- Introduction to Python Web Development
- Pros and Cons of Python for Web Development
- Key Concepts in Python Web Development
- Python Frameworks for Web Development
- Python Libraries for Web Development
- Pure Python Web Development vs Frameworks
- Python Web Development Step By Step Process
- How to Create Your First Python Web Application
- Advanced Concepts in Python Web Development
- Deploying and Hosting Python Web Applications
- Best Practices in Python Web Development
- Common Challenges in Python Web Development
- Career Opportunities and Resources for Python Web Developers
- Python Web Development for Businesses
- Future Trends of Python for Web Development
- Conclusion
- FAQs for Python Web Development
Python web development is popular for building dynamic websites and web applications. Did you know that Google, Netflix, and Spotify use Python to deliver top-tier web experiences that reach millions?
The Python ecosystem consists of a robust set of frameworks, libraries, and tools that simplify web development and help developers create scalable and efficient web solutions.
I have designed this Python web development all-in-one guide to be a comprehensive resource for business leaders, technical teams, and anyone interested in understanding how Python can transform web development.
Are you ready? Let’s get started!
Why Should You Read This Guide?
Before we dive into the specifics of Python website development, I want to give you an overview of what you will learn.
- Comprehensive Overview of Python Web Development:
Get a complete picture of Python web development, from foundational concepts to advanced topics, without having to piece together information from multiple sources. - Real-World Case Studies: See how other businesses (Google, Spotify, Netflix) have successfully leveraged Python for various applications—from e-commerce platforms to internal tools—offering inspiration and practical examples.
- Strategic Insights for Business Leaders: Learn how Python can support your business goals with cost-effective, scalable, and secure web applications. This guide breaks down the “why” behind Python’s popularity and what it can mean for your business regarding growth, efficiency, and long-term sustainability.
- Framework Selection Guidance: Understand the strengths and weaknesses of popular Python frameworks like Django, Flask, and FastAPI, and discover which option best suits your specific needs and budget.
- Hiring and Collaboration Advice: If you’re considering hiring Python developers or working with a development agency, this guide provides tips on what to look for, how to vet candidates, and how to ensure a productive working relationship.
Whether you’re new to Python or looking to deepen your understanding, this guide will help you make confident, informed decisions for your next web development project.
Explore More Web Development Guides:
Introduction to Python Web Development

Python is one of the most well known programming languages for web development. Known for its readability, versatility, and vast library of frameworks, Python allows developers to create a wide range of web applications, starting from simple websites to complex, data-driven platforms.
In this section, we’ll explore what makes Python a standout choice for web development and how businesses are leveraging it to build scalable, efficient, and secure applications. We cover:
- What is Python?
- What is Web Development?
- What is Python Web Development?
- History of Python in Web Development
- Why Use Python for Web Development?
- Applications of Python in Web and Internet Development
What is Python?
Python is a high-level, versatile programming language known for its simplicity, readability, and broad applicability.
Created by Guido van Rossum and first released in 1991, Python was designed with a philosophy that emphasizes code readability and ease of use, making it accessible to both beginner and experienced developers.
Its clear syntax and flexibility have made Python one of the most popular programming languages worldwide, widely used in web development, data science, artificial intelligence, automation, and beyond.
What is Web Development?

Web development is the process of designing and building websites and web applications accessible through the Internet. It involves utilizing various technologies, coding languages, and tools to create, maintain, and enhance websites for diverse purposes and functionalities.
At its foundation, web development is divided into two primary components:
1. Front-End Development
This aspect of web development focuses on the visual and interactive elements that users see and interact with directly. Front-end development includes designing the user interface (UI), ensuring a positive user experience (UX), and implementing the overall layout and style. Technologies such as HTML (Hypertext Markup Language), CSS (Cascading Style Sheets), and JavaScript are used to create visually engaging, responsive, and user-friendly websites.
2. Back-End Development
Back-end development handles the behind-the-scenes functionality of a website, focusing on the server-side elements. This includes creating the logic and infrastructure that power the website, process data, and connect with databases. Back-end developers use languages like Python, Ruby, Java, and PHP to construct the core components that support and enable the web application’s functionality.
Together, front-end and back-end development bring websites to life, ensuring they are both engaging for users and technically sound for optimal performance.
What is Python Web Development?
Python web development involves building web applications and websites using Python as the primary programming language. Known for its clarity, flexibility, and an extensive ecosystem of libraries and frameworks, Python has become a go-to language for web development projects of all sizes.
In Python web development, developers write server-side code in Python to manage the core functionalities of a web application. This includes processing HTTP requests and responses, managing data storage and retrieval, implementing application logic, and generating dynamic content for users.

History of Python in Web Development
Python’s journey in web development has evolved significantly since its inception, from a general-purpose language to one of the most popular choices for building dynamic, scalable web applications. Understanding Python’s history in web development provides insights into its strengths, growth, and why it’s now widely used in this field.
1. The Early Days of Python (Late 1980s – 2000s)
Python was created by Guido van Rossum in the late 1980s and officially released in 1991. Its design philosophy emphasized readability, simplicity, and ease of use, making it accessible to both novice and experienced programmers. While web development was not initially its primary focus, Python’s versatility and clear syntax laid the groundwork for it to be used in many programming domains.
First Web Development Frameworks
In the early 2000s, as the internet grew, Python began gaining traction in web development with the emergence of frameworks designed to make building websites and web applications simpler. Frameworks like Zope and Plone were among the first, enabling Python developers to create dynamic websites and manage content more effectively.
2. The Rise of Django and Flask (Mid-2000s)
Two of Python’s most popular web development frameworks were introduced in the mid-2000s; Django and Flask.
Introduction of Django
Django, launched in 2005, was a major milestone for Python web development. Created as a high-level framework focused on fast development and clean design, Django offered a “batteries-included” approach with built-in features such as ORM (Object-Relational Mapping), an admin interface, and user authentication. Its versatility and reliability led to widespread adoption among developers looking to build complex, data-driven applications quickly and efficiently.
The Flexibility of Flask
Around the same time, Flask emerged as a lightweight alternative to Django. Officially released in 2010, Flask is a microframework that gives developers more control over their applications by keeping things minimal. Without the built-in features of Django, Flask appeals to developers who prefer flexibility, making it ideal for smaller projects or those requiring highly customized setups.
Growth in Popularity
During this period, Python’s popularity surged, especially among startups and technology-driven businesses. Django and Flask gained substantial user bases, positioning Python as a solid choice for both large-scale applications and small, focused projects. These frameworks also made Python a strong competitor to other web development languages, like PHP and Ruby.
3. Expansion with Data Science and Machine Learning (2010s)
The 2010s saw an explosion of Data Science, AI, and Machine Learning, with Python at the forefront of the revolution. As a result, Python web development began leveraging data.
Integration with Data Science and AI
By the 2010s, Python had become the go-to language for data science, machine learning, and AI applications due to its extensive libraries (e.g., Pandas, NumPy, and TensorFlow). As data-driven applications became more common, developers could easily integrate machine learning models into their Python web applications, making it a powerful choice for businesses focused on analytics, personalization, and predictive capabilities.
Web Applications Leveraging Data
With the rise of data-centric applications, Python web frameworks adapted to accommodate these new requirements. Developers could build web applications that seamlessly integrated complex data analytics, dashboards, and machine learning models, giving Python a unique advantage for organizations looking to leverage data.
4. FastAPI and Modern Web Development (Late 2010s – Present)
Modern web development has embraced asynchronous programming, and Python is no different. It introduced FastAPI to serve the trend of real time applications.
The Advent of FastAPI
Released in 2018, FastAPI is a relatively new Python framework specifically designed for building high-performance APIs. Known for its speed and efficiency, FastAPI uses asynchronous programming, making it suitable for applications with high concurrency demands, such as real-time data processing, streaming services, and large-scale APIs. FastAPI’s performance rivals that of frameworks like Node.js, making it popular among developers who need speed and reliability.
Popularity in Asynchronous Programming
As web applications become more interactive and real-time, asynchronous programming has become essential. FastAPI and the introduction of async/await in Python’s syntax have allowed developers to build faster, more responsive applications that can handle thousands of requests simultaneously. This feature has positioned Python as a robust choice for modern web applications requiring real-time functionality.
5. Python’s Current Position in Web Development
Python has emerged as one of the best choices for web developers due to its mature ecosystem of tools and libraries. As a result, it is used by small, medium, and large companies globally.
A Mature Ecosystem of Tools and Libraries
Today, Python boasts a mature ecosystem of web development tools and libraries, covering a wide range of use cases from full-stack development (Django) to lightweight, flexible projects (Flask) and high-performance APIs (FastAPI). Python’s extensive library support has also fostered a vibrant community and countless resources for developers.
Wide Adoption Across Industries
Python is now used by companies of all sizes across industries, from tech giants like Google and Instagram to startups and enterprises in finance, healthcare, and retail. Python’s flexibility and robustness make it adaptable to both traditional web applications and innovative data-driven or AI-powered platforms, solidifying its role as a staple in web development.
Why Use Python for Web Development?
Python has become a top choice for web development due to its simplicity, versatility, and strong support ecosystem. Its features make it ideal for building both simple and complex applications that are reliable, scalable, and easy to maintain. Here are some of the primary reasons why Python is so widely used for web development:
Readable and Easy-to-Learn Syntax
Python’s clean and intuitive syntax allows developers to write code that’s easy to understand and maintain, streamlining the development process. Its readability encourages best practices in code organization and makes collaboration between developers—whether they are beginners or experienced professionals—more efficient and productive.
Large, Active Community and Support Resources
Python is backed by a massive community of developers who contribute to its continuous improvement. This community-driven support means that Python offers a wealth of resources, from libraries and frameworks to tutorials and forums, which can address almost any web development requirement.
Extensive Frameworks and Libraries for Web Development
Python’s rich ecosystem includes powerful frameworks that simplify web development, such as Django and Flask.
Django provides an all-inclusive toolkit for building feature-rich web applications, following the Model-View-Template (MVT) pattern, and comes with built-in tools for authentication, ORM (Object-Relational Mapping), and URL routing.
Flask, a lightweight alternative, is known for its flexibility, making it ideal for developers who prefer greater control over app structure and components.
Other frameworks like Pyramid and Bottle further expand Python’s versatility in web development.
Scalability and Performance Efficiency
Python is highly scalable, making it suitable for web applications that need to handle high volumes of traffic. Recent advancements, such as support for asynchronous programming, allow frameworks like Django and FastAPI to manage multiple requests simultaneously, maximizing server efficiency. Python’s compatibility with high-performance libraries in C or C++ also allows developers to integrate additional speed when needed.
Seamless Integration with Other Technologies
Python’s compatibility extends across various technologies, making it easy to integrate with SQL databases like MySQL and PostgreSQL, NoSQL options like MongoDB, web servers, caching systems, and APIs. This interoperability allows developers to build applications that connect smoothly with multiple services and data sources, making Python highly adaptable for diverse web development needs.
Built-in Tools for Testing and Debugging
Python comes equipped with powerful testing and debugging tools, including unittest and pytest, which streamline the testing process for web applications. Python also offers debugging tools like pdb and a variety of IDEs that help developers quickly identify and resolve issues, ensuring that code is reliable and ready for production.
Rapid Development and Time-to-Market Advantage
Python’s focus on simplicity and productivity, combined with a large selection of pre-built modules, enables fast development. This allows developers to avoid building everything from scratch, accelerating the process and reducing time to market. This efficiency is especially valuable for startups and projects where quick deployment is crucial.
Python’s blend of readability, scalability, and extensive support resources makes it a robust choice for web development, offering solutions that are efficient, easy to manage, and adaptable to a variety of business needs.
Applications of Python in Web and Internet Development
Python provides a wealth of options for web development, catering to various needs and preferences:

Full-Featured Frameworks
Robust frameworks like Django and Pyramid offer comprehensive tools for building complex web applications. These frameworks are designed to streamline the development process by providing pre-built functionalities and a solid structure, enabling developers to focus on creating unique features.
Micro-Frameworks
For those seeking more lightweight solutions, micro-frameworks such as Flask and Bottle allow for greater flexibility and minimalism. These frameworks are ideal for smaller projects or applications where developers want to maintain full control over the components and architecture.
Content Management Systems (CMS)
Advanced content management systems like Plone and django CMS make it easier to build and manage content-heavy websites. These systems provide user-friendly interfaces and a variety of features that facilitate the management of content without requiring extensive coding knowledge.
Web APIs Development
Python is a popular choice for developing RESTful APIs, allowing different applications to communicate and share data. With frameworks like FastAPI and Flask, developers can quickly set up APIs that support JSON and other data formats, facilitating seamless integration with front-end applications and third-party services.
E-commerce Platforms
Python is often used to develop e-commerce websites and platforms, providing the necessary tools for handling product catalogs, shopping carts, payment processing, and user authentication. Frameworks like Django can be extended with libraries like Django Oscar to create feature-rich e-commerce solutions that meet the specific needs of businesses.
Internet Protocol Support
Python’s standard library is equipped with support for numerous Internet protocols, enhancing its capabilities for web and network programming:
- Data Formats
Python natively handles various data formats, including HTML, XML, and JSON, allowing developers to work with different types of data efficiently. - Email Processing
The language includes built-in support for processing email, making it easier to create applications that send and receive messages. - Protocol Support
Python supports several Internet protocols, such as FTP, IMAP, and others, enabling developers to interact with remote servers and manage file transfers effectively. - Socket Programming
Python’s easy-to-use socket interface allows for low-level networking, making it straightforward to implement communication between different networked devices.
Additional Libraries from the Python Package Index (PyPI)
The Python Package Index (PyPI) offers a variety of additional libraries that extend Python’s functionality for web and Internet development:
- Requests
This powerful HTTP client library simplifies the process of making HTTP requests, providing an easy-to-use interface for interacting with web services and APIs. - Beautiful Soup
An HTML parser capable of handling various forms of malformed HTML, Beautiful Soup is widely used for web scraping and extracting data from web pages. - Feedparser
This library is designed for parsing RSS and Atom feeds, making it easy to integrate content syndication into applications. - Paramiko
An implementation of the SSH2 protocol, Paramiko enables secure connections to remote servers, facilitating file transfers and command execution. - Twisted
Twisted is a framework for asynchronous network programming that simplifies the development of network applications, allowing for high levels of concurrency and responsiveness.
With these frameworks, libraries, and protocol support, Python proves to be a powerful and versatile language for web and Internet development, catering to a wide range of application requirements.
Key Takeaways from Introduction to Python Web Development
- Definition: Python web development involves creating websites and web applications using the Python programming language, leveraging its simplicity and readability.
- Core Components: Web development encompasses two main areas: front-end development (user interface and user experience) and back-end development (server-side logic and database management).
- Frameworks and Libraries: Python offers various frameworks like Django, Flask, and Pyramid that facilitate web application development by providing built-in functionalities and tools.
- History: Originally developed to make code more readable, Python has emerged as a solid option for web development and real time applications with Django, Flask, and FastAPI.
Pros and Cons of Python for Web Development

