- Android App Development Summary
- What is Application Development?
- What is Android?
- What is an Operating System?
- What is Android Operating System?
- Why should you learn Android app development?
- Benefits of Android App Development
- Low cost and high ROI
- Faster Deployment
- Multiple Platforms
- Versatility and Scalability
- Enhanced Security
- Customization
- Devices & Platforms for Android App Development
- Android Mobile App Development
- Android Tablet App Development
- Android Wear App Development
- Android TV App Development
- Android App Development for AR/VR Devices
- Chromebooks Apps
- Industry-Specific Android App Development
- Android apps for Travel and Hospitality
- Android Apps for Healthcare
- Android Apps for FinTech
- Android Apps for Sports and Teams
- Android Apps for eCommerce
- Android Apps for Automotive
- Android Apps for Entertainment
- The Functionality of the Android Application
- Step-by-Step Process of Android App Development
- Analyze Your Initial Requirements
- Select Experts for Your Team
- Generate Technical Documents
- Make a Basic Prototype
- Android App Development Environment
- Install Android SDK, Android Studio & Eclipse
- Install and Setup Android Studio
- Android App Development Technologies
- Programming Languages
- Tools You Should Know as an Android Developer
- Libraries
- Database & Frameworks
- Modern Android App Architecture
- Modern UI with Jetpack Compose
- Kotlin Coroutines for Background Operations
- Development of the App
- Use an Appropriate Methodology
- Start a New Project
- Know the Files
- The Layout Files
- Build the User Interface
- Run & Test Drive your App with an Emulator
- Testing Stage of Android App Development
- Performance Testing
- Testing Security of the App
- Usability Testing
- Supporting Stage
- AI & ML in Modern Android Development
- Android App Development Costs
- Android App Development Costs Based on the App Complexity
- Android App Development Cost Based on App Nature
- Android Development Cost Based on the Features
- Android App Development Cost Based on the Types
- Conclusion
- Android App Development FAQ
Android app development is making apps for devices running by Android OS (Operating system). Going through this process all along can be a daunting task for a beginner. But Android app development is much easier in Android Studio than iOS development. If you have read the previous article about iOS app development, this path will be easier for you.
It is no secret that you can open up many possibilities by learning Android app development. You are going to create something amazing that is going to change everything that we know.
Through Android software development, you can build some tools to improve your workflow. Not only for yourself, but you can also use your Android development skills to change the future era.
You can turn dreams into reality because Android lets you explore every possibility. With proper guidelines and technology, you can also master this skill. It is not that difficult.
All you need is a smooth roadmap to master Android software development. And in this post, we will give you a complete roadmap to Android app development. So follow these step-by-step guidelines and become an Android app developer in no time.
Android App Development Summary
In this guide, we will help you learn many things related to Android application development. But if you could know the summary of the whole article at the beginning, then the whole process would seem easier. So, in the chart below, we have made things short for you. So, here, you will get a total overview of Android development at a glance.
| Android Devices | Mobile, Android Tablet, Android Wearable devices, Android TV, AR/VR Devices, Chromebooks |
| Development Process | Planning Stage & Analyzing → Development Stage → Testing Stage → Deployment → Supporting Stage |
| Platforms | Android Studio, Android SDK, JDK, IDE, Native Android Development Kit, Xamarin, Cordova, and React Native |
| Programming Languages | Java, Kotlin, JavaScript, XML |
| Frameworks | React Native, RetroFit, Volley, Dagger2, Gradle, Glide, Picasso, etc. |
| Development Cost | Average cost around $10,000-$150,000 (depends on the size, types, features, etc.) |
What is Application Development?
App development is a step-by-step process of developing computer programs. The goal of developing apps is to perform different tasks and find a solution to specific problems.
Mobile applications and computer programs help people in different ways. For example, apps can automate business processes and enhance productivity.
Whatever it is Android, iOS, or Windows, every app development process follows the same steps. The steps include collecting data, planning, prototyping, development, testing, launch, and support.
The ultimate Android app development guide will make all the processes easier for you. Continue reading the full Android development tutorial, and you will become an Android Developer.
What is Android?
Android is a mobile operating system. It is built on top of the open-source Linux kernel and includes its own libraries, runtime, and frameworks for powering modern devices.
Android was designed mainly for touchscreen mobile devices like smartphones and tablets. Today, it also supports wearables, TVs, cars, foldables, and many other smart devices.
Tech giant Google acquired Android Inc. in 2005 and continued developing the platform. Then the developers of the Open Handset Alliance community worked together to expand and improve it.
They launched Android in November 2007 for the first time. The first commercial Android device was the HTC Dream.
What is an Operating System?
As computer software, an OS integrates resources between hardware and software. In an operating system, different types of hardware can work together simultaneously. And it provides a platform to run different bits of software to work with that hardware.
To put it simply, the analogy of stage acting can be shown here as an example. A stage play needs so many things, doesn’t it? Various appliances like lights, costumes, decorations, etc.
Besides, what is a stage drama without a director and actors? So, consider the equipment of stage drama as computer hardware.
Now, place the actors as different applications of that computer. Then, put the director as the operating system.
What is the Android Operating System?
Google’s Android and Apple’s iOS are the two main OS in today’s technology-based world. There are other OS (operating systems) like Windows.
But pretty much every flagship mobile phone runs on either Android or iOS.

So, as the article is about Android app development, you might want to know a little in-depth about the Android OS. But, of course, the answer will be more specific if the question is what Android is. And what do you mean by the Android operating system? So, let’s do some in-depth discussion about Android and Android operating systems here.
As a mobile operating system, Android has been reigning for over 17 years. As a result, a massive number of mobile phones and tablets are running this base OS globally. Besides, other operating systems also support Android applications. ChromeOS offers native support, while Windows 11 provides limited support through the Amazon Appstore.
The tech giant Google owns this open-source platform. It means anyone has access to use it for different purposes, such as individual or commercial. That is why Android is different from Apple’s iOS or Microsoft’s Windows.
Why should you learn Android app development?
Android is the world’s most popular OS, and 70% (Thirty-nine percent) of the global population uses it. Over 2.5 billion active devices are running on it, while Android has more than 3 billion users.
Besides, there are over 3 million Android apps on the Google Play Store, which is more than on iOS. Not only on Google Play, but other platforms also provide custom Android applications on the web. Android apps are customizable, too. Reference: Number of Android apps on the Play Store.
Here are some reasons why developers should learn Android development.
- Android is a Linux-based, open-source mobile operating system. So, the source code is available for anyone to use or modify.
- Not only smartphones, but many devices like Wear OS watches, tablets, TVs, e-readers, car systems (Android Auto), and even foldable devices use Android.
- Android has a huge global market share. As a result, big organizations across different industries are constantly looking for skilled Android app developers.
- Developers can choose jobs from a variety of Opportunities.
