- Introduction to HTML5 Web Development
- Benefits of HTML5 Web Development
- New and Removed Features in HTML5
- Core Concepts of HTML5
- HTML5 Advantages and Disadvantages
- Advanced HTML5 Elements and APIs
- HTML5 and Front-End Technologies
- HTML5 for Mobile Applications
- HTML5 Game Development
- HTML5 for Modern Web Applications
- HTML5 Web Development Process
- Tips for Writing Clean and Organized HTML5 Code
- HTML5 Performance Optimization
- HTML5 in Specialized Applications
- HTML5 for Business and Strategy
- Security, Privacy, and Compliance in HTML5
- Cutting-Edge Technologies and HTML5
- Tools and Best Practices in HTML5 Development
- HTML5 Web Development Books
- Enhancing User Experience with HTML5
- Future of HTML5 Web Development
- Common HTML5 Development Challenges and Solutions
- Conclusion
- FAQs on HTML Web Development
HTML has significantly evolved the way we structure and deliver web experiences. The modern HTML standard, commonly referred to as HTML5, introduces a range of new features and capabilities that enhance web development efficiency, scalability, and accessibility.
HTML is now maintained as a living standard by WHATWG and is commonly referred to as HTML5 in practice, even though it no longer follows versioned releases. Today, HTML works alongside CSS, JavaScript, and frameworks like React, Angular, and Vue to power modern web applications.
With HTML5, the modern web is more visually engaging, mobile-responsive, and capable of supporting complex applications like games and progressive web apps when combined with JavaScript and modern web APIs. Its ability to seamlessly integrate multimedia elements (without relying on third-party plugins like Flash) has set a new standard in web design and development. Moreover, it has improved how developers structure content for accessibility, performance, and search engine understanding.
This guide will explore every aspect of HTML5 web development, from the core concepts to advanced APIs, helping businesses understand its value and empowering developers to build faster, more powerful, and user-friendly websites. By the end, you’ll not only know why modern HTML remains a critical foundation of the web, but you’ll also have the knowledge to use it effectively for your projects.
Whether you’re a newcomer or an experienced developer, this comprehensive guide will walk you through the benefits, tools, and strategies essential to mastering HTML5 in today’s digital landscape. So, let’s dive in and discover the full potential of HTML5 web development!
Explore More Web Development Guides:
1. Introduction to HTML5 Web Development

This section gives an introduction to HTML and explores how HTML5 revolutionizes the way websites and web applications are built.
In the ever-evolving landscape of the internet, HTML is a foundational pillar of modern web development for building modern websites and applications. The modern HTML standard, commonly referred to as HTML5, brings a suite of powerful features that enhance the functionality, accessibility, and interactivity of web content.
HTML5 HTML remains essential for developers and businesses alike due to its ability to support responsive, mobile-friendly websites when combined with modern CSS techniques that do not compromise on quality or performance. HTML works alongside CSS and JavaScript, allowing for the development of rich user experiences that engage visitors and keep them coming back.
Today, HTML is typically used within modern frameworks and Progressive Web App architectures rather than in isolation.
The significance of HTML5 extends beyond mere aesthetics. With its support for multimedia elements such as audio and video, developers can create immersive web experiences without relying on deprecated plugin-based technologies. This shift not only streamlines development but also improves site performance and compatibility across different browsers and devices.
What is HTML5?
HTML is maintained as a living standard and is commonly referred to as HTML5 in practice, the standard language used for creating and structuring content on the web. It was designed to provide a richer set of semantic elements and APIs that work alongside JavaScript and CSS, allowing for the creation of more dynamic and interactive websites. HTML5 incorporates a variety of features that improve multimedia integration, support mobile-friendly layouts when combined with responsive CSS techniques, and enhance user experience, making it a foundational component of modern web development.
Key Features of HTML5:
- Semantics: Modern HTML includes <header>, <footer>, <article>, and <section>, which help define the structure of web pages. This enhances accessibility and SEO by providing clear context to search engines about the content of a page. In practice, semantic HTML is often combined with ARIA roles and attributes to meet modern accessibility standards.
- Multimedia Support: Modern HTML includes native audio and video playback without the need for external plugins like Flash. The <audio> and <video> tags enable developers to easily embed multimedia content, which is crucial for modern web applications.
- APIs and Features: The modern web platform includes APIs such as Canvas, Geolocation, and Web Storage, which work alongside HTML. These features empower developers to build rich, interactive web applications.
- Mobile-First Design: HTML provides a device-agnostic structure that supports mobile-first design strategies, making it an essential tool for responsive web design. This aligns with the growing trend of mobile browsing, as it enables developers to create websites that look and function well on various screen sizes.
- Cross-Browser Compatibility: HTML5 is supported by all major web browsers, with broad support across modern browsers, though individual features may vary. This reliability is crucial for businesses that want to reach a broad audience.
In practice, HTML is most often used within modern frameworks and Progressive Web App architectures rather than on its own.
Key Takeaways
Modern HTML (commonly called HTML5) provides semantic structure and native multimedia support, forming the foundation of responsive and interactive web experiences when combined with CSS and JavaScript.
HTML5 Logo
The HTML5 logo is a crucial element of the HTML5 brand, representing its identity and the advancements it brings to web development. This section explores the significance, design, and usage of the HTML5 logo.
1. Design and Elements of the HTML5 Logo
- The HTML5 logo features a bold, orange shield shape with a white outline. Inside the shield, the number “5” is prominently displayed in white, representing the fifth major version of HTML. This minimalist yet striking design effectively communicates the modernity and robustness of HTML5.
- The choice of orange is intentional, symbolizing energy and innovation. This color scheme sets HTML5 apart from previous versions and conveys a sense of progress in web development.
2. Symbolism and Significance
- The logo embodies the transition from older versions of HTML to HTML5, emphasizing the evolution of web standards and the introduction of new features that enhance user experience and interactivity.
- By using a recognizable shield shape, the logo conveys a sense of protection and reliability, assuring developers and users that HTML5 is a stable and secure platform for building modern web applications.
3. Usage Guidelines
- The HTML5 logo is widely used by developers, organizations, and educational institutions to signify their commitment to modern web standards. It can be found on websites, promotional materials, and educational resources.
- To maintain brand integrity, it’s essential to follow the official guidelines provided by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) regarding the logo’s usage. This includes maintaining proper sizing, colors, and placement in relation to other branding elements.
4. HTML5 Logo in the Community
- The logo has become a symbol of the HTML5 community, representing collaboration and innovation among developers, designers, and tech enthusiasts. It appears at various web development conferences, workshops, and online forums, fostering a sense of belonging and shared purpose.
- Many educational resources and courses highlight the HTML5 logo to indicate that they cover modern web development practices, making it easier for learners to identify relevant content.
History and Evolution of HTML5
The evolution of HTML5 can be traced back to the inception of HTML itself, which was first introduced in 1993. HTML has undergone several revisions since then, but the transition to HTML5 marked a significant paradigm shift in how web content is structured and delivered. Here’s a detailed look at the history and evolution of HTML5:
Early Development (1990s)
- HTML 1.0 (1993): The first official version of HTML was released, providing basic markup for structuring text documents.
- HTML 2.0 (1995): This version included support for standardized forms and basic document structure.
The Rise of HTML4 (1997)
- HTML 4.0: Released in 1997, this version introduced significant improvements, including better support for multimedia, improved accessibility, and better integration with scripting via the DOM. It set the standard for web development for nearly a decade.
The Need for Change
By the early 2000s, the rapid evolution of the web and user expectations highlighted the limitations of HTML4. The emergence of rich internet applications, mobile browsing, and the need for enhanced multimedia support demanded richer semantics and better support for web applications.
The Birth of HTML5
- 2004 – WHATWG: The Web Hypertext Application Technology Working Group (WHATWG) was formed to develop a new standard for web applications. WHATWG began developing HTML as a living standard focused on web applications, which aimed to address the shortcomings of HTML4 and provide features that met the needs of modern web development.
- 2008 – W3C and HTML5: Today, WHATWG maintains the HTML Living Standard, while W3C publishes snapshot recommendations. This collaboration led to the merging of various specifications, resulting in a more comprehensive framework.
HTML5 Becomes a Standard
- 2014 – Recommendation: After years of development and testing, this recommendation represented a snapshot in an ongoing, continuously evolving standard. This landmark achievement validated the efforts of developers and organizations that contributed to the evolution of web standards.
Core Features of HTML5
HTML5 brought numerous advancements, including:
- New Semantic Elements: Elements like <header>, <footer>, <article>, and <section> improved the semantic structure of web documents.
- Native Multimedia Support: The introduction of <audio> and <video> elements allowed for easier integration of multimedia without relying on plugins.