When considering Python for web development, it’s essential to weigh its advantages against its limitations. Understanding both the pros and cons will help developers and businesses make informed decisions about using Python for their web projects.
In this section of the Python Web Development All-in-One Guide, we cover:
Pros of Python for Web Development
- Readability and Simplicity
Python’s syntax is clear and straightforward, making it easy to read and write. This readability allows developers to maintain code more effectively and reduces the learning curve for new programmers, facilitating collaboration within teams. - Rapid Development
Python’s extensive libraries and frameworks, such as Django and Flask, enable rapid development. These tools come with built-in features that save time on common tasks, allowing developers to focus on building unique functionalities and speeding up the overall development process. - Large Ecosystem and Libraries
Python has a rich ecosystem of libraries and frameworks tailored for web development, providing solutions for various needs, including database integration, data visualization, user authentication, and more. This extensive support simplifies complex tasks and enhances productivity. - Strong Community Support
Python boasts a vibrant and active community that contributes to its continuous growth. This community provides ample resources, documentation, and forums for support, making it easier for developers to find solutions to challenges they encounter. - Versatility
Python is a multi-paradigm language that supports various programming styles, including procedural, object-oriented, and functional programming. This versatility allows developers to choose the best approach for their specific projects and requirements. - Scalability
Python is capable of handling the demands of high-traffic web applications. Frameworks like Django support scalability through features such as database migrations, caching, and load balancing, enabling applications to grow and adapt as user demands increase. - Integration Capabilities
Python can easily integrate with other technologies and platforms, including databases, APIs, and third-party services. This flexibility allows developers to build complex applications that leverage various tools and resources, enhancing overall functionality. - Cross-Platform Compatibility
Python is a cross-platform language, meaning that applications developed in Python can run on different operating systems without requiring significant modifications. This compatibility is beneficial for developers targeting multiple platforms.

Cons of Python for Web Development
- Performance Limitations
While Python is suitable for many web applications, it may not match the performance of languages like Java or C++ for compute-intensive tasks. The interpreted nature of Python can result in slower execution times, which may be a concern for applications that require high performance. - Threading Issues
Python’s Global Interpreter Lock (GIL) can be a limitation for multi-threaded applications, as it restricts the execution of multiple threads in a single process. This can lead to performance bottlenecks in CPU-bound applications, requiring developers to explore alternative solutions such as multiprocessing or asynchronous programming. - Memory Consumption
Python applications tend to consume more memory than those developed in lower-level languages. This higher memory usage can be a drawback for applications running on limited-resource environments or those that require optimization for performance. - Deployment Complexity
While development with Python can be straightforward, deploying Python web applications can sometimes be complex due to dependencies and environment configurations. Ensuring that the correct versions of libraries and frameworks are installed and compatible can be challenging. - Less Mobile Development Support
Although Python is powerful for web development, it is not commonly used for mobile app development. Developers may need to use other languages or frameworks (like Java or Swift) for creating mobile applications, which can complicate projects that aim for cross-platform functionality. - Limited Built-in Tools
Unlike some other languages that come with robust built-in tools for web development, Python relies on third-party frameworks and libraries. While this provides flexibility, it can also lead to challenges in standardization and compatibility.
Key Takeaways from Python’s Pros and Cons
Python is a powerful and flexible choice for web development, offering numerous benefits such as rapid development, strong community support, and a rich ecosystem of libraries and frameworks.
However, it is essential to consider its limitations, including performance constraints and deployment complexities, when deciding if Python is the right fit for a specific web development project. By carefully evaluating these pros and cons, developers can make informed decisions that align with their project goals and requirements.
Key Concepts in Python Web Development

Understanding the foundational concepts in Python web development is crucial for building effective web applications. Developers should be familiar with some key concepts to build functional web applications.
In this section of this Python Web Development All-in-One Guide, we will cover the following key concepts:
Understanding Backend vs. Frontend Development
Backend development is often called “Server-Side” while the Frontend is referred to as the “Client-Side”. Let’s learn the difference between the two:
| Frontend (Client-Side) | Backend (Server-Side) |
| The visual part of a web application that users interact with directly. It involves technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. Frontend developers focus on designing user interfaces and enhancing user experience. | The server-side of a web application. It deals with the business logic, database interactions, and server configuration. Backend developers work with programming languages like Python, Ruby, and Java, and they manage how data is processed and served to the frontend. |
HTTP Basics and Web Protocols
Before beginning Python web development, a developer must understand the basics of HTTP and Web Protocols. Let’s dive into them!
HTTP Requests and Responses
The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is the foundation of data communication on the web. It defines how messages are formatted and transmitted. When a client (such as a web browser) makes a request to a server, it sends an HTTP request, which can include methods such as GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE, each indicating a different type of operation.
Status Codes, Headers, and JSON
What are status codes, headers, and JSON?
- Status Codes: These are three-digit codes returned by the server to indicate the result of a client’s request. Common status codes include 200 (OK), 404 (Not Found), and 500 (Internal Server Error).
- Headers: HTTP headers contain metadata about the request or response, such as content type, length, and cache settings. They are essential for controlling how information is transmitted between clients and servers.
- JSON: JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) is a lightweight data interchange format that is easy for humans to read and write and easy for machines to parse and generate. It is commonly used for sending and receiving data in web applications.
REST Principles and API Endpoints
REST (Representational State Transfer) is an architectural style for designing networked applications. It relies on stateless communication and the use of standard HTTP methods. API endpoints are specific paths in a web application that allows clients to access certain functionalities or resources, adhering to RESTful principles.
MVC Architecture
A key concept in Python website development is the MVC architecture. Let’s explore it in more detail!
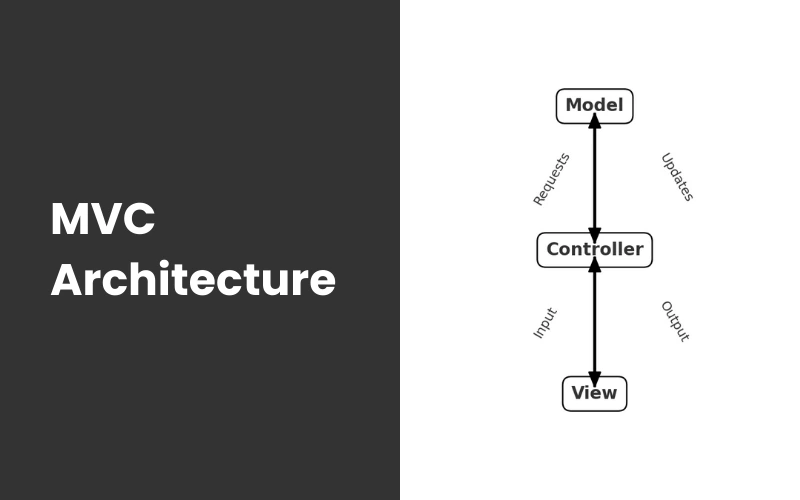
MVC (Model-View-Controller) is a software architectural pattern that separates an application into three interconnected components:
- Model: Represents the data and business logic of the application. It directly manages the data and rules for updating it.
- View: Represents the user interface and the presentation layer of the application. It displays the data provided by the model in a format that users can interact with.
- Controller: Acts as an intermediary between the model and view. It processes user inputs, interacts with the model to retrieve data, and updates the view accordingly.
This separation allows for organized code, easier maintenance, and better scalability of applications.
What Python Frameworks Use MVC?
Many Python frameworks, such as Django, adopt the MVC architecture (often referred to as MTV—Model-Template-View—in Django).
This structure enables developers to build modular applications, facilitating collaboration among team members and improving the overall development process.
Other popular frameworks like Flask and Pyramid provide excellent support for implementing the MVC pattern in Python.
Key Takeaways from Core Concepts in Python Web Development
These key concepts provide a solid foundation for understanding how Python fits into the broader landscape of web development. Familiarity with backend and frontend roles, HTTP protocols, and the MVC architecture is essential for any developer looking to leverage Python effectively in their web projects.
Python Frameworks for Web Development

Python provides various web frameworks for a wide range of purposes and tastes. Discover the most popular Python frameworks for web development.
In this section of the Python Web Development All-in-One Guide, we cover the following topics regarding Python frameworks:
What is a Web Framework?
A web framework is a software framework designed to aid in the development of web applications, including web services, APIs, and web resources. It provides a standard way to build and deploy web applications by offering a collection of tools and libraries to manage various aspects of web development, such as:
- Routing: Managing how URLs are mapped to specific functions or controllers in the application.
- Database Interactions: Facilitating connections to databases and performing data manipulation through Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) or direct SQL queries.
- User Authentication: Implementing systems for user login, registration, and permission management to secure applications.
- Template Rendering: Generating HTML dynamically based on data and logic, allowing developers to separate application logic from presentation.
- Form Handling: Simplifying the process of processing user input, including validation and error handling.
Types of Web Frameworks
Web frameworks can generally be categorized into two main types:
- Full-Stack Frameworks: These frameworks provide a complete set of tools to handle both the front-end and back-end aspects of web development. They include everything needed to build a web application from the ground up. Examples include Django and Ruby on Rails.
- Micro-Frameworks: These are lightweight frameworks that focus on simplicity and minimalism. They offer only the essential components needed to build a web application, allowing developers to add libraries as needed. Examples include Flask and Bottle.
Top Frameworks for Python Web Development
Python offers a variety of frameworks that simplify and accelerate the web development process. Each framework has its own unique features and capabilities, making it suitable for different types of projects. Here’s an overview of some of the most popular Python frameworks for web development:

1. Django
- Overview: Django is a high-level web framework that promotes rapid development and clean, pragmatic design. It is known for its “batteries-included” philosophy, meaning it comes with many built-in features to streamline development.
- Key Features:
- ORM (Object-Relational Mapping): Simplifies database interactions by allowing developers to work with Python objects instead of writing raw SQL queries.
- Admin Interface: Automatically generates an admin panel for managing application data, which is useful for backend management.
- Security: Offers built-in protection against common security threats such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting, and cross-site request forgery.
- Scalability: Designed to handle high-traffic applications, making it suitable for projects of any size.
- Use Cases: Ideal for large-scale applications, content management systems, and e-commerce platforms.
2. Flask
- Overview: Flask is a lightweight micro-framework that provides the essential tools needed for web development without imposing a specific project structure. This flexibility allows developers to create applications quickly and easily.
- Key Features:
- Simplicity: Flask has a minimalistic approach, making it easy for beginners to get started while also allowing for complex applications as developers gain experience.
- Extensibility: Supports numerous extensions that add functionalities, such as authentication, form validation, and database integration.
- RESTful Request Dispatching: Makes it straightforward to create RESTful APIs and web services.
- Use Cases: Great for small to medium-sized applications, prototypes, and RESTful APIs.