- Android app development is easier to learn, especially with modern tools like Kotlin, Jetpack Compose, and Android Studio.
How Small and Large Businesses Benefit from Android App Development?
Large and small enterprises are benefiting from Android by creating custom mobile applications. They are using Android to solve customer problems and increase their brand value. But how is Android app development helping small and large businesses? Here are some advantages, and as a developer, you should also know this before starting.
Low cost and high ROI (Return on Investment)
You can get increased user engagement from Android apps by making a little investment. In return, you can provide an interactive user experience for the users, which will lead to a higher return on investment (ROI).
Faster Deployment
Building an Android app is a fast development cycle. Besides, the versatility of Android applications is integrated with the complete system. So, businesses can increase scalability with the faster deployment of Android apps.
Android apps also allow integration with new and emerging technologies. New technologies such as IoT (Internet of Things), Augmented Reality, and Virtual Reality.
So, the flexibility of Android allows software companies to bring the best solution.
Multiple Platforms
Android apps can run on a wide range of devices and platforms, such as smartphones, tablets, TVs, wearables, foldable devices, and even ChromeOS. This broad compatibility helps businesses reach more users through a single app. With Android development, companies can leverage multiple environments and form factors without rebuilding the entire system from scratch.
Versatility and Scalability
Developers find Android’s ecosystem highly versatile and scalable. With tools like Android Studio, Jetpack libraries, and cloud integrations, apps can easily grow as the business grows. Android works across smartphones, tablets, Android TV, wearable devices, and IoT systems. It also supports advanced technologies like AR, VR, machine learning, and cloud computing. So, there is no lack of scalability on the Android development platform.
Enhanced Security
Android continues to improve its security with every new version. Modern Android platforms include built-in features such as app sandboxing, secure permissions, Google Play Protect, and the Play Integrity API to safeguard users from malware or unauthorized access. As a result, many businesses trust Android for secure transactions and data protection.
Customization
Google always gives priority to the User Interface. That is why they make a customizable OS, allowing businesses to get unlimited opportunities. Thus, enterprises and software developers get the best out of the UI by making one.
Besides, we all know that Android is a versatile platform. It means it has high flexibility and easy customization options. As a result, you can innovate and make interesting apps with diverse functionalities.
No one can limit the advantages of Android app development. If you look, you will find many. And this is how enterprises are leveraging Android. So, to conclude the advantages of Android, here we have listed the most valuable points. Have a look.
- Android provides a better User Experience (UX)
- Businesses can easily get improved branding
- Developers can make attractive Designs
- Loyal user base & empower your business
- It has an international presence
- Provide secure transactions
- And increased customer satisfaction
Finally, the benefits that Android provides is unlimited. You can address your every need through Android development. Most importantly, Android is the most popular platform, and it can win the Race of Business Competitors for you.
Devices & Platforms for Android App Development
Android is an open-source OS designed to run on many devices. From phones to tablets, televisions, and wearables, all kinds of devices support this platform. So, the huge range of devices provides great potential for Android apps.
To learn Android app development, you must know the devices on which your app will run. So let’s look at what kind of devices and platforms you need to target for developing Android apps.

Android Mobile App Development
Android has become one of the dominant OS since Google launched it publicly in 2008. It has been gaining success, especially for mobile devices. Android maintained its position as the leading mobile operating system worldwide in the third quarter of 2025, with a market share of about 73.75 percent. Its closest rival, Apple’s iOS, held approximately 25.87 percent during the same period. So, Android mobile app development offers you numerous business advantages. Reference: Market share of Android OS
The good news is that developers around the world are well aware of this platform. How it works, what it is capable of, and what more it can do soon is no longer a mystery to them. But the good news is that an Android app can be easily created in less time, and the cost is much lower.
Android Tablet App Development
Tablets today are powerful productivity and entertainment devices built on the Android ecosystem. Unlike earlier generations that were mainly used for media consumption, modern Android tablets support multitasking, split-screen workflows, stylus input, large-screen optimized UIs, and even desktop-like modes such as Samsung DeX and Lenovo’s productivity environments.
Android tablet app development now focuses on adaptive layouts, responsive UI components, and enhanced interactions for reading, drawing, video conferencing, learning, financial management, design work, and business tasks. As a result, Android tablet apps play an equally important role as smartphone apps, offering both mobility and a larger workspace for users.
Smartphones are the most used devices now. Users mostly use them for common daily actions like communication, listening to music, playing games, etc. On the other hand, tablets offer some next-level tasks like watching video content, studying, financial management, reading, business tasks, and more. So, the importance of Android tablet app development is equal to smartphone app development.
Android Wear App Development
Android wearable app development has become very popular these days. Now it is a game-changer in the technology market. With Android app development, developers can execute attractive-looking wearable apps. This specific app development also requires great ideas to capture customers’ attention. There are different kinds of wearable devices that need Android app development. Such as-
- Smartwatch App Development
- Fitness Tracking App Development
- AR/VR Companion and Sensor-Based Apps
- IoT-Based Wearable App Development
- Wearable messaging app
- Smart digital payments app
- Nutrition monitoring app
- Communication synchronizers app
- Navigation, GPS, and Maps Apps
Android TV App Development
What Google wants now is to keep users connected to smartphones, watches, cars, and smart TVs. With this in mind, Google first launched its Google TV in 2010. But in mid-2014, it was officially replaced by Android TV. Then Android TV became much more popular than Google TV as it was very close to standard Android.
For the first time, manufacturers used the Android 5.0 (Lollipop) version to run Android TV. But now they are using the latest versions, and it’s creating more opportunities.
Android TV needs innovative apps that provide a rich user experience. And when it comes to streaming on a large screen, there is no option for a good Android TV application. Usually, TV apps use phone and tablet structures. Thus, Android Developers can create new TV apps using Android app development.
Android App Development for AR/VR Devices
Tech giants like Google, Microsoft, and Apple are pouring billions of dollars into developing AR and VR. As a result, these emerging technologies are now changing lifestyles as well as businesses.
Android Apps Development for Augmented Reality (AR) has already made huge potential. It is going to dominate the future marketplace of Android application development.
Again, VR technology is pretty much like AR, but both have significant differences. With VR or Virtual Reality, we can transform how we live, work, and interact with outsiders. So, all these complex technologies need easier navigation for the users. That’s why these technologies need apps with innovative ideas. With Android app development, these technologies are going to change the world.
Chromebooks Apps
Usually, we are all familiar with Apple’s macOS and Windows. But Chromebooks are new players in the game and have offered a third option since 2011. Unfortunately, you can’t run these computers with Windows or macOS as they run on Linux-based Chrome OS.
Chrome OS is an operating system for the Chrome browser. You can do anything on the Chrome browser as you can do on Windows or Mac. However, these devices have changed a lot in recent days. Now, Chromebooks can run Android applications.