- APIs for Enhanced Functionality: HTML5 introduced APIs such as the Geolocation API, Web Storage API, and Canvas API, empowering developers to create more interactive and dynamic web applications.
Today, HTML5 continues to evolve as new specifications are developed and implemented. HTML continues to evolve through the WHATWG Living Standard and is adaptable to the ever-changing landscape of web technology.
Key Takeaways
HTML has evolved continuously to address modern web demands and is maintained today as a living standard by WHATWG. Commonly referred to as HTML5, it provides semantic structure and native multimedia capabilities that support richer, more interactive web experiences when combined with CSS, JavaScript, and modern web APIs.
Why Businesses Should Invest in HTML5 Web Development
In today’s digital landscape, investing in HTML5 web development is crucial for businesses looking to enhance their online presence and meet the evolving needs of their customers. With the rise of mobile browsing and the increasing demand for interactive and engaging web experiences, HTML5 offers numerous advantages that can significantly benefit businesses. Here are several key reasons why companies should consider embracing HTML5:
1. Enhanced User Experience
HTML5 provides the structural foundation for developers to create more dynamic and interactive websites, which can lead to a superior user experience. The integration of multimedia elements, animations, and responsive designs allows businesses to engage users more effectively. Research indicates that enhanced user experience can improve customer satisfaction and increase conversion rates.
2. Cross-Platform Compatibility
One of the standout features of HTML5 is its cross-platform compatibility. Websites developed using HTML5 function seamlessly across various devices, including desktops, tablets, and smartphones. This is particularly important in a mobile-first world, where the majority of users access the web via mobile devices. By adopting HTML5, businesses can ensure that their websites are accessible to a broader audience.
3. Cost-Effective Development
Investing in HTML5 web development can lead to cost savings in the long run. With its built-in features for multimedia and rich user interactions, businesses can reduce reliance on proprietary or deprecated technologies and additional software, which often incur extra costs. Moreover, the development process is generally faster with HTML5, allowing businesses to launch their websites or applications more quickly.
4. Improved Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
HTML5 provides a cleaner and more semantic structure compared to previous versions of HTML. Semantic HTML improves content structure and accessibility, which can indirectly support search engine understanding, making it easier for search engines to crawl and index content effectively. Improved SEO can lead to higher rankings in search results, driving more organic traffic to a business’s website.
5. Future-Proofing Your Business
As web technologies continue to evolve, HTML5 remains relevant due to its ongoing updates and enhancements. Investing in HTML5 web development ensures that businesses are equipped to adapt to future trends and technological advancements. This future-proofing is critical for maintaining a competitive edge in a rapidly changing market.
6. Supporting Multimedia and Interactive Content
With the ability to easily integrate audio, video, and interactive graphics, HTML5 allows businesses to create engaging content that captures users’ attention. This capability is particularly beneficial for industries such as e-learning, entertainment, and marketing, where rich media plays a vital role in user engagement.
In summary, the investment in HTML5 web application development presents numerous advantages for businesses. From enhancing user experience and improving SEO to ensuring cross-platform compatibility and reducing development costs, HTML5 is a powerful tool that can help businesses thrive in the digital age. As companies look to strengthen their online presence, adopting HTML5 should be a strategic priority.
Key Takeaways
Investing in HTML5 web development enhances user experience, improves cross-platform compatibility, and increases engagement. It allows businesses to leverage advanced features, boost SEO, and stay competitive in the digital landscape.
HTML5 is the Future of the World Wide Web
As technology continues to advance at a rapid pace, HTML5 emerges as a pivotal component in shaping the future of the web. This latest version of the Hypertext Markup Language not only improves upon its predecessors but also introduces capabilities that align with modern user expectations and technological advancements. Here’s a closer look at why HTML5 is seen as the future of the World Wide Web:
1. Rich Media Support
HTML5 supports seamless integration of audio, video, and interactive graphics without relying on third-party plugins like Flash. This native support for multimedia is crucial as user engagement increasingly hinges on rich content. Businesses can deliver dynamic experiences that capture attention and encourage interaction, vital for industries such as gaming, e-learning, and digital marketing.
2. Improved Mobile Compatibility
With the rise of mobile browsing, HTML5’s ability to support responsive design ensures that websites function smoothly across various devices and screen sizes. This mobile-first approach is essential for reaching a broader audience, as more users access the web from smartphones and tablets. HTML5’s features are optimized for touch interfaces, which enhances user experience on mobile devices.
3. Enhanced Web Applications
HTML5 provides a robust framework for developing web applications that are fast, reliable, and capable of working offline. By utilizing technologies like the Application Cache, Local Storage, and Service Workers, developers can create Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) that offer app-like experiences directly in the browser. This trend is transforming how users interact with applications, making web apps more appealing and functional.
4. Stronger Community and Ecosystem
The widespread adoption of HTML5 is supported by a vibrant community of developers and ongoing contributions from organizations such as W3C and WHATWG. This collaborative environment fosters continuous improvement and innovation, ensuring that HTML5 remains relevant and equipped to meet future web development challenges.
5. Future-Proofing Web Development
As web standards evolve, HTML5 provides a forward-looking foundation for developers. Its modular architecture allows for the gradual integration of new features without breaking existing functionality. This adaptability ensures that businesses can easily implement updates and enhancements, keeping pace with technological advancements.
In summary, HTML5 is not just a technology of the present; it is a cornerstone for the future of the World Wide Web. With its rich media capabilities, improved mobile compatibility, and support for modern web applications, HTML5 positions itself as an indispensable tool for developers and businesses alike. As the web continues to evolve, investing in HTML5 web development is essential for staying competitive and meeting user expectations.
Key Takeaways
HTML5 is crucial for the future of the web, enabling responsive design, multimedia integration, and advanced APIs. Its widespread adoption ensures a richer, more interactive online experience for users.
HTML5 vs. Previous Versions: What’s Changed?
HTML5 represents an evolution of HTML standards, introducing changes that improved structure, media handling, and application support. Understanding these changes is crucial for developers, businesses, and users alike. Here’s a detailed comparison highlighting what has changed with HTML5 compared to previous versions of HTML:
1. Semantic Elements
One of the most notable changes in HTML5 is the introduction of semantic elements. Previous versions of HTML primarily relied on generic tags like <div> and <span>, which did not convey any meaning about the enclosed content. HTML5 includes semantic elements such as:
- <header>: Defines the header section of a document or a section.
- <footer>: Represents the footer for a document or section.
- <article>: Encapsulates a self-contained composition that could be distributed independently.
- <section>: Groups related content together, enhancing the document’s structure.
Modern HTML also commonly uses elements like <main>, <nav>, and <aside> to define page landmarks and improve accessibility.
These semantic tags improve the readability of the code and make it easier for search engines and assistive technologies to understand the content’s structure, thus improving accessibility and helping search engines better understand content structure.
2. Multimedia Support
HTML5 standardized native multimedia handling on the web. Earlier approaches required non-standard technologies, whereas modern browsers now handle multimedia natively. HTML5 provides built-in support for:
- <audio>: For embedding sound content.
- <video>: For integrating video files directly into web pages.
This change simplifies the integration of rich media and enhances the user experience, as users no longer need to install additional plugins.
3. New Input Types for Forms
HTML5 introduces new input types for forms, making it easier to create user-friendly forms with better validation. For example:
- type=”email”: Automatically validates email addresses.
- type=”date”: Provides a date picker interface.
- type=”range”: Allows users to select a value from a specified range using a slider.
These new input types enhance the usability of web forms and assist with basic validation and formatting, often supplemented by JavaScript in real-world applications.
4. APIs and Advanced Features
The modern web platform includes APIs that work alongside HTML5, which facilitate more complex functionalities without relying on legacy plugin-based solutions. Key APIs include:
- Canvas API: Enables dynamic, scriptable rendering of 2D shapes and bitmap images.
- Geolocation API: Provides the ability to retrieve the geographical location of the user.
- Web Storage API: Offers a way to store data locally within the user’s browser, which can persist even when the browser is closed.
In addition to these APIs, modern web applications commonly rely on technologies such as Service Workers, IndexedDB, and the Cache API to enable offline functionality, performance optimization, and advanced data storage.
These features significantly enhance the interactivity and capabilities of web applications, making them more capable and reliable across modern browsers.
5. Improved Parsing and Error Handling
HTML5 standardized parsing rules and error handling behavior across browsers, making it easier for browsers to interpret HTML documents. Unlike previous versions, which often rendered documents unpredictably when encountering errors, HTML5 provides a more consistent and forgiving parsing model. This means that web pages are more likely to display correctly across different browsers, improving user experience and developer efficiency.