3. FastAPI
- Overview: FastAPI is a modern web framework designed for building APIs with high performance. It leverages Python type hints to provide automatic validation, serialization, and documentation.
- Key Features:
- Asynchronous Support: Built on top of Starlette, FastAPI allows for asynchronous programming, enabling applications to handle a high number of concurrent connections efficiently.
- Automatic Documentation: Generates interactive API documentation (Swagger UI and ReDoc) automatically based on the defined endpoints and parameters.
- Performance: FastAPI is one of the fastest Python frameworks available due to its asynchronous capabilities and optimizations.
- Use Cases: Best suited for high-performance APIs, microservices, and applications requiring real-time capabilities.
4. Pyramid
- Overview: Pyramid is a flexible web framework that can be used for both small and large applications. It emphasizes simplicity and scalability, allowing developers to choose their preferred components.
- Key Features:
- Flexible Architecture: Pyramid can adapt to the needs of the project, supporting both simple applications and complex enterprise solutions.
- Security Features: Provides built-in security features like authentication and authorization, helping developers secure their applications easily.
- Extensible: Allows developers to integrate third-party libraries and tools seamlessly.
- Use Cases: Suitable for applications that require flexibility and scalability, such as enterprise solutions and complex web applications.
5. Bottle
- Overview: Bottle is a simple, lightweight micro-framework that is ideal for building small web applications and prototyping.
- Key Features:
- Single-file Deployment: Bottle is contained in a single file, making it easy to deploy and use for small projects.
- Built-in Server: Comes with a built-in development server, which is convenient for testing applications quickly.
- Routing: Provides simple routing for defining URL patterns and request handling.
- Use Cases: Best for small applications, APIs, and learning purposes.
6. Tornado
- Overview: Tornado is an asynchronous networking library and web framework designed to handle thousands of simultaneous connections efficiently.
- Key Features:
- Asynchronous Networking: Built for handling long-lived network connections, making it ideal for WebSockets and real-time applications.
- Non-blocking: Tornado uses a non-blocking network I/O, allowing it to handle many requests without the overhead of traditional threading.
- Use Cases: Excellent for real-time web services, long polling, and WebSocket applications.
7. CherryPy
- Overview: CherryPy is an object-oriented web framework that provides a simple interface for building web applications. It allows developers to build web applications in a similar way to writing regular Python programs.
- Key Features:
- Minimalistic Design: CherryPy is lightweight and allows developers to use any type of data storage and data handling as they see fit.
- Built-in HTTP Server: Includes a built-in HTTP server for testing and development, though it can be deployed on any WSGI-compliant server.
- Flexible: Supports the MVC pattern and offers the ability to create applications with a modular structure.
- Use Cases: Ideal for small to medium-sized applications and those looking for flexibility in design.
8. Grok
- Overview: Grok is a Python web application framework built on top of Zope Toolkit, focusing on ease of use and rapid development. It emphasizes convention over configuration.
- Key Features:
- Component-based Architecture: Encourages the use of reusable components, making it easier to manage large applications.
- Easy to Learn: Designed to be simple for beginners to grasp while still providing powerful capabilities for experienced developers.
- Integration with Zope: Leverages the features of Zope, such as security and session management.
- Use Cases: Best suited for developers familiar with Zope who want to build robust web applications quickly.
9. TurboGears
- Overview: TurboGears is a full-stack web application framework that combines the best aspects of various frameworks and tools to provide a powerful development experience.
- Key Features:
- Full-Stack Capabilities: Integrates various libraries and frameworks, including SQLAlchemy and Pylons, allowing developers to work efficiently at every layer of their application.
- Flexible Configuration: Offers flexibility in choosing components, making it suitable for different project needs.
- Rapid Development: Emphasizes fast development cycles with features like scaffolding to generate application structure quickly.
- Use Cases: Ideal for full-stack development and projects that require a robust feature set.
10. BlueBream
- Overview: BlueBream is a lightweight web framework based on the Zope Toolkit that emphasizes the use of reusable components and clear separation of concerns.
- Key Features:
- Component Architecture: Promotes reusability and modularity in web applications through a component-based architecture.
- Integration with Zope: Inherits features from Zope, including security and URL routing capabilities.
- Extensibility: Supports adding new features through plugins and extensions easily.
- Use Cases: Suitable for developers looking to build modular web applications with a focus on component reuse.
Key Takeaways from Python Frameworks for Web Development
Frameworks provide a diverse range of options for Python web development, each catering to different project requirements and developer preferences.
Whether you are building a simple website, a robust web application, or a high-performance API, there’s a Python framework suited to your needs. Understanding these frameworks will empower developers to choose the right tools for their projects and enhance their overall development experience.
Python Libraries for Web Development
Python provides a robust ecosystem of libraries that streamline web development, boosting productivity and simplifying complex tasks. Discover some popular Python libraries used in web development.
In this section of the Python Web Development All-in-One Guide, we cover the following libraries:
- Requests
- Beautiful Soup
- Pillow
- Scrapy
- SQLAlchemy
- Celery
- Flask-SQLAlchemy
- Flask-WTF
- Zappa
- PyJWT
- Redis-py
- Pydantic
- Jinja2
- Dash
Requests
Known for its simplicity, Requests is a popular library for making HTTP requests. It facilitates easy interaction with APIs, handling HTTP methods, headers, cookies, and authentication seamlessly.
Beautiful Soup
This library is ideal for parsing HTML and XML documents. With a straightforward API, Beautiful Soup is commonly used for web scraping, allowing developers to explore and extract data from web pages efficiently.
Pillow
A powerful image-processing library, Pillow offers features for resizing, cropping, adding filters, and overlaying text on images. It is frequently used in web applications where image manipulation and processing are required.
Scrapy
Scrapy is a powerful library for building web crawlers, ideal for extracting data from websites. It’s commonly used for web scraping, data mining, and automated testing, offering developers a fast, efficient way to gather large volumes of structured data.
SQLAlchemy
SQLAlchemy is an advanced ORM (Object-Relational Mapping) library that simplifies working with databases in Python. Supporting multiple database engines, it provides a high-level API for interacting with databases, making it a great choice for managing data in web applications.
Celery
Celery is a task queue library that supports asynchronous task execution. By offloading time-consuming or resource-heavy tasks to the background, it enhances application responsiveness, making it suitable for applications that require task scheduling.
Flask-SQLAlchemy
An extension that integrates SQLAlchemy with Flask, this tool allows for smooth database interactions within Flask applications, combining the simplicity of Flask with SQLAlchemy’s robust ORM capabilities.
Flask-WTF
This extension aids in handling web forms in Flask applications. It provides form rendering, submission handling, and validation, making form management in Flask easier and more efficient.
Zappa
Zappa is an excellent choice for developers building serverless applications on AWS Lambda. It allows you to deploy Python web applications and microservices in a serverless environment, reducing infrastructure management needs and improving scalability.
PyJWT
PyJWT is a library designed for working with JSON Web Tokens (JWTs). It simplifies the process of creating, decoding, and verifying JWTs, which are frequently used for user authentication and authorization in web applications.
Redis-py
Redis-py is a client library that enables Python applications to interact with Redis, an in-memory data store. It’s commonly used for caching, pub/sub messaging, and quick data retrieval in web applications, improving performance and scalability.
Pydantic
Pydantic is a data parsing and validation library that simplifies handling complex data structures. It allows developers to define data models with type hints, automatically validating and serializing data, which is particularly useful for managing incoming request data in web applications.
Jinja2
A versatile and powerful template engine, Jinja2 provides a templating syntax that allows for dynamic generation of HTML pages, emails, and other content. It’s widely used with frameworks like Flask and Django to render data-rich, dynamic web content.
Dash
For developers working on data visualization in web applications, Dash is an invaluable library. Built on top of Flask, Dash is specifically designed for creating interactive data visualizations such as charts, graphs, and dashboards, making it ideal for applications requiring data analytics and visualization capabilities.
Key Takeaways from Python Web Development Libraries
These libraries represent a fraction of Python’s extensive toolkit for web development. Depending on the project requirements, exploring and using these tools can significantly enhance your development workflow and lead to more efficient, maintainable code.
Pure Python Web Development vs Frameworks

When building web applications in Python, developers can choose between using pure Python or leveraging frameworks. Each approach has its own advantages and challenges. Discover the pros and cons of both.
In this section of the Python Web Development All-in-One Guide, we cover the following topics:
Pure Python Web Development
Pure Python web development involves writing the entire codebase without the help of external frameworks, relying solely on Python’s standard libraries and custom-built components.
Advantages:
- Greater Flexibility: Pure Python allows for complete control over the application structure and features, enabling developers to design tailored solutions that meet specific needs without predefined constraints.
- Fine-Grained Optimization: With no framework overhead, developers can optimize each part of the application, potentially improving performance and resource efficiency.
- Learning Opportunity: Working in pure Python helps developers gain a deep understanding of how web servers, routing, data handling, and HTTP protocols work, leading to stronger foundational skills.
Challenges:
- Time-Consuming: Building everything from scratch is labor-intensive, requiring additional time and effort for common tasks such as routing, database interaction, and user authentication.
- Reinventing the Wheel: Many common features (e.g., session management, form validation) require significant development time to recreate when not using a framework.
- Limited Scalability: Without framework support, it can be challenging to scale and maintain a complex codebase as the application grows.
Best Suited For: Pure Python is ideal for small projects, educational purposes, or highly customized applications where developers need full control over every aspect of the code.
Python Web Development with Frameworks
Using a framework allows developers to leverage pre-built components and a structured architecture. Frameworks are designed to simplify and expedite the development process, providing useful abstractions for common tasks.
Advantages:
- Rapid Development: Frameworks offer built-in components and tools, drastically reducing the time required for tasks like routing, templating, and database management.
- Consistent Structure: Most frameworks follow established design patterns (e.g., MVC), ensuring code consistency and making it easier for teams to collaborate on larger projects.
- Built-in Security: Many frameworks come with built-in security features, such as protection against SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and cross-site request forgery (CSRF), which can help mitigate common vulnerabilities.
- Community and Support: Popular frameworks have large communities that provide libraries, plugins, documentation, and support, making development smoother and troubleshooting easier.
Challenges:
- Learning Curve: Frameworks require developers to learn specific structures and conventions, which can be challenging for those new to web development.
- Less Flexibility: Frameworks impose certain structures and limitations, which may restrict customizability or add unnecessary overhead for simple applications.
- Dependency Management: Frameworks come with dependencies, and as these frameworks evolve, dependencies may require updates that could lead to compatibility issues.
Best Suited For: Frameworks are ideal for projects where development speed, scalability, and maintainability are priorities. They’re especially well-suited for medium to large applications and projects that require rapid iteration or collaboration among multiple developers.

Example: Python Web Development With Django
Django is a Python-based web framework designed to help developers build fast, efficient websites. Often referred to as a “batteries-included” framework, Django provides a wide range of built-in features, such as the Django Admin interface and a default SQLite3 database, streamlining the development process.
When creating a website, many components are frequently needed: user authentication (such as sign-up, login, and logout), a site management interface, form handling, file uploads, and more. Django simplifies these tasks by offering pre-built modules and tools, enabling developers to focus on unique aspects of their applications rather than foundational setup work. This combination of speed and convenience makes Django a popular choice for web development in Python.
Key Takeaways: Pure Python vs. Frameworks
Choosing between pure Python and frameworks largely depends on the project’s size, complexity, and goals:
- Pure Python: Recommended for small applications, learning purposes, or projects that demand complete flexibility and minimal dependencies.
- Frameworks: Best for robust, scalable applications that need faster development and follow best practices, as well as projects that involve collaboration or frequent updates.
Ultimately, frameworks offer the advantage of speed and structure, while pure Python provides flexibility and full control. Assessing the project’s needs and development resources will help in making the right choice.
Python Web Development Step By Step Process

Creating a web application in Python can be straightforward with a structured approach. Learn the step-by-step guide to the process, from setting up the environment to deploying the final product.
In this section of the Python Web Development All-in-One Guide, we explore the following processes:
- Define Project Goals and Requirements
- Choose a Framework or Pure Python Approach
- Set Up the Development Environment
- Install Framework and Dependencies
- Initialize Your Project
- Design the Database
- Set Up Application Structure and Routing
- Develop Frontend Components
- Implement Backend Functionality
- Integrate APIs and Additional Features
- Testing and Debugging
- Deploy the Application
- Monitor and Maintain
1. Define Project Goals and Requirements
First up, before you even start development, is the planning phase. In this step, you have to perform the following:
- Identify Objectives: Begin by clarifying the application’s purpose, target audience, and key features.
- Scope and Specifications: Outline the specific functionalities required, such as user authentication, file handling, database integration, and UI components.
2. Choose a Framework or Pure Python Approach
Python offers a variety of web frameworks that simplify development by providing essential tools and structure. Choose a framework that best fits your project needs and your familiarity with it. Therefore, you must:
- Select a Web Framework: Decide on a framework based on project needs. Popular choices include Django for full-featured applications, Flask for lightweight projects, and Pyramid for flexible options.
- Consider Pure Python for Small Projects: For minimal or highly customized projects, consider using pure Python.
3. Set Up the Development Environment
When setting up the development environment, it is helpful to visit the official Python website to download the latest version compatible with your operating system. Other important steps include:
- Install Python: Ensure Python is installed on your system and is up to date.
- Set Up Virtual Environment: Virtual environments are useful for isolating project packages and avoiding conflicts with global Python installations. Create a virtual environment to keep dependencies isolated and make project management easier. You can create a virtual environment using virtualenv or Python’s built-in venv module.
- Install Required Packages: Use pip to install libraries and dependencies necessary for your project, such as Flask, Django, or specific database connectors.
4. Install Framework and Dependencies
With the virtual environment activated, use pip to install the selected framework along with any other dependencies. For example, to install Django, run pip install Django.
5. Initialize Your Project
Each framework has its unique way to set up a new project. Check the framework’s documentation for setup details. For Django, initiate a new project by running django-admin startproject projectname.
6. Design the Database
Most frameworks have configuration files where you can set project-specific options, such as database connections, static file paths, and security settings. Adjust these configuration files as needed for your project.
- Determine Database Type: Choose a database that fits the application’s needs (e.g., SQLite for simple applications, PostgreSQL for complex ones).
- Define Data Models: Create models representing data structure and relationships. For Django, define models in models.py; for Flask, use SQLAlchemy or another ORM.
7. Set Up Application Structure and Routing
In this step, set up the URL routing within your framework. This routing connects specific URLs to designated views or functions. Define URL patterns for each route and specify the corresponding function or view that should handle it.
- Organize Project Files: Create folders for templates, static files, views, and any specific modules.
- Configure Routing: Define URL routes for each page or API endpoint. In Django, configure URLs in urls.py; in Flask, use route decorators.
- Implement MVC Pattern: Separate code into models, views, and controllers to promote organized, maintainable code.
8. Develop Frontend Components
A strong Python backend first requires a frontend to showcase the business logic.
Develop your front-end components:
- Create HTML Templates: Design web pages using HTML templates, incorporating placeholders for dynamic content.
- Style with CSS: Use CSS to add styling, creating a consistent and visually appealing user experience.
- Add Interactivity with JavaScript: For applications needing interactive elements, add JavaScript or integrate libraries like jQuery or Vue.js.
9. Implement Backend Functionality
You can implement your business logic by adding the code needed to support your application’s core functionality. This can involve authentication, business rules, data processing, and integrating with external APIs or services.
- Write Server-Side Logic: Develop functions to handle user interactions, process data, and manage application flow.
- Handle User Authentication: Implement login, logout, registration, and password management functionalities. Django provides built-in tools for authentication; Flask has extensions like Flask-Login.
- Set Up Forms and Validation: If your app requires form submissions or user input, utilize the framework’s built-in tools for handling form processing, validation, and data storage.
10. Integrate APIs and Additional Features
Make your Python web application truly multi-functional by adding additional features and API integrations.
For example:
- Connect to External APIs: If the application requires external data or services, integrate APIs (such as payment gateways, social media, or maps).
- Implement Asynchronous Tasks: Use tools like Celery to handle background tasks or high-volume processing outside of the main application flow.
- Optimize for Performance: Implement caching (e.g., Redis or Memcached) and optimize database queries for speed and efficiency.
11. Testing and Debugging
It is important to write tests to verify that your application functions as expected. Most frameworks include built-in testing tools to streamline the testing process. Use debugging tools to identify and resolve any errors.
Types of Testing in Python Web Development Include:
- Unit Testing: Write unit tests for key functions to ensure each part of the application works as expected.
- Integration Testing: Test interactions between different components, such as frontend and backend or database connectivity.
- User Testing and Debugging: Test the application from a user perspective to identify and resolve any issues.
12. Deploy the Application
Once your application is complete, select a hosting environment that meets your requirements and deploy it.
The steps to deploy your Python web application include:
- Choose a Hosting Provider: Select a provider suitable for the project, such as Heroku, AWS, or DigitalOcean.
- Set Up a Production Database: Configure a scalable and secure database for production use, such as PostgreSQL or MySQL.
- Configure Server and SSL: Set up the web server and enable SSL certificates for secure connections.
- Automate with CI/CD: For larger projects, implement Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines for efficient updates and maintenance.
13. Monitor and Maintain
Regular maintenance, updates, and monitoring will keep your Python application running smoothly over time.
Monitor and maintain your Python website by:
- Set Up Monitoring Tools: Use monitoring tools (e.g., New Relic, Datadog) to track application performance and server health.
- Gather User Feedback: Use feedback to identify areas for improvement and release updates.
- Maintain and Scale: Regularly maintain the application, add new features, and adjust resources to handle growing user demand.
Key Takeaways from Python Web Development Step by Step Process
Following a structured approach to Python web development that covers everything from installation to deployment will aid in your project’s success. With the right framework and tools, you can efficiently build and deploy a robust Python web application.
How to Create Your First Python Web Application