Industry-Specific Android App Development
In this article, we have discussed various devices and platforms so far. Although my main topic of discussion is how to create an Android app, we need to have a clear idea of something more. So at this stage, we will discuss some industry-specific Android Apps because most Android apps are developed for e-industry purposes. So, it is crucial to have a basic idea about them. So let’s have a look at what fields of industry mostly need Android app development.

Android apps for Travel and Hospitality
Nowadays, the travel industry is highly dependent on mobile applications. Those who use digital platforms can reach customers more easily. Travel and hospitality industries can use Smart room systems apps, hotel apps, AR (Augmented Reality), VR (Virtual Reality), and Big Data solutions for gaining customer satisfaction. In this case, they can apply innovative ideas through Android application development for travel and hospitality.
Android Apps for Healthcare
Android app development has had a great impact on the modern medical industry. Today, patients can easily book their appointments with specific doctors through mobile apps. Thus, they can use Android applications for better healthcare. Besides, there has already been a lot of development happening in this industry. For example, IoMT (Medical Things Internet) is one of the best examples of them. But, again, the present healthcare system needs more improvement. So, the medical industry can develop Android apps for patient monitoring, notifications, scheduling, tracking, and more. Through Android app development, they can provide better treatment.
Android Apps for FinTech
Banking, fund transactions, and all electronic systems for financial activities are called FinTech or Financial technologies. Android app development has made these technologies easier for consumers. FinTech industries can use Android apps for Mobile banking, e-wallet, real-time fraud detection, AI chatbots, etc.
Android Apps for Sports and Teams
The sports industry is a billion-dollar industry at the present time. Cricket, football, soccer, tennis, baseball, rugby, basketball, etc., are very popular because they have the highest number of audience. So, sports news channels can benefit from Android app development. With Android software development, industries can reach more audiences through sports apps, IoT, chatbots, beacons, geofencing, and other features.
Android Apps for eCommerce
In this electronic era, everything is going digital. The internet can do almost every job now. Thus, the commercial activities that are carried out through the internet are called eCommerce. Consumers can maintain commercial transactions by using an eCommerce platform. That means buying or selling products or services through the internet is eCommerce.
And Android applications are best suited for eCommerce. Developers can easily make an Android eCommerce store within hours. Android app development also ensures greater conversions and loyalty. You can learn more about eCommerce application development from here.
Android Apps for Automotive
Android applications for Automotive are providing promising results so far. For example, ride-sharing app Uber. Now it makes life easier as anyone can call an Uber through ride-sharing apps. Besides, there are other automotive apps for parcel and food delivery. These are included in Automotive, and Android app development has made it possible.
Android Apps for Entertainment
Can you imagine our lives without any entertainment these days? Entertainment is a basic need for human beings. From the primitive stage, humans looked for entertainment in various ways. Now, with the advancement of technology, we can all enjoy limitless entertainment. Even with Augmented Reality and 3D devices, people can find amazing ways for entertainment. For example, we have already seen the power of Android apps for playing games and watching movies. With Android app development, you can bring more innovative ideas for entertainment.
The Functionality of the Android Application
At this stage of Android app development, we will explain how Android applications work. Because soon after, we will show you how to do step-by-step Android application development. And as a beginner, it’s important to know how an Android app works. Otherwise, many things may be difficult for you to understand. But you can understand the development stage with ease if you know how the process works.
There are different ways to run an Android program on different platforms. However, microprocessors can run primitive Android software written in machine code. But it is impossible to run complex Android programs with machine code. That’s why different types of operating systems need to run them. But how?
Usually, operating systems provide a control layer that coordinates between apps and hardware. In Android, your app’s Kotlin or Java code is compiled into bytecode, which runs on the Android Runtime (ART). ART is the system that executes Android apps, manages memory, schedules processes, and connects your code with device hardware.
For native code written in languages like C++ (using the Android NDK), the compiler and linker generate native shared libraries. These libraries run side-by-side with your Kotlin or Java code and allow you to access low-level system features when needed.
This entire process enables the operating system to run the app smoothly, no matter how simple or complex it is.

Step-by-Step Process of Android App Development
Now, we have reached the core point of this article. Here, we will explain one by one what to do to develop a complete Android app and what kind of resources you need.
But you need to understand some important things first. We already know the details about Android Fundamentals. But when you go to develop an app, you must create a development environment. And that’s why you need to have some Android development tools before starting.
Below, you will find the key stages of the Android app development process that guide you from the initial idea to the final testing of your application.
- Analyze Your Initial Requirements
- Select Experts for Your Team
- Generate Technical Documents
- Make a Basic Prototype
- Android App Development Environment
- Android App Development Technologies
- Development of the App
- Testing Stage of Android App Development

1. Analyze Your Initial Requirements
Before starting your Android software development, it is necessary to analyze the basic requirements. First, you should fix the purpose of the application. Why you should develop an Android application and how the app could solve real-life problems.
Not only the purpose, but you also need to find the business scopes for the application. You may have to spend a lot of money developing an Android app, but it will be a total loss if you can’t achieve ROI.
Once the initial analysis is complete, you can move to the next step: setting up the essential Android software development tools. Before you start building the app, make sure the following tools are installed and ready. You should have basic knowledge of how to manage them.
- Install Android Studio (latest version)
Android Studio is the official IDE for Android development and includes everything you need to start building apps.
- Configure Kotlin and Jetpack Libraries
Modern Android development is Kotlin-first. Jetpack libraries, including Jetpack Compose, help you build clean, efficient UIs.
- Install Android SDK Components (via SDK Manager)
The SDK Manager inside Android Studio lets you install platform tools, build tools, and device support packages.
- Set Up an Android Emulator or Physical Device
Use the Device Manager in Android Studio to create an emulator, or connect a physical device for real-time testing.
With your requirements defined and your tools ready, you can begin the Android app development process with confidence.
2. Select Experts for Your Team
If you are going to work on a big project, you might need an expert Android app development team. What kind of experts the Android software development team should hire depends on the project.
First, you will need developers with strong expertise in Android programming languages. Modern Android development primarily uses Kotlin, along with Jetpack libraries and frameworks. So, it is important to know your exact requirements for Android application development before selecting the team.
Then find the perfect expert team at several Android development platforms, languages, frameworks, databases, tools, and solutions. You can also search for an Android app development company on Google to find the best experts in Android software Development, IDE, Android Development Tools, Android Apps Development Libraries, Android Application Development Languages, and Android App Development Frameworks.
3. Generate Technical Documents
Technical documentation in software engineering is very crucial to keep the flow of development. It is often called the umbrella term that covers everything from written documents and materials. No one can ignore this step, and it is essential for software product development.
A whole software development lifecycle (SDLC) needs countless documents. With all these, you can explain product functionality, unify project-related information. It also allows for discussing all the confusion happening between clients and developers.
So, Android software development also needs proper technical documentation. And you must ensure technical documentation before starting your Android development.
