- Introduction to Learning Management Systems (LMS)
- Who Uses a Learning Management System (LMS) and What Is It Used For?
- What are the Common Use Cases of LMS
- Types of Learning Management Systems
- What are the Key Features of a Learning Management System
- What are the Top Benefits of Using an LMS
- What Are The Popular Learning Management Systems?
- How Does An Learning Management System (LMS) Work?
- What are Challenges and Limitations of Learning Management Systems
- How to Choose the Right LMS
- How To Develop A Learning Management System?
- How Much Does it Cost to Build an LMS
- How To Come Up With Your LMS Idea?
- What are the Key Future Trends in Learning Management Systems
- Final Note
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The future of learning is here, thanks to the rise of Learning Management Systems.
Think about it: classrooms are no longer tied to four walls, and workplace training isn’t stuck in boardrooms.
Instead, LMS has made it possible to learn anywhere and anytime, establishing itself as a powerful and versatile online learning platform.
A learning management system (LMS) is a software platform that helps create, deliver, and manage online courses, training programs, or any type of learning content.
It acts as a central hub where educators, trainers, and organizations can organize lessons, track learner progress, and provide flexible eLearning experiences accessible to anyone, anywhere.
Now, it has become an all-in-one online learning platform for every industry. With an LMS, you get:
- A learning portal where instructors design and deliver courses.
- On-demand access to lessons, quizzes, and resources for learners.
- Powerful tools for organizations to track progress and measure results.
The growth of LMS shows no signs of slowing down. This transformation in digital education systems brings unmatched flexibility, scalability, and engagement to the learning process.
According to MarketsandMarkets, the global LMS market is set to skyrocket from $18.7 billion in 2022 to $46.9 billion by 2027.
In this guide, we’ll take you on a deep dive into Learning Management Systems, exploring their evolution, features, benefits, and future trends, and share how they’re reshaping the way people learn, teach, and grow across the globe.
But what exactly is a Learning Management System, and why has it become the backbone of modern education and training? Let’s break it down.
Introduction to Learning Management Systems (LMS)
Learning Management Systems (LMS) are reshaping how we teach, train, and learn in the digital age. This guide explores what an LMS is, its features, benefits, types, development steps, challenges, costs, and future trends, everything you need to know in one place.
So, what exactly is a Learning Management System (LMS), and what makes an LMS powerful?
What is a Learning Management System (LMS)?
A Learning Management System (LMS) is a software platform that delivers, manages, and tracks courses or training programs. Acting as an online learning platform, it supports eLearning, remote learning, and blended learning, with modern LMS solutions using AI to personalize education and improve results.
Here’s what makes an LMS powerful:
- It works as an online learning platform where instructors can create and share structured lessons.
- It serves as an online course delivery system, organizing modules, quizzes, and assignments for easy access.
- Learners benefit from interactive tools like video conferencing, forums, and collaborative features.
- Administrators can automate training, manage users, and track results with detailed reports.
Because of this versatility, LMS platforms are widely used across industries, from universities and schools to corporate training, nonprofits, and government agencies. They power different approaches, including:
- Fully digital eLearning systems for online education.
- Remote learning platforms that connect learners across locations.
- Blended learning platforms that mix classroom instruction with digital experiences.
With the rise of AI in LMS, these platforms have become even more advanced. They can now recommend personalized learning paths, evaluate skills gaps, and boost engagement while ensuring compliance and measurable results.
In essence, an LMS is more than just software; it’s a complete learning ecosystem that transforms how knowledge is delivered, consumed, and managed in today’s connected world.
LMS platforms didn’t appear overnight; instead, their journey of evolution tells a fascinating story of innovation in learning.
History and Evolution of Learning Management Systems
The rise of Learning Management Systems (LMS) is the result of centuries of innovation in distance learning and education technology (EdTech), from mail-based lessons to today’s AI-powered online platforms.
Early Beginnings: Distance Learning
- 1723 – Caleb Phillips advertised shorthand lessons in the Boston Gazette.
- 1840s – Isaac Pitman introduced interactive correspondence learning.
- 1856 – Europe’s first distance learning institution was founded for language study.
The Multimedia Shift (1920s–1950s)
- Teaching machines, radio, TV, and video opened access to mass education.
- Universities began experimenting with computer-assisted instruction and televised courses, paving the way for early virtual learning environments (VLEs).