In conclusion, HTML5 standardized several advancements that improved structure, media handling, and application support. These changes not only improve the developer experience but also contribute to a more engaging and accessible web for users. Understanding these differences is essential for anyone involved in web development today.
Key Takeaways
HTML5 standardized improvements, such as native multimedia support and semantic elements, while working alongside modern web APIs. These changes help improve accessibility, consistency across browsers, and overall user experience on the web.
H5 Development
H5 development has become a powerful trend in China’s digital landscape, offering mobile-first solutions that emphasize fast, lightweight web applications. In China, H5 development focuses primarily on mobile interactions through popular platforms such as WeChat, making it a key tool for businesses looking to engage users via dynamic, interactive experiences.
Why is H5 Development Popular in China?
H5’s popularity in China stems from the country’s mobile-first digital culture. With platforms like WeChat dominating the mobile ecosystem, H5 offers businesses a convenient way to engage their audience through interactive campaigns. Here are a few reasons behind its widespread adoption:
- WeChat Mini-Programs: WeChat, China’s largest social platform, allows users to run ‘mini-programs’ that are built using WeChat’s own framework, while H5 pages are often embedded or linked within the WeChat ecosystem.
- Interactive Marketing Campaigns: H5 pages are heavily used for interactive and gamified marketing campaigns, allowing brands to reach millions of mobile users quickly.
- Low Development Cost: Unlike native apps that require specialized development for Android and iOS, H5 apps can run across multiple platforms, often reducing development time compared to building separate native applications.
- Seamless Integration: H5 apps can integrate with platforms such as Weibo, Douyin, and e-commerce systems, although integration often depends on platform-specific APIs and approval processes.
H5 Development vs. Native Mobile App Development
A critical decision for businesses is whether to invest in H5 development or build native mobile apps. For example, Kotlin app development is a popular way to develop native Android apps. Here’s a quick comparison:
- Development Speed and Cost: H5 is faster and cheaper to develop, but may lack the performance of native apps, which are better for resource-heavy tasks like gaming or data processing.
- User Experience: Native apps provide a smoother, more robust experience, especially offline, but H5 offers quick updates and cross-platform compatibility.
Usage Scenarios: H5 is ideal for short-term campaigns, mobile marketing, and quick-to-market apps, while native apps are better suited for long-term engagement and complex functionalities. In China, WeChat Mini-Programs are often considered a third option alongside H5 pages and native mobile apps, offering deeper platform integration than H5 but less flexibility than fully native apps.
Which Browsers Support HTML5?
HTML5 has been designed to be compatible with a wide array of web browsers, ensuring a seamless user experience across different platforms and devices. Understanding browser support is essential for developers to leverage HTML5 features effectively. Here’s an overview of the major browsers that support HTML5:
1. Major Browser Support
- Google Chrome: As one of the first browsers to embrace HTML5, Chrome supports the majority of HTML5 features, including the <video> and <audio> tags, the Canvas API, and numerous other elements and attributes. Chrome frequently updates, ensuring users have access to the latest HTML5 enhancements.
- Mozilla Firefox: Firefox has strong support for HTML5 and is known for quickly implementing new standards. It fully supports semantic elements, multimedia features, and many HTML5 APIs, making it a preferred choice for web developers.
- Apple Safari: Safari also provides robust support for HTML5, especially on iOS devices. It has implemented essential features like the Web Storage API, the Geolocation API, and multimedia elements, allowing for smooth playback of video and audio content.
- Microsoft Edge: The newer iterations of Edge, built on the Chromium engine, offer extensive support for HTML5. Edge has adopted many features present in Chrome, providing a modern browsing experience with comprehensive HTML5 compatibility.
- Opera: Opera supports HTML5 features similar to those in Chrome, thanks to its Chromium-based architecture. It includes support for audio, video, and various APIs, allowing developers to create engaging web applications.
2. Mobile Browsers
Mobile browsers have also embraced HTML5, ensuring that users can enjoy rich web experiences on their smartphones and tablets:
- Mobile Safari (iOS): As the default browser on Apple devices, Mobile Safari provides excellent HTML5 support, including features like the <video> tag and various APIs, contributing to a smooth mobile browsing experience.
- Chrome for Mobile: This browser mirrors its desktop counterpart in terms of HTML5 support, offering users access to the same features and functionalities.
- Firefox for Mobile: Similar to its desktop version, Firefox for mobile supports a wide range of HTML5 features, ensuring users can access modern web applications on their mobile devices.
3. Checking Compatibility
To check the compatibility of specific HTML5 features across different browsers, developers can utilize resources like:
- Can I Use: A website that provides up-to-date compatibility tables for HTML5 features across different browsers.
- MDN Web Docs: The Mozilla Developer Network offers detailed documentation and compatibility tables for various HTML5 elements and APIs.
In summary, HTML5 is supported by all major web browsers, making it a viable option for developers looking to create modern, interactive websites. As browsers continue to evolve and update, HTML5 remains an integral part of the web development landscape.
Key Takeaways
HTML5 is widely supported by all major browsers, including Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge. Regular updates ensure compatibility, enabling developers to create consistent experiences across various platforms and devices.
Interesting Facts About HTML5
HTML5 is not just a standard; it’s a major milestone in the evolution of web development. Here are some intriguing facts that highlight its significance and capabilities:
1. Origin and Development
- Introduction: HTML5 was officially released in October 2014, but its development began much earlier, with discussions starting around 2004. It was a response to the growing demands for multimedia content and the need for a more robust markup language.
- W3C and WHATWG: The development of HTML5 was a collaborative effort between the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) and the Web Hypertext Application Technology Working Group (WHATWG). This dual approach ensured that both standards and practical implementations evolved together.
2. Emphasis on Semantics
Semantic Markup: One of the core principles of HTML5 is the focus on semantic markup, which improves accessibility and SEO. By using semantic tags like <article>, <section>, and <aside>, developers can create a more meaningful structure that is easier for search engines and assistive technologies to interpret.
3. Multimedia without Plugins
Built-in Support for Multimedia: HTML5 has made it possible to embed audio and video directly into web pages using <audio> and <video> tags, eliminating the need for plugins like Flash. This shift has made websites more secure and user-friendly.
4. Offline Capabilities
Offline Access: HTML5 introduced features such as the Application Cache and Web Storage, allowing web applications to function offline. This was a game-changer for users with unreliable internet connections and has led to the rise of Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) that provide app-like experiences.
5. Global Adoption
Widely Supported: HTML5 is supported by all major browsers, including Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge, and Opera. This broad compatibility has made it a standard choice for web developers worldwide, promoting a consistent experience across platforms.
6. Focus on Performance
Performance Improvements: HTML5 introduces features that optimize page loading times and improve overall performance, such as lazy loading and the use of SVG for scalable graphics. This has a direct impact on user experience and SEO rankings.
7. Community and Resources
Vibrant Community: The HTML5 community is vibrant, with numerous resources, forums, and tutorials available for developers. Websites like MDN Web Docs and W3Schools provide extensive documentation, making it easier for newcomers to learn and adopt HTML5.
HTML5 has revolutionized the web development landscape with its emphasis on semantic markup, multimedia support, and offline capabilities. Its widespread adoption and continuous evolution make it an essential tool for developers aiming to create modern, interactive web applications. These interesting facts highlight not only the capabilities of HTML5 but also its role as a foundational element in the future of web technology.
Key Takeaways
HTML5 has transformed web development with features like native audio/video support, semantic elements, and offline capabilities. It promotes mobile-friendly design and is continually evolving to meet modern web standards.
2. Benefits of HTML5 Web Development

This section explores the benefits of HTML5 Web Development. These benefits extend to both businesses and developers, making it a go-to solution for modern web experiences.
HTML5 has fundamentally transformed the web development landscape, providing numerous benefits that enhance user experience, streamline development processes, and optimize performance. Here, we explore some of the key advantages of utilizing HTML5 for web development:
Benefits of HTML5 Web Development for Businesses
Investing in HTML5 web development offers numerous advantages for businesses looking to enhance their online presence and engage with their target audience effectively. Here are some key benefits that highlight why businesses should prioritize HTML5 in their web development strategies:
1. Cost-Effective Development
- Reduced Development Time: HTML5 simplifies the development process with its built-in features and semantic elements, allowing developers to create applications more quickly. This efficiency translates into lower costs for businesses, as projects can be completed faster and with fewer resources.
- Single Codebase for Multiple Platforms: With HTML5, developers can create a single codebase that works across various devices and platforms, reducing the need for separate versions for desktop and mobile. This cross-platform compatibility further cuts down on development and maintenance costs.
2. Enhanced User Engagement
- Rich Multimedia Experiences: HTML5 allows businesses to integrate rich media content directly into their websites, such as video and audio, without relying on external plugins. This capability not only enhances user engagement but also keeps visitors on the site longer, improving conversion rates.
