning and designing to testing and deployment. Here’s a breakdown of the key steps in the API development lifecycle.
1. Define the Purpose and Scope of Your API
Before diving into coding, it’s essential to define the goals of your API. Consider:
- What problem is your API solving?
- Who will be using it (internal developers, third-party developers, or external clients)?
- What data or services will the API provide?
This clarity will guide your design decisions and ensure your API addresses the right needs.
2. Choose the Right API Architecture
Selecting the right architecture is crucial for the success of your API. Common choices include:
- REST (Representational State Transfer): Simple, scalable, and ideal for web and mobile applications.
- SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol): More rigid and used in enterprise applications that require high security.
- GraphQL: A flexible query language that allows clients to request exactly the data they need.
- gRPC: High-performance protocol, perfect for low-latency microservices.
3. Design Your API Endpoints
Endpoints are where users and systems interact with your API. Make sure they are intuitive:
- Use descriptive names for endpoints, like /users or /products/{id}.
- Ensure you follow HTTP methods correctly: GET (retrieve), POST (create), PUT (update), DELETE (remove).
- Structure endpoints logically and hierarchically.
4. Implement Authentication and Authorization
API security is critical. Implement authentication and authorization to ensure that only authorized users can access the API:
- OAuth 2.0: Standard for user authentication, often used in public APIs.
- JWT (JSON Web Tokens): A stateless method for secure token-based authentication.
- API Keys: Simple but less secure, usually for public APIs.
Always use HTTPS to encrypt data.
5. Test Your API
Testing ensures your API functions correctly. Types of testing include:
- Functional Testing: Ensures each endpoint works as expected.
- Load Testing: Simulates heavy traffic to test scalability.
- Security Testing: Identifies vulnerabilities like SQL injection.
- Performance Testing: Optimizes response times.
Use tools like Postman and Swagger for testing and documentation.
6. Document Your API
Clear documentation is essential for users to understand and integrate with your API. It should include:
- Endpoint Descriptions: Details on each endpoint’s method, parameters, and expected responses.
- Request and Response Examples: Real-world usage examples.
- Authentication Details: How users can securely authenticate.
Tools like Swagger and Postman are useful for auto-generating documentation.
7. Deploy and Maintain Your API
Once developed and tested, deploy your API to a cloud platform like AWS or Google Cloud. Regular maintenance tasks include:
- Versioning: Updating your API while ensuring backward compatibility.
- Monitoring: Use tools like Datadog or New Relic to track API performance.
- Security: Apply regular updates to patch vulnerabilities.
Why APIs Matter to Developers and Businesses
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) are vital tools that connect applications, streamline development, and drive business innovation. They help developers work faster and allow businesses to scale, collaborate, and unlock new revenue opportunities.
For Developers
1. Simplified Development:
APIs let developers integrate existing services instead of building every feature from scratch. For example, adding Stripe’s payment API saves time and resources compared to developing a payment system internally.
2. Focus on Core Features:
By offloading secondary tasks like authentication (OAuth), email delivery, or data storage to APIs, developers can concentrate on building the core functionality of their applications.
3. Seamless Integration:
APIs enable interoperability between systems built on different technologies, ensuring smooth communication across platforms and devices.
4. Innovation and Agility:
APIs allow developers to quickly adopt new technologies, such as AI or machine learning APIs, without needing deep expertise in those domains, accelerating innovation and flexibility.
For Businesses
1. Faster Time to Market:
Using APIs reduces development time by leveraging ready-made solutions, helping businesses launch products faster and with more features.
2. New Revenue Opportunities:
By offering APIs to third-party developers, businesses can monetize their data and services, like Twilio or Stripe, whose APIs power countless apps globally.
3. Scalability and Efficiency:
APIs support scalable operations by integrating cloud-based solutions that automatically adapt to changing demand and workload.
4. Global Reach and Collaboration:
Through APIs, businesses can easily connect with international services, like Google Maps or PayPal, enabling global accessibility without custom development for each market.
5. Ecosystem Growth:
APIs foster strategic partnerships by allowing secure data and service sharing, expanding business ecosystems and driving mutual growth.
How Do You Test and Maintain APIs?
API testing ensures that your API functions as expected, handles errors properly, and delivers performance under load. Ongoing maintenance is necessary to keep the API secure, update it for new requirements, and monitor its performance in real-time.
1. Types of API Testing:
To ensure your API works efficiently and securely, comprehensive testing is essential. There are several key types of API testing:
- Functional Testing:
This tests whether the API performs as expected for all defined endpoints. It ensures that each API call provides the correct response, such as retrieving data or modifying resources correctly.
Example: Test if the GET /products/{id} endpoint returns the correct product information when given a valid product ID.
