Businesses today are racing to automate everything from data entry to decision-making. But simple automation isn’t enough anymore. Hyperautomation takes automation to the next level by combining AI, RPA, and intelligent workflows to create smarter, faster, and self-optimizing business processes.
It’s not just about saving time it’s about transforming how organizations operate, innovate, and grow in the digital era.
What is Hyperautomation?
Hyperautomation is the strategic and intelligent expansion of automation across an entire organization. It combines Robotic Process Automation (RPA), Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and other advanced technologies to automate complex, end-to-end business processes rather than just individual tasks.
In simpler terms, hyperautomation connects multiple automation tools and layers them with intelligence enabling systems to analyze, learn, and make decisions with minimal human input.
Unlike traditional automation, which typically focuses on repetitive rule-based tasks, hyperautomation builds an integrated ecosystem where bots, data, and AI models work together to streamline workflows, enhance accuracy, and continuously optimize operations.
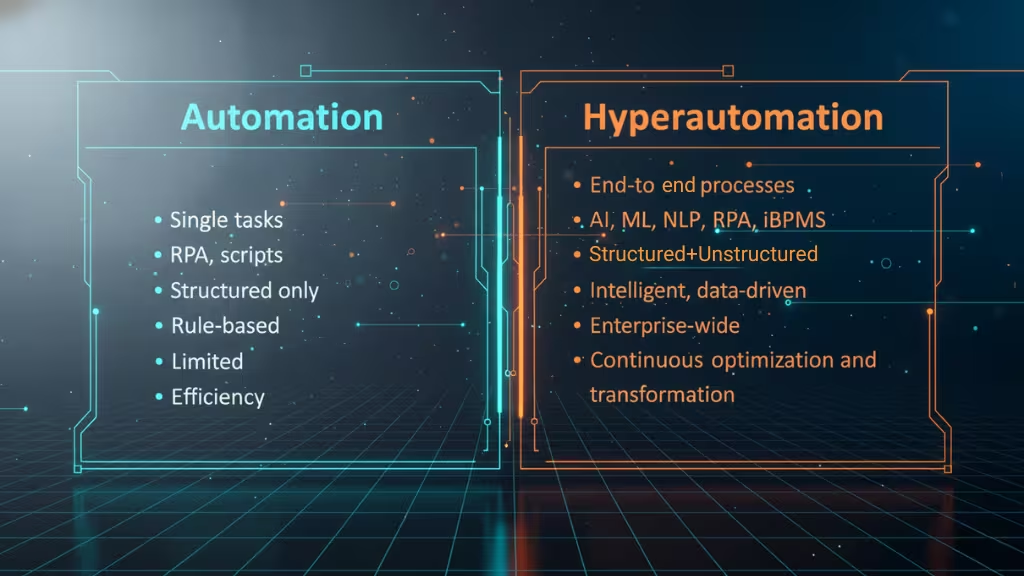
The Difference Between Automation and Hyperautomation
While both automation and hyperautomation aim to improve efficiency, they differ vastly in scope, intelligence, and business impact.
Traditional automation focuses on specific, repetitive tasks such as data entry or report generation using predefined rules. It’s effective for reducing manual work but limited when processes involve decision-making, multiple systems, or unstructured data.
Hyperautomation, on the other hand, goes beyond automating tasks it automates entire workflows and processes across departments. By integrating RPA with AI, ML, and process orchestration tools, hyperautomation allows systems to learn, adapt, and optimize in real time.
The Components of Hyperautomation
Hyperautomation works by bringing together a suite of advanced technologies that complement one another. Each component plays a unique role in transforming how work is done turning disconnected automation tools into a unified, intelligent system.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial Intelligence is the brain of hyperautomation. It enables systems to mimic human reasoning, analyze data, and make informed decisions. AI helps automation move beyond simple “if-then” rules to handle complex scenarios such as predicting customer needs, identifying anomalies, or generating personalized recommendations.