Now that you know the step by step process of Python Web Development, it’s time to create your first Python application! Creating your first web application in Python is an exciting step that helps you get hands-on experience with the basics of web development, from setting up your environment to deploying a simple app.
In this section of the Python Web Development All-in-One Guide, we will learn how to create your first Python web application using Flask. We will cover:
- Set Up Your Development Environment
- Create a Basic Flask Application
- Run Your Application
- Add Dynamic Content with Templates
- Add More Routes and Views
- Handle Forms and User Input
- Test and Debug Your Application
- Deploy Your Application
1. Set Up Your Development Environment
As discussed in the step-by-step process, you need to set up your development environment.
- Install Python: Make sure Python is installed on your computer. You can download it from the official Python website.
- Install Flask: Open a terminal (or command prompt) and create a virtual environment for your project to isolate dependencies. Navigate to your project folder and run the following commands:
python -m venv myenv # Create a virtual environment
source myenv/bin/activate # Activate the environment (Linux/Mac)
myenv\Scripts\activate # Activate the environment (Windows)Then install Flask using pip:
pip install Flask2. Create a Basic Flask Application
- Inside your project folder, create a new file called app.py. This file will contain the code for your Flask application.
- Open app.py in a code editor and add the following code:
from flask import Flask
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/')
def home():
return "Hello, World! Welcome to your first Python web app."
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug=True)- This code does the following:
- Imports the Flask class from the Flask library.
- Creates an instance of the Flask class (our application).
- Defines a single route (/) that returns a “Hello, World!” message.
- Runs the application if the file is executed as the main program.
3. Run Your Application
- Save app.py, go to your terminal, and make sure your virtual environment is activated.
- In the terminal, navigate to the directory where app.py is located and start the application by running:
python app.py- You should see output indicating that the application is running on http://127.0.0.1:5000/.
- Open your web browser and go to http://127.0.0.1:5000/. You should see the message “Hello, World! Welcome to your first Python web app.”
4. Add Dynamic Content with Templates
- Create a new folder called templates in your project directory. This folder will contain HTML files for your application.
- Inside the templates folder, create an HTML file called index.html with the following content:
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>My First Flask App</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to My First Flask Application!</h1>
<p>This is a dynamic web page rendered with Flask.</p>
</body>
</html>- Modify app.py to render this HTML template:
from flask import Flask, render_template
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/')
def home():
return render_template('index.html')
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug=True)- Now, when you reload http://127.0.0.1:5000/, you should see the HTML content defined in index.html, displayed with styling and structure.
5. Add More Routes and Views
You can add additional routes to handle different pages or content within your application. For example, add an “About” page by creating another route:
@app.route('/about')
def about():
return "<h2>About Page</h2><p>This is the About page of our application.</p>"6. Handle Forms and User Input
- Web applications often need to handle user input. You can create a form to collect information. For instance, create a new file form.html in the templates folder with a simple HTML form:
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Simple Form</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Simple Form</h1>
<form action="/submit" method="post">
<label for="name">Name:</label>
<input type="text" id="name" name="name"><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>- Update app.py to handle the form’s submission:
from flask import Flask, render_template, request
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/')
def home():
return render_template('index.html')
@app.route('/form')
def form():
return render_template('form.html')
@app.route('/submit', methods=['POST'])
def submit():
name = request.form.get('name')
return f"<h2>Form Submitted</h2><p>Thank you, {name}!</p>"
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug=True)- Now, navigating to http://127.0.0.1:5000/form displays the form. When submitted, it redirects to a confirmation page displaying the entered name.
7. Test and Debug Your Application
- Use Flask’s built-in debugging features by setting debug=True in app.run(). This will show errors in the terminal if anything goes wrong, helping you fix issues quickly.
- Flask also offers testing capabilities to write unit tests for your app, which is essential for larger applications.

8. Deploy Your Application
Once your application is complete, you can deploy it to a hosting service such as Heroku, AWS, or PythonAnywhere. This often involves creating a requirements.txt file to list dependencies and setting up configuration files for the server environment.
Key Takeaways from How to Create Your First Python Web Application
Following these steps, you’ll have a basic yet functional web application and an understanding of the core principles involved in Python web development. Building on this, you can explore additional features and frameworks to create more complex applications!
Advanced Concepts in Python Web Development

As you become proficient with the basics of Python web development, understanding advanced concepts can help you build more robust, scalable, and secure applications. Explore some key advanced topics and techniques to enhance your skills in Python web development.
In this section of the Python Web Development All-in-One Guide, we will cover the following advanced concepts:
- Asynchronous Programming
- WebSockets and Real-Time Communication
- API Development and RESTful Architecture
- Security Best Practices
- Database Optimization and Indexing
- Testing, Mocking, and Test-Driven Development (TDD)
- Task Queues and Background Processing
- Containerization and Deployment
- Integrating Back-End Code with Front-End Libraries and Frameworks
- Social Authentication
- Improving Application Performance Through Caching
- Logging and Monitoring
1. Asynchronous Programming
Asynchronous programming is a form of parallel programming that enables a task to execute independently of the main application thread.
Once the task is finished, it communicates the result—whether successful or not—back to the primary thread.
This approach offers several advantages, including increased application performance and improved responsiveness for users.
- Concurrency and Parallelism: Asynchronous programming in Python allows for handling multiple tasks simultaneously, which is essential for improving performance in applications with high traffic or multiple I/O operations.
- Asyncio and Aiohttp: Python’s asyncio library and aiohttp framework enable asynchronous I/O operations. Using asynchronous programming, you can handle requests more efficiently, reduce latency, and improve the overall user experience.
- FastAPI: This modern, high-performance framework is built on asynchronous principles and is particularly effective for building APIs and microservices.
2. WebSockets and Real-Time Communication
The WebSocket API is a sophisticated technology that facilitates a two-way interactive communication channel between a user’s browser and a server. This API allows for the sending of messages to a server while also receiving event-driven responses, eliminating the need to repeatedly poll the server for replies.
- WebSockets: Unlike traditional HTTP, WebSockets provide a persistent, two-way connection between the client and server, enabling real-time data transfer. This is particularly useful for applications requiring live updates, such as chat applications, notifications, and live data feeds.
- Socket.IO and Channels: Libraries like Flask-SocketIO and Django Channels add WebSocket support to Flask and Django applications, respectively. Django Channels allows you to handle asynchronous WebSocket connections using Django, expanding the possibilities for real-time communication.
3. API Development and RESTful Architecture
A RESTful API is an architectural approach for application programming interfaces that utilizes HTTP requests to retrieve and manipulate data. It supports various operations, including GET, PUT, POST, and DELETE, which correspond to reading, updating, creating, and removing resources, respectively.
- REST and RESTful APIs: Representational State Transfer (REST) is a widely used architectural style for APIs that handle HTTP requests in a structured way. REST APIs organize data through resources, making endpoints easily consumable by front-end or third-party clients.
- JSON and XML: RESTful APIs typically use JSON for data interchange, but XML can be an alternative in certain cases. Understanding data serialization and deserialization is crucial for API responses and request handling.
- GraphQL: For more flexible querying of data, GraphQL is an alternative to REST. GraphQL allows clients to request only the data they need and makes nested and complex queries simpler.
4. Security Best Practices
Like any programming language, Python is susceptible to security vulnerabilities. To mitigate risks posed by attackers, it is essential to implement secure coding best practices. This involves exploring and adopting Python security measures that should be considered when developing safe applications.
- Authentication and Authorization: Properly implementing secure user authentication (using JWTs, OAuth, or session-based authentication) and authorization is essential to protecting sensitive data. Django has built-in authentication tools, while Flask can use libraries like Flask-Login for similar functionality.
- Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) and Cross-Site Scripting (XSS): Protecting against CSRF attacks and XSS vulnerabilities is essential. Frameworks like Django provide CSRF tokens out of the box, and tools like bleach can sanitize user input to prevent XSS.
- Data Encryption: Encrypting sensitive data, both in transit (using HTTPS) and at rest (using database encryption), ensures data security. Using libraries such as cryptography in Python can help encrypt sensitive data.

5. Database Optimization and Indexing
Database optimization and indexing are crucial components in Python web development to improve performance, scalability, user experience, and resource management.
- SQL Query Optimization: Writing optimized SQL queries and reducing the number of database calls can significantly improve performance. Using Python’s ORM libraries like Django ORM and SQLAlchemy, you can create efficient queries to reduce load times.
- Indexing: Adding indexes to frequently queried database fields can speed up query performance. Analyzing and optimizing database indexes becomes critical as the application grows in scale.
- Caching: Caching results from database queries using Redis or Memcached can reduce load on the database and improve page response times for frequently accessed data.
6. Testing, Mocking, and Test-Driven Development (TDD)
Testing, mocking, and Test-Driven Development (TDD) are essential practices in Python web development that contribute significantly to the overall quality, reliability, and maintainability of applications.
- Unit and Integration Testing: Writing tests for individual components (unit tests) and entire workflows (integration tests) helps ensure that your application functions as expected. Frameworks like pytest and Django’s built-in test framework simplify the testing process.
- Mocking: Using mocking libraries like unittest.mock allows you to simulate the behavior of complex objects, making it easier to isolate and test components without dependencies.
- Test-Driven Development: TDD is a software development process that emphasizes writing tests before writing the actual code. This approach helps ensure that the code meets the specified requirements from the outset.
7. Task Queues and Background Processing
A task queue is a data structure that holds a list of tasks that need to be executed asynchronously. It allows developers to delegate tasks to be processed outside of the main application thread, ensuring that the application remains responsive to user requests.
Background processing refers to the execution of tasks in a separate thread or process that runs independently of the main application thread. This allows for non-blocking operations, improving the overall user experience.
Use the following tools and libraries to perform Task Queues and Background Processing:
- Celery: Celery is a popular library for distributed task processing in Python. It allows you to offload time-consuming tasks like data processing, image resizing, or email sending to background workers, keeping your application responsive.
- Redis and RabbitMQ: These tools are commonly used as message brokers with Celery. They queue tasks and handle their distribution to worker nodes.
8. Containerization and Deployment
Containerization is a lightweight form of virtualization that allows developers to package an application and its dependencies into a single container. This container can then run consistently across various computing environments, whether on a developer’s local machine, a testing server, or a production cloud environment.
Deployment refers to the process of making an application available for use. It involves transferring the application from a development environment to a production environment where end users can access it.
Some popular concepts in Containerization and Deployment of web applications in Python:
- Docker: Containerization using Docker helps to package applications and their dependencies into isolated environments. This ensures consistency across development, testing, and production environments.
- Kubernetes: Kubernetes orchestrates Docker containers, providing scalability and management tools for large-scale applications.
- Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS): Services like Heroku, AWS Elastic Beanstalk, and Google App Engine simplify deployment by handling much of the infrastructure, letting developers focus on the application code itself.
- Deploying Your Application: Understanding the deployment process involves choosing the right environment, configuring your server, and ensuring that your application meets all operational requirements.
9. Integrating Back-End Code with Front-End Libraries and Frameworks
Having a back-end without a solid connection with your application’s front-end is a recipe for disaster. Learn how to seamlessly integrate your back-end code with front-end libraries and frameworks:
- Seamless Communication: Knowledge of how to connect back-end services to front-end applications using RESTful APIs or GraphQL enables a smooth flow of data and user interactions.
- Frontend Frameworks: Understanding how to integrate popular front-end libraries like React, Angular, or Vue.js with your Python back end will create a more dynamic and responsive user experience.
10. Social Authentication
Social Authentication is the process of allowing users to log in to web applications using their existing social media accounts, such as Facebook, Google, Twitter, and others.
This method simplifies the registration and login process for users by eliminating the need to create new credentials, thereby improving user experience and increasing the likelihood of user engagement.
- OAuth and Third-Party Logins: Implementing social authentication allows users to sign in using their existing accounts from platforms like Google, Facebook, or Twitter, enhancing user experience and simplifying the login process.
- Django Allauth and Flask-Dance: These libraries simplify the process of integrating social authentication in Django and Flask applications, providing easy-to-use tools for handling user sessions and credentials.
11. Improving Application Performance Through Caching
Caching is a technique of storing the results of expensive function calls and returning the cached result when the same inputs occur again.
This is especially useful in web development and applications where performance and speed are critical, as it can significantly reduce the amount of time required to retrieve data or compute results.
- Caching Strategies: Utilizing caching mechanisms can dramatically improve the performance of web applications. Implementing in-memory caching solutions like Redis or Memcached helps reduce database load and speed up response times.
- Browser Caching: Understanding how to use HTTP caching headers can allow browsers to cache static resources, further enhancing application performance.
12. Logging and Monitoring
Logging refers to the practice of recording events, errors, and other significant occurrences within an application. This helps in monitoring, which is the continuous observation of an application’s performance, health, and resource usage.
Python has libraries and tools to help optimize logging and monitoring:
- Centralized Logging: Logging errors and application events using tools like the Python logging library or integrating with services like Loggly or the ELK (Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana) stack helps in monitoring app performance.
- Application Performance Monitoring (APM): Tools like New Relic, Datadog, or Sentry provide real-time monitoring of your application’s health, resource usage, and error tracking, making it easier to troubleshoot issues in production.
Key Takeaways from Advanced Concepts in Python Web Development
These advanced concepts empower you to handle larger, more complex web applications, meet high user demands, and maintain security and performance standards. Understanding and applying these principles will prepare you to build scalable, production-ready Python applications that can effectively handle real-world challenges.
Deploying and Hosting Python Web Applications