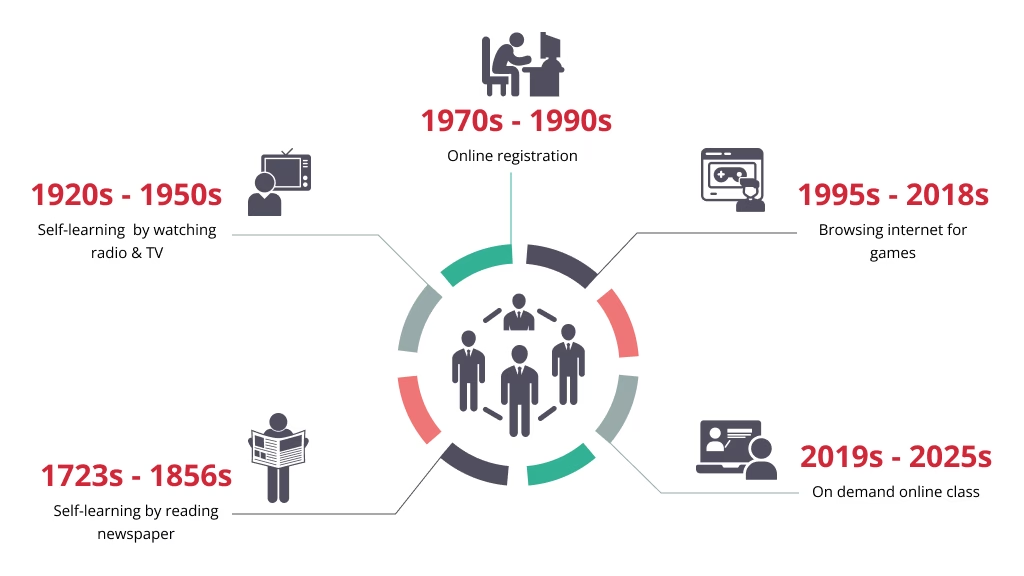
Rise of Computers and Early LMS
- 1970s – PLATO pioneered one of the first networked knowledge management systems.
- 1990s – Norway’s NKI launched EKKO, the first fully featured LMS, followed by course management systems and training software.
The Internet & Digital Education Boom
- Early online course delivery systems like FirstClass enabled global remote learning.
- Standards such as SCORM and xAPI ensured cross-platform compatibility.
- Businesses adopted corporate learning platforms, while universities integrated higher education LMS.
COVID-19 Acceleration
- School closures affected 95% of global learners.
- Cloud-based LMS became the backbone of remote education and workplace training.
- Student activity and submissions nearly doubled compared to pre-pandemic levels.
Today’s LMS: Smarter, Faster, Mobile
- Mobile learning enables anytime, anywhere access.
- AI in LMS powers personalized learning paths and skills gap analysis.
- Blended learning platforms support both education and business upskilling.
From correspondence letters to intelligent digital education systems, LMS has continually evolved, leading us to a key question: who uses these platforms today, and what exactly do they use them for?
Who Uses a Learning Management System (LMS) and What Is It Used for?
A Learning Management System (LMS) isn’t just for universities anymore; it’s become the backbone of modern learning, training, and upskilling.
From classrooms to corporate offices, more and more people rely on LMS platforms because they make learning flexible, organized, and accessible anytime, anywhere.
Here’s a quick look at who actually uses an LMS:
Education
- Schools & Universities – manage lessons, track progress, deliver online courses
- Teachers – grading, assessments, classroom management tools
- Students – access materials, submit assignments, learn remotely
Businesses & Organizations
- Corporations – onboarding, compliance training, skill development
- Small Businesses – affordable LMS for streamlined employee training
- Enterprises – training management & knowledge-sharing systems
Beyond Traditional Learning
- EdTech Startups – build cloud-based & AI-powered LMS platforms
- Nonprofits & Associations – run workshops, certifications, community programs
- Trainers & Coaches – deliver global courses via blended learning systems
- Nonprofits & governments: training volunteers, educating communities, and running large-scale programs with remote learning platforms.
In short, whether it’s for digital education systems in schools or LMS systems for business, these platforms are transforming how knowledge is shared and managed in today’s fast-paced world.
In every sector, the demand for smarter, scalable, and user-friendly LMS platforms keeps growing, raising the next big question: which systems are leading the way?
What Are the Common Use Cases of LMS
LMS platforms are applied in countless real-world scenarios, from boosting employee performance to streamlining academic learning and even supporting small businesses. They make it easier to deliver training, manage progress, and adapt learning to different needs across industries. Let’s look at the top use cases where a learning management system makes the biggest impact:
- Employee Training Software: Standardize onboarding and professional development.
- Corporate Learning Platform: Deliver compliance and role-based training at scale.
- Higher Education LMS: Manage online classes, grading, and student engagement.
- Blended Learning Platform: Support hybrid models combining in-person and online training.
- Knowledge Management System: Store and share organizational know-how in one hub.
- Course Management System: Create, organize, and deliver structured learning content.
- Remote Learning Platform: Provide access to education anytime, anywhere.