- Interactive Features: The use of HTML5 APIs enables businesses to create interactive features, such as geolocation services, drag-and-drop functionalities, and offline capabilities. These interactive elements can significantly enhance the user experience and increase customer satisfaction.
3. Improved SEO and Visibility
- Semantic Markup: HTML5’s focus on semantic elements helps search engines understand the content and structure of a website better. This improved indexing can lead to higher search engine rankings, increasing visibility and attracting more traffic to business websites.
- Faster Load Times: Websites built with HTML5 typically load faster due to efficient multimedia handling and local storage capabilities. Fast-loading websites are favored by search engines and provide a better user experience, contributing to improved SEO rankings.
4. Future-Proof Technology
- Adaptability to Emerging Trends: As web technologies continue to evolve, HTML5 remains relevant and adaptable. Its ongoing development and support from major browsers ensure that businesses can implement new features and keep their websites up to date without significant overhauls.
- Integration with Modern Technologies: HTML5 easily integrates with modern technologies like CSS3 and JavaScript frameworks, allowing businesses to leverage the latest advancements in web development. This compatibility enables the creation of more dynamic and feature-rich web applications.
5. Strengthened Branding and Marketing
- Customizable User Interfaces: HTML5 enables businesses to design custom user interfaces that align with their brand identity. A well-designed website that reflects a company’s branding can enhance customer trust and loyalty.
- Engagement Analytics: HTML5 also supports web analytics tools that help businesses track user engagement and behavior. By understanding how users interact with their site, companies can make informed decisions to improve marketing strategies and enhance user experience.
In summary, HTML5 web development offers businesses a multitude of benefits, from cost-effectiveness and enhanced user engagement to improved SEO and adaptability to future technologies. By investing in HTML5, businesses can create dynamic, user-friendly websites that not only attract visitors but also drive conversions and strengthen their online presence.
Key Takeaways
HTML5 web development offers businesses enhanced user engagement, improved SEO, and cross-platform compatibility. Its rich features allow for faster development cycles and a more dynamic online presence, driving growth and customer satisfaction.
Benefits of HTML5 Web Development for Developers
HTML5 has revolutionized the way developers create web applications, offering a wide range of features and benefits that enhance productivity, flexibility, and collaboration. Here are some key advantages of using HTML5 for web development from a developer’s perspective:
1. Streamlined Development Process
- Simplified Coding with Semantic Elements: HTML5 introduces a variety of semantic tags, such as <header>, <footer>, <article>, and <section>. These tags allow developers to create more readable and maintainable code, making it easier to understand the structure and purpose of different sections within a web page.
- Built-in Multimedia Support: Developers no longer need to rely on third-party plugins to handle multimedia content. HTML5’s native support for audio and video embedding simplifies the process of integrating rich media, thus streamlining development efforts.
2. Enhanced Compatibility and Flexibility
- Cross-Browser and Cross-Device Compatibility: HTML5 is designed to work seamlessly across all major browsers and devices. This universal compatibility reduces the time developers spend on testing and debugging for different platforms, allowing for a more efficient development cycle.
- Responsive Design Capabilities: HTML5 works harmoniously with CSS3, enabling developers to implement responsive design techniques. This allows websites to adapt to different screen sizes and orientations, ensuring a consistent user experience across devices.
3. Rich APIs and Features
- Access to Advanced APIs: HTML5 includes a plethora of APIs that empower developers to create dynamic and interactive web applications. Features such as the Canvas API for drawing graphics, the Geolocation API for location-based services, and the Web Storage API for local data storage significantly enhance development capabilities.
- Improved Performance: With local storage and caching features, HTML5 applications can run more efficiently, as they minimize server requests. This leads to faster load times and a smoother user experience, which are crucial for modern web applications.
4. Strong Community and Support
- Active Community and Resources: HTML5 is supported by a robust community of developers, which fosters collaboration and knowledge sharing. Numerous resources, tutorials, and forums are available, making it easier for developers to find solutions to common challenges and learn best practices.
- Continuous Evolution: HTML5 is continually being updated and improved. This commitment to evolution ensures that developers can leverage the latest features and enhancements, keeping their skills relevant and up-to-date.
5. Opportunities for Innovation
- Potential for Creative Solutions: The versatility of HTML5 encourages developers to experiment with new ideas and techniques. The combination of HTML5 with CSS3 and JavaScript allows for the creation of innovative applications that push the boundaries of traditional web development.
- Ease of Learning: For new developers, HTML5 is relatively easy to learn, especially when compared to more complex programming languages. Its straightforward syntax and structure enable beginners to quickly grasp the fundamentals of web development.
In summary, HTML5 web development offers numerous benefits to developers, from streamlined coding and enhanced compatibility to access to rich APIs and a supportive community. By embracing HTML5, developers can create dynamic, efficient, and innovative web applications that meet the demands of today’s users.
Key Takeaways
HTML5 simplifies coding with cleaner syntax, supports multimedia without plugins, and enhances cross-device compatibility. Developers benefit from faster development cycles, easier maintenance, and access to advanced features for creating dynamic applications.
3. New and Removed Features in HTML5

This section explores the introduction of new elements and the removal of outdated ones from HTML5. Explore the key updates that make HTML5 a game-changer.
HTML5 represents a significant evolution in web technology, introducing new features and modernizing how web content is structured and delivered. This section explores the notable additions and removals in HTML5, providing insight into how these changes affect web development.
What is New in HTML5?
HTML5 builds on earlier HTML specifications, introducing features that expand the language’s capabilities for modern web development. These changes cater to modern web needs, allowing developers to create richer, more interactive, and user-friendly web applications. Here are some of the standout new features in HTML5:
1. New Semantic Elements
HTML5 introduces several new semantic elements that make it easier to structure web pages meaningfully. Key elements include:
- <header>, <footer>, <nav>, and <section>: These elements help define the layout and organization of a web page, improving accessibility and search engine optimization (SEO) by providing clear contextual meaning.
- <article>: Represents self-contained content that could stand alone, making it ideal for blog posts, news articles, or forum posts.
2. Multimedia Support
One of the most significant advancements in HTML5 is the native support for multimedia elements, which simplifies embedding audio and video:
- <audio> and <video>: These tags allow developers to integrate multimedia content directly into web pages without relying on third-party plugins like Flash, improving both usability and performance.
3. The Canvas Element
The <canvas> element is a major addition that enables dynamic rendering of 2D graphics within the browser. Developers can use JavaScript to draw shapes, create animations, and manipulate images, making it particularly useful for game development and data visualization.
4. New Input Types and Attributes for Forms
HTML5 enhances form handling with new input types, which improve data validation and user experience:
- New Input Types: These include date, email, url, tel, and range, which provide tailored interfaces for user input, such as date pickers and numeric sliders.
5. APIs for Enhanced Functionality
HTML5 comes packed with APIs that extend its capabilities:
- Geolocation API: Allows developers to access a user’s geographical location, which can be leveraged for location-based services.
- Web Storage API: Offers a way to store data locally in the browser, facilitating offline web applications and quicker access to frequently used data.
- Web Workers: These allow for background processing, enabling scripts to run in parallel, enhancing performance for web applications that require heavy computation.
6. Improved Support for Responsive Design
HTML5 enhances support for responsive web design, enabling developers to create fluid layouts that adapt seamlessly to different screen sizes and orientations. This is crucial for providing a consistent user experience across various devices, from desktops to smartphones.
The new features introduced in HTML5 mark a significant leap forward in web development capabilities. By providing semantic elements, multimedia support, advanced APIs, and enhanced form handling, HTML5 empowers developers to create engaging, efficient, and modern web applications that cater to users’ diverse needs.
Key Takeaways
HTML5 includes semantic elements such as <header>, <footer>, and <article>, improving document structure. It also supports native multimedia elements and works alongside web APIs for features like client-side storage, contributing to richer and more interactive web applications.
Deprecated and Obsolete Elements in HTML5
HTML5 formalized the deprecation of several older elements and attributes that were already discouraged in earlier HTML specifications. This decision was made to streamline the language, enhance semantic clarity, and improve the overall web experience. Below are some of the notable elements that have been deprecated in HTML5:
1. Presentational Elements
One of the key changes formalized in HTML5 was marking certain presentational elements as obsolete in favor of CSS-based styling. These include:
- <font>: This tag was used to specify font size, color, and face. HTML5 encourages the use of CSS for styling, as it separates content from presentation.
- <center>: This element was used to center-align text. Instead, developers should use CSS text alignment properties to achieve the same effect, promoting a cleaner and more maintainable code base.