Deploying and hosting Python web applications involves making your application available to users on the internet or an intranet. This process includes choosing the right hosting solution, configuring the server environment, deploying your application code, and ensuring that it runs smoothly and securely.
In this section of the Python Web Development All-in-One Guide, we will cover the following:
- Choosing a Hosting Option
- Preparing Your Application for Deployment
- Deployment Process
- Monitoring and Maintenance
1. Choosing a Hosting Option
There are several hosting options available for Python web applications, each with its own advantages and use cases:
- Shared Hosting: Cost-effective and user-friendly, shared hosting allows multiple websites to share the same server resources. While it’s suitable for small projects and personal websites, it may not provide the performance or customization needed for larger applications.
- Virtual Private Server (VPS): VPS hosting offers a dedicated portion of a server’s resources, providing more control and flexibility than shared hosting. It’s suitable for medium to large applications that require specific configurations and performance.
- Cloud Hosting: Services like AWS, Google Cloud Platform, and Microsoft Azure provide scalable cloud hosting solutions. You can easily scale your application based on demand, and these platforms offer various services, including databases, storage, and load balancing.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS providers like Heroku and PythonAnywhere simplify deployment by handling infrastructure management. You can focus on coding and deploying your application without worrying about server configurations.
2. Preparing Your Application for Deployment
Before deploying your application, ensure it is production-ready:
- Environment Configuration: Set up your application’s environment variables, such as database URLs, API keys, and secret keys, to keep sensitive information secure and separate from your codebase.
- Dependencies: Create a requirements.txt file (or equivalent for your framework) listing all the packages and libraries your application depends on. This ensures that your production environment has the necessary dependencies installed.
- Static Files: Configure your application to collect and serve static files (CSS, JavaScript, images) properly. Most web frameworks provide commands to manage static files, ensuring they are accessible in a production environment.
3. Deployment Process
The deployment process may vary based on the hosting option you choose, but the general steps include:
- Upload Your Code: Transfer your application files to the server using methods such as FTP, SCP, or Git. If you’re using a cloud provider or PaaS, you may deploy directly from a repository (e.g., GitHub).
- Set Up the Web Server: Configure a web server (e.g., Nginx, Apache) to serve your application. This includes setting up reverse proxies, handling incoming requests, and serving static files efficiently.
- Configure Application Server: If your application requires a specific application server (e.g., Gunicorn for Flask/Django), install and configure it to serve your application. This server will run your Python application and handle requests.
- Database Configuration: Ensure that your database is set up and properly configured. This may include creating the database, running migrations, and configuring connection settings.
- Start Your Application: Start your application server and ensure it’s running. You may also want to set up a process manager (e.g., Supervisor, systemd) to manage your application’s lifecycle and ensure it restarts automatically if it crashes.

4. Monitoring and Maintenance
Once your application is deployed, it’s essential to monitor its performance and perform regular maintenance:
- Log Monitoring: Keep an eye on application logs to track errors and performance metrics. Implement log rotation and retention policies to manage log files effectively.
- Performance Monitoring: Use monitoring tools to track key metrics (response times, error rates) and set up alerts for any anomalies. This helps you proactively address performance issues.
- Security Updates: Regularly update your application dependencies and server software to mitigate security vulnerabilities. Implement security best practices to protect your application and data.
- Backup and Recovery: Set up regular backups for your application data and codebase to ensure you can recover quickly in case of data loss or server failure.
Key Takeaways from Deploying and Hosting Your Python Web Application
Deploying and hosting Python web applications involves careful planning and execution to ensure your application is accessible, performant, and secure. By choosing the right hosting solution, preparing your application properly, and implementing effective monitoring and maintenance strategies, you can successfully deploy your Python web application and provide a seamless experience for your users.
Best Practices in Python Web Development

When engaging in Python web development, adhering to best practices is essential for creating clean, efficient, and maintainable code.
In this section of the Python Web Development All-in-One Guide, we cover the following topics:
- Importance of Python Development Best Practices
- What are the Best Practices of Python Web Development?
Importance of Python Development Best Practices
Python is renowned for its versatility, scalability, and flexibility, making it a preferred programming language for many developers. However, adhering to best practices in Python development is crucial, especially for novice programmers. Here are several reasons why these best practices are important:
- Enhanced Readability: Implementing best practices ensures that Python code is highly readable and easily understandable. This clarity is particularly beneficial for collaboration among team members, as it allows others to quickly grasp the code’s functionality and purpose.
- Streamlined Development Process: Following best practices can significantly expedite the entire development phase. Developers can leverage existing code libraries from resources like PyPI (Python Package Index), which speeds up coding and helps achieve project objectives more efficiently.
- Increased Productivity: Best practices promote efficient coding habits, which can lead to higher productivity levels among developers. By adhering to proven methodologies, developers can focus more on functionality rather than spending excessive time on troubleshooting and rework.
- Effective Bug Management: With established best practices, Python developers and testers can thoroughly check for and address bugs and errors more effectively. This proactive approach helps ensure that issues are resolved promptly, allowing teams to meet tight deadlines without sacrificing code quality.
What are the Best Practices of Python Web Development?
To ensure effective and maintainable Python development, it’s important to follow several best practices. Here are key guidelines to help you write better code:
Utilize a Web Framework
Python provides various web frameworks, such as Django, Flask, and Pyramid. These frameworks come equipped with essential features for web development, including routing, request handling, and template rendering. By selecting a framework, you can better structure your codebase and promote code reuse.
Implement the MVC Pattern
The Model-View-Controller (MVC) architectural pattern is widely used in web development. It helps separate concerns by dividing your application into three components: models (which represent data and business logic), views (which manage the user interface), and controllers (which handle the interaction between models and views). Following this pattern enhances modularity and maintainability in your code.
Use Virtual Environments
Virtual environments allow you to create isolated environments for your projects, making it easier to manage dependencies and avoid package conflicts. Tools like virtualenv or Python’s built-in venv module enable you to set up and activate virtual environments. This practice ensures that each project has its own dependencies without cluttering the global Python installation.
Adopt Database Abstraction Layers
When working with databases, consider using an Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) library, such as SQLAlchemy. ORMs abstract the database layer, allowing you to interact with your database using Python objects rather than raw SQL queries. This approach simplifies database operations, enhances security by reducing the risk of SQL injection attacks, and makes it easier to switch between different database systems if needed.
Write Unit Tests
Unit testing is crucial for maintaining high code quality and catching potential bugs early in the development process. Python offers a built-in testing framework called unittest, as well as third-party libraries like pytest. It’s important to write comprehensive unit tests for the various components of your web application, including models, views, and controllers. Automating tests helps ensure that future code changes do not introduce unexpected issues.
Prioritize Security
Web applications are susceptible to numerous security threats. Some fundamental security practices include:
- Input Validation: Always validate and sanitize user inputs to prevent vulnerabilities like SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS).
- Password Security: Securely store passwords using hashing and salting techniques to protect user credentials.
- Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) Protection: Implement CSRF tokens to prevent unauthorized requests.
- Secure Session Management: Use secure practices for session management, such as using session cookies with secure flags and establishing session timeouts.
- Regularly Update Dependencies: Keep your Python packages and web frameworks updated to ensure you benefit from the latest security patches.
Maintain Code Structure
Writing well-organized, concise, and readable code is fundamental in Python development. While some may view it as complicated, producing clean code is an art form. Key practices to consider include:
- Adhere to PEP 8: This comprehensive style guide, published by Guido van Rossum and others, provides rules for writing ideal Python code. Following PEP 8 helps maintain consistency and clarity in your code.
- Ensure code readability: Readable code facilitates collaboration and contributes to timely project delivery.
- Follow Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) principles: This allows for code reuse, making your development process more efficient.
- Limit code to one statement per line to reduce complexity and enhance clarity.
- Keep line length to a maximum of 79 characters, promoting simplicity and ease of understanding.
- Maintain proper indentation, with four spaces per indentation level, to improve code organization and readability.
Structure the Project
A well-defined project structure is vital for meeting deadlines and achieving project goals. It enables developers to write code more effectively. Utilize project structure tools like cookiecutter, which helps in creating project templates and streamlining the setup process.
Maintain Documentation and Comments
Proper documentation and comments are essential, especially in collaborative environments. Clear documentation helps prevent confusion and makes it easier for developers to understand the code when multiple parties are involved.
Use Meaningful Naming Conventions
Developers should give appropriate names to variables, classes, modules, functions, and packages. This practice aids in clarity and helps avoid common errors, especially when working under tight deadlines.
Utilize Separate Environments
Create virtual environments for your projects to isolate dependencies and avoid library conflicts. This practice prevents issues that may arise from different versions of libraries being used across multiple projects. Consider using virtualenv to manage these environments effectively.
Leverage the Python Logging Module
Python’s built-in logging module provides flexibility for developers to create customized logging configurations. This allows for effective tracking and management of application logs.
Conduct Code Testing
Testing your Python code is crucial before deploying any web application. Regularly write and execute test cases to identify bugs and errors early in the development process. This practice helps ensure that the final product is reliable and bug-free.
Address Code Issues Promptly
If you encounter bugs or errors during development, fix them immediately. Timely resolution of issues helps maintain the integrity of your code and allows for efficient retesting.
Key Takeaways from Best Practices in Python Web Development
Embracing Python development best practices is essential for improving code quality, maintainability, streamlining workflows, and enhancing collaboration among developers. These practices lay the groundwork for successful project execution and contribute to the overall effectiveness of Python development.
Common Challenges in Python Web Development

While Python is a powerful and versatile language for web development, developers may encounter various challenges throughout the development process. Discover some of the most common issues faced in Python web development.
In this section of the Python Web Development All-in-One Guide, we cover the following challenges in Python website development:
- Performance Issues
- Scalability Issues
- Dependency Management
- Security Vulnerabilities
- Complexity of Frameworks
- Testing and Debugging Challenges
- Limited Asynchronous Support
- Integration with Frontend Technologies
- Deployment Challenges
Performance Issues
Python, being an interpreted language, can face performance challenges, especially in high-load scenarios. Developers need to implement optimization techniques such as code profiling, caching, and using efficient algorithms to mitigate these issues.
Scalability Issues
As web applications grow in user base and complexity, scalability becomes a concern. Python frameworks like Django and Flask offer scalability options, but developers must plan the architecture carefully to handle increased traffic and data load effectively.
Dependency Management
Managing dependencies in a Python project can be challenging, particularly when different projects require different versions of libraries. Using virtual environments helps, but developers must also keep track of updates and compatibility issues to prevent conflicts.
Security Vulnerabilities
Web applications are susceptible to various security threats, including SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and cross-site request forgery (CSRF). Developers must stay informed about security best practices and implement appropriate measures to safeguard their applications.
Complexity of Frameworks
While Python frameworks like Django provide a lot of built-in functionality, they can also introduce complexity. New developers might struggle with the learning curve associated with these frameworks, especially when dealing with their extensive features and configurations.
Testing and Debugging Challenges
Ensuring that a web application is bug-free and functions as intended requires thorough testing. Implementing automated testing can be difficult, and developers must invest time in writing tests and debugging code to maintain quality.
Limited Asynchronous Support
Although Python has libraries like Asyncio for asynchronous programming, it can be less straightforward compared to other languages that are designed with concurrency in mind. This can create challenges for developers who need to build applications that handle many simultaneous connections efficiently.
Integration with Frontend Technologies
As web development increasingly involves the integration of backend systems with various frontend technologies, developers may find it challenging to establish smooth interactions between the two. Understanding JavaScript frameworks and managing API communications effectively is crucial.

Deployment Challenges
Deploying Python web applications can be complicated due to the need for configuring servers, managing dependencies, and ensuring proper performance and security settings. Developers must be familiar with various deployment methods and tools to streamline this process.
Key Takeaways from Common Challenges in Python Web Development
By recognizing these common challenges, Python web developers can better prepare themselves to address potential issues and improve their overall development practices. Emphasizing robust architecture, thorough testing, and adherence to best practices can help mitigate these challenges effectively.
Career Opportunities and Resources for Python Web Developers

As Python continues to gain popularity in the web development landscape, it opens up a myriad of career opportunities for those skilled in this versatile programming language. Learn about important opportunities and resources for Python developers.
In this section of the Python Web Development All-in-One Guide, we will cover the following:
- What is a Python Fullstack Developer?
- Roles and Job Titles in Python Web Development
- Key Skills and Knowledge for Python Web Developers
- Tips for Effectively Working in Python Full-Stack Development
- Benefits of Becoming a Python Full-Stack Developer
- Learning Resources for Aspiring Python Web Developers
- Portfolio Building and Interview Preparation for Python Web Developers
What is a Python Fullstack Developer?

A Python full stack developer is a proficient programmer who possesses expertise in both front-end and back-end development, with a strong focus on Python.
They use the Python programming language to develop the entire technology stack of a web application.
Front-end development entails designing and implementing the user interface of an application, while back-end development involves handling the underlying logic and database interactions.
To excel as a Python full stack developer, one must cultivate robust skills in both realms, enabling them to create comprehensive web applications that seamlessly integrate user-facing elements with server-side functionality.
Roles and Job Titles in Python Web Development
Understanding the various job titles in Python development is essential for anyone aspiring to enter the field or advance their careers. This knowledge helps clarify the skills required and the potential career paths available.
Junior Python Developer
This entry-level position is ideal for those beginning their journey in Python development. Junior Python Developers focus on writing basic code, debugging applications, and learning industry best practices under the guidance of more seasoned developers.
Python Developer
In this mid-level role, developers are tasked with creating reusable, testable, and efficient code. Python Developers are typically involved in enhancing application functionality, collaborating with team members, and integrating user-facing elements with server-side logic.
Senior Python Developer
An experienced professional in this role leads the design and implementation of intricate software applications. Senior Python Developers often mentor junior staff, review code, and play a significant part in architectural decision-making.
Python Web Developer
These specialists concentrate on building server-side logic for web applications. Proficient in frameworks like Django and Flask, Python Web Developers collaborate closely with front-end developers to ensure seamless integration with the application’s user interface.
Python Data Scientist
This role focuses on analyzing and interpreting complex datasets to inform business decisions. Python Data Scientists utilize libraries such as pandas, NumPy, and SciPy to develop algorithms, create predictive models, and generate data visualizations.
Machine Learning Engineer
Professionals in this capacity design and implement machine learning solutions. Machine Learning Engineers harness Python’s powerful libraries, including TensorFlow and Keras, to develop systems capable of learning from data and making predictions.
DevOps Engineer (Python)
A cross-functional position, DevOps Engineers leverage Python to script and automate processes related to the development, deployment, and integration of software projects. They work to enhance system performance and establish workflows that promote continuous integration and deployment.
Python Full Stack Developer
These developers have expertise in both front-end and back-end technologies. Python Full Stack Developers are well-versed in backend frameworks and frontend languages, allowing them to manage all facets of web application development effectively.