In a hyperautomation ecosystem, AI powers intelligent bots, enhances decision-making, and allows continuous process improvement through insights and predictions.
Machine Learning (ML)
Machine Learning is the learning engine behind hyperautomation. It allows systems to recognize patterns in data, learn from outcomes, and improve performance over time without explicit programming.
For instance, ML algorithms can analyze past transactions to predict delays in a supply chain or detect fraudulent financial activities automatically. As processes repeat, ML models refine their accuracy making automation smarter and more adaptive.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural Language Processing enables systems to understand and interact with human language both written and spoken. NLP allows hyperautomation platforms to process emails, chat messages, forms, and documents, extracting meaning and intent.
This capability powers AI chatbots, sentiment analysis tools, and automated customer service assistants that can interpret requests and respond conversationally.
Optical Character Recognition (OCR)
Optical Character Recognition transforms unstructured documents into machine-readable data. It scans invoices, forms, contracts, or handwritten notes, accurately extracting key information that can then feed into other automated workflows.
When OCR is combined with AI and NLP, the system not only reads text it also understands context, classifies information, and initiates actions (like processing an invoice or updating a CRM).
Steps and Components in Navigating the Hyperautomation Journey
Implementing hyperautomation is not just about deploying technology, it’s about transforming how your organization operates. The journey follows a structured path that combines strategic planning, process discovery, and technology integration to build an intelligent, scalable automation ecosystem.

Here’s a breakdown of the essential steps and components:
Identify and Analyze Processes
Start by identifying which business processes are most repetitive, time-consuming, or error-prone. Tools like process mining and task mining help visualize real workflows, detect inefficiencies, and uncover hidden automation opportunities.
Select the Right Technologies
Each process may require different automation tools. Combine RPA for repetitive tasks, AI/ML for cognitive decisions, and integration platforms (like iPaaS) to connect systems and data across departments.
Design and Orchestrate Intelligent Workflows
Once technologies are chosen, create end-to-end workflows that integrate humans and machines. Use intelligent business process management systems (iBPMS) to orchestrate these workflows, ensuring seamless collaboration between bots, systems, and people.
Implement and Scale
Begin with pilot projects to prove value quickly, gather insights, and refine the model. Then scale across departments with a Center of Excellence (CoE) to manage standards, governance, and best practices.
Monitor, Optimize, and Evolve
Continuous monitoring ensures that automated processes remain efficient and accurate. Use analytics and feedback loops to measure performance, track ROI, and fine-tune workflows as business needs evolve.
Empower Employees
Successful hyperautomation involves people, not just technology. Empower teams with low-code/no-code tools so they can build simple automations themselves, helping to democratize innovation across the organization.
The Benefits of Hyperautomation
Hyperautomation delivers far more than process efficiency it reshapes how organizations work, scale, and compete. Connecting systems and intelligence across operations, it creates smarter workflows, improves accuracy, and frees teams to focus on higher-value innovation.
Here are the most impactful benefits:
Reducing Operational Obstacles
Manual, repetitive tasks often slow down productivity and introduce human error. Hyperautomation eliminates these bottlenecks by streamlining workflows from start to finish.
For example, an automated order-processing system can verify payments, generate invoices, and update records across multiple platforms all without human intervention. The result: fewer delays, lower error rates, and faster turnaround times.
Transforming Live Agents to Digital Workers
One of the most transformative impacts of hyperautomation is the rise of digital workers software bots and AI agents that perform structured, rule-based tasks traditionally handled by people.
These digital workers operate 24/7, never tire, and maintain consistent accuracy. They free up human employees to focus on creative, strategic, or customer-facing tasks enhancing both productivity and employee satisfaction.
Accelerating Compound Tasks
Some business activities involve multiple systems and data types like onboarding a new customer or processing an insurance claim. Hyperautomation connects these tasks through intelligent orchestration, enabling end-to-end execution without manual switching between platforms.