- Mobile Learning: Enable learners to study on the go via apps and smartphones.
- AI in LMS: Personalize learning paths with smart recommendations and analytics.
- Best LMS for Small Business: Offer affordable, scalable solutions to upskill teams.
From employee onboarding to mobile and AI-driven learning, the use cases of an LMS prove just how versatile and impactful these platforms are across industries. Next, let’s dive into the key features that make a Learning Management System truly effective.
Types of Learning Management Systems
Not all Learning Management Systems (LMS) are built the same. What sets them apart is how they’re deployed, priced, and how well they support modern eLearning systems and content standards.
Choosing the right type impacts cost, flexibility, and scalability for your organization, whether you’re running a corporate learning platform, a higher education LMS, or a remote learning platform for nonprofits. Here’s a quick side-by-side look at the most common LMS types to guide your decision:
LMS Deployment Models
LMS deployment models define how a learning management system is delivered and managed, whether through the cloud, on-premise, or hybrid solutions.
| Deployment Type | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Cloud-Based LMS | Vendor-hosted, quick to deploy, scalable, and updated automatically. Accessible via web or mobile with minimal IT effort. |
| SaaS LMS | Subscription-based cloud LMS with multi-tenant architecture. Includes automatic upgrades, security patches, and predictable pricing. Ideal for organizations seeking fast rollout and low maintenance. |
| Self-Hosted LMS | Installed on your own servers for full control and customization. Requires strong IT support and ongoing maintenance. |
| Hybrid LMS | Combines cloud scalability with on-premise data control. Suitable for enterprises with compliance, data residency, or legacy system requirements. More complex to set up and manage. |
| Third-Party Hosted LMS | Managed by an external provider on private or public cloud. Reduces IT workload but limits flexibility and depends on vendor reliability. |
| Single-Tenant LMS | Dedicated infrastructure for one organization. Offers higher security, performance isolation, and customization, but comes at a higher cost compared to shared environments. |
| Multi-Tenant LMS | Shared infrastructure across multiple organizations. Cost-effective and easy to scale, but customization and control are more limited. Common in SaaS LMS platforms. |
| Desktop LMS | Installed locally on individual computers. Works offline but lacks scalability and remote access. |
| Mobile LMS | Designed for smartphones and tablets. Enables anytime-anywhere learning but may offer fewer features than full platforms. |
| Custom-Built LMS | Tailored to specific needs with maximum flexibility. Expensive and time-consuming to develop. |
| Open-Source LMS | Free and highly customizable. Requires in-house IT or contractors for setup, support, and security. Popular in schools and startups. |
LMS Pricing Models
LMS pricing models vary from free open-source options to paid subscriptions and custom-built solutions, depending on features, users, and scalability needs.
| Pricing Model | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Open-Source LMS | Free to use, highly customizable. Hidden costs for hosting, setup, security, and maintenance. Best for teams with technical expertise. |
| Freemium LMS | Free basic plan with paid upgrades. Good for small teams testing LMS adoption. |
| Subscription-Based LMS | Recurring fee with hosting, updates, and support included. Easy to deploy and scale. |
| License-Based LMS | One-time or annual license. More control, but requires IT resources for hosting and updates. |
| Pay-Per-User LMS | Cost scales with number of users. Affordable initially, expensive at scale. |
| Pay-Per-Course LMS | Pricing based on courses offered. Ideal for training and education businesses. |
| Usage-Based LMS | Charges based on active users or usage. Flexible but costs may vary. |
| Enterprise LMS | Custom pricing for large organizations with complex needs. |
| Custom-Built LMS | High upfront cost with full ownership and flexibility. Ongoing maintenance required. |
LMS Content Standards
LMS content standards, such as SCORM and xAPI, ensure that learning materials are compatible, reusable, and trackable across different platforms.
| Standard | Key Points |
|---|---|
| SCORM | Widely supported; makes courses reusable and trackable across different LMS platforms. Ideal for traditional online course delivery. |
| xAPI | Tracks detailed learning activities across apps, devices, and even outside the LMS. A flexible choice for modern digital learning. |
| cmi5 | Combines SCORM’s structure with xAPI’s flexibility. Promising but still in early adoption stages. |
| AICC | An older standard once used in compliance-heavy industries. Now largely outdated and replaced by newer options. |
| LTI (Learning Tools Interoperability) | Enables seamless integration between LMS platforms and external learning tools. Commonly used in education and higher learning environments. |
With so many deployment options, pricing models, and content standards, each LMS type serves a different purpose. And once you’ve identified the right LMS type for your needs, the next step is understanding how these platforms are actually applied in real-world scenarios. Let’s explore the most common use cases of an LMS.