Key Skills and Knowledge for Python Web Developers
To excel as a Python web developer, there are several key skills and areas of knowledge that are essential. These competencies enable developers to create efficient, scalable, and maintainable web applications. Here’s a breakdown of the critical skills needed in this field:

1. Proficiency in the Basics of Python
Understanding Python is fundamental for any developer in this domain. A strong grasp of the language’s syntax, data structures, functions, and libraries is essential. Familiarity with Python’s features, such as list comprehensions, decorators, and context managers, can enhance coding efficiency and readability.
2. Knowledge of Web Frameworks
Proficiency in popular Python web frameworks is crucial. Developers should be well-versed in frameworks such as Django, Flask, and Pyramid which provide essential tools for building web applications. Knowledge of the framework’s structure, routing, ORM, and templating systems is necessary to leverage their full potential.
3. Front-End Technologies
While Python is primarily used for back-end development, understanding front-end technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript is important. Familiarity with front-end frameworks such as React, Angular, or Vue.js can also be beneficial, especially when integrating user interfaces with back-end systems.
4. Database Management
Developers should have experience with database systems, including SQL and NoSQL databases. Understanding how to interact with databases using Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) tools like SQLAlchemy or Django ORM is vital for data manipulation and management.
5. RESTful API Development
Knowledge of RESTful API principles is essential for building web services that communicate between the front end and back end. Developers should understand how to design, implement, and consume APIs, ensuring secure and efficient data exchange.
6. Testing and Debugging Skills
Testing is a critical aspect of software development. Familiarity with testing frameworks such as unittest, pytest, or Selenium allows developers to write unit tests, integration tests, and end-to-end tests to ensure the application functions as expected. Debugging skills are also crucial for identifying and resolving issues during development.
7. Version Control
Proficiency in version control systems, particularly Git, is necessary for collaborating with other developers and managing code changes. Understanding branching, merging, and pull requests helps maintain a clean project history and facilitates teamwork.
8. Understanding of Security Practices
Web applications are susceptible to various security threats. Knowledge of security best practices, including input validation, authentication methods, and data protection, is essential to safeguard applications against vulnerabilities.
9. Familiarity with Deployment and DevOps
Understanding how to deploy web applications in various environments, including cloud services like AWS, Heroku, or Azure, is vital. Familiarity with containerization tools such as Docker and concepts related to Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines can streamline deployment processes.
10. Strong Problem-Solving Skills
Effective web development often involves troubleshooting and problem-solving. Developers should possess analytical thinking skills to break down complex problems and devise practical solutions.
11. Authentication and Authorization
It is helpful to understand the concepts of user authentication and authorization. As a python web developer, you should learn how to implement secure user registration, login, and access control mechanisms using your web framework’s built-in features or extensions.
By cultivating these skills and knowledge areas, aspiring Python web developers can build a solid foundation for a successful career in web development, capable of tackling diverse challenges and creating high-quality applications.
Tips for Effectively Working in Python Full-Stack Development
- Stay Organized: Keeping track of your tasks and projects is crucial. Utilize version control systems like Git or Subversion to manage changes, create branches for different features, and seamlessly switch between coding sessions.
- Automate Repetitive Tasks: Leverage scripts and automation tools to handle time-consuming tasks. This approach can help streamline your development process and improve overall efficiency.
- Master Core Concepts: Before delving into specific frameworks or libraries, ensure you have a solid understanding of the fundamental principles of Python full-stack development, such as object-oriented programming and database management.
- Engage with Other Developers: Collaborating with a team can enhance your skills and keep you updated on industry trends. Use communication tools like Slack or JIRA to discuss challenges, share solutions, and work together on projects.
- Embrace a Growth Mindset: Full-stack development encompasses a variety of technologies and frameworks. Stay open to learning new concepts and don’t hesitate to experiment with unfamiliar tools. Learning from mistakes is a vital part of becoming a better developer.
- Have Fun: Enjoying the coding process is key to long-term success. Make time to appreciate your work and continuously practice your skills to foster a positive and fulfilling development experience.
Benefits of Becoming a Python Full-Stack Developer
Becoming a Python Full Stack Developer offers numerous advantages. This role equips you with a wide range of skills, including web development, backend programming, and data analysis, making you a valuable asset to any organization.
As companies increasingly seek professionals who can navigate both front-end and back-end functions, full stack developers are in high demand. This diverse skill set allows you to switch seamlessly between different aspects of a project, enhancing your versatility as a developer.
Moreover, pursuing a career in full stack development typically leads to greater job security and the potential for higher salaries. With organizations recognizing the importance of comprehensive technical expertise, full stack developers are often well-compensated for their ability to contribute across various stages of web development projects.
Learning Resources for Aspiring Python Web Developers
As you embark on your journey to becoming a proficient Python web developer, a wealth of resources is available to help you gain the necessary skills and knowledge. Here’s a curated list of valuable resources across various formats:

Online Courses
- Coursera: Offers courses from renowned universities on Python programming, web development, and full stack development. Look for specializations that include projects to apply what you learn.
- Udemy: Features a wide range of affordable courses focused on Python and web development frameworks like Django and Flask. Courses often include hands-on projects.
- edX: Similar to Coursera, edX provides courses from universities and institutions, covering various topics in Python and web development.
Books
- “Python Crash Course” by Eric Matthes: A great introductory book that covers the basics of Python and includes practical projects.
- “Flask Web Development” by Miguel Grinberg: An excellent resource for learning how to build web applications using the Flask framework.
- “Django for Beginners” by William S. Vincent: A beginner-friendly guide to Django that walks you through the creation of web applications.
- “Python Web Development with Django” by Jeff Forcier: In this book, three experienced Django and Python developers cover various techniques, tools, and concepts you need to make the most of Django 1.0, including all the major features of the new release.
Documentation and Official Guides
- Python Official Documentation: Essential for understanding the core language and its features. It’s comprehensive and frequently updated.
- Django Documentation: Detailed documentation that provides tutorials and guides for building applications with Django.
- Flask Documentation: The official Flask documentation is well-structured, making it easy to understand how to use the framework effectively.
Online Communities and Forums
- Stack Overflow: A valuable platform where you can ask questions and find answers from experienced developers. It’s an excellent resource for troubleshooting and learning from real-world scenarios.
- Reddit: Subreddits like r/Python and r/learnpython are great places to connect with other learners and experienced developers, share resources, and discuss best practices.
- GitHub: Explore open-source projects, contribute to repositories, and learn from the code of experienced developers. You can also showcase your projects to potential employers.
Practice Platforms
- LeetCode: Ideal for practicing coding challenges and algorithms that are often asked in technical interviews.
- Codecademy: A great way to practice the basics of Python
- HackerRank: Offers challenges specifically focused on Python and web development, allowing you to improve your coding skills in a competitive environment.
- Codewars: A platform where you can solve coding challenges (katas) to hone your Python skills and learn from the community.
YouTube Channels
- Corey Schafer: Offers a range of tutorials on Python and web development, including Flask and Django.
- Traversy Media: Provides tutorials on full stack development, covering various frameworks and technologies relevant to Python developers.
- Tech With Tim: Focuses on Python programming with tutorials that include game development, web applications, and more.
By utilizing these resources, you can build a solid foundation in Python web development, enhance your skills, and stay updated with the latest trends and best practices in the field.
Portfolio Building and Interview Preparation for Python Web Developers
Building a strong portfolio and preparing for interviews are crucial steps for aspiring Python web developers. Here’s how you can effectively showcase your skills and get ready for job opportunities in this competitive field.
Portfolio Building
Build your portfolio to stand out from the crowd of python developers. Some of the best ways to build your portfolio are:
- Create Personal Projects:
- Develop a variety of projects that demonstrate your proficiency in Python and web development frameworks. Consider building:
- A personal blog using Django or Flask.
- An e-commerce site with user authentication and a payment system.
- A RESTful API that interacts with a front-end application.
- A data visualization project that presents insights from a dataset.
- Develop a variety of projects that demonstrate your proficiency in Python and web development frameworks. Consider building:
- Contribute to Open Source:
- Engage with open-source projects on platforms like GitHub. Contributing to existing projects allows you to collaborate with other developers, improve your coding skills, and showcase your ability to work in a team environment.
- Document Your Work:
- Maintain a clean and organized codebase, and use comments to explain your logic. Additionally, create documentation for your projects that outlines features, installation instructions, and usage. This demonstrates professionalism and attention to detail.
- Host Your Projects:
- Deploy your web applications on platforms like Heroku, AWS, or PythonAnywhere. This not only allows potential employers to see your work in action but also helps you gain experience with deployment processes.
- Create a Personal Website:
- Build a portfolio website that showcases your projects, skills, and contact information. Include case studies for your significant projects, highlighting your problem-solving skills and the technologies you used.
- Include a Blog:
- Consider writing blog posts about your learning experiences, challenges you faced, or tutorials on specific topics. This can demonstrate your knowledge and passion for the field, and help others in the community.
Interview Preparation
Once your portfolio is ready, you might want to start getting prepared for interviews. Some essential tips for interviewing include:
- Understand Common Interview Questions:
- Familiarize yourself with the types of questions commonly asked in Python web development interviews. These may include:
- Technical questions about Python, frameworks, and databases.
- Scenario-based questions to evaluate your problem-solving skills.
- Behavioral questions to assess how you work in a team and handle challenges.
- Familiarize yourself with the types of questions commonly asked in Python web development interviews. These may include:
- Practice Coding Challenges:
- Use platforms like LeetCode, HackerRank, or Codewars to practice coding problems. Focus on algorithms and data structures, as these are often part of technical interviews.
- Prepare for System Design Questions:
- As you progress in your career, you may encounter system design interviews. Study how to design scalable and maintainable applications, focusing on architecture, database design, and API interactions.
- Mock Interviews:
- Participate in mock interviews with peers or use platforms like Pramp or Interviewing.io to practice your interviewing skills. This helps you gain confidence and receive constructive feedback.
- Review Your Projects:
- Be prepared to discuss your portfolio projects in detail. Know the technical choices you made, the challenges you faced, and how you solved them. This can provide insights into your thought process and technical skills.
- Stay Updated with Industry Trends:
- Follow Python and web development blogs, podcasts, and social media channels to stay informed about the latest technologies and best practices. This knowledge can help you impress interviewers and show your enthusiasm for the field.
By focusing on portfolio building and thorough interview preparation, you can significantly enhance your chances of landing a position as a Python web developer. Your portfolio will serve as a testament to your skills, while effective preparation will ensure you’re ready to showcase your expertise in interviews.
Key Takeaways from Career Opportunities and Resources for Python Web Developers
By understanding the various roles in Python development, learning the essential skills required, aspiring Python developers can build a successful and fulfilling career in the rapidly evolving field of web development. Further growth can be achieved by using various learning resources like courses, books, practice platforms, and engaging with online communities. Finally, a strong portfolio alongside interview preparation can lead to a successful career.
Python Web Development for Businesses

Python has become an increasingly popular choice for businesses looking to develop web applications due to its versatility, scalability, and robust ecosystem. Explore how Python web development can benefit businesses and the key considerations involved.
In this section of the Python Web Development All-in-One Guide, we will cover the following topics relevant to businesses:
- Key Benefits of Python for Business Web Development
- Choosing the Right Python Web Development Framework for Your Business
- Choosing the Right Python Web Development Service Provider
- How Much Does It Cost to Develop Web Applications Using Python?
- Cost of Hiring Python Web Developers
- Case Studies: Successful Python Web Development Projects in Business
- Deciding Between In-House Development, Outsourcing, or Hiring Freelancers
Key Benefits of Python for Business Web Development
Python has become a favored language for business web development due to its many advantages. Here are some key benefits that make Python an excellent choice for building web applications:
1. Rapid Development
Python’s simplicity and readability allow developers to write code quickly and efficiently. Its extensive libraries and frameworks, such as Django and Flask, provide pre-built components that accelerate the development process. This rapid prototyping capability enables businesses to bring their ideas to market faster, giving them a competitive edge.
2. Scalability for Business
Python is designed to handle growth, making it suitable for applications that need to scale. Businesses can start with a simple application and expand its functionality as needed. Frameworks like Django are particularly well-suited for developing scalable web applications, allowing businesses to accommodate increasing user loads and data volumes without compromising performance.
3. Versatility
Python can be used for a wide range of applications, from simple websites to complex enterprise-level solutions. This versatility makes it easy for businesses to implement a variety of features, such as data analysis, machine learning, and web scraping, all within the same technology stack.
4. Strong Community Support
Python has a large and active community of developers who contribute to its growth by creating libraries, frameworks, and tools. This extensive community support ensures that businesses have access to a wealth of resources, documentation, and third-party packages, facilitating troubleshooting and development.
5. Integration Capabilities
Python easily integrates with other languages and technologies, making it ideal for businesses that require interoperability with existing systems. Whether integrating with databases, cloud services, or third-party APIs, Python’s flexibility allows for seamless communication and data exchange across platforms.
6. Security Features
Security is a crucial aspect of web development, and Python offers robust security features that help protect applications from vulnerabilities. Frameworks like Django include built-in protection against common threats such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and cross-site request forgery (CSRF), enabling businesses to build secure applications from the ground up.
7. Cost-Effectiveness
Using Python can be cost-effective for businesses, as its simplicity reduces the time and resources required for development. Additionally, Python’s open-source nature means there are no licensing fees, making it an attractive option for startups and small businesses with budget constraints.
8. Enhanced Maintainability
Python promotes clean and readable code, which simplifies maintenance and updates. A well-structured Python application is easier to debug and modify, allowing businesses to adapt their web applications to changing requirements or fix issues promptly without extensive rework.
9. Cross-Platform Compatibility
Python is compatible with various operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Linux. This cross-platform capability enables businesses to deploy their web applications in different environments without significant modifications, ensuring a broader reach and accessibility.
10. Support for Data Science and Machine Learning
With the increasing importance of data analytics and machine learning in business, Python’s strong support for these fields is a significant advantage. Libraries like Pandas, NumPy, and TensorFlow allow businesses to leverage data-driven insights and incorporate machine learning models into their web applications, enhancing functionality and user experience.