- Load Testing:
Load testing simulates heavy traffic to evaluate how the API handles large volumes of requests. This is crucial for scaling your API as your application grows. Use tools like Apache JMeter or Artillery to simulate multiple users accessing your API at once.
Example: Test if your API can handle thousands of requests per second without crashing or slowing down.
- Performance Testing:
Performance testing checks how the API performs under different conditions, such as varying response times and how well it handles errors. This helps to identify bottlenecks and optimize response times.
Example: Evaluate how fast an API endpoint responds to a request. A slow response might indicate the need for optimization or additional caching.
- Regression Testing:
Every time you make changes to the API (such as adding a new feature or fixing a bug), regression testing ensures that existing functionality isn’t broken. It’s critical to run regression tests before releasing updates.
2. Tools for API Testing:
- Postman: One of the most popular tools for API testing. It allows you to send requests, inspect responses, and automate tests.
- Swagger/OpenAPI: Useful for documenting, testing, and simulating API calls in a structured way.
- SoapUI: A tool for testing SOAP and REST APIs with advanced features for performance and security testing.
- Newman: A command-line tool that runs Postman collections, useful for integrating API tests into CI/CD pipelines.
3. Ongoing API Maintenance:
Once an API is deployed, regular maintenance is crucial to ensure it continues to meet user needs and operates efficiently.
- Monitor API Performance:
Use monitoring tools like Datadog, Prometheus, or Grafana to track key performance metrics, such as response time, uptime, and error rates. This helps you identify issues before they impact users. - Versioning:
As your API evolves, you’ll need to ensure that existing users don’t experience disruptions. Implement API versioning to manage changes to your API without breaking backward compatibility.
Example: Use versioning in your API endpoint paths (e.g., /v1/products, /v2/products) to allow clients to continue using the old version until they are ready to upgrade.
- Security Updates:
Regularly update your API to patch security vulnerabilities. Stay informed about the latest security threats and implement fixes promptly. - Handling Deprecation:
If your API introduces new versions or endpoints, be sure to notify users of deprecated functionality. Provide sufficient time for them to migrate to the new version. - Data Integrity:
Continuously ensure that the data returned by your API is accurate and up-to-date. Regularly check for data discrepancies or errors that may arise during API calls.
4. Documentation Updates:
API documentation must be updated as the API evolves. New endpoints, parameters, and changes to existing functionality should be clearly documented. Tools like Swagger can auto-generate updated documentation as you modify your API.
- Automatic Documentation: Tools like Swagger and Redoc can integrate with your API code to auto-generate documentation based on your endpoint definitions.
- Clear Communication: Inform developers using your API about new updates, deprecated features, and any changes to the data structure or authentication methods.
How to Scale APIs for Global Applications
Scaling APIs is crucial for handling increasing traffic and expanding into new markets. Effective API scaling involves optimizing performance, using cloud services, and implementing strategies like load balancing and caching to ensure that your API can meet global demands.
1. Load Balancing for Scalability:
As your API becomes more popular, it’s likely to experience higher volumes of traffic. Load balancing distributes incoming API requests across multiple servers, preventing any single server from becoming overwhelmed.
- Horizontal Scaling: This involves adding more servers or instances of your API to handle increased traffic. Cloud services like AWS Elastic Load Balancing or Google Cloud Load Balancing automatically adjust based on traffic.
- Round-Robin Distribution: A common load balancing technique where requests are evenly distributed across available servers.
- Global Load Balancing: Use GeoDNS or services like Cloudflare to direct users to the nearest server, improving response times globally.
2. Caching for Improved Performance:
Caching helps reduce load on your servers by temporarily storing copies of frequently requested data. This is particularly useful for data that doesn’t change frequently, such as product details or user profiles.
- API Caching: Use CDN (Content Delivery Networks) like Cloudflare or Amazon CloudFront to cache API responses at edge locations worldwide. This reduces latency and improves load times for global users.
- In-Memory Caching: Use in-memory caching systems like Redis or Memcached to store API responses on the server side, making subsequent requests faster and reducing database load.
3. Database Optimization:
As your API grows, so does the demand on your databases. Optimizing database performance is crucial for maintaining a fast, responsive API.
- Sharding: Split your database into smaller, more manageable pieces (shards) to distribute the load across different servers. This allows the API to access data more efficiently.
- Database Replication: Use master-slave replication or multi-region replication to distribute your database across different geographical regions, improving data access speed and fault tolerance.
- Read/Write Splitting: Split database operations into read-heavy and write-heavy operations, with separate databases for each. This ensures that read operations don’t overwhelm the write operations.
4. Cloud-Based Solutions for Scalability:
Cloud services offer flexibility in scaling your API globally without having to maintain physical infrastructure. These services automatically scale resources based on traffic and provide tools for high availability and fault tolerance.