By linking AI, RPA, and integration tools, companies can complete complex workflows in minutes instead of hours or days, improving overall speed and customer experience.
Increasing Business Agility
In a rapidly changing market, agility is everything. Hyperautomation allows organizations to adapt quickly by continuously monitoring performance, learning from outcomes, and updating workflows automatically.
This dynamic adaptability means businesses can respond to new opportunities or challenges such as sudden demand spikes or regulation changes with minimal disruption.
Challenges of Hyperautomation
While hyperautomation offers enormous potential, implementing it across an enterprise comes with real challenges. Success depends on how well an organization manages its technology integration, data quality, workforce transition, and governance.
Here are the main obstacles businesses often face:
1. Technical Complexity
Hyperautomation involves integrating multiple technologies AI, RPA, ML, and iPaaS across legacy systems that were never designed to work together. Without careful architectural planning, these integrations can create data silos, inconsistent workflows, or maintenance bottlenecks.
Solution:
Adopt a scalable architecture with open APIs and modular design. Start small, standardize integrations, and expand gradually with clear governance and documentation.
2. High Initial Investment
Building a hyperautomation ecosystem requires upfront investment in software licenses, infrastructure, training, and change management. Smaller organizations may find this barrier daunting.
Solution:
Focus on high-ROI use cases first processes that deliver measurable impact quickly. Once these pilots prove value, reinvest the savings into broader automation initiatives.
3. Data Quality and Availability
Automation is only as good as the data it relies on. Inconsistent, incomplete, or outdated data can cause automation failures and poor decision-making.
Solution:
Implement strong data governance frameworks, ensure data cleansing routines, and use AI tools to detect anomalies and maintain data integrity continuously.
4. Change Resistance and Workforce Concerns
Employees may fear job loss or struggle to adapt to automated systems. Without clear communication and reskilling, even the best technology can face internal resistance.
Solution:
Position hyperautomation as an augmentation strategy, not ra eplacement. Provide upskilling programs and highlight how automation removes repetitive work allowing employees to focus on strategic and creative tasks.
5. Security and Compliance Risks
As automation expands, so does the attack surface. Bots, APIs, and AI models can become potential security risks if not properly managed.
Solution:
Implement Identity and Access Management (IAM), encrypt sensitive data, and ensure every automation has built-in auditability and compliance checks. Continuous monitoring and strong governance are key to maintaining trust and safety.
Hyperautomation Use Cases
Hyperautomation isn’t limited to one industry it’s reshaping operations across sectors by combining AI-driven insights, automation, and human collaboration. Let’s look at how it transforms four major industries:
Hyperautomation in Healthcare
In healthcare, hyperautomation enhances patient care while improving efficiency and compliance.
- Administrative automation: RPA bots process patient intake forms, verify insurance details, and update electronic health records (EHRs) automatically.
- Claims management: AI-powered systems analyze claims, detect discrepancies, and process approvals, reducing human error and speeding up reimbursements.
- Predictive insights: Machine learning models identify patient risk factors and optimize appointment scheduling or treatment plans.
Example: A hospital network using AI-driven hyperautomation reduced billing errors by 50% and improved patient throughput by 25%, freeing clinical staff to focus on care delivery.
Hyperautomation in Supply Chain
Supply chains benefit immensely from automation that connects planning, logistics, and analytics.
- Demand forecasting: AI predicts product demand using historical sales, seasonality, and external data.
- Inventory management: Automated workflows adjust stock levels and trigger reorders before shortages occur.
- Order fulfillment: Integrated RPA and IoT systems track shipments in real time, reducing delays and improving visibility.
- Supplier collaboration: Intelligent systems automate purchase orders, invoicing, and performance analysis.
Example: A global logistics company achieved a 30% reduction in inventory costs and a 25% improvement in delivery times after implementing hyperautomation.