Recommended Technical Documents for Android App Development:
| Document Type | Purpose / Description |
|---|---|
| Product Requirements Document (PRD) | Defines the app’s purpose, target users, core features, and business goals. |
| Software Requirements Specification (SRS) | Detailed list of functional and non-functional requirements, workflows, and system behaviors. |
| Technical Architecture Document | Describes architecture patterns, modules, data flow, APIs, backend integration, and chosen tech stack. |
| UI/UX Design Documentation | Includes wireframes, mockups, user flows, design guidelines, and screen specifications. |
| API Documentation | Lists endpoints, request/response formats, authentication rules, and error handling. |
| Database Design Document | Contains schema diagrams, entity definitions, relationships, and data sync logic. |
| Test Plan & QA Documentation | Covers test cases, scenarios, device matrix, performance testing, and automation scripts. |
| Security & Compliance Documentation | Details encryption, permissions, secure coding practices, and Play Store policy compliance. |
| Deployment & Release Notes | Instructions for building, signing, uploading to Play Store, and version release history. |
| Maintenance & Support Guidelines | Outlines bug reporting, update cycles, monitoring tools, and long-term support procedures. |

4. Make a Basic Prototype
When you are finished with all the primary procedures, you can make a basic prototype for your Android app. In this stage, use all the relevant information and make a basic design of the Android app.
First, sketch the app idea on paper or on a design tool. This sketch helps you outline the app’s main screens and features. After the sketch, create a basic prototype that shows the layout and flow of the app. It does not need to be perfect, just clear enough to understand how the app works.
Next, you will move on to mockups. In this phase, you design the user interface (UI) by deciding how each screen will look, what elements will appear on it, and how users will navigate through the app. This includes buttons, colors, text, icons, and basic interactions.
A good prototype ensures that the app layout and user journey make sense before development begins, saving time and reducing mistakes later.
| Step | Example (Food Delivery App) |
|---|---|
| Sketch the Idea | Draw Home, Menu, and Checkout screens as simple boxes. |
| Build Prototype | Create clickable screens: Home → Menu → Checkout. |
| Create Mockups | Add colors, images, icons, text, and layout styling. |
5. Setting up Android App Development Environment
Now is the time you create an Android app development environment. If you do not build a proper environment, then where are you going to write the code? There is much popular software for writing your code and setups. Choose some of the applications as per the expertise of the Android development team.
The first step is downloading the necessary tools and SDK components. Modern Android Studio includes everything you need to begin development, so you only need to install it and configure the SDK from within the IDE. To set up the environment for Android development, you can use macOS, Windows, or Linux, as Android Studio supports all three platforms.
5.1. Install Android SDK, Android Studio & Eclipse
Android SDK is also a must-have tool you need for the development of your Android app. In addition, it will provide more essential tools such as libraries, a debugger, an emulator, and more. As a result, you can also prepare documentation, sample codes, and watch tutorials.
SDK was the only Android App development tool before Android Studio.
Besides, Android SDK is part of Android Studio, developed by Google. It is the official IDE for Android application development.
5.2. Set Up Android Studio
If you are a beginner and have never used Android Studio, you may face difficulties the first time. So, in the following section of this Android app development, we will show you how to set up Android Studio.
- Download and install the latest version of Android Studio. It comes with a built-in JDK, so you don’t need to install Java separately
- Now, double-click on the .exe File of the Android Studio
- Now, please select the proper location where you want to install it, then click the Next button
- Click on the Install button
- After a while, it will show that “Android Studio has been installed successfully, and it is ready for use.”
- When you see the pop-up, click on the finish button to open it
6. Android App Development Technologies
When you complete the app development environment, you need the right technologies. Therefore, it should be your first concern in the development stage.
For complete software development, you will require a different set of technologies. These Android development technologies include programming languages, libraries, databases & frameworks, Android Studio, and more.
As mentioned earlier in this tutorial, the type of app you want to build will guide your technology choices. In this stage, the technologies you use will depend entirely on your app’s requirements, complexity, and long-term goals.
In Android app development, the most important technologies include:
- Programming languages (Kotlin, Java)
- UI technologies (Jetpack Compose, XML)
- Development tools (Android Studio, Gradle)
- Libraries & frameworks (Jetpack, Retrofit, Hilt, Room, etc.)
- Databases (Room, SQLite, Realm, Firestore)
- Testing tools (JUnit, Espresso)
- Cloud & backend tools (Firebase, AWS, custom APIs)
To build a complete Android application, developers typically work with several core technology categories, such as programming languages, UI tools, development tools, libraries, frameworks, databases, testing tools, and cloud services. Each of these will play a role in building, running, and maintaining your Android app.
However, let’s start with the programming languages you will need for the coding of your application.
6.1. Which Programming Languages Do You Need to Develop an Android App?
Kotlin is the recommended and preferred programming language for Android app development. It offers concise syntax, null-safety, modern concurrency with coroutines, better performance, and full interoperability with Java.
You can still use Java and integrate it with the Android Software Development Kit (SDK). With Java, you can maintain existing Android apps and continue development seamlessly through the Studio environment, as Java and Kotlin work together without issues.
The next platform for a programming language is C++. In that case, you will need the Native Android Development Kit (NDK). Using C++ with the NDK allows you to build performance-critical parts of your app, such as game engines or low-level libraries, while still writing the main app logic in Kotlin or Java.
There are also some third-party tools like Flutter, React Native, and Xamarin for Android app development. These cross-platform frameworks allow developers to use a single codebase to build apps for both Android and other platforms.
Look at the list, and you will find the most popular programming languages and technologies for Android apps.
- Kotlin
- Java
- C++ (via NDK)
- JavaScript or Dart (via cross-platform frameworks)
- XML (used in legacy layout systems; modern apps often use Jetpack Compose)
6.2. Tools You Should Know as an Android Developer
Besides the core technologies you use to build an Android application, there are some additional tools that make development easier. These tools help you test the app, fix issues, check performance, and manage your code properly. So, knowing them will help you work more efficiently.
Here are some important tools every Android developer should know:
➤ Android Debug Bridge (ADB): ADB is a command-line tool that lets you communicate with real or virtual Android devices. Developers use it to install or uninstall apps, capture logs, run shell commands, simulate inputs, and debug device-specific issues that may not appear in the emulator.
➤ Device Manager & Virtual Device Tools: While Android Studio includes emulators, the Device Manager gives you more control to create, configure, and manage virtual devices. Developers often test on multiple screen sizes, chipsets, and Android versions—something Device Manager simplifies greatly.
➤ Android Studio Profiler Suite: The profiler tools help identify issues related to performance, such as:
- CPU usage
- Memory leaks
- Network consumption
- Frame rate and rendering problems
➤ Logcat: Logcat provides real-time logs from your app or device. It helps you trace crashes, warnings, lifecycle events, and app behavior while debugging. With filters and search options, it’s one of the most relied-upon diagnostic tools.
