It’s the end of the quarter, and the finance team is drowning in invoices, approvals, and reports. Deadlines are looming, and the pressure is on to ensure everything is processed accurately and on time. But despite their best efforts, mistakes slip through data entries are duplicated, approvals get missed, and hours are spent on tasks that could be automated.
This is where workflow automation comes in. By automating repetitive tasks, like invoice processing and report generation, workflow automation eliminates bottlenecks, reduces human error, and saves valuable time. It empowers teams to focus on more strategic work, driving efficiency across departments and improving overall productivity.
What Is Workflow Automation?
Workflow automation refers to the use of software to automatically execute a series of tasks based on predefined rules and triggers, eliminating the need for manual effort. These workflows are typically designed to streamline repetitive tasks, enhance efficiency, and reduce errors. By automating processes, businesses can ensure that tasks are completed faster, more accurately, and with greater consistency.
In the context of business operations, IT network administration, and DevOps, workflow automation plays a crucial role. For businesses, it simplifies processes like data entry, approvals, and document management, allowing teams to focus on higher-value tasks. IT teams benefit from automated network monitoring and system management, ensuring that potential issues are detected and resolved proactively. For DevOps teams, workflow automation accelerates the development and deployment process, facilitating smoother collaboration between developers and IT operations.
By removing the bottlenecks created by manual tasks, workflow automation enhances overall productivity and allows organizations to scale more effectively.
Types of Workflow Automation
Workflow automation can be categorized into different types based on the processes and tasks being automated. The two main categories are business process workflows and robotic process workflows. Each type has its own set of applications and benefits, depending on the complexity and nature of the tasks involved.
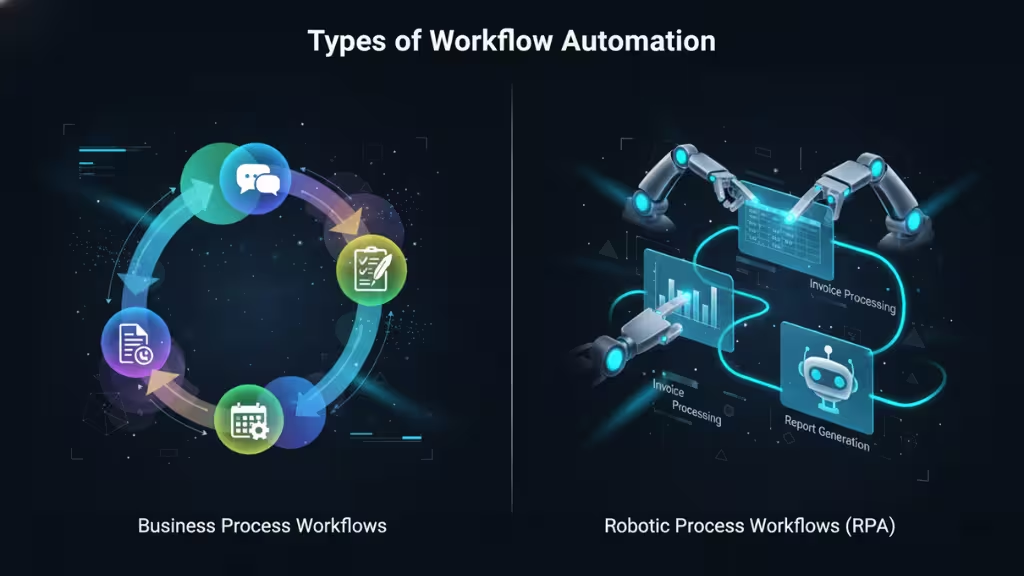
Business Process Workflows
Business process workflows focus on automating the overall flow of tasks within a business process. These are often broader workflows that span multiple departments or functions. For example, automating the sales process could involve triggering notifications, creating tasks, and generating reports as leads move through different stages of the sales funnel.
Key characteristics of business process workflows include:
- End-to-End Automation: These workflows automate entire processes, from initiation to completion, making them suitable for processes that require multiple touchpoints across different teams.
- Flexibility: Business process workflows can be customized to suit the specific needs of different business functions, whether it’s HR, finance, customer support, or sales.
- Collaboration-Driven: Since business processes often involve cross-functional collaboration, business process workflows facilitate communication and ensure that tasks are handed off smoothly from one team to another.
Robotic Process Workflows
Robotic process automation (RPA) is a more specialized type of workflow automation that focuses on automating rule-based tasks using software robots. These robots are designed to mimic human actions within digital systems, such as copying and pasting data between applications or generating reports based on structured data inputs.