Choosing the Right Python Web Development Framework for Your Business
Selecting the appropriate Python web development framework is crucial for the success of your application. Each framework has its strengths and is suited for different types of projects. Below, we explore three popular frameworks—Django, Flask, and FastAPI—and provide guidance on when to choose each, along with a comparison of costs and development timelines.

When to Choose Django for Business Applications
Django is a high-level web framework that encourages rapid development and clean, pragmatic design. It is particularly well-suited for larger applications that require a robust structure and a wide array of features out of the box. Here are some scenarios where Django shines:
- Complex Applications: If your business application requires complex features such as user authentication, database management, and content management, Django’s built-in functionalities can save significant development time.
- Rapid Prototyping: Django allows businesses to quickly develop prototypes due to its extensive libraries and components. If you need to get a working version of your application to market fast, Django is a strong choice.
- Enterprise Solutions: For applications that require scalability, security, and a high level of customization, Django provides a solid framework that can handle growth effectively.
- Robust Community Support: Django’s large community means that you can find plenty of resources, third-party packages, and support for common challenges.
When to Opt for Flask for Lean and Custom Solutions
Flask is a micro-framework that is lightweight and easy to use, making it ideal for smaller applications or when you need complete control over the components you use. Consider Flask in the following situations:
- Simple Applications: If you are developing a small web application or API, Flask’s simplicity allows for quick setup and deployment without the overhead of a larger framework.
- Custom Solutions: When your project requires unique architecture or specific components, Flask gives you the flexibility to choose only the libraries and tools you need, avoiding unnecessary features.
- Learning and Prototyping: Flask’s straightforward approach makes it an excellent choice for beginners who want to learn web development or for developers who want to create prototypes without the complexity of larger frameworks.
Exploring FastAPI for High-Performance Applications
FastAPI is a modern web framework for building APIs with Python 3.6+ based on standard Python type hints. It is particularly noted for its performance and is a great option for the following scenarios:
- Asynchronous Applications: If your application requires high concurrency, FastAPI’s asynchronous capabilities allow it to handle multiple requests simultaneously, making it ideal for high-performance applications.
- API-First Development: FastAPI is designed for building APIs quickly and efficiently, making it an excellent choice for businesses focused on creating microservices or RESTful APIs.
- Type Safety: FastAPI’s use of type hints can improve code quality and make it easier to catch bugs early in the development process, enhancing maintainability.
Comparing Costs and Development Timelines for Each Framework
When choosing a framework, it’s essential to consider the costs associated with development and the expected timeline for completion. Here’s a comparison of the three frameworks based on various factors:
| Framework | Development Speed | Initial Cost | Long-Term Maintenance Cost | Best For |
| Django | Moderate to Fast | Moderate | Moderate to High | Large, complex applications requiring scalability and security. |
| Flask | Fast | Low to Moderate | Low to Moderate | Small applications or custom solutions with specific needs. |
| FastAPI | Fast | Moderate | Moderate | High-performance APIs and applications requiring asynchronous processing. |
Choosing the Right Python Web Development Service Provider
Selecting the right Python web development service provider is critical to the success of your project. A capable provider not only brings technical expertise but also understands your business needs and can translate them into effective web solutions. Here are some key factors to consider when choosing a Python web development service provider:
1. Assess Their Expertise and Experience
- Technical Skills: Ensure that the provider has a strong background in Python development and is familiar with popular frameworks like Django, Flask, and FastAPI. Look for proficiency in web development best practices, databases, APIs, and front-end technologies.
- Portfolio: Review their past projects to evaluate their experience. A diverse portfolio demonstrating a range of projects—especially those similar to your requirements—can provide insights into their capabilities and style.
2. Evaluate Their Approach to Development
- Agile Methodology: Consider providers that utilize Agile methodologies. This approach allows for iterative development, enabling flexibility and adaptability throughout the project lifecycle.
- Customization and Scalability: Discuss their ability to customize solutions based on your specific needs. The provider should be able to build scalable applications that can grow with your business.
3. Communication and Collaboration
- Clear Communication: Effective communication is vital for project success. Choose a provider that prioritizes transparency and regular updates. They should be accessible and willing to discuss progress and challenges openly.
- Collaboration Tools: Inquire about the tools they use for project management and collaboration. Familiarity with platforms like JIRA, Trello, or Slack can facilitate better interaction and tracking of project milestones.
4. Support and Maintenance Services
- Post-Launch Support: Your relationship with a provider shouldn’t end once the project is complete. Look for companies that offer ongoing support and maintenance services to address any issues that arise after deployment.
- Training and Documentation: A good provider will not only deliver a finished product but also provide documentation and training for your team to ensure smooth operation and management of the web application.
5. Check Client Testimonials and Reviews
- Reputation: Research the provider’s reputation in the industry. Client testimonials, case studies, and online reviews can provide valuable insights into their reliability, quality of work, and customer satisfaction.
- Long-Term Relationships: Consider whether they have established long-term relationships with clients. A provider that fosters ongoing partnerships is often more committed to delivering quality results.
6. Cost Considerations
- Budget Alignment: Clearly define your budget and discuss it upfront with potential providers. Be wary of extremely low-cost options, as they may compromise quality. Instead, look for providers that offer a good balance between cost and quality.
- Value for Money: Assess the overall value you receive for the price. This includes the provider’s expertise, the quality of the final product, and the level of support provided throughout the project.
How Much Does It Cost to Develop Web Applications Using Python?
The cost of developing web applications using Python can vary widely based on several factors. Understanding these variables will help businesses better estimate their budgets and make informed decisions throughout the development process.
Factors Affecting Development Costs
- Project Complexity: The overall complexity of the application significantly influences development costs. More complex applications that require advanced features, integrations, and functionality will generally require more time and expertise, leading to higher costs.
- Development Team Location: The geographical location of your development team can greatly affect labor costs. Teams in regions with a high cost of living tend to charge more for their services compared to those in regions with lower living costs. Outsourcing to countries with lower development costs can be an effective way to manage expenses.
- Experience and Expertise of the Development Team: The level of experience and specialization of the developers plays a crucial role in pricing. Highly skilled developers or agencies with a strong track record may charge premium rates, but their expertise can lead to a more efficient development process and higher-quality outcomes.
- Timeframe and Deadlines: Projects with tight deadlines may incur additional costs. Accelerated timelines often require more developers to work simultaneously or may necessitate overtime, resulting in higher overall expenses.
- Technology Stack: The choice of frameworks and tools also impacts costs. Some frameworks may have associated licensing fees or require specific resources, which can affect the overall budget. However, open-source frameworks can help mitigate these costs.
Choosing Between Open-Source and Paid Solutions
- Open-Source Solutions: Python offers a variety of open-source frameworks, such as Django and Flask, which are free to use. While utilizing open-source solutions can reduce upfront development costs, businesses should consider the costs associated with customization, implementation, and potential ongoing support.
- Paid Solutions: Paid platforms or proprietary software may come with licensing fees but often provide more robust support, security features, and out-of-the-box functionality. It is essential to weigh the benefits of reliability and support against the additional costs involved.
Managing Ongoing Costs: Hosting, Maintenance, and Scaling
- Hosting Costs: After development, hosting your web application incurs ongoing costs. These can vary based on the hosting provider, server specifications, and the level of traffic the application receives. Cloud hosting services like AWS, Google Cloud, or Heroku offer scalable solutions, but costs can increase with usage.
- Maintenance Costs: Regular maintenance is vital for keeping your application secure and functional. This includes updates, bug fixes, and monitoring performance. Budgeting for ongoing maintenance is crucial, as neglecting this can lead to higher costs down the line due to increased downtime or security vulnerabilities.
- Scaling Costs: As your application grows, scaling may become necessary to accommodate increased user demand. This can involve additional costs for infrastructure, development resources, and potential redesign efforts to ensure the application remains responsive and efficient.
Python Web Development Cost by Development Type
To help you make an informed decision, I have compiled cost estimates for Python web development.
- Simple Applications: For basic applications, costs typically range from $5,000 to $15,000. These projects usually require straightforward features and limited functionality.
- Medium Complexity Applications: For applications that are moderately complex, the development cost can vary from $15,000 to $50,000. These projects might include user authentication, database management, and some integrations with third-party services.
- Complex Applications: High-end, complex applications can range from $50,000 to over $200,000. These might involve advanced features, extensive integrations, and a larger team of developers
Cost of Hiring Python Web Developers
When considering the cost of hiring Python web developers, several factors influence the overall expense. This includes the developer’s experience level, location, and the complexity of the project. Here’s a breakdown of the typical costs associated with hiring Python web developers.
1. Experience Level
- Junior Developers: Entry-level Python web developers usually have less than two years of experience. Their hourly rates can range from $25 to $50. They often require more supervision and mentorship.
- Mid-Level Developers: With two to five years of experience, mid-level Python web developers typically charge between $50 and $100 per hour. They are more independent and can manage more complex tasks.
- Senior Developers: Highly experienced Python web developers, usually with five or more years in the field, can command rates from $100 to $200 per hour or more. They often take on leadership roles and can handle intricate and high-stakes projects
2. Geographical Location
According to Indeed, Python developers command an average base salary of $125,395 per year ($59.79 per hour) in the United States (US).
A good tactic to reduce the cost of hiring Python developers is to go to other markets.
Python developers cost lower in Asia, South America, and Eastern Europe compared to Western Europe and North America.
In countries like Bangladesh, India, and the Philippines, salaries for Python developers can be significantly lower, ranging from $10,000 to $30,000 annually.
3. Hiring Model
There are two main ways of hiring Python web developers: Contractual or Full-Time Employees.
Freelancers: They might charge on an hourly basis or per project, which can lead to cost savings for short-term needs. However, rates can be higher for experienced freelancers.
Full-Time Employees: Hiring full-time Python web developers may lead to better long-term project outcomes but comes with additional overhead costs such as benefits and taxes
For example, according to the latest data from Upwork, the cost of hiring Python developers ranges from $20-$40 per hour.
Case Studies: Successful Python Web Development Projects in Business
Python’s versatility and efficiency make it a popular choice for web development across various industries. Below are some notable case studies demonstrating the successful application of Python in business projects:

Netflix
One of the most popular streaming companies in the world, Netflix, has Python at the core of their technology stack.
According to developers at Netflix, they use Python at the base of many of their applications like security tools, recommendation engine, and in-house content distribution network (Open Connect), which delivers streaming content to their end users.
Source: Python at Netflix, Published in Netflix TechBlog.
The go-to forum for everything from news to niche hobbies, Reddit is a beloved platform globally. And guess what their technology their server-side is coded with? Python!
According to Reddit themselves, they use the Pylons framework. An example of their use includes routing, where every request is translated using Python.
The community-driven platform has benefited from Python’s extensive libraries, which facilitate rapid development and the implementation of new features, keeping the user base engaged.
Source: Official Reddit Support – What is Reddit written in?
Spotify
Spotify, the leading music streaming service, uses Python extensively for data analysis and backend services.
The company has developed a range of tools that allow it to handle vast amounts of data related to music recommendations and user behavior. By leveraging Python’s simplicity and robust libraries, Spotify can iterate quickly on features, ensuring a seamless user experience.
For example, the developers at Spotify have created a proprietary data analytics package called Luigi. They use it to quickly prototype complex data jobs. Luigi is the tech behind Spotify’s Radio and Discover features, as well as recommendations for people you might want to follow.
The use of Python has enabled Spotify to scale effectively while maintaining a high-performance environment.
Source: Engineering at Spotify – How we use Python at Spotify
Dropbox
Dropbox, a file hosting service launched in 2008, started as a Python-based application and continues to use Python for many of its core functions. According to an article on their blog, “Dropbox is a big user of Python”.
The development team at Dropbox has praised Python for its readability and ease of use, which accelerates the development process. Python allows Dropbox to manage its vast infrastructure efficiently and implement new features quickly while maintaining reliability and security.
Source: Dropbox Tech Blog – Our journey to type checking 4 million lines of Python
Google, the renowned technology company famous for its search engine, has integrated Python into its operations since the company’s early days.
For instance, Guido van Rossum, creator of Python, worked at Google from 2005 to December 2012, where a big part of his work was developing the Python Language. van Rossum developed Mondrian, a web-based code review system written in Python and used within Google.
Source: Wikipedia – Guido van Rossum
As a result, the use of Python at Google is extensive, affecting not only search algorithms but also a range of other applications and tools.
Key Uses of Python at Google:
- System Administration and Automation: Python scripts play a vital role in automating routine tasks, managing servers, and conducting system maintenance efficiently.
- Machine Learning and Data Analysis: Google utilizes powerful Python libraries such as TensorFlow and Pandas, which allow the company to create sophisticated machine learning models and carry out intricate data analysis.
- Web Development: The Django framework, built on Python, is employed by Google to facilitate the rapid development of robust web applications.
Deciding Between In-House Development, Outsourcing, or Hiring Freelancers
When deciding how to develop Python web applications, businesses face three primary options: in-house development, outsourcing, or hiring freelancers. Each approach comes with its own set of advantages and challenges, making it essential to evaluate which method aligns best with your project needs, budget, and long-term goals.
In-House Development
Advantages:
- Control and Communication: Having a dedicated in-house team allows for direct communication and greater control over the project. This facilitates quick adjustments and decision-making.
- Company Knowledge: In-house developers often have a deep understanding of the company’s goals, culture, and existing systems, which can enhance productivity and alignment with business objectives.
Challenges:
- Cost: Building an in-house team can be expensive due to salaries, benefits, and overhead costs associated with hiring and training developers.
- Resource Limitations: Depending on the size of your organization, you may not have enough personnel to cover all necessary skill sets, leading to potential skill gaps.
Outsourcing
Advantages:
- Cost Efficiency: Outsourcing can significantly reduce development costs, especially if you engage teams in regions with lower labor costs.
- Access to Expertise: Outsourcing firms often provide a wide range of specialized skills and experience, allowing you to leverage the latest technologies and best practices without having to hire full-time staff.
Challenges:
- Less Control: Working with an external team can sometimes lead to challenges in communication and control over the project timeline and quality.
- Cultural Differences: There may be differences in time zones and business practices that could impact collaboration.