- <b> and <i>: In HTML5,
<b> and<i>remain valid elements with defined semantic purposes, but<strong><em>They are preferred when emphasis or importance needs to be conveyed.
2. Deprecated Elements
Certain elements have been deprecated in HTML5 due to redundancy or the evolution of web standards. Some of these include:
- <applet>: This element was used to embed Java applets and became obsolete as browser plugin support was discontinued.
- <marquee>: This tag was used to create scrolling text effects, which are now considered outdated. CSS animations provide more control and flexibility for creating dynamic text effects.
3. Obsolete Attributes
In addition to elements, several attributes have been deprecated or are no longer recommended for use:
- align: This attribute, used to align elements like images and tables, has been deprecated in favor of CSS styles that provide more comprehensive alignment options.
- bgcolor: This attribute was commonly used to set background colors for elements. HTML5 recommends using CSS instead for styling, ensuring separation of content and presentation.
The removal of certain elements and attributes in HTML5 reflects a shift toward a more semantic and standards-based approach to web development. By encouraging the use of CSS for presentation and eliminating redundancy, HTML5 enables developers to create cleaner, more maintainable code and better user experiences.
Key Takeaways
HTML5 deprecates elements such as <font>, <center>, and <marquee>, reflecting modern web design practices. This streamlining promotes cleaner, more semantic markup and encourages the use of CSS for styling and layout.
4. Core Concepts of HTML5
This section explores the core elements and structure of HTML5. Let’s dive into the syntax, semantic elements, and accessibility features that define HTML5.
Understanding the core concepts of HTML5 is essential for any web developer looking to harness the full potential of this modern markup language. These concepts provide the foundational knowledge necessary to create well-structured, semantic, and accessible web pages. Here are some of the key areas to explore:
- Common HTML5 Elements
- HTML5 Syntax and Structure
- What are Tags and Attributes?
- Understanding Semantic Elements in HTML5
- HTML5 for Accessibility
- Progressive Enhancement vs. Graceful Degradation in HTML5
- Polyfills and Backward Compatibility
Common HTML5 Elements
HTML5 includes structural and semantic elements that improve the organization and meaning of web content. Here are some of the most common HTML5 elements that developers should be familiar with:
1. Structural Elements
These elements help define the overall layout and organization of a web page:
- <header>: Represents introductory content or a group of navigational links. Typically contains the site logo, title, and navigation links.
- <nav>: Denotes a section of the page intended for navigation links. It enhances the semantic meaning of navigation areas within the layout.
- <main>: Represents the dominant content of the <body> of a document. This is where the primary content resides, excluding headers, footers, and sidebars.
- <section>: Defines a section of content that is thematically related. It often contains a heading and can be used to group related content.
- <article>: Represents a self-contained piece of content that can stand on its own, such as a news article, blog post, or user comment.
- <footer>: Contains information about the document or section, such as the author, copyright information, or links to related documents.
2. Multimedia Elements
HTML5 has made it easier to incorporate multimedia into web pages without relying on third-party plugins:
- <audio>: Enables the embedding of audio content. It includes attributes such as
controls,autoplay, andloop, with playback behavior typically managed through JavaScript.. - <video>: Allows the embedding of video content, providing built-in controls for play, pause, and volume. It supports multiple video formats, with actual support depending on the browser and device and can include subtitles with the <track> element.
- <canvas>: A versatile element used for drawing graphics on-the-fly via JavaScript. This is useful for rendering visualizations, animations, or even games.
3. Form Elements
HTML5 enhances forms with new input types and attributes to improve user experience and validation:
- <form>: Represents a section of the document that contains interactive controls for submitting data to a web server.
- <input>: A versatile element that has various types (text, password, email, number, etc.), enabling different kinds of user inputs.
- <button>: Creates a clickable button that can submit forms or trigger actions through JavaScript.
- <label>: Associates a text label with a form control, improving accessibility and usability by making it easier for users to understand what data is expected.
4. Semantic Elements
Using semantic elements in HTML5 provides meaning to the content, improving SEO and accessibility:
- <strong>: Indicates strong importance. The text inside this element is typically displayed in bold.
- <em>: Denotes emphasized text. This element is usually rendered in italics, helping to convey the importance or urgency of the content.
- <blockquote>: Used for quoted content from another source. It typically contains a citation and can enhance the semantic structure of a webpage.
The introduction of these common HTML5 elements allows developers to create cleaner, more organized, and semantically meaningful web pages. Understanding how to use these elements effectively can significantly enhance user experience and improve accessibility and SEO.
Key Takeaways
Common HTML5 elements include <section>, <article>, <header>, and <footer>, which enhances the semantic structure of web pages. These elements improve accessibility and SEO while simplifying content organization for developers.
HTML5 Syntax and Structure
Understanding the syntax and structure of HTML5 is crucial for creating well-formed web pages. HTML5 builds on the foundations of previous versions of HTML while introducing new elements and simplifying the overall markup process. Here’s a detailed look at its key aspects.
1. Doctype Declaration
HTML5 introduces a simplified doctype declaration:
<!DOCTYPE html>This single line of code informs the browser that the document is using HTML5. Unlike previous versions, which required more complex declarations, this simplicity improves readability and reduces potential errors during coding.
2. Basic Structure of an HTML5 Document
An HTML5 document consists of several key components, which include:
- <html> Element: This is the root element that wraps all the content of the web page.
- <head> Section: Contains metadata about the document, such as the title, character set, stylesheets, and scripts. Key elements within the head include:
- <title>: Sets the title of the web page, which appears in the browser tab.
- <meta charset=”UTF-8″>: Specifies the character encoding for the document, ensuring proper text rendering.
- <link>: Links to external stylesheets.
- <script>: Includes or links JavaScript files, often using attributes such as
defer,async, ortype="module"in modern applications.
- <body> Section: Contains all the visible content of the web page, including text, images, and multimedia elements.
Example of Basic HTML5 Structure:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>My HTML5 Web Page</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="styles.css">
</head>
<body>
<header>
<h1>Welcome to My Website</h1>
</header>
<main>
<section>
<h2>About Us</h2>
<p>This is a sample HTML5 web page.</p>
</section>
</main>
<footer>
<p>© 2024 My Website</p>
</footer>
</body>
</html>3. Element Nesting
HTML5 allows developers to nest elements within each other, enabling a hierarchical structure. For instance, a <div> element can contain multiple <p> elements, lists, or images. Proper nesting is essential for maintaining a clear structure and improving readability.
4. Self-Closing Tags
HTML5 simplifies the syntax by allowing certain elements to be self-closing. For example, the <img> tag and line breaks can be used without a closing tag:
<img src="image.jpg" alt="A sample image">
<br>This feature makes the markup cleaner and reduces the overall code length.
5. Comments
A comment in HTML5 can be added using the following syntax:
<!-- This is a comment -->You can add comments without worry as they are ignored by browsers but can help developers annotate their code for better understanding or collaboration.
6. Whitespace Management
HTML5 ignores extra spaces, tabs, and line breaks, which allows developers to format their code for readability without affecting how the page is rendered in the browser. However, maintaining a clean and organized codebase is recommended for collaboration and future modifications.
7. Key Elements of Basic Markup
- Semantic Elements: HTML5 encourages the use of semantic elements like <header>, <footer>, <article>, and <section>, which help in defining the structure of the document and improve accessibility and help search engines better understand document structure.
- Accessibility: Including attributes like lang in the <html> tag aids in accessibility, allowing screen readers to interpret the content correctly.
- Viewport Meta Tag: The <meta name=”viewport” content=”width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0″> tag is essential for responsive design, ensuring that the webpage displays correctly on various devices, including smartphones and tablets.
HTML5’s syntax and structure provide developers with a flexible and intuitive framework for building web pages. By understanding the essential components, nesting capabilities, and self-closing tags, developers can create clean, semantic, and efficient markup that enhances both user experience and SEO.
Key Takeaways
HTML5 syntax is straightforward, featuring a simplified doctype declaration and clear nesting of elements. Its structure emphasizes semantic markup, enabling better organization and improved readability, which enhances both development and user experience.
What are Tags and Attributes?
In HTML5, tags and attributes are fundamental components that form the building blocks of web pages. Understanding how to use them is essential for effective web development.
1. Tags
Tags are the markup elements that define the structure and content of an HTML document. Each tag is usually enclosed within angle brackets (< >). HTML tags typically come in pairs: an opening tag and a closing tag, which contain content between them. For example:
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>- Opening Tag: <p> indicates the start of a paragraph.
- Closing Tag: </p> signifies the end of that paragraph.
Some elements are void elements, meaning they do not require a closing tag. Examples include:
- <img>: Used to embed images.
- <br>: Inserts a line break.