What are the Key Features of a Learning Management System
When choosing a Learning Management System (LMS), the real value lies in its features. Here are the essentials every effective online learning platform should offer:
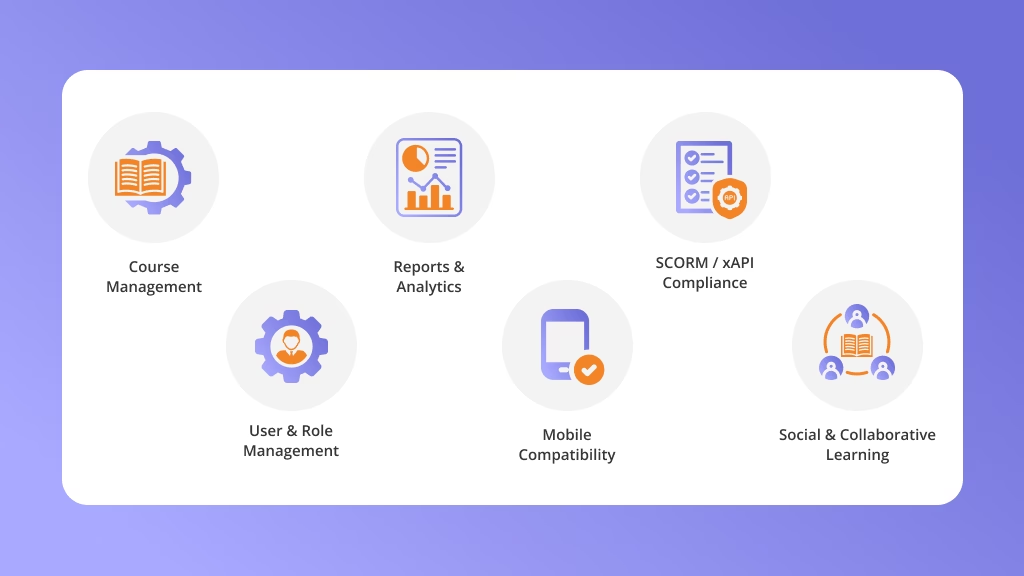
- Course Management – Create and deliver structured training content
- SCORM / xAPI Compliance – Ensure courses are reusable and trackable
- User & Role Management – Control access for learners, instructors, and admins
- Assessments & Quizzes – Test knowledge and track learning outcomes
- Certification & Compliance – Automate certificates and compliance reporting
- Reports & Analytics – Monitor performance with real-time insights
- Mobile Compatibility – Access training anytime on any device
- Social & Collaborative Learning – Encourage interaction through forums and groups
- Gamification – Drive engagement with points, badges, and leaderboards
- Integrations – Connect seamlessly with HR and business systems
These features form the foundation of a powerful LMS, making it not just a course delivery tool but a complete learning ecosystem. Now, let’s explore how these capabilities translate into real-world impact and the top benefits of using an LMS.
What Are the Top Benefits of Using an LMS
Using a Learning Management System (LMS) comes with clear advantages; for instance, it saves time, reduces costs, and makes learning more accessible. Beyond convenience, it also drives better engagement, performance, and long-term results.
Benefits for Administrators
- Lower Training Overhead: Reduces costs tied to physical classrooms, travel, and instructor-led sessions.
- Simplified Training Operations: Courses, users, and learning data are managed from one system.
- Quicker Employee Readiness: New hires and teams reach productivity faster through structured learning paths.
- Clear Visibility Into Learning Progress: Dashboards show who has completed training and where gaps exist.
- Easier Compliance Management: Mandatory training and certifications are monitored automatically.
- Data-Driven Learning Decisions: Training outcomes can be reviewed to improve programs and performance.
Benefits for Learners
- Learning on Their Own Schedule: Content is available whenever and wherever learners need it.
- Stronger Understanding Over Time: Self-paced access allows repetition and deeper comprehension.
- Continuous Skill Growth: Learners can build new skills beyond initial training.
- More Relevant Learning Paths: Training can be tailored to roles, goals, or performance needs.
- Better Learning Experience: Interactive formats increase engagement and motivation.
While these benefits make a Learning Management System a powerful tool, it’s equally important to recognize the challenges and limitations that come with it.
Understanding these hurdles will help you make smarter decisions when implementing an LMS.
What Are the Popular Learning Management Systems in 2026
With so many Learning Management Systems available, choosing the right one can feel overwhelming. In 2026, popular LMS platforms stand out by combining ease of use, scalability, and strong education technology (EdTech) features. From corporate training platforms to higher education LMS solutions, these systems support modern online learning worldwide.
So, which LMS platforms are most widely used today? Below is a snapshot of some of the most popular learning management systems in 2026, covering education, business, and professional training needs.