➤ Git & GitHub / GitLab / Bitbucket
Version control is vital for any development project. Git allows you to track changes, collaborate with other developers, and manage releases. Platforms like GitHub and GitLab also offer issue tracking, pull requests, and project automation that make team-based Android development far easier.
➤ Postman or Insomnia (API Testing Tools): Most apps communicate with APIs. Tools like Postman allow you to:
- Test API endpoints
- Inspect responses
- Validate authentication
- Troubleshoot backend communication
➤ JSON Validators & Data Format Tools: Since modern apps exchange data in JSON, using tools to format, validate, and mock JSON responses saves time and reduces integration errors.
➤ Firebase Crashlytics & Analytics Dashboards: For production apps, Crashlytics helps monitor crashes, ANRs (Application Not Responding errors), and stability trends. Analytics tools (e.g., Firebase Analytics) give insights into user behavior, feature usage, and retention critical for iterative product improvement.
➤ Lint & Static Code Analysis Tools: Tools such as Android Lint, Detekt (for Kotlin), and SonarLint help detect:
- Code smells
- Bad practices
- Security vulnerabilities
- Performance issues
➤ Continuous Integration / Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) Tools: Modern teams automate their build, test, and deployment pipelines using:
- GitHub Actions
- GitLab CI
- Bitrise
- CircleCI
- Jenkins
➤ Design & Prototyping Tools: While not directly coding tools, Android developers frequently collaborate with designers using:
- Figma
- Adobe XD
- Sketch
6.3. Which Libraries Do You Need to Follow?
You will need a set of libraries for developing an Android app. Along with Android app development technologies, a set of must-have libraries will help you save a lot of time. If you want to make a bug-free Android application, then libraries can help.
| #JetpackCompose #Room #Retrofit #OkHttp #Coil #Hilt #WorkManager #ARCore #TensorFlowLite #Lottie #ObjectBox |
At this stage, we have included a list of some best Android Apps development libraries. Check out those from here.
When developing an Android application, you may need a unit testing library, image libraries, networking libraries, and others. But there are some other facts that you should consider when choosing a library.
| #See the popularity of the library you are going to choose #Look for the reliability of the author of the library #Consider a well-written library #See if the library has the proper license #Choose Open Source Libraries #Check out the core features that you need for your app |
How can you evaluate the best library for your Android app development? Here, consider the tips and suggestions for the library evaluation process.
6.4. Database & Frameworks
For storing and managing data of your Android application, you will need a suitable database. Using databases will help you make a more responsive app with less dependence on network connectivity.
It is becoming a popular trend for offline usage. Everyone likes to keep app data locally or make copies of databases in the cloud. So that they can sync data once a day whenever the network is available. With this, the app becomes faster and functional even when there is a limited internet connection. And users like it.
There are some popular databases. You can use any of that according to your needs. Here is a list of the most common and popular databases that Android developers use.
Databases:
- Room (built on SQLite)
- SQLite
- Realm Mobile Database
- Couchbase Lite
- ObjectBox
- MongoDB Atlas / Realm Sync (for cloud-backed apps)
- Firebase Realtime Database
- Firebase Firestore
Example: Room Database Entity
@Entity
data class User(
@PrimaryKey val id: Int,
val name: String
)DAO
@Dao
interface UserDao
@Query("SELECT * FROM User")
suspend fun getUsers(): List<User>
}Room provides a modern, type-safe way to work with data in Android apps and replaces the old SQLiteOpenHelper approach.
Frameworks:
| #React Native #Flutter #JetpackCompose #Retrofit #OkHttp #Hilt #Koin #Glide #Coil | #Picasso #JUnit #Espresso #Mockito #Robolectric #RxJava (legacy but still used in some projects) #Coroutines #WorkManager #Braintree |
6.5. Modern Android App Architecture
When you build an Android app, it is important to follow a clean structure so your code stays easy to manage as the app grows. Modern Android app development uses the MVVM (Model–View–ViewModel) architecture. In this approach, the UI layer shows data on the screen, the ViewModel prepares and manages that data, and the Model layer handles where the data actually comes from.
Most apps use a Repository to collect data from different sources, such as an API or a local database. This keeps the rest of your app simple because it only needs to talk to the repository, not every data source directly. For bigger projects, developers sometimes add a Domain layer with “use cases,” which helps keep business logic separate from UI and data.
To avoid writing the same setup code again and again, Android developers use Hilt for dependency injection. It helps the app create and share important components, such as ViewModels, network clients, and repositories.
6.6. Modern UI with Jetpack Compose
Modern UI with Jetpack Compose is Android’s declarative, Kotlin-based toolkit for building native user interfaces. It simplifies Android app development by letting developers describe what the UI should look like at any state, rather than how to update it, resulting in less code, powerful tools, faster development, and seamless adaptive design across devices.
It replaces traditional XML layouts with composable functions, making UIs more intuitive, reactive, and maintainable.
Basic Example: A Simple Composable Function
The example below shows how Compose displays a simple greeting message:
@Composable
fun GreetingScreen() {
Text(
text = "Hello Android!",
modifier = Modifier.padding(24.dp)
)
}This small function creates a UI element without any XML. Compose automatically renders the text and applies padding.
Previewing the UI in Android Studio
Compose includes built-in preview support, allowing developers to see UI changes instantly without running the app on a device.
@Preview(showBackground = true)
@Composable
fun PreviewGreeting() {
GreetingScreen()
}Previews help designers and developers iterate faster and maintain a smoother workflow.
Managing UI State in Compose
Modern apps often need to respond to user interactions. Compose makes this easier by providing state management tools:
@Composable
fun CounterScreen() {
var count by remember { mutableStateOf(0) }
Column(modifier = Modifier.padding(16.dp)) {
Text(text = "Count: $count")
Button(onClick = { count++ }) {
Text("Increase")
}
}
}The UI updates automatically when the state changes, without requiring manual refreshes or complex lifecycle handling.
6.7. Kotlin Coroutines for Background Operations
Modern Android apps often need to perform work in the background, such as loading data, calling an API, or saving information. In modern Android app development, Kotlin Coroutines simplify this process by allowing apps to run tasks without blocking the user interface. They help keep the app smooth and responsive, even when handling heavy operations.
Coroutines are now the recommended way to manage asynchronous work in Android development.
Simple Coroutine Example
suspend fun loadData(): String {
return withContext(Dispatchers.IO) {
"Data loaded"
}
}Here, the task runs on a background thread while the UI remains fast and responsive. This makes coroutines a powerful tool for building modern, efficient Android apps.
7. Development of the App
After collecting all the necessary tools, the main development will start. But in the early stages of Android development, some urgent work has to be done. To make the whole development process easy, we have arranged each step one by one.
So, read the rest of the article carefully to create an app by yourself. Then, find what you need to do in the development stage.