Key characteristics of robotic process workflows include:
- Repetitive Task Automation: RPA is ideal for automating high-volume, repetitive tasks that follow clear, predefined rules. These tasks include data entry, invoice processing, and report generation.
- Efficiency Gains: By automating these repetitive tasks, RPA allows employees to focus on higher-value activities that require human judgment and decision-making.
- Cost Reduction: RPA can help businesses significantly reduce the cost of manual labor by replacing human effort with bots that can work continuously without fatigue.
Both business process workflows and robotic process workflows play an essential role in optimizing operations, with business process workflows focusing on cross-departmental processes and RPA targeting task automation.
Benefits of Workflow Automation
Implementing workflow automation can provide a range of advantages, benefiting businesses, developers, IT network administration, and operations teams. Let’s explore these benefits in more detail.
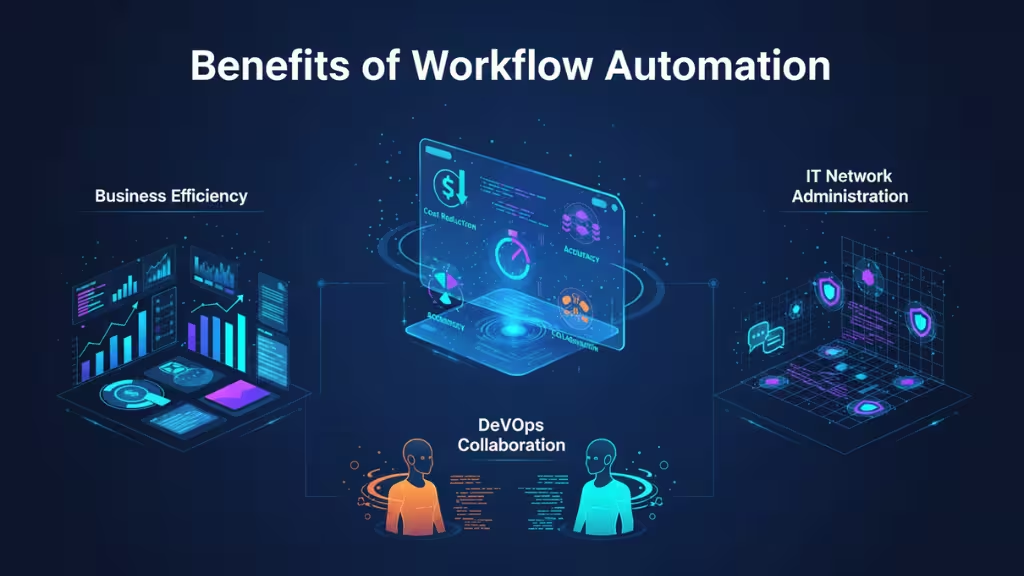
Benefits for Businesses
Workflow automation transforms how businesses operate by reducing human errors and eliminating time-consuming, repetitive tasks like manual data entry. In organizations with outdated, manual processes, scaling can be a challenge due to the labor- and capital-intensive nature of operations. Automation increases capacity for scalability and improves efficiency.
Here are some key benefits for businesses:
- Reduces Costs: By automating repetitive tasks, businesses can reduce labor costs and increase operational efficiency.
- Streamlines Task Management: Automation allows businesses to organize and prioritize tasks, ensuring that work is completed on time and with fewer resources.
- Reduces Time in Process Cycles: With automated workflows, businesses can speed up processes, leading to faster decision-making and quicker delivery of products or services.
- Decreases Errors: Automating manual data entry and task tracking minimizes the chance of human errors and oversight, leading to more accurate results.
- Automates Approval and Document Flows: Workflow automation can streamline approval processes and document management, ensuring faster approvals and better compliance with regulations.
Benefits for Developers and Operations (DevOps)
In the DevOps space, workflow automation bridges the gap between development and operations teams. It simplifies the release process and fosters clearer communication between traditionally siloed departments. By automating manual tasks, workflow automation eliminates common bottlenecks and delays caused by repetitive follow-ups and miscommunications between teams.
Key benefits for DevOps teams include:
- Improved Release Management: Automation accelerates development cycles, enabling faster and more reliable releases.
- Enhanced Communication: By automating routine tasks and sharing information across systems, developers and operations teams can communicate more effectively and collaborate seamlessly.
- Reduces Silos: Workflow automation breaks down the traditional barriers between developers and IT operations, facilitating a more integrated workflow and reducing inefficiencies.
Benefits for IT Network Administration
Automation brings critical benefits to IT network administration, particularly in improving oversight and network management. It enhances the ability to monitor, configure, and analyze systems in real time, providing IT teams with valuable insights into network health, security, and performance.