- Moodle: A leading open-source course management system widely used in schools and universities.
- Blackboard Learn: A higher education LMS supporting blended and online learning at scale.
- Canvas: A modern, cloud-based LMS known for its clean interface and flexibility.
- TalentLMS: A lightweight training management software, ideal for small businesses.
- Docebo: An AI-driven corporate learning platform built for enterprise training.
- SAP Litmos: A trusted employee training software with compliance and mobile learning features.
- Absorb LMS: A scalable online training system designed for businesses of all sizes.
- Schoology: A virtual learning environment (VLE) tailored for K–12 and higher education.
- iSpring Learn: A fast-to-deploy online course delivery system for corporate training.
- LearnDash: A WordPress-based learning portal popular with entrepreneurs and course creators.
These popular LMS platforms highlight the range of options available, from education-focused solutions to corporate training powerhouses.
How Does a Learning Management System (LMS) Work?
At its core, a Learning Management System (LMS) is an online learning platform that simplifies how education and training are delivered, managed, and tracked, bringing content, learners, and progress together in one place.
The Basic Flow of an LMS
Here’s how most digital education systems operate:
- Upload or Create Content → Add PDFs, SCORM/xAPI courses, videos, quizzes, podcasts, or build lessons directly in the platform.
- Add Users & Roles → Import or sync learners, instructors, and admins from databases or HR systems.
- Enroll & Deliver Training → Assign courses manually or automatically; learners access via desktop or mobile for flexible remote learning.
- Track & Measure Results → Monitor completions, quiz scores, time spent, and certifications with detailed reports to spot skill gaps and improve training.
What Happens Behind the Scenes in an LMS?
Login → User signs in securely
Role check → Learner / Instructor / Admin access is set
Course assignment → Courses added automatically
Learning activity → Videos, quizzes, lessons tracked
Assessment results → Pass/fail recorded
Certificates → Issued automatically when requirements are met
Reports → Progress and performance shown in dashboards
System sync → User data updated via HR or other systems
What Are the Challenges and Limitations of Learning Management Systems
While a Learning Management System (LMS) is a powerful tool for modern training and education, it isn’t without limitations. Many organizations find that even the best online learning platforms or corporate learning systems come with hurdles in setup, usage, and long-term adoption. No tool is flawless, and a Learning Management System is no exception. Let’s look at its main limitations.
- Complex setup and integration: Implementing a new LMS and connecting it with HR or IT systems often requires technical expertise.
- High implementation costs: Even a cloud-based LMS can involve licensing, customization, and training expenses.
- Limited personalization: Many LMS platforms struggle to fully support adaptive or personalized learning experiences.
- Weak reporting features: Some systems lack advanced dashboards for analyzing learner performance and compliance.
- Low learner engagement: Without gamification or interactive tools, employees and students may lose interest.
- Scalability issues: Certain LMS systems for business can’t handle rapid growth or large global teams effectively.
- Mobile learning gaps: Not every LMS offers a smooth mobile experience, limiting access for on-the-go learners.
- Content compatibility problems: Non–SCORM/xAPI compliant systems may restrict reusability and tracking of learning content.
- User adoption resistance: Learners and instructors may resist switching to a new digital education system due to unfamiliarity.
- Limited support services: Some vendors provide minimal customer support, leaving organizations struggling during downtime.
These challenges highlight why choosing the right LMS is more than just picking a platform; it’s about finding one that aligns with your goals and overcomes these common hurdles.
So, how do you identify the best LMS for your organization? Let’s break it down.
How to Choose the Right LMS
Selecting the right Learning Management System (LMS) can feel overwhelming, but the process becomes easier when you focus on your goals. Whether you’re a business, school, or solo course creator, the best LMS balances usability, scalability, and the right mix of features to support your learning strategy. Not sure which Learning Management System is right for you? Start with these simple questions.
Quick Checklist: 5 Questions to Ask Before Choosing an LMS
- Is it easy to use? → A clean, intuitive interface makes adoption smoother.
- Does it support SCORM/xAPI? → Ensures content works across platforms.
- Can learners access it on mobile? → Crucial for flexible, on-the-go training.
- Will it scale with my needs? → From small teams to enterprise-level growth.
- Does it integrate with my systems? → Sync with HR, CRM, or performance tools.
By asking the right questions, you’ll be able to pinpoint the LMS that truly fits your needs and sets your learning strategy up for success.
Key Features to Consider When Choosing an LMS
- Intuitive User Interface (UI): A clean, easy-to-use interface helps learners and administrators adopt the system quickly.
- Accessibility: Supports different content formats and devices to accommodate diverse learning needs.
- Automation: Automates enrollments, reminders, certifications, and learning paths.