7.1. Use an Appropriate Methodology
Though many still follow the traditional approach, you can choose one that aligns best with your app. But for strict planning, documentation, and build processing, the traditional approach is great. Some methodologies lie at the core of managing app development projects. Which are-
- Agile
- Scrum
- Kanban
- Waterfall
Most modern Android developers follow Agile-based methodologies, as they support iterative development, frequent updates, faster feedback cycles, and continuous improvement. Agile frameworks like Scrum or Kanban allow teams to adapt quickly to changing requirements.
Waterfall methodologies, on the other hand, are still used for projects that require predictable, highly structured phases such as analysis, design, implementation, and maintenance. However, they are less common for contemporary mobile app development, where flexibility and rapid iteration are important.
7.2. Start a New Project
After having Android Studio and all other tools in your machine, start a new project.
First, make a new project from File>New>New Project in Android Studio. Then choose a project template that will define your code and UI elements. You will find a word called “Activity,” a “screen” for showing the app’s activities.
But for the first time, select an “empty activity” to create an activity and some files. Now, give a name and “package name” for your new application.
When your users install the app, they will see this name on their device. But, the package name is for the internal reference that Android will differentiate from other apps. So, compose it using your top-level domain and app name.
Finally, select a location where you need to save the files. Also, select the language you are going to use for programming.

7.3. Know the Files
The files and folders are important for developing Android apps. Unfortunately, in Android Studio, you cannot rename these files as you want. So keep them as they are.
If you are a first-time developer, then you may find it hard with so many files. But don’t worry! Here is what you need to do.
Files you see in MainActivity.kt or MainActivity.java are the main logic files. These help you define how they behave.
Now, look on the left. There you will find
MyApplication > app > src > main > java (or kotlin) > com > companyname > myapplication
You may notice some codes that are already on the main page. These are called “boilerplate code.” It means that the code is similar across different app projects for performing some basic tasks.
The good thing is that modern Android development reduces a lot of this boilerplate. Kotlin helps minimize repetitive code, and Jetpack Compose reduces the need for XML layout files. This makes your app easier to build and maintain, even if you are a beginner.
7.4. The Layout Files
This part of coding is to define the location of the layout files. A layout file allows you to define activity looks and add elements like buttons, text, and windows.
By going MyApplication > app > src > res > layout, you will find this file. If you double-click on this File, it will open in the main window, where you can edit the XML structure. You can also switch to the “Code” or “Split” view to see both the design and XML side-by-side.
In modern Android development, you can create your UI using XML layouts or Jetpack Compose. XML is still widely supported, especially in existing projects, while Jetpack Compose is the recommended approach for building new UI because it reduces boilerplate and makes UI development faster and more flexible.
Ultimately, you will need to learn either Kotlin or Java along with the appropriate UI system your project uses. Mastering these will help simplify the development process in the long run.
7.5. Build the User Interface
If your project uses XML layouts, locate the “activity_main.xml” file from the “res/layout” folder to access the current activity’s UI.
You can open an XML file outside Android Studio in any text editor or browser. When you open it inside Android Studio, the IDE reads the XML file and displays the corresponding layout in the design editor.
Then, you will see the layout activity in the middle pane. And the name of the app will appear at the top.
At the top left, locate a tab called “Palette.” This tab includes all the available user interface components, such as Text fields, Widgets, and Layouts. You can drag and drop these elements directly into your UI.
Once you add a UI element, Android Studio will show two panes: the design preview and the XML code. From there, you can drag items into place and adjust them visually.
Let’s write a text on the screen. In the image, Android Studio already placed a “Hello World” text at the top left. From there, you can now change the properties of the TextView.
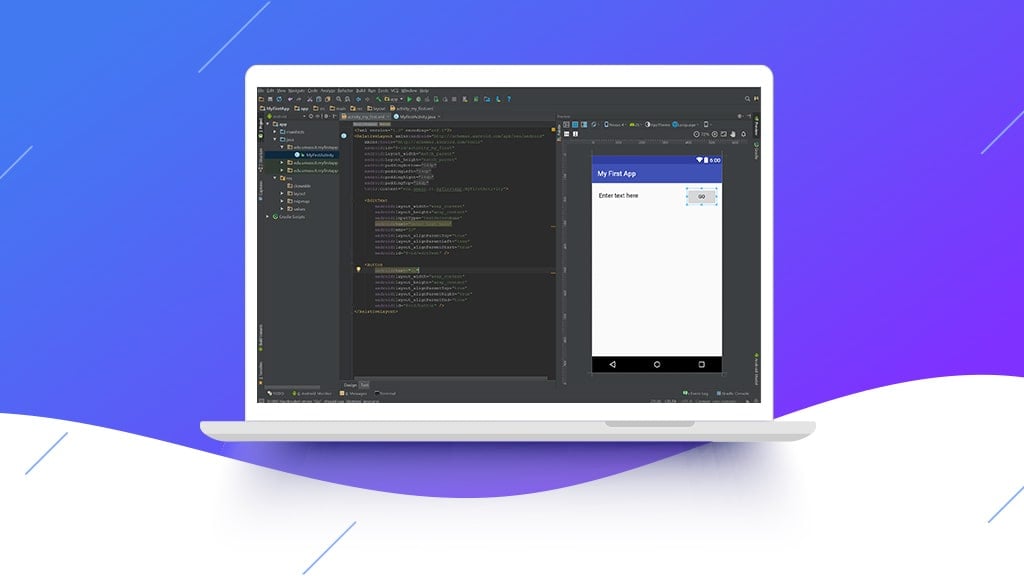
You can make changes to the editable properties of the TextView component. For example, if you want to show the “Hello World” text more uniquely, change its text size to 24sp. The term SP is for scale-independent pixels. Now, make the style bold by clicking the B button in the TextStyle. Finally, you are done setting up the User Interface.
In modern Android development, you can also build your UI using Jetpack Compose, which lets you write UI directly in Kotlin code without XML. Compose makes it easier to manage layouts, state, and animations. Whether you choose XML or Compose, Android Studio provides powerful tools to help you set up the User Interface.
7.6. Run & Test Drive your App with an Emulator
When you think the development is complete, it’s time to test the app. First, you will need to run your newly developed Android app on an emulator.
In Android Studio, you can do it easily. If you have installed an emulator, then the only things you need to do are
- Build the code
- Selecting the emulator
- And run the app on the emulator
To run the project, click the “Run” button. Then you will see the emulator and device selection dialog box. Some virtual devices can automatically detect the app/project. Select your preferred device, click Next, and the emulator will boot just like a real phone. The process may take a moment, depending on your system performance.
Android Studio will use the Apply Changes feature to quickly update your app without a full rebuild, making testing much faster.
Modern versions of Android Studio use Apply Changes, which allows you to update certain parts of your running app without performing a full reinstall. This helps shorten the development and testing cycle.