Key benefits for IT network administration include:
- Better Administrative Oversight: Workflow automation provides IT teams with greater visibility into network and system operations, improving decision-making and responsiveness.
- Improved Network Health: By automating network monitoring and issue detection, IT teams can quickly address potential problems before they escalate, ensuring continuous system uptime.
- Enhanced Security: Automated security workflows allow IT teams to quickly apply patches and monitor systems for vulnerabilities, reducing the risk of cyberattacks or breaches.
- Efficient Resource Allocation: Automation frees up time for IT teams to focus on strategic initiatives, rather than constantly addressing routine tasks and maintenance.
Workflow Automation Use Cases
Workflow automation is applicable across a wide range of industries and departments. Below are some of the most common use cases where workflow automation delivers tangible benefits by streamlining tasks and improving efficiency.
Employee Onboarding
Employee onboarding is a crucial process for integrating new hires into an organization. Automating this workflow ensures that new employees are set up for success from day one. Tasks like document submission, benefits enrollment, and training assignments can be automated, reducing the administrative burden on HR teams and providing new hires with a smooth and consistent experience.
- Automation Benefits: Speeds up the onboarding process, minimizes human error in document handling, and ensures compliance with onboarding regulations.
- Example: When a new employee is hired, a workflow automation tool can automatically trigger the creation of email accounts, access to internal systems, and enrollment in required training modules.
Approval Workflows
Approval workflows are common across organizations, involving processes like budget approvals, leave requests, or project sign-offs. Automating these workflows ensures that requests are routed to the appropriate stakeholders and that approvals happen promptly. Workflow automation can send automatic reminders, ensure timely approvals, and even escalate requests if needed.
- Automation Benefits: Reduces delays in approval processes, ensures transparency, and helps keep track of approval timelines.
- Example: A manager submits a request for time off, which is automatically routed to their supervisor for approval. Once approved, HR is notified, and the employee’s schedule is updated.
Document Management
Managing documents, such as contracts, reports, and client records, is a task that can be streamlined with workflow automation. Automated systems can classify, store, and retrieve documents based on predefined rules, ensuring that employees can easily access the information they need without manual searching or filing.
- Automation Benefits: Increases document retrieval speed, reduces errors in filing, and ensures compliance with storage protocols.
- Example: After a contract is signed, an automated workflow can route it to the appropriate department, categorize it, and upload it to a secure cloud storage platform.
IT Operations
In IT departments, routine maintenance tasks like system monitoring, updates, and incident management can be automated for better efficiency. Workflow automation tools can be set to detect potential issues, trigger alerts, and even execute predefined troubleshooting steps, ensuring that IT teams can focus on more complex issues.
- Automation Benefits: Improves system uptime, minimizes human intervention, and ensures faster incident resolution.
- Example: A server monitoring tool automatically detects when a system is nearing capacity and triggers a workflow that reallocates resources to prevent downtime.
HR Processes
HR departments deal with various processes such as payroll, performance evaluations, and benefits administration. Workflow automation simplifies these tasks by automating the tracking of employee hours, generating pay slips, and scheduling performance reviews, ensuring consistency and timely processing.
- Automation Benefits: Reduces the administrative workload, ensures compliance with HR policies, and speeds up processing times.
- Example: An employee’s leave request automatically triggers an HR workflow that adjusts payroll, updates the team calendar, and notifies the department head.
Sales and Marketing
Sales and marketing teams often handle tasks like lead generation, follow-ups, and campaign reporting. Workflow automation can ensure that leads are nurtured effectively, that marketing campaigns run on schedule, and that reports are automatically generated.
- Automation Benefits: Increases lead conversion rates, improves customer engagement, and reduces time spent on administrative tasks.
- Example: When a new lead is captured through a website form, the system automatically sends a welcome email and assigns the lead to a sales representative for follow-up.
Implementing Workflow Automation
Successfully implementing workflow automation within an organization involves several key steps, from identifying suitable tasks for automation to configuring the right tools for the job. Below is a step-by-step guide to help you understand how to implement workflow automation in a structured and effective manner.