- Auto-Scaling: Cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud offer auto-scaling solutions that automatically add or remove instances of your API depending on the demand.
- Global Infrastructure: Use cloud services with a global infrastructure to deploy your API in multiple regions. This allows users to access the API from the nearest data center, reducing latency.
- Serverless Architecture: With AWS Lambda or Google Cloud Functions, you can scale your API without managing servers. The cloud provider automatically handles the scaling based on demand, enabling high flexibility and cost-efficiency.
5. Monitoring and Analytics:
Real-time monitoring and analytics are crucial for scaling your API effectively. They allow you to track performance, identify bottlenecks, and monitor global usage patterns.
- API Monitoring Tools: Use tools like Prometheus, Datadog, or New Relic to monitor the health of your API, track response times, and detect anomalies.
- Error Tracking: Tools like Sentry or Loggly help you monitor and log errors, providing valuable insights into the API’s behavior across different regions.
6. Multi-Region Deployment:
Deploying your API across multiple regions ensures that users around the world experience fast and reliable access. This is especially important for global applications with a diverse user base.
- Edge Locations: Use CDNs to cache data at edge locations closer to your users. This significantly reduces latency and speeds up response times for global users.
- Region-Specific Endpoints: Some cloud providers, like AWS, allow you to set up regional endpoints for your API, ensuring that requests are served from the nearest server.
What is the Best Practices of API Security

API security is critical to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access. Implementing strong authentication, encryption, and validation methods is essential to safeguarding your API from potential threats and ensuring trust with users.
1. Authentication and Authorization:
Authentication and authorization are the cornerstones of API security. Ensuring that only authorized users can access certain API endpoints is essential for protecting data and preventing malicious use.
- OAuth 2.0: OAuth is widely used for secure authentication. It allows third-party services to access your API on behalf of the user without sharing their credentials. OAuth 2.0 is highly recommended for public APIs that require user authentication (e.g., logging in via Google or Facebook).
- JWT (JSON Web Tokens): JWT is another popular authentication method for stateless APIs. It involves generating a token that encodes user information, which is then sent with each request. The server verifies the token before granting access to resources.
- API Keys: A simple method where each user or system accessing the API is assigned a unique API key. Although API keys are easy to implement, they are less secure compared to OAuth or JWT since they can be intercepted if not properly encrypted.
2. Encryption:
Encrypting both data in transit and at rest is essential for ensuring the security of your API, particularly when dealing with sensitive information like passwords, financial data, or personal user data.
- Use HTTPS: Always use HTTPS to encrypt data in transit. HTTP can be intercepted, leading to potential data breaches. SSL/TLS certificates ensure that all data between the client and server is encrypted and secure.
- Data Encryption at Rest: Store sensitive data in an encrypted format within your database. This ensures that even if an attacker gains access to the database, the data remains protected.
3. Input Validation and Sanitization:
Allowing user input without validating it can leave your API vulnerable to attacks like SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS). Proper input validation is key to preventing these threats.
- Validate Input: Ensure that all incoming data is validated for type, length, format, and range. For example, if you expect a user ID to be an integer, ensure the input meets this condition before processing.
- Sanitize Input: In addition to validation, sanitize user input to remove any harmful characters or scripts that could be executed by the server.
- Use Parameterized Queries: To protect against SQL injection attacks, always use parameterized queries when interacting with the database. This ensures that input is treated as data, not executable code.
4. API Gateway for Security:
An API Gateway acts as a barrier between your API and external users, adding an additional layer of security. It can manage traffic, authenticate requests, enforce rate limiting, and prevent unauthorized access.
- Access Control: The API Gateway can enforce access control policies, ensuring that only requests from authorized sources reach your backend systems.
- Logging and Monitoring: API Gateways also help with logging requests, providing valuable information for security audits and real-time monitoring of API usage.
6. Secure Data Storage and Access:
Secure the data that your API uses and handles, including sensitive information such as passwords, personal details, and credit card numbers.
- Encrypt Passwords: Never store passwords in plain text. Always hash passwords using strong hashing algorithms like bcrypt or Argon2. Additionally, salt the hashes to make it harder for attackers to crack them.
- Least Privilege Principle: Grant users and applications the minimum level of access necessary for them to perform their tasks. This limits the impact of potential security breaches.
7. Regular Security Audits:
Conduct regular security audits and penetration testing on your API to identify vulnerabilities. Regular testing helps catch security flaws before attackers can exploit them.
- Penetration Testing: Hire security experts to simulate attacks on your API, helping you identify weaknesses in your security measures.
- Security Tools: Use tools like OWASP ZAP, Burp Suite, or Nessus to scan your API for vulnerabilities.
8. Implement Logging and Monitoring:
Tracking API activity in real time is crucial for identifying suspicious behavior or unauthorized access. By monitoring traffic patterns and logging key events, you can detect potential threats before they become serious security incidents.