You can also re-run the app anytime. For that, press the “Run” or “Apply Changes” button again, and the emulator will install the updated version of the app for testing.
From your very first project, Android Studio provides a powerful and user-friendly environment. With its debugging tools, device manager, and real-time previews, you can quickly test your ideas and transform them into fully functional Android applications.
8. Testing Stage of Android App Development
After you finish running the app, testing processes begin. Android app testing is a necessary procedure. You can save valuable time and cost if you start the process in the early stage of Android app development. Anyway, your app needs several tests and QA through an expert QA team. They should perform usability, compatibility, security, UI checks, and performance testing to make the app consistent.
Every Android app needs three three-step testing phase. Such as-
- Performance Testing
- Security Testing
- Usability Testing

8.1. Performance Testing
Performance testing is essential for determining system performance under a specific load. In addition, through performance testing, you can ensure other attributes like scalability and reliability. Besides, it would tell how well the app responds and how fast its screens are loading.
After passing all the performance testing, go for the API and backend testing. In this stage, ensure that the app is capable of handling a high load.
8.2. Testing the Security of the App
Testing an Android application is one of the most important parts of Android app testing. Successful security testing prevents any potential vulnerability that can lead to a hack.
A third party should not access confidential user data. That is why personal user data, such as date of birth, residential address, and personal and private info such as passwords, credit card PINs, and bank account numbers, needs to be protected.
In that case, security testing can enhance the Android mobile app’s security. Here, the QA team searches for any weaknesses, technical flaws, or vulnerabilities in the app.
8.3. Usability Testing
The success of Android app development depends on the usability of the app. So, in this stage, you should perform usability testing to make the app more user-friendly. You may have detected many problems and identified them before or during the interface design.
That is why you need to test usability to solve those issues in the final stage of the development. Next, you must ensure that your app works smoothly with no bugs. To do that, perform beta testing. It is where you will need external user testing. External users are a limited, targeted audience that uses a beta version of your app. Then they provide real feedback with bug reports.
9. Supporting Stage
There is still 10% work remaining after you fully develop the app. And this 10% is the total time for supporting your app.
Now we are at the final stage of Android app development. It is where you are ready to launch the app in the marketplace. Then start providing ongoing support.
But there are also some crucial facts you should keep in mind while deploying the app on the Google Play Store. Usually, app stores have some specific policies for verifying the new app. For example, it goes through a review process after the deployment and takes a few days to months. But don’t worry. If your app quality is good enough and you have maintained all the policies, it will be fine.
After the deployment, it is crucial to keep track of the trends, upgrade the features. Then, improve the app as the audience demands and provide regular updates. Here are the three most important supports you will need to provide for the app’s success.
- Ongoing maintenance and monitoring
- Appointing developers to fix bugs and add improvements
- 24/7 support for handling user issues or technical problems
AI & ML in Modern Android Development
AI and Machine Learning are now key parts of modern Android app development. As user expectations grow, apps need to offer faster performance, smarter interactions, and more personalized experiences. AI helps Android apps analyze data, recognize patterns, and automate tasks, while ML allows them to learn and improve over time.
Today, many popular Android features are powered by AI technologies. Modern Android apps commonly use AI and ML for:
- Image Recognition: Identifying objects, products, or scenes
- Face Detection & Biometrics: Strengthening security and authentication
- Speech Recognition: Enabling voice commands, assistants, and audio processing
- Recommendation Engines: Suggesting products, videos, music, or content
- AI Chatbots & Virtual Support: Automating customer service inside the app
- Predictive Analytics: Forecasting trends, user actions, or business outcomes
- Text Understanding: Sentiment analysis, translation, summaries, and classification
Android developers use several modern tools to bring AI and ML to mobile apps:
- TensorFlow Lite: Runs ML models efficiently on Android devices
- Firebase ML Kit: Offers ready-made ML APIs for text, face, and object detection
- ONNX Runtime: Deploys optimized and portable ML models
- Google AI Services: Power apps with speech, translation, and natural language processing
These tools simplify development and allow apps to run advanced AI features with high performance.
AI-powered capabilities help businesses increase user retention, reduce manual processes, improve decision-making, and deliver more meaningful digital experiences. As Android continues to evolve, AI and ML will play a bigger role in building smarter, more responsive, and more efficient mobile apps.
Android App Development Costs
Android application development costs depend on some factors. Generally, the app’s size matters the most. Then comes the nature of the app, whether it is online or offline. Another important fact is the features of the app. Finally, complexity and the types of development will cost you differently for making an Android app. Here, we have outlined Android software development costs based on different factors.
Android App Development Costs Based on the App Complexity
The intricacy of your app is one of the most significant Android app development cost factors. As the complexity increases, the development cost rises as well.
Here’s a breakdown to help you understand how different feature levels affect the total development costs.
| App Complexity | Functionality | Average Costs |
| Basic Android App | MVP functionality, Standard UI Components, Single platform | $5000-$12,000 |
| Medium Android App | Multiple integrations, Tailored UI, Single platform | $10000-$50000 |
| Enterprise Android App | Advanced functionality, Real-time features, Complex architecture | More than $50000 |
| Time of Development x Hourly Rate = App Cost |
Simple apps with basic features might cost $5,000–$12,000, while more advanced apps with complex functionality, such as real-time data processing, AI-driven features, animations, or highly polished UI/UX, can range from $50,000 to $150,000+, depending on the scope.
The more features and complex functionality you require, the higher the Android app development price will be.
Android App Development Cost Based on App Nature
An online Android app will cost you a higher price, but it has some great benefits. On the other hand, an offline Android app is cheaper.
Android Development Cost Based on the Features
Costs depend on features (user auth, payments, GPS), design (UI/UX), backend, team location/experience, and ongoing maintenance (15-20% annually). A basic app with few features costs less, while extensive features like real-time sync, custom admin panels, and third-party integrations significantly increase development hours and budget
Android App Development Cost Based on the Types
Types of Android application development greatly impact the total cost. It depends on which platform you are developing the app for. You can choose Native, Cross-Platform, or Progressive Web Apps development. Each one has its complexity and time frame. So, different types of Android app development will cost you differently.
Additional Cost of Adding AI Features to an Android App
If you want to add AI features like Image Recognition, Face Detection & Biometrics, Speech Recognition, Recommendation Engines, AI Chatbots & Virtual Support, Predictive Analytics, or Text Understanding, the development cost will increase. These features require specialized AI models, extra engineering work, and sometimes cloud services. As a result, AI integration typically adds 20% to 50% extra cost for basic features and even more for advanced or custom machine learning models.
Conclusion
After the deployment of your Android app, you will face much user feedback. Then you may need to fix upcoming issues or bugs. However, as a beginner, you will find little difficulty in developing your first app. But the more you work, the whole process will be easier gradually. So, build something every day.