- <hr>: Creates a horizontal rule.
HTML5 includes semantic tags that describe the meaning of content, which helps describe the meaning of the content within, enhancing accessibility and helping search engines better understand content structure. Examples include:
- <article>: Represents a self-contained piece of content.
- <section>: Groups related content within a document.
- <aside>: Contains content tangentially related to the main content.
2. Attributes
Attributes provide additional information about HTML elements and are always specified in the opening tag. They consist of a name-value pair and provide additional information and configuration for HTML elements. The basic syntax for an attribute is:
<tagname attributeName="value">Content</tagname>For example:
<img src=”image.jpg” alt=”Description of the image”>
- src: The source of the image file.
- alt: Provides a textual description of the image for accessibility purposes and displays when the image cannot be loaded.
3. Common Attributes
Here are some common attributes used in HTML5:
- id: Provides a unique identifier for an element, which can be used for styling or scripting.
- class: Allows you to classify multiple elements with the same name, making it easier to apply styles or JavaScript functions to them.
- style: Inline CSS for individual elements, though inline styles are generally discouraged in favor of external or internal CSS.
- title: Offers additional information about an element, displayed as a tooltip when a user hovers over the element.
4. Global Attributes
HTML5 defines global attributes that can be applied to any HTML element:
- data-*: Allows developers to store custom data attributes on elements, which can be accessed via JavaScript.
- contenteditable: Indicates whether an element is editable by the user.
- hidden: Hides elements from view, useful for dynamically displaying content.
Understanding tags and attributes is essential for creating structured, meaningful, and functional HTML5 documents. Tags define the elements of the web page, while attributes provide additional context and functionality. Together, they allow developers to create interactive and engaging user experiences.
Key Takeaways
Tags are the building blocks of HTML, defining elements within a document, while attributes provide additional information about these elements. Together, they enhance functionality and control the presentation of web content.
Understanding Semantic Elements in HTML5
Semantic elements in HTML5 are critical for enhancing both the structure of a web page and its accessibility. These elements convey meaning and context to both browsers and developers, improving the overall user experience. By using semantic tags, developers can create more meaningful and easily navigable web content.
1. What are Semantic Elements?
Semantic elements are HTML tags that clearly describe their meaning in a human- and machine-readable way. They provide more specific alternatives to generic <div> and <span> when semantic meaning is needed. For example:
- <header>: Represents the introductory content, typically containing headings, logos, and navigation links.
- <footer>: Contains information about its containing element, such as copyright details, links to privacy policies, or related documents.
- <article>: Represents a self-contained composition that could be distributed independently, such as a blog post or news article.
- <section>: Defines a thematic grouping of content, typically with a heading.
Using semantic elements helps create a logical structure, which is beneficial for both human readers and search engine bots.
2. Benefits of Using Semantic Elements
- Improved Accessibility: Semantic tags improve accessibility for users with disabilities. In modern applications, semantic elements are often combined with ARIA attributes to meet accessibility standards, providing users with context and improving their navigation experience.
- SEO Advantages: Semantic HTML helps search engines better understand the structure and context of a web page, which can support indexing and content interpretation.
- Maintainability: Semantic markup is easier for developers to read and maintain. When developers use meaningful tags, they can quickly understand the structure of the document, making it easier to update and manage.
- Consistent Styling: Semantic elements can help streamline CSS styling. For example, targeting specific tags like <article> or <nav> allows developers to apply consistent styles across similar sections of a website.
3. Examples of Semantic Elements in Action
Here’s an example illustrating how semantic elements can be used effectively in HTML5:
<article>
<header>
<h2>The Importance of Semantic HTML</h2>
<p>Published on <time datetime="2024-10-17">October 17, 2024</time></p>
</header>
<section>
<h3>What Are Semantic Elements?</h3>
<p>Semantic elements help convey meaning through markup...</p>
</section>
<footer>
<p>Author: Jane Doe</p>
<p>Tags: HTML5, Semantic, Web Development</p>
</footer>
</article>In this example, the <article> tag clearly indicates that the enclosed content is a standalone piece. The use of <header>, <section>, and <footer> organizes the information logically and semantically.
Understanding and utilizing semantic elements in HTML5 is essential for modern web development. By providing clear meaning and structure, these elements improve accessibility, SEO, and maintainability of web pages, ultimately leading to a better user experience.
Key Takeaways
Semantic elements in HTML5, like <article>, <nav>, and <aside>, provide meaningful structure to web content, enhancing accessibility and SEO. They make code more readable and better convey the content’s purpose to both browsers and developers.
HTML5 for Accessibility
Accessibility in web development refers to the practice of ensuring that websites are usable by individuals with various disabilities. HTML5 includes semantic elements and patterns that support accessible web development when used correctly, making it easier for people with disabilities to interact with web content. This section will explore the key aspects of using HTML5 for accessibility.
1. Importance of Accessibility
Web accessibility is essential for creating an inclusive digital environment. According to the World Health Organization, about 15% of the world’s population lives with some form of disability, which can affect their ability to access digital content. Therefore, making websites accessible not only broadens the audience but also helps organizations align with accessibility standards such as WCAG and accessibility requirements interpreted under laws like the ADA.
2. Semantic HTML for Enhanced Accessibility
Semantic HTML should be combined with proper keyboard support and ARIA attributes where necessary to meet modern accessibility standards. As discussed in the previous section, semantic tags like <header>, <footer>, <nav>, and <article> help define the structure of the content, making it easier for screen readers to navigate and interpret the page. These elements provide context to assistive technologies, allowing users to understand the content better.
3. ARIA Roles and Attributes
The Accessible Rich Internet Applications (ARIA) specification offers additional attributes that enhance accessibility. These attributes can be added to standard HTML elements to define roles, states, and properties that assistive technologies can interpret. Some key ARIA attributes include:
- role: Defines what an element is or does, such as role=”navigation” for navigation links.
- aria-label: Provides a label for an element that may not have a visible label.
- aria-hidden: Indicates whether an element should be exposed to accessibility APIs.
Using ARIA roles and attributes judiciously can significantly enhance user experience for individuals relying on assistive technologies.
4. Form Accessibility
HTML5 includes several features that improve form accessibility:
- New Input Types: HTML5 introduces new input types such as email, tel, and url, which provide better context for screen readers and improve user input accuracy.
- Placeholder Text: Placeholder text can guide users in filling out forms, but should not replace labels. Always include <label> elements for clarity.
- Validation Messages: HTML5 provides basic form validation features, which are often supplemented with custom validation to ensure accessible error handling, improving the overall user experience.
Here’s an example of an accessible form:
<form>
<label for="email">Email:</label>
<input type="email" id="email" name="email" required>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>5. Multimedia Accessibility
HTML5 also improves accessibility for multimedia content:
- Text Alternatives: Use the <track> element to provide subtitles and captions for <video> and <audio> elements. This helps deaf or hard-of-hearing users understand multimedia content.
- Descriptive Titles: Always include descriptive titles and alternative text (alt attributes) for images to convey information to visually impaired users.
Example of using <video> with subtitles:
<video controls>
<source src="video.mp4" type="video/mp4">
<track src="subtitles.vtt" kind="subtitles" srclang="en" label="English">
Your browser does not support the video tag.
</video>HTML5 provides a foundational markup layer that supports accessible web content when combined with best practices and assistive technologies. By leveraging semantic elements, ARIA roles, improved form controls, and multimedia accessibility features, developers can ensure their websites are usable by everyone, regardless of their abilities. Implementing these practices not only meets legal requirements but also fosters an inclusive digital landscape.
Key Takeaways
HTML5 enhances accessibility by introducing semantic elements like <header>, <nav>, and <footer>, which helps assistive technologies better interpret page content. These elements improve navigation for users with disabilities, ensuring inclusive web experiences.
Progressive Enhancement vs. Graceful Degradation in HTML5
When developing websites with HTML5, it is crucial to consider how different users and devices will interact with your web applications. While both approaches have historically influenced web development, progressive enhancement is now the preferred strategy for building resilient, accessible web applications. Understanding these approaches can lead to better user experiences across diverse environments.
1. Progressive Enhancement
Progressive Enhancement is a strategy that focuses on delivering the basic content and functionality of a website to all users, regardless of their device or browser capabilities. It emphasizes building the web application from a solid foundation and then enhancing it with advanced features for users with more capable browsers.
Key Features:
- Core Functionality: The primary content is accessible to everyone, including users with older browsers or those with disabilities. This ensures that the essential features of the site work universally.
- Layered Enhancements: After establishing the basic functionality, developers can add layers of enhancements (like JavaScript features or CSS styling) that improve the experience for users with modern browsers.