Hyperautomation in Banking and Finance
Financial institutions use hyperautomation to enhance accuracy, security, and customer experience.
- Loan processing: RPA and OCR automatically extract and validate customer data, reducing approval times from days to hours.
- Fraud detection: AI continuously monitors transactions to flag anomalies in real time.
- Regulatory compliance: Automated workflows ensure accurate reporting and maintain audit trails.
- Customer onboarding: NLP and document automation speed up KYC verification and reduce manual checks.
Example: A major bank deployed an AI-RPA solution to automate loan processing, cutting turnaround time by 70% and improving customer satisfaction significantly.
Hyperautomation in Retail
In retail, hyperautomation helps companies keep pace with rapidly changing customer behavior.
- Inventory and pricing: AI analyzes market trends and automates dynamic pricing strategies.
- Customer engagement: NLP chatbots manage support tickets and assist with personalized recommendations.
- Supply chain automation: End-to-end automation links suppliers, warehouses, and stores for real-time coordination.
- Marketing optimization: Machine learning automates campaign targeting and customer segmentation.
Example: A large e-commerce brand used hyperautomation to streamline its returns and refund process, cutting resolution time by 60% and boosting customer satisfaction scores.
Conclusion
Hyperautomation marks the next major leap in digital transformation. It goes beyond simply automating repetitive tasks combining AI, RPA, and intelligent workflows to build systems that can think, learn, and optimize continuously.
By connecting every layer of a business data, systems, and people hyperautomation enables organizations to operate with greater speed, precision, and agility. It reduces costs, improves accuracy, and allows teams to focus on innovation rather than administration.
In short, hyperautomation isn’t just a trend it’s becoming a strategic necessity for organizations that want to stay competitive in a rapidly evolving digital economy.
FAQs
What is the main goal of hyperautomation?
The goal of hyperautomation is to automate as many business processes as possible using a combination of advanced technologies like AI, RPA, and machine learning. It aims to improve efficiency, reduce human error, and create smarter workflows that can adapt and learn over time.
How is hyperautomation different from traditional automation?
Traditional automation focuses on single, rule-based tasks like data entry or form filling. Hyperautomation, however, connects multiple tools and technologies to automate entire end-to-end processes, allowing systems to analyze, make decisions, and continuously optimize themselves.
Which technologies drive hyperautomation?
The core technologies include Artificial Intelligence (AI), Robotic Process Automation (RPA), Machine Learning (ML), Natural Language Processing (NLP), and Optical Character Recognition (OCR). These work together with process mining, analytics, and low-code platforms to create intelligent, connected workflows.
What are the biggest benefits of hyperautomation?
a. Faster, more efficient operations
b. Reduced manual errors and costs
c. Better compliance and data accuracy
d. Enhanced employee productivity
e. Greater business agility and adaptability
What challenges do companies face when implementing hyperautomation?
Common challenges include technical complexity, high initial costs, poor data quality, employee resistance to change, and security concerns. Overcoming these requires strong governance, clear ROI goals, and proper training and communication.
Is hyperautomation suitable for small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs)?
Yes. Thanks to cloud-based platforms and low-code tools, SMBs can start small automating specific workflows and gradually scale up. The key is to focus on high-impact processes that deliver measurable value quickly.
What industries benefit most from hyperautomation?
Nearly every industry can benefit, but the leading adopters include healthcare, banking and finance, manufacturing, supply chain, and retail, where data-intensive and repetitive workflows dominate.
What’s the future of hyperautomation?
The future lies in AI-driven, self-learning systems that operate autonomously across the enterprise. As technologies like large language models (LLMs) and agentic AI mature, hyperautomation will enable businesses to achieve near real-time adaptability and intelligent decision-making at scale.
This page was last edited on 5 November 2025, at 4:27 pm
Contact Us Now

Contact Us Now
Start a conversation with our team to solve complex challenges and move forward with confidence.