- Centralized Training Management: Keeps all courses, users, and learning data in one platform.
- AI-Powered Personalization: Helps recommend content and personalize learning paths based on user behavior.
- Content Management: Supports course creation, updates, certifications, and retraining.
- Localization Support: Enables multi-language training and region-specific learning delivery.
- Standards Compliance: Supports SCORM, xAPI, and other content interoperability standards.
- Mobile Learning Support: Allows learners to access training on mobile devices.
- Platform Integrations: Connects with HR, CRM, authentication, and other business systems.
- Gamification Features: Uses points, badges, or leaderboards to improve engagement.
- Content Marketplace Access: Provides ready-made courses or third-party learning content.
- Reports and Analytics: Offers dashboards and reports to track learning progress and performance.
- Ongoing Support: Ensures regular updates, technical assistance, and system reliability.
- Scalability: Supports growing teams, multiple audiences, and expanding use cases.
- Social Learning Capabilities: Encourages peer learning through discussions and collaboration tools.
- Multi-Location Support: Manages training across teams, departments, or locations.
LMS Platform Red Flags to Watch For
- Limited integration options
- Poor mobile experience
- Weak security measures
- Basic or unclear reporting
- Slow or unreliable support
- Hidden or unclear pricing
- Overly complex user interface
How to Develop a Learning Management System?
Building a learning management system (LMS) requires careful planning, the right technology, and a learner-first approach.
Whether you’re creating a corporate learning platform, an online learning system, or a higher education LMS, the development process ensures scalability, engagement, and smooth course delivery.
And with the rise of mobile learning and AI in LMS, modern platforms are more interactive, personalized, and business-friendly than ever.
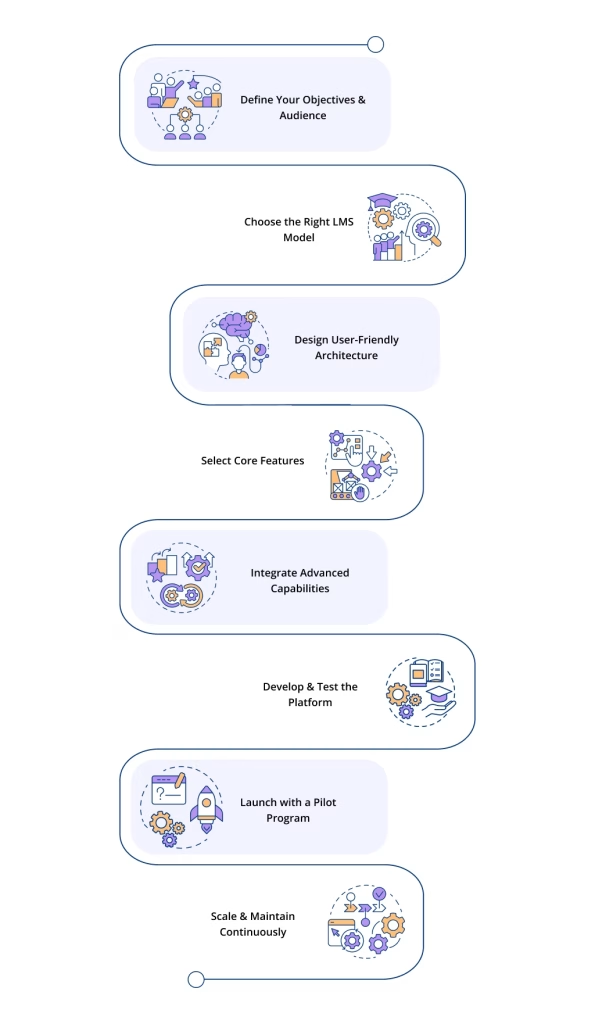
So, how do you turn the idea of a learning management system into a fully functional platform? Let’s walk through the process step by step:
Step 1: Define Your Objectives & Audience
Identify whether you’re building an eLearning system for employees, students, or customers. Clear goals help shape features like course tracking, assessments, and certifications.
Step 2: Choose the Right LMS Model
Decide between a cloud-based LMS, a remote learning platform, or a blended learning platform depending on your organization’s needs and budget.
Step 3: Design User-Friendly Architecture
Focus on intuitive navigation and responsive design for mobile learning so learners can access content anytime, anywhere.
Step 4: Select Core Features
Include essentials like course creation, video hosting, quizzes, progress tracking, and reporting. For businesses, add employee training software and compliance management tools.
Step 5: Integrate Advanced Capabilities
Enhance your platform with AI in LMS for personalized learning paths, SCORM/xAPI-compliant systems for compatibility, and a virtual learning environment (VLE) for interactive sessions.