- Accessibility and SEO: Because basic content is accessible to all, this method naturally enhances accessibility and search engine optimization (SEO).
Example: A simple HTML5 page might display a text-based version of a form for users with older browsers. If the browser supports modern features, JavaScript can enhance the form with real-time validation or visual cues.
2. Graceful Degradation
Graceful Degradation, on the other hand, starts with a fully developed website that utilizes the latest technologies and features. The goal is to ensure that if a user accesses the site from an outdated browser, the core functionality still works, albeit with limited features.
Key Features:
- Full-Featured Design: Developers design the site with all available features, assuming modern technology is in use.
- Fallbacks for Older Browsers: For users on older browsers, the site must offer fallbacks, providing a less rich experience but still maintaining functionality.
- Focus on Modern Users: This approach often caters primarily to the latest browsers and devices, which can alienate users with less sophisticated technology.
Example: A video player might use native HTML5 video on modern browsers while providing a static poster image or download link in constrained environments.
3. Choosing Between the Two Approaches
When deciding between progressive enhancement and graceful degradation, several factors come into play:
- User Base: If your audience primarily uses modern browsers, graceful degradation might be acceptable. However, if you have a diverse audience or expect users from various backgrounds, progressive enhancement is the safer choice.
- Content Importance: If the primary content of the site is critical (like news articles or critical information), ensure that it’s accessible to everyone by using progressive enhancement.
- Development Resources: Progressive enhancement can sometimes require more initial planning and foresight, whereas graceful degradation may allow for quicker deployment with a focus on modern features.
Key Takeaways
Progressive enhancement focuses on building a solid, accessible base and adding advanced features for modern browsers, while graceful degradation ensures older browsers can still display basic content, despite lacking newer capabilities. Both methods ensure a wide range of user compatibility.
Polyfills and Backward Compatibility
In web development, ensuring that new features work across all browsers, including older versions, is a significant concern. Polyfills and backward compatibility are crucial concepts that address this challenge, especially when working with HTML5.
1. Understanding Polyfills
A polyfill is a piece of code (typically JavaScript) that implements a feature on web browsers that do not natively support it. By using polyfills, developers can leverage the latest web standards while maintaining functionality for users with older browsers.
Key Functions of Polyfills:
- Feature Detection: Polyfills often use feature detection techniques to check if a browser supports a particular HTML5 feature. If not, they provide a fallback to ensure that the feature works correctly.
- Code Reusability: Polyfills allow developers to write code that can be reused across different projects without worrying about browser compatibility issues.
- Seamless Integration: They can be integrated into existing codebases with minimal disruption, allowing for progressive enhancement without completely overhauling the website.
Example: A commonly used polyfill is HTML5 Shiv, which enables the use of HTML5 elements (like <article> and <section>) in older versions of Internet Explorer.
2. Backward Compatibility
Backward compatibility refers to the ability of a system to utilize the features or data from an older version of itself. In the context of HTML5, this means that web applications built using HTML5 standards should still function correctly in older browsers that do not fully support these standards.
Importance of Backward Compatibility:
- User Experience: Users accessing a website from outdated browsers should still have a functional experience, even if it lacks some modern features.
- Business Considerations: Many businesses have clients or users who may not upgrade their browsers regularly. Ensuring backward compatibility can prevent potential customer loss and dissatisfaction.
- Gradual Adoption: By allowing older browsers to access essential features, developers can encourage users to upgrade their browsers over time without forcing an immediate switch.
3. Strategies for Implementing Polyfills and Ensuring Backward Compatibility
- Using a Polyfill Library: Developers can incorporate popular libraries like Polyfill.io, which automatically serves the appropriate polyfills based on the user’s browser capabilities.
- Conditional Comments: For older versions of Internet Explorer, conditional comments can be used to load specific scripts or stylesheets that ensure proper functionality.
- Progressive Enhancement: By adopting a progressive enhancement strategy, developers can build a solid foundation of basic functionality that is enhanced by additional features for modern browsers.
Polyfills and backward compatibility are essential components of modern web development with HTML5. They help create a more inclusive web experience by ensuring that all users, regardless of their browser capabilities, can access and enjoy web content. Understanding and implementing these concepts allows developers to utilize the latest features while maintaining the functionality of their applications across various browser versions.
Key Takeaways
Polyfills are scripts that enable modern HTML5 features in older browsers, ensuring backward compatibility. They help websites utilize advanced HTML5 capabilities while still providing a functional experience for users with outdated browsers.
5. HTML5 Advantages and Disadvantages

This section explores the advantages and disadvantages of HTML5. We’ll weigh the pros and cons to give a balanced view of HTML5’s capabilities.
HTML5 has revolutionized web development by providing new features and capabilities that enhance the user experience and make it easier for developers to create rich web applications. However, like any technology, it comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these can help businesses and developers make informed decisions about adopting HTML5 for their projects.
HTML5 Advantages
HTML5 brings a myriad of advantages that enhance web development, improve user experiences, and enable developers to create more interactive and dynamic web applications. Below, we delve deeper into the key advantages of HTML5, supported by various sources.
1. Native Multimedia Support
One of the standout features of HTML5 is its ability to natively support audio and video through the <audio> and <video> tags. This eliminates the need for third-party plugins like Flash, which have been largely phased out due to security and compatibility issues. As a result, developers can create multimedia-rich applications that load faster and provide a more seamless user experience.
2. Improved Semantic Structure
HTML5 introduces a range of semantic elements that help structure web content more meaningfully. Tags such as <header>, <footer>, <article>, and <section> improve the readability of HTML documents for both developers and search engines. This semantic richness enhances SEO, making it easier for search engines to index and rank pages appropriately.
3. Responsive and Mobile-Friendly Design
Designed with mobile devices in mind, HTML5 facilitates responsive web design. Features like flexible grid layouts and CSS3 media queries enable developers to create websites that adapt to different screen sizes. This adaptability is essential in today’s mobile-first world, where users access the web through a variety of devices.
4. Enhanced Form Elements
HTML5 brings an array of new input types and attributes, such as date, email, tel, and range, which streamline form validation and improve user interaction. These enhancements reduce the need for JavaScript for basic form handling, making the development process more straightforward and user-friendly.
5. Offline Capabilities
With HTML5, developers can create web applications that function offline through the use of Application Cache and Service Workers. This is particularly beneficial for users with intermittent internet connections, allowing them to access content and perform tasks without a continuous online connection.
6. Cross-Platform Compatibility
HTML5 applications are designed to run on any modern web browser, regardless of the operating system. This cross-platform functionality reduces the need for separate development processes for different environments, resulting in significant time and cost savings for developers.
7. Community and Open Standards
As an open standard, HTML5 encourages collaboration within the developer community, fostering innovation and adaptability. The evolution of HTML5 is driven by the needs and feedback of its users, ensuring that it remains relevant and useful in a rapidly changing digital landscape.
The advantages of HTML5 make it a compelling choice for modern web development. From native multimedia support to improved semantic structure and offline capabilities, HTML5 offers tools and features that enhance both developer productivity and user experience. Understanding these advantages is crucial for businesses and developers looking to harness the power of HTML5 for their web projects.
Key Takeaways
HTML5 enhances web development with features like multimedia support, cross-browser compatibility, offline capabilities, and improved SEO. It promotes cleaner code, faster load times, and enables rich, interactive web experiences, making it ideal for modern websites and applications.
HTML5 Disadvantages
While HTML5 offers numerous advantages for web development, it also presents some challenges that developers and businesses need to consider. Understanding these disadvantages can help inform decisions about when and how to implement HTML5 effectively.
1. Browser Compatibility Issues
Despite significant advancements, HTML5 can still face compatibility problems, especially with older browsers that do not support all of its features. For instance, while modern browsers like Chrome, Firefox, and Safari have robust HTML5 support, Legacy browsers and constrained WebView environments may lack support for certain features. This inconsistency can lead to a fragmented user experience, requiring developers to rely on feature detection and selective fallbacks when necessary.
2. Learning Curve for Developers
Although HTML5 retains much of the simplicity of its predecessors, while HTML5 itself is straightforward, working with related web APIs and JavaScript-based features can introduce a learning curve. For instance, understanding how to implement complex functionalities, like the Web Storage API or Canvas for graphics, may require additional training and experience. Developers familiar with older HTML versions may need to invest time in learning about the latest standards, which can slow down initial project development.
3. Performance Concerns
In certain cases, Web applications that rely heavily on multimedia and complex JavaScript interactions can be resource-intensive, particularly when they incorporate heavy multimedia elements or complex JavaScript interactions. Such applications may result in slower load times and higher memory usage, especially on older or lower-end devices. This can lead to a subpar user experience, which may drive users away.