Hiring Freelancers
Advantages:
- Flexibility: Hiring freelancers provides flexibility in scaling your development team up or down based on project needs without long-term commitments.
- Cost Savings: Freelancers can often be more affordable than hiring a full-time employee or outsourcing to a company, particularly for short-term projects.
Challenges:
- Quality Assurance: Ensuring consistent quality can be difficult when working with multiple freelancers, especially if they are located in different regions.
- Limited Engagement: Freelancers may not have the same level of commitment to your project as in-house staff, potentially leading to issues with availability or dedication.
Which is Better?
The choice between in-house development, outsourcing, or hiring freelancers ultimately depends on your specific project requirements, budget constraints, and desired level of control. It’s important to weigh the pros and cons of each option and consider factors such as team dynamics, project timelines, and the complexity of the development tasks.
Key Takeaways from Python Web Development for Businesses
- Business Advantages: Python offers numerous benefits for businesses, including rapid development capabilities, scalability, versatility, robust community support, strong security features, and cost-effectiveness. These attributes make Python an attractive choice for a wide range of web applications.
- Framework Selection: The choice of Python web development framework is critical. Django is ideal for large and complex applications, providing a comprehensive set of tools and features. Flask is better suited for smaller applications or specific needs, allowing for greater flexibility and simplicity. FastAPI is essential for projects that require high performance and asynchronous processing.
- Service Provider Reliability: Engaging a reliable Python web development service provider is crucial for the successful execution of projects. A reputable provider can help navigate the complexities of development and ensure timely delivery of high-quality applications.
- Cost Considerations: The cost of developing applications using Python can vary significantly, typically starting from around $5,000 for simpler projects and escalating to $200,000 or more for complex applications that require advanced features and functionalities.
- Geographical Cost Efficiency: Hiring Python developers from regions such as Asia or Eastern Europe can be more cost-effective compared to sourcing talent from the USA or Western Europe, allowing businesses to optimize their development budgets while still accessing high-quality expertise.
- Notable Companies: Many large organizations, including Netflix, Reddit, Spotify, Google, and Dropbox, leverage Python for their web development needs, highlighting its effectiveness and reliability in building scalable applications.
- Development Approach: Companies must carefully consider their approach to development, deciding between in-house teams, outsourcing, or hiring freelancers. Each option has its advantages and trade-offs, which should align with the company’s specific project goals and resource availability.
Future Trends of Python for Web Development

As Python continues to evolve, several trends are emerging that are likely to shape the future of web development using this versatile programming language. Read about some of the key trends to watch.
In this section of the Python Web Development All-in-One Guide, we cover the following future trends:
- Increased Adoption of Python Frameworks
- Integration of Machine Learning and AI
- Emphasis on Asynchronous Programming
- Rise of API-First Development
- Focus on Security
- Serverless Architecture
- Growing Community and Ecosystem
1. Increased Adoption of Python Frameworks
Frameworks such as Django and Flask are becoming more popular as they simplify the development process and enhance productivity. The rise of microservices architecture is pushing developers to adopt lightweight frameworks like FastAPI and Falcon, which facilitate building high-performance APIs. As organizations look to streamline their applications and make them more modular, the adoption of these frameworks is expected to grow.
2. Integration of Machine Learning and AI
Python’s stronghold in the machine learning and artificial intelligence domains is influencing web development. More applications will integrate AI-driven functionalities, such as recommendation systems, chatbots, and predictive analytics. Tools like TensorFlow and PyTorch are expected to be increasingly used alongside web frameworks to create intelligent applications.
3. Emphasis on Asynchronous Programming
As web applications demand greater speed and responsiveness, asynchronous programming is gaining traction in Python development. Libraries such as Asyncio and frameworks like FastAPI support asynchronous programming paradigms, enabling developers to write concurrent code more efficiently. This trend will likely lead to the development of more responsive web applications.
4. Rise of API-First Development
With the increasing reliance on APIs for building web applications, there is a shift towards API-first development. This approach allows developers to create the API before building the front-end, facilitating easier integration and collaboration between front-end and back-end teams. Python’s capabilities for building RESTful APIs with frameworks like Flask and Django REST framework make it a preferred choice for API-first development.
5. Focus on Security
As cyber threats become more sophisticated, there will be a heightened emphasis on security practices in Python web development. Developers will need to prioritize secure coding practices, implement robust authentication mechanisms, and regularly update dependencies to mitigate risks. Tools and libraries that enhance security measures will become more prominent in the Python ecosystem.
6. Serverless Architecture
The adoption of serverless computing is on the rise, allowing developers to focus more on code rather than managing infrastructure. Python’s compatibility with serverless platforms like AWS Lambda and Google Cloud Functions will drive this trend, enabling developers to build scalable applications with reduced operational overhead.
7. Growing Community and Ecosystem
The Python community is continuously expanding, contributing to a rich ecosystem of libraries and frameworks. This growth not only enhances the resources available for developers but also fosters collaboration and innovation within the community. More educational resources, open-source projects, and forums will likely emerge, providing support for new and experienced developers alike.
Key Takeaways from Future Trends of Python Web Development
The future of Python in web development appears bright, with continuous advancements and growing community support. By staying informed about these trends, developers and businesses can better prepare for the changes in the landscape and leverage Python’s capabilities to build innovative web applications.
Conclusion
Python has established itself as a formidable force in web development, offering a blend of simplicity, versatility, and power that appeals to developers and businesses alike. Its rich ecosystem of frameworks and libraries facilitates rapid application development, while its readability and community support make it an ideal choice for both new and experienced developers.
As businesses increasingly look for efficient and scalable web solutions, Python’s capacity to integrate with emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning is becoming a significant advantage. Additionally, trends toward microservices and serverless architectures are likely to further enhance Python’s relevance in the web development landscape.
I hope you enjoyed reading this Python Web Development All-in-One Guide! Personally, I enjoy Python the most compared to other high-level programming languages. So this article was a blast to write!
However, for backend web development, I would recommend you judge Python after trying out other technologies like ASP.NET Core, Laravel, Ruby on Rails, Express.js, and CakePHP. You will thank me later when you select the best technology for your bespoke needs based on rigorous research!
FAQs for Python Web Development
Before ending this Python Web Development All-in-One Guide, I would like to answer some frequently asked questions (FAQs) that readers might have. Let me know if you have further questions in the comments section down below!
Why would you use Python for web development?
Python is similar to older web development languages like PHP and Perl but it is modern and popular. Furthermore, Python is lightweight, simple to set up, and easy to maintain. Do note that Python isn’t a framework, but a programming language. Frameworks based on Python include Django, Flask, Bottle, FastAPI, and more. Other benefits of using Python for the backend of your web dev projects include access to a lot of great python libraries like machine learning, APIs, and more.
What is the best way to learn web development with Python?
The most effective way to learn Python is by using it. Building real projects allows you to put learned concepts into practice and gain valuable, hands-on experience. Begin with simpler projects to reinforce foundational skills, then gradually progress to more complex projects as your knowledge and confidence grow. This approach helps solidify your understanding while also allowing you to tackle practical challenges commonly faced in Python development.
What does Python do in web development?
In web development, Python is primarily used to create the back end, or server-side, of a website or application. This back-end functionality includes managing data flow between the server and the user interface, processing and storing data, handling database interactions, routing URLs, and managing security protocols. Python’s role in these tasks often involves using frameworks like Django and Flask, which simplify tasks like database communication and web request handling. Additionally, Python’s versatility and extensive libraries make it well-suited for integrating complex features such as data processing and machine learning into web applications.
Why is Python popular for web development?
Python is favored for web development due to its readability, extensive library support, and active community. Its frameworks, like Django and Flask, streamline development, allowing for rapid prototyping, scalability, and robustness in both small and large-scale applications.
Which Python framework is best for web development?
The choice of framework depends on project requirements:
- Django is ideal for large, complex applications that need built-in functionalities and a structured approach.
- Flask is a lightweight option for smaller projects or those needing a highly customized approach.
- FastAPI is excellent for high-performance and asynchronous applications, particularly when speed and real-time data processing are essential.
Is Python suitable for both front-end and back-end development?
Python is primarily used for back-end development, handling server-side operations, data processing, and API integration. For front-end work, developers often use JavaScript frameworks (React, Vue) alongside Python for a full-stack approach.
How does Python compare to other languages for web development?
Python stands out for its simplicity and efficiency, especially when compared to languages like Java, which has a steeper learning curve. Unlike PHP, which is also popular for web development, Python is known for its versatility and application beyond web projects, such as in data science and automation.
What are the costs associated with Python web development?
Python web development costs vary based on the project’s complexity, ranging from $5,000 for simple applications to over $200,000 for complex, feature-rich systems. Factors like geographical location of developers, project scope, and choice of framework affect the overall cost.
What skills should a Python web developer have?
Essential skills include a strong grasp of Python and its frameworks (Django, Flask), understanding of RESTful APIs, proficiency in front-end technologies (HTML, CSS, JavaScript), and experience with databases (SQL, NoSQL). Familiarity with DevOps and cloud platforms is also beneficial.
How do I choose between in-house, freelance, or outsourced Python development?
- In-house teams provide direct control and close collaboration, ideal for long-term or continuously evolving projects.
- Freelancers are cost-effective for smaller, short-term tasks but may lack consistent availability.
- Outsourcing provides scalability and expertise across various areas, making it a flexible choice for mid-to-large projects with diverse requirements.
How can Python web applications be scaled?
Python applications scale well with efficient coding practices, optimized database queries, caching, and using cloud services like AWS or Google Cloud for hosting. Django’s ORM and FastAPI’s asynchronous capabilities are particularly advantageous for scalability.
What are the future trends in Python web development?
Python’s use in web development is expected to expand, with growth in asynchronous processing (FastAPI) and microservices architectures. AI and machine learning integrations are also on the rise, especially with Python’s extensive libraries (TensorFlow, PyTorch) for data processing.
What are common challenges in Python web development?
Challenges include managing performance in high-traffic applications, ensuring security, maintaining cross-framework compatibility, and handling asynchronous data processing effectively. Choosing the right tools, frameworks, and development practices helps mitigate these challenges.
Can Python be used for web development?
Yes, Python is widely used for web development, particularly for building the backend of web applications. With frameworks like Django, Flask, and FastAPI, developers can create web apps efficiently, handle server-side logic, and manage data interactions.
Is Python good for making websites?
Yes, Python is excellent for making websites, especially when using frameworks like Django and Flask. These frameworks offer robust tools for building dynamic, data-driven websites and support scalable, secure applications.
Is Python enough for Web Developers?
Python can be sufficient for backend web development, but full-stack web developers should also be proficient in frontend technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to handle user-facing aspects of web apps.
Is Python good for backend web development?
Python is well-regarded for backend development due to its readability, versatility, and strong frameworks like Django and Flask, which provide tools for database management, user authentication, and RESTful API creation.
Should I learn Node.js or Python?
The choice depends on your goals:
- Python is strong for data-heavy, machine-learning-integrated applications and is often chosen for data science, web development, and academic research.
- Node.js is ideal for real-time applications and situations requiring fast, scalable I/O operations, like chat apps or collaborative tools.
Is Python better than JavaScript for web development?
Python excels in backend development and is often preferred for its readability and rich library ecosystem. JavaScript, however, is essential for frontend development and can also handle backend logic through Node.js, making it highly versatile for full-stack development.
Who gets paid more, Python or JavaScript developers?
Salaries can vary by location, experience, and industry, but Python developers generally command slightly higher salaries due to Python’s use in specialized fields like machine learning and data science.
Should I learn Python or JavaScript in 2024?
Both languages are valuable, but the decision depends on your career goals:
- Python: Ideal for backend development, data science, AI, and machine learning.
- JavaScript: Essential for frontend and full-stack roles and highly versatile with backend frameworks like Node.js.
Is Python or C++ better for web development?
Python is generally better for web development due to its simpler syntax and web frameworks. C++ is rarely used in web development, as it’s more suited for system programming, high-performance applications, and embedded systems.
Which is the No 1 programming language for web development?
JavaScript is often considered the top language for web development because it’s essential for both frontend and backend development (with Node.js). Python is also highly valued for backend web development.
Should I learn Python or web development first?
It’s helpful to start with basic Python programming, as it’s easier for beginners and builds foundational programming skills. Afterward, you can learn web development, where you’ll use Python frameworks like Django or Flask for backend development.
Is Python slow for web development?
Python is generally slower in execution than languages like JavaScript or C++. However, frameworks like FastAPI make it competitive for web applications that require quick response times, and Python’s ease of use often outweighs performance considerations for many applications.
Will AI replace Python web developers?
AI tools can assist in coding and automation but are unlikely to replace web developers entirely. Creative, complex problem-solving and understanding user needs require human insight, although AI may change some aspects of development workflows.
Will Python web development exist in 10 years?
Yes, Python web development will continue to be relevant, evolving with new technologies and adapting to changing user needs. AI, AR/VR, and new web technologies will likely influence future trends in Python web development.
Is Python in-demand in 2025?
Python is expected to remain in high demand in 2025, especially in fields like web development, data science, AI, machine learning, and automation. Its versatility and ease of use contribute to its popularity across various industries.
This page was last edited on 19 October 2025, at 9:54 am
Contact Us Now

Contact Us Now
Start a conversation with our team to solve complex challenges and move forward with confidence.