You can also take help from expert developers to build your Android app. After reading this whole article, you might have some questions. Please do not feel any hesitation in asking questions about Android application development by simply commenting below. It will clear all the confusion you have with Android app development. There will be some frequently asked questions after this. You may also find your answers in that.
Android App Development FAQ
In this stage, we will share some frequently asked questions with you. The most common questions about Android app development are-
Is it worth learning Android development?
There is no debate that Android app development is dominating the app industry. Therefore, it is worth learning Android application development for those who want to be app developer. As a highly skilled Android app developer, you can solve millions of problems by making an app.
Is Python necessary for Android app development?
Python is not necessary for Android app development, and Android does not support Python as a native development language. Modern Android apps are primarily built using Kotlin (the recommended language) or Java.
Which app is best for Android app development?
The best app for Android development is Android Studio, the official IDE from Google. It includes everything you need to design, code, test, and debug Android apps, such as the Android SDK, emulators, profiling tools, and built-in support for Kotlin and Jetpack Compose.
What is an API in Android?
The application programming interface is known as the API. It is a software tool that allows two apps to talk to each other.
How long does it take to develop an Android app?
The development timeline depends on the app’s size, features, and complexity. A simple Android app may take 4 to 8 weeks, while more advanced apps with backend systems, AI features, or complex UI design can take several months.
Is Kotlin better than Java for Android development?
Yes. Kotlin is now Google’s recommended language for Android development because it is more concise, safer, and better suited for modern app architecture.
Can I build an Android app without coding?
It is possible to build simple apps using no-code platforms, but professional, scalable, and customized apps still require traditional Android development.
Is Jetpack Compose better than XML for UI development?
Jetpack Compose offers faster development, cleaner code, and better state handling compared to XML. It is now the recommended modern UI toolkit for building Android interfaces.
Can AI be added to an existing Android app?
Yes. AI features can be integrated into an existing app, but the amount of required modification depends on the app’s current architecture and data sources.
Why do developers use Room instead of SQLite?
Room is easier to use, safer, and better integrated with modern Android tools. It reduces boilerplate code and eliminates many common errors found in raw SQLite.
What does a ViewModel do in Android development?
A ViewModel stores and manages UI-related data so the user interface stays stable during configuration changes like screen rotations.
How do I publish an Android app on Google Play?
Publishers must prepare an Android App Bundle (AAB), write app descriptions, upload screenshots, complete policies and content forms, and submit the app for review through the Google Play Console.
This page was last edited on 14 December 2025, at 10:12 am
Contact Us Now

Contact Us Now
Start a conversation with our team to solve complex challenges and move forward with confidence.











Great guide try adding some screenshots as well so that beginners can understand in even better manner.
Thank you so much for showing interest in this article. I will definitely try to make this article more user-friendly.
I’m looking to start my own Android app and this android app development guide helped me learn a lot about android app development!
Thank you so much!
Great piece of content! This blog piece seems so intuitive to me now like – Why didn’t I read it before. Quite informative!
Thank you so much for your encouraging feedback.
Its very good Guide About Android app development.
Thank you so much.
I likewise believe hence, perfectly indited post! .
Thank you so much!
Thanks for sharing such amazing information and i hope you keep on share such kind of useful information daily.
Thank you so much!
Thanks for sharing such an amazing information i hope you keep on sharing such interesting and informative articles
Thank you so much!
Thanks for sharing such an amazing information i hope you keep on sharing such interesting and informative articles.
Thank you so much for your feedback. Please stay connected with us!
Thanks for sharing such a nice guide on Android app development. I found it very effective for learning!
Thank you very much to you too for the feedback!
This guide on android app development is very helpful!
Thank you so much for your nice feedback!
Very nice post. I just stumbled upon your weblog and wanted to say that I ve really enjoyed surfing around your blog posts.
Thank you so much!
Greetings! Very helpful advice in this particular article! It is the little changes which will make the most important changes. Thanks a lot for sharing!
Thank you so much!
I wanted to thank you for this fantastic read I definitely loved every little bit of it. I have you book marked to check out new stuff you post.
Thank you so much for your feedback. Please read more from our knowledge base and let us know your thoughts.
I was suggested this web site by my cousin. Im not sure whether this post is written by him as nobody else know such detailed about my difficulty. You are incredible! Thanks!
Thank you so much for your effective feedback.
Thanks for sharing excellent informations. Your web site is so cool. I’m impressed by the details that you¦ve on this site. It reveals how nicely you understand this subject. Bookmarked this web page, will come back for more articles. You, my friend, ROCK! I found simply the information I already searched everywhere and simply could not come across. What a perfect site.
Thank you so much for reading the article. Please stay put.
Your post served as a wonderful reminder that even tiny adjustments can result in large gains.
Thank you so much!
Hi just wanted to giѵe you a quiсk һeаds up. You have shared a really great post.
Thank you so much for your nice feedback!
Your blog article is informative and engaging, offering valuable information in a concise and concise manner. The website’s attractive design and user-friendly interface improve the overall reading experience. Keep up the great work!
Thank you so much Gerry for your nice feedback!
An impresive guide on Android app development. I have discovered a lot of information here.
Thanks Alberto for your feedback. Please continue reading more article on Riseup Labs.
This guide is very helpful!
Thank you so much Michael!
How great! This article is very resourceful to use its information for my project! Thanks for the help!
Welcome Graciela! And also thank you so much for your valuable feedback!
This guide is very helpful!
Thanks Hunter!
Hi, Your article is really great! Actually, I was looking at to Fantasy Basketball app. Your article really helped me a lot. I also visit your website, and I am really impressed with your website. Now I am subscribing to your newsletter for the daily update. Good Luck! Keep sharing like this.
Thanks Chad for your valuable feedback.
This guide is very helpful!
Thank you so much D. Maxwell. Please Read More
This is very helpful, Thank you so much!
Thank you so much John!
Your article is really great! A lot of information about Android App development will be helpful to me, so keep sharing like this Mam/Sir. Good luck!
Your article is really great! A lot of information about Live cricket score App development will be helpful to me, so keep sharing like this Mam/Sir. Good luck!
Great post! I found it very informative and helpful in understanding the entire process of Android app development. As a beginner, I find it helpful to have a step-by-step guide to follow. Thank you for sharing your knowledge and experience with us!
Thank you so much Akbar, for your kind words! I’m always here to share knowledge and experiences, and I truly appreciate your feedback. If you have any more questions or if there’s anything specific you’d like to see in future posts, feel free to let me know.
Fantastic guide on Android app development! Your step-by-step breakdown is super clear, and I love the practical tips. Consider adding more visuals for an even better user experience. Keep up the great work! Looking forward to more.
Thank you so much Cooper, for the positive feedback! I’m thrilled to hear that you found the guide helpful. Great suggestion on adding visuals—I’ll definitely incorporate more images for an improved user experience in future articles.Stay tuned for more content, and I really appreciate your support!