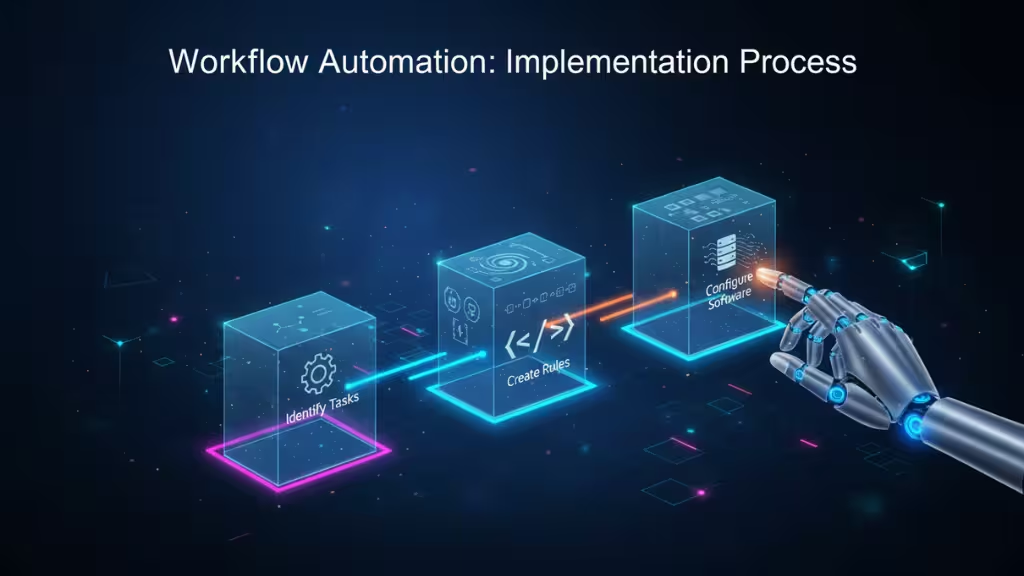
Identifying Tasks for Automation
The first step in implementing workflow automation is identifying which tasks are best suited for automation. Not all tasks should be automated, so it’s important to focus on repetitive, rule-based activities that can be performed without human intervention. These are typically tasks that involve handling structured data or follow a predictable process.
- Criteria for automation: Look for tasks that are time-consuming, prone to human error, or require little decision-making. Examples might include data entry, document routing, or approval workflows.
- Prioritize high-impact tasks: Focus on automating tasks that will provide the most significant efficiency gains, cost savings, or error reduction for your team or organization.
Creating Rules and Logic
Once the tasks for automation have been identified, the next step is to define the rules and logic that will govern the automation process. This involves outlining the sequence of actions and decisions that need to be made for each task. These rules are the core of any automated workflow, as they determine how the process will unfold without human intervention.
- Define triggers and actions: For each task, determine what triggers the automation (e.g., a new lead is captured, an employee submits a leave request) and what actions should follow (e.g., sending a confirmation email, notifying a manager).
- Map out the process: Visualize the flow of tasks, decisions, and handoffs to ensure clarity and accuracy in how the automation will work. This step is crucial for creating efficient workflows that deliver consistent results.
Programming and Configuring Software
The final step in implementing workflow automation is configuring and programming the software tools that will carry out the automation. This is where you select the right workflow automation software and set up the rules, triggers, and actions you’ve previously defined.
- Choose the right software: There are various workflow automation tools available, ranging from simple task automation platforms to more sophisticated systems capable of handling complex workflows. Some popular tools include Zapier, Trello, Monday.com, and Microsoft Power Automate.
- Integrate with existing systems: Ensure the automation tool integrates with your existing systems and software platforms. This ensures smooth data flow and allows for seamless automation across your tech stack.
- Test the automation: Before fully deploying the automation, it’s essential to test it in a controlled environment. This ensures that the workflow performs as expected and that any issues can be addressed before going live.
The Future of Workflow Automation
As the landscape of workflow automation continues to evolve, several key trends are shaping the future of the industry. New startups and established companies alike are pushing the boundaries of automation with innovative solutions that offer greater flexibility, intelligence, and ease of use. Here are some of the most significant trends in the future of workflow automation:
Low-Code and No-Code Automation
One of the most significant trends in workflow automation is the rise of low-code and no-code platforms. These solutions are designed to democratize automation by making it accessible to a wider range of users beyond just developers. Decision-makers, business analysts, and direct collaborators can now design and deploy workflows without needing advanced coding knowledge. This shift is expected to foster more collaborative, symmetrical workflows within organizations, moving away from traditional top-down structures. As a result, workflow automation will be more agile, with process improvements being driven by those closest to the work.
- Impact: Low-code platforms empower teams to automate processes quickly, iterate on workflows in real-time, and accelerate decision-making by involving more stakeholders in the automation process.
AI and Machine Learning in Workflow Automation
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is playing an increasingly important role in workflow automation, particularly in the enterprise. By integrating machine learning and predictive analytics, AI-powered automation systems can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns, forecast future needs, and suggest process improvements. This enables businesses to not only automate routine tasks but also make more informed, data-driven decisions to optimize workflows.