Step 6: Develop & Test the Platform
Build the LMS using scalable frameworks and education technology (EdTech) standards. Rigorously test for performance, security, and cross-device compatibility.
Step 7: Launch with a Pilot Program
Start with a small group of users, such as staff or select students, to gather feedback and refine the system.
Step 8: Scale & Maintain Continuously
Keep your LMS updated with fresh content, integrations, and analytics. Use feedback loops to ensure long-term success and adaptability.
Developing an LMS is a structured journey, from setting clear goals to scaling the platform for long-term success. But before any of this can happen, you need one critical starting point: the right idea. So, how do you come up with your LMS concept?
How Much Does It Cost to Build an LMS
The cost of building a learning management system (LMS) depends on its complexity, integrations, and target users. Whether it’s a corporate learning platform, a cloud-based LMS, or a higher education system, expenses vary greatly. Understanding these factors ensures you invest wisely in a scalable and efficient solution.
Now, let’s break down the main factors that shape the overall cost of an LMS:
Cost Breakdown of LMS Development:
| Type of LMS | Best For | Estimated Cost Range |
|---|---|---|
| Basic LMS | Small businesses, startups, or organizations with limited users and simple training needs | $12k – $18k |
| Advanced LMS | Mid-sized companies and online learning platforms needing custom features and integrations | $20k – $40k |
| Enterprise LMS | Large organizations, corporate training platforms, and universities with high scalability needs | $45k – $70k+ |
Custom-Built vs. Ready-Made LMS vs.Professional LMS
| Type | Key Benefits | Cost Range |
|---|---|---|
| Custom-Built LMS | Fully tailored to specific business or academic needs; highly scalable and flexible | $50k – $150k+ |
| Ready-Made LMS | Quick deployment with built-in features; limited customization; may require add-ons | $5k – $20k annually |
| Professional LMS | Balanced option with customizable features, integrations, and scalability | $25k – $150k+ |
Knowing the costs helps you plan smarter and choose the LMS model that fits your goals. But beyond budgets, it’s equally important to look ahead, so what future trends are shaping the next generation of Learning Management Systems?
How to Come Up With Your LMS Idea?
Before you jump into building your learning management system, pause for a moment to ask yourself: What real problem will my LMS solve?
The most successful platforms don’t just deliver courses; they make learning easier, faster, and more engaging for the people using them.
By shaping your idea around your learners’ and organizations’ actual needs, you’ll create an LMS that’s not only practical and impactful but also stands out in today’s crowded world of online learning platforms and digital education systems. However, turning an LMS idea into reality starts with these essential building blocks:
- Identify the Target Audience: Define if it’s for students, employees, or professionals.
- Research Market Needs: Explore existing LMS platforms to find gaps.
- Define Key Features: Add essentials like course creation, tracking, mobile learning, or AI.
- Choose the Right Model: Pick cloud-based, blended, or remote learning options.
- Ensure Compliance & Integration: Support SCORM/xAPI and smooth integrations.
- Focus on User Experience: Keep it simple, engaging, and mobile-friendly.
- Validate with Feedback: Test prototypes with real users before scaling.
Once you’ve shaped a solid LMS idea, the next big question is cost, because turning vision into reality requires the right investment. So, how much does it actually cost to build an LMS?
What Are the Key Future Trends in Learning Management Systems
The future of learning management systems is smarter, faster, and more learner-focused than ever. From AI-powered personalization to mobile-first learning, LMS platforms are reshaping how businesses and educators deliver knowledge. So, what does the future of learning management systems actually look like? Let’s break it down:
AI-Powered Learning and Automation
Artificial intelligence is transforming how LMS platforms adapt to both learners and administrators by making learning more personalized, efficient, and intelligent.
- Personalized learning paths based on learner behavior, progress, and performance
- Smart content recommendations aligned with identified skill gaps
- Automated assessments, certifications, and learning reminders to reduce manual effort
- AI-driven insights to identify training needs and performance gaps
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) to improve content search, enable intelligent chatbots, and analyze learner feedback
Advanced Analytics and Learning Insights
LMS platforms are becoming data-driven decision tools.
- Real-time tracking of learner progress and engagement
- Predictive analytics to improve learning outcomes
- Performance insights tied to business or academic goals
- Skills analytics for workforce and talent planning
Immersive and Experiential Learning
Learning experiences are becoming more interactive and practical.
- Virtual Reality (VR) for simulations and hands-on training
- Augmented Reality (AR) for real-world, on-the-job guidance
- Scenario-based learning for soft skills and complex workflows
Mobile-First and Microlearning Experiences
Learning is increasingly designed for flexibility and speed.