4. Limited SEO for Certain Features
While semantic HTML helps search engines understand page structure, dynamic content rendered via technologies like <canvas> requires additional strategies, such as alternative text or server-rendered content, to remain discoverable. This limitation can affect the visibility of certain web applications in search engine results, making it harder for businesses to attract organic traffic.
5. Fragmentation of Standards
While baseline HTML5 support is consistent across modern browsers, differences in support for certain advanced web APIs can still require careful testing. in how different browsers implement their features. This can create challenges for developers trying to ensure a consistent user experience across multiple platforms. Variability in support for specific features may lead to additional development time and complexity as developers must test and adapt their applications for various environments.
While HTML5 brings many advantages that make it a popular choice for modern web development, it also comes with several disadvantages, including browser compatibility issues, a learning curve, potential performance concerns, limited SEO features for certain elements, and fragmentation of standards. By being aware of these challenges, businesses and developers can better prepare to implement HTML5 in a way that maximizes its benefits while mitigating its drawbacks.
Key Takeaways
HTML5, while powerful, has some limitations, such as inconsistent browser support for newer features, reliance on JavaScript for complex functionality, and limited offline capabilities compared to native apps. Additionally, older devices may struggle with resource-heavy HTML5 features.
6. Advanced HTML5 Elements and APIs
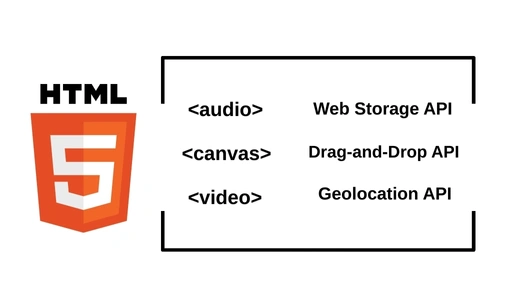
This section explores HTML5’s advanced features like Canvas, Web Storage, and APIs unlock powerful functionality for developers. Learn about the tools that help create dynamic, interactive, and responsive web applications.
HTML5 introduces a variety of advanced elements and APIs that empower developers to build more dynamic, interactive, and efficient web applications. These features improve everything from multimedia handling to real-time communication, making HTML5 a powerful tool in modern web development.
Here’s a breakdown of some of the most significant advanced elements and APIs in HTML5:
1. HTML5 Forms and Input Types
HTML5 enhances form creation by introducing new input types and attributes. These new elements, such as date, email, URL, and range, simplify the development process by assisting with basic validation and formatting, often supplemented by JavaScript in real-world applications. Attributes like placeholder, autofocus, and required further streamline form building, improving the user experience and accessibility.
2. HTML5 Multimedia: Audio and Video
HTML5 introduces native support for multimedia elements through the <audio> and <video> tags. This allows for the seamless embedding of media content without relying on external plugins like Flash. Developers can easily control multimedia playback, manipulate tracks, and handle media events using JavaScript. Additionally, Support for codecs such as MP4, WebM, and Ogg varies by browser and platform, allowing for better cross-browser compatibility.
3. Graphics on the Web: Canvas and SVG
The <canvas> element in HTML5 allows for the dynamic rendering of 2D graphics directly on the web page. Developers can use JavaScript to draw and manipulate graphics, enabling applications such as games, visual data presentations, and interactive visualizations. On the other hand, SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics) is ideal for defining vector-based graphics using XML, which can be scaled to any size without loss of quality, making it a crucial tool for responsive designs and graphical elements.
4. HTML5 and Web Storage API
The Web Storage API in HTML5 provides two mechanisms for storing data on the client side: localStorage and sessionStorage. Unlike cookies, these storage options provide more capacity and allow developers to store data directly in the browser without affecting server performance. This is especially useful for saving user preferences, session states, and other lightweight data that enhances the user experience.
5. HTML5 Geolocation API
The Geolocation API enables web applications to retrieve the geographical location of the user in real time. With the user’s permission, developers can use this feature to create location-based services like maps, localized search results, or targeted marketing campaigns. The API retrieves data such as latitude, longitude, and even altitude, enhancing personalized experiences on web platforms.
6. HTML5 Drag-and-Drop API
The Drag-and-Drop API simplifies the task of enabling drag-and-drop functionality on web pages. Developers can make HTML elements draggable using the draggable attribute and then capture drop events to perform actions like file uploads, rearranging lists, or dragging and dropping items between different sections of a page. This API enhances interactivity and user engagement.
7. HTML5 Web Workers
Web Workers in HTML5 allow developers to run scripts in the background without affecting the performance of the web page. This is particularly useful for handling resource-intensive tasks like large data processing or image manipulation. By offloading such tasks to a separate thread, Web Workers prevent the main thread from being blocked, improving overall page responsiveness.
8. HTML5 WebSockets and Real-Time Communication
The WebSocket API provides full-duplex communication channels over a single TCP connection, enabling real-time data exchange between the client and server. This is crucial for applications like online gaming, live chat, stock price updates, and collaborative editing tools, where real-time interactions are essential. WebSockets offer a more efficient alternative to traditional AJAX for real-time data streams, with lower latency and reduced overhead.
HTML5’s advanced elements and APIs greatly enhance the capabilities of modern web applications. From seamless multimedia integration and dynamic 2D graphics to efficient data storage and real-time communication, these features allow developers to build more robust and engaging web experiences.
Key Takeaways
HTML5 introduces powerful elements like <canvas> and <video>, and APIs like Web Storage, Geolocation, and Web Workers, enabling rich multimedia, interactive content, offline storage, and enhanced performance, making it a versatile platform for modern web applications.
7. HTML5 and Front-End Technologies
This section explores how HTML5 works in tandem with technologies like CSS3 and JavaScript to deliver rich web experiences. Discover how HTML5 integrates with these front-end technologies to create responsive, interactive sites.
HTML5 works seamlessly with several front-end technologies to create modern, responsive, and highly interactive web applications. These technologies, primarily CSS3 and JavaScript, along with various frameworks, are key to enhancing user experiences and making web development more dynamic. Here’s an overview of how HTML5 integrates with front-end technologies:
1. HTML5 with CSS3
CSS3, the latest evolution of the Cascading Style Sheets language, is a crucial partner of HTML5 in modern web design. Together, they enhance the appearance and layout of websites, providing advanced features for responsiveness, animations, and transformations.
- Responsive Design: HTML5’s semantic elements (<header>, <footer>, <section>, etc.) combined with CSS3 media queries enable responsive web design, making websites adaptable to different screen sizes and devices.
- Animations and Transitions: CSS3 enables smooth animations and transitions, such as hover effects or element fading, eliminating the need for JavaScript in many scenarios.
- Flexbox and Grid Layout: These CSS3 layout models work with HTML5 to create flexible, responsive layouts that adjust based on the content and screen size.
2. HTML5 with JavaScript and Frameworks
JavaScript is the backbone of dynamic and interactive websites. When used alongside HTML5, JavaScript transforms static web pages into interactive web applications.
- DOM Manipulation: JavaScript interacts with HTML5 elements via the Document Object Model (DOM), allowing developers to dynamically change content, styles, or structure in real-time without reloading the page.
- JavaScript Frameworks and Libraries: Frameworks like React.js, Vue.js, and Angular make it easier to build large-scale web applications with HTML5. These frameworks provide tools for managing state, rendering HTML5 components dynamically, and handling user interactions smoothly.
- Single Page Applications (SPAs): With the power of JavaScript frameworks and HTML5, SPAs deliver seamless user experiences where the content dynamically loads without refreshing the entire page.
3. HTML5 and Responsive Web Design
HTML5 plays a critical role in responsive web design, a methodology that ensures web applications look and function well across a variety of devices and screen sizes.
- Media Queries: HTML5 in conjunction with CSS3 media queries, allows developers to apply different styles depending on the device’s width, height, or resolution, thus providing an optimized viewing experience.
- Viewport Meta Tag: By defining the viewport in HTML5 (<meta name=”viewport” content=”width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0″>), developers ensure that websites render correctly on mobile devices.
4. HTML5 and Web Components
Web Components is a suite of technologies that allows developers to create custom, reusable HTML5 elements with their own encapsulated styles and functionality.
- Custom Elements: Developers can define their own HTML5 tags with custom behavior, extending the capabilities of standard HTML.
- Shadow DOM: Shadow DOM encapsulates a component’s internal structure, preventing its styles from affecting the rest of the document and vice versa, leading to cleaner code.
- HTML Templates: HTML5’s <template> tag allows for reusable markup that can be cloned and inserted into the DOM without the need for external libraries.
HTML5, when paired with CSS3, JavaScript, and frameworks like React or Angular, forms the foundation of modern front-end development. These technologies work together to create visually appealing, interactive