- Impact: AI-driven insights will lead to more dynamic and responsive workflows that can adapt to changing business conditions. For example, predictive analysis can help identify bottlenecks in real-time and automate corrective actions before issues arise, improving overall operational efficiency.
Automation in IT Network Administration
One of the last areas where manual processes still dominate is IT network administration. However, workflow automation is now extending to this crucial aspect of business operations. The future of workflow automation will see innovations in network issue management, where visual workflows and advanced automation tools will enable IT teams to manage, control, and navigate network issues with greater ease and precision.
- Impact: The automation of IT network management will allow for faster issue resolution, reduced downtime, and better resource utilization. Visual workflows will simplify the creation and mediation of network tasks, making it easier for IT professionals to build and maintain automation systems.
Templatized and Integrative Workflows
Another key trend is the increased availability of templatized workflows. These pre-built templates will serve as foundational building blocks for businesses looking to automate common processes. Whether it’s onboarding new employees, handling customer support requests, or processing invoices, businesses will be able to leverage templates to quickly deploy automation solutions without starting from scratch.
Moreover, workflow automation tools are becoming increasingly integrative, offering seamless connections with pre-existing systems and automations. This will allow organizations to build on their current infrastructure and integrate new automation capabilities with minimal disruption.
- Impact: Templatized workflows and enhanced integration capabilities will simplify the adoption of workflow automation, reduce setup times, and improve the scalability of automation across the organization.
These trends represent just a glimpse of what’s to come in the future of workflow automation. As AI, low-code platforms, and integrative solutions continue to develop, businesses will have more powerful and flexible tools to streamline operations, enhance collaboration, and stay competitive in a rapidly evolving digital landscape.
Conclusion
Workflow automation is a powerful strategy for enhancing operational efficiency, reducing errors, and freeing up valuable human resources to focus on higher-value tasks. Whether in business operations, IT management, or DevOps, automating repetitive tasks provides tangible benefits in terms of time savings, cost reduction, and consistency. By identifying tasks that are suitable for automation, creating well-defined rules, and implementing the right software, organizations can reap the rewards of a more streamlined and effective workforce.
In the future, workflow automation will continue to play a key role in business transformation, especially as it integrates with AI, machine learning, and robotic process automation (RPA) to handle even more intricate tasks. By adopting automation technologies, businesses can not only increase efficiency but also improve the quality of their services, enhance customer satisfaction, and drive sustainable growth.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What types of tasks are best suited for workflow automation?
The tasks that are best suited for workflow automation are repetitive, rule-based tasks that don’t require human decision-making. These include data entry, report generation, approval processes, and document routing. Automating these tasks helps free up time for employees to focus on more strategic, value-added activities.
Can workflow automation be used across all industries?
Yes, workflow automation can be applied to a wide range of industries, including healthcare, finance, manufacturing, retail, and IT. Whether you’re automating HR processes, IT system monitoring, or customer service workflows, automation can improve efficiency and reduce costs across virtually any sector.
How do I choose the right workflow automation tool?
When selecting a workflow automation tool, consider factors like integration capabilities with your existing systems, ease of use, scalability, and pricing. Tools like Zapier and Microsoft Power Automate are good options for businesses looking for easy integration with popular apps, while ServiceNow might be more suitable for larger organizations with complex IT processes.
Is workflow automation difficult to implement?
The complexity of implementing workflow automation depends on the scope and scale of the workflows you want to automate. For simple tasks, tools like Zapier or Trello can be set up easily without technical expertise. For more complex automation needs, you may need to invest in more advanced tools or work with an IT team to configure and integrate the systems.
What are the long-term benefits of implementing workflow automation?
The long-term benefits of workflow automation include sustained efficiency gains, cost reductions, fewer errors, and greater scalability. As businesses grow, automation ensures that processes remain efficient and consistent without requiring proportional increases in workforce size. Additionally, automation frees up human resources for more creative and strategic tasks, contributing to overall business growth and innovation.
Can workflow automation integrate with existing software?
Most modern workflow automation tools are designed to integrate seamlessly with popular software systems and applications. For example, Microsoft Power Automate connects with Office 365, SharePoint, and Azure, while Zapier supports integration with thousands of apps. This integration ensures that data flows smoothly between systems, eliminating silos and creating more cohesive workflows.
This page was last edited on 2 December 2025, at 4:09 pm
Contact Us Now

Contact Us Now
Start a conversation with our team to solve complex challenges and move forward with confidence.