- Mobile-friendly and app-based learning platforms
- Bite-sized microlearning content for busy learners
- Offline access for uninterrupted learning
- Progressive web apps for consistent cross-device experiences
Collaborative and Social Learning
Future LMS platforms support shared learning environments.
- Peer-to-peer learning and discussion tools
- Virtual coaching and mentoring features
- Social learning integrations to build learning communities
Seamless Integrations and Interoperability
LMS platforms are becoming part of a larger digital ecosystem.
- Integration with HR, CRM, and enterprise systems
- Compatibility with LXP platforms and third-party tools
- Continued support for SCORM, xAPI, and emerging standards
Secure Credentials and Compliance
Trust and verification are becoming more important.
- Secure digital certificates and credentials
- Blockchain-based credential verification (emerging use cases)
- Stronger data privacy and compliance controls
With these trends shaping what’s next, it’s the perfect time to wrap up with a final note on why choosing the right LMS matters more than ever.
Final Note
In a world where learning never stops, a learning management system is the engine that keeps education and training moving forward. Whether you’re running a corporate learning platform, a higher education LMS, or an online learning portal, the right choice can turn learning into a powerful growth driver, not just for your institution, but for every learner you serve.
Don’t just pick an LMS, pick the one that fits your vision. From mobile learning and blended learning platforms to AI-powered LMS systems, today’s options are built to be flexible, scalable, and future-ready. Choosing wisely means creating a smarter, more connected learning experience that actually delivers results.
Key Takeaways:
- An LMS is the backbone of modern learning and training.
- The best LMS is the one that grows with your goals, is flexible, scalable, and easy to use.
- Innovations like AI in LMS and cloud-based systems are redefining education.
- Aligning your LMS with business or institutional needs is the true success factor.
- The smartest next step? Test, compare, and commit to the platform that unlocks your learners’ potential.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About LMS
Got questions about Learning Management Systems? Here you’ll find clear answers to the most common queries, from features and costs to benefits and best use cases.
What is LMS?
Ans: A Learning Management System (LMS) is a software application or online platform designed to create, deliver, and manage learning programs.
It acts as a central hub where instructors can build courses, share content, track progress, and assess performance, while learners can access training materials anytime, anywhere.
What is the Main Purpose of an LMS?
Ans: The main purpose of an LMS is to centralize learning, making it easy to deliver courses, track progress, ensure compliance, and improve learner engagement.
Is LMS Suitable for Small Businesses?
Ans: Yes, many cloud-based and affordable LMS systems are designed for small businesses, offering scalability, mobile learning, and cost-efficient employee training.
Why should I hire an LMS development company?
Ans: Hiring an LMS development company ensures you get a tailored, scalable, and future-proof solution built around your unique goals.
Professional developers bring expertise in cloud-based systems, mobile learning, AI in LMS, and SCORM/xAPI compliance, making sure your platform is not only technically sound but also engaging and user-friendly.
What Are the Best Open-Source LMS Platforms?
Ans: Popular open-source LMS platforms include Moodle, Open edX, and Canvas, offering flexibility, customization, and cost-effectiveness.
Why Businesses and Educational Institutions Use LMS?
Ans: Organizations use LMS to streamline training, improve knowledge retention, ensure compliance, and provide flexible learning at scale.
Why your Business Needs a Learning Management System?
Ans: An LMS saves time, reduces training costs, boosts employee skills, and ensures consistent learning across teams, driving growth and efficiency.
What’s the best LMS system for business?
Ans: The best LMS depends on your needs, but popular business-ready options include TalentLMS, Docebo, SAP Litmos, and Cornerstone OnDemand.
What is LMS, LXP, and LLP?
Ans: LMS, LXP, and LLP may share similarities, but each plays a unique role in shaping modern learning experiences.
LMS (Learning Management System): Focuses on delivering and tracking training.
LXP (Learning Experience Platform): Personalizes learning with AI-driven recommendations.
LLP (Learning & Leadership Platform): Designed to build leadership and management skills.
What is SCORM, xAPI, cmi5, AICC?
Ans: These are eLearning standards that ensure courses and Learning Management Systems (LMS) work together seamlessly:
SCORM (Sharable Content Object Reference Model): The most widely used standard for packaging and tracking online courses.
xAPI (Experience API or Tin Can API): Tracks learning experiences both inside and outside the LMS (e.g., mobile learning, simulations, real-world activities).
cmi5: A modern specification that combines the tracking power of xAPI with the course structure of SCORM, designed for next-gen LMSs.
AICC (Aviation Industry CBT Committee): One of the earliest eLearning standards, mainly for course interoperability, though less common today.
This page was last edited on 21 December 2025, at 5:55 pm
Contact Us Now

Contact Us Now
Start a conversation with our team to solve complex challenges and move forward with confidence.