- Event Logging: Log all API requests, especially failed authentication attempts or requests to sensitive endpoints. Store logs securely and ensure they are regularly reviewed.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Use monitoring tools like Datadog, Prometheus, or New Relic to track performance and detect abnormal usage patterns, such as spikes in traffic or suspicious API calls.
How Much Does It Cost to Build an API?
The cost to build an API can vary significantly depending on factors like complexity, features, development time, team size, and whether you’re building a public or private API. Generally, costs include development, testing, security, and ongoing maintenance.
| Category | Estimated Cost | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Basic API Development | $5,000–$20,000 | A simple CRUD API with minimal features. |
| Complex API Development | $20,000–$100,000+ | Includes advanced features like authentication, integration, and scalability. |
| Cloud Hosting | $50–$2,000/month | Costs vary depending on traffic and the services used (AWS, Google Cloud). |
| Security & Compliance | $5,000–$20,000 | Encryption, authentication, and legal compliance (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA). |
| Ongoing Maintenance | $1,000–$5,000/month | Includes bug fixes, updates, scaling, and security patches. |
Conclusion
API development is a critical skill for modern software systems, allowing seamless communication and integration between applications. Throughout this guide, we’ve covered the essential steps and best practices for designing, building, securing, deploying, and maintaining APIs. By following these principles, you can create APIs that are scalable, secure, and easy to use, ensuring a smooth experience for developers and users alike.
Building a high-quality API requires careful planning and ongoing maintenance. From selecting the right tools to continuously monitoring and updating your API, every stage plays a role in ensuring long-term success. Whether you’re creating an API for internal use or for third-party integrations, adopting these best practices will help you navigate the complexities of API development and deliver robust, efficient solutions.
Key Takeaways:
- Prioritize simplicity, consistency, and security in your API design to ensure ease of use and scalability.
- Choose the right development stack, plan your endpoints, and test thoroughly to build a robust API.
- Implement strong authentication, data encryption, rate limiting, and input validation to protect your API from threats.
- Select the right hosting environment, automate deployment with CI/CD pipelines, and monitor performance in real-time.
- Regularly update your API with new features, bug fixes, and security patches while managing versions and communicating changes effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
In this section, we address the most common queries surrounding API development. Whether you’re just getting started or looking for advanced solutions, find answers to your most pressing questions on topics like API security, versioning, tools, and best practices.
What is API development?
API development refers to the process of designing, building, and maintaining APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) that allow software applications to communicate with each other. APIs are essential for integrating different systems and enabling automation.
How do I create an API?
To create an API, you need to design endpoints that define how different parts of your system interact. Choose the right programming language and framework, such as Node.js with Express or Python with Flask. Write the logic for handling requests and responses, then test and deploy your API.
What is the difference between REST and GraphQL?
REST is a traditional architecture that defines operations (like GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) on resources, often using URLs. GraphQL, on the other hand, is a query language that allows clients to request exactly the data they need, reducing over-fetching. REST is simpler, while GraphQL provides more flexibility and control.
How can I secure my API?
API security can be achieved through various measures like using HTTPS for encrypted communication, implementing OAuth or JWT for authentication, and setting up rate limits to prevent abuse. Regularly monitor your API for vulnerabilities and apply security patches as needed.
What tools are available for API development?
Popular tools for API development include Postman for testing, Swagger/OpenAPI for designing and documenting APIs, and frameworks like Express (Node.js), Flask (Python), and Spring Boot (Java) for building APIs.
How do I version my API?
To version your API, you can include the version number in the API URL (e.g., /v1/users), or use request headers to define the version. Versioning ensures that older clients continue to work while new features are added without breaking existing functionality.
What are the best practices for API documentation?
Clear and detailed documentation is essential for an API’s success. Use tools like Swagger or Postman to auto-generate documentation. Ensure that each endpoint, input parameter, and response type is well-documented with examples. Keep the documentation updated with each new version.
Can I build an API without coding?
Yes, low-code and no-code platforms like Bubble, Retool, and OutSystems allow developers and non-technical users to build APIs with minimal coding. These platforms provide drag-and-drop interfaces and pre-built integrations to accelerate the API development process.
How do I deploy an API?
To deploy an API, you can use cloud hosting platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, or Heroku. Set up continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines to automate testing and deployment. Ensure that your API is monitored for performance, and implement scaling strategies as needed.
How can I test my API?
Testing an API involves verifying that all endpoints return the correct responses. Tools like Postman and Insomnia allow for manual testing of API requests and responses. For automated testing, you can write unit and integration tests using frameworks like Mocha or PyTest.
This page was last edited on 29 October 2025, at 2:33 pm
How can we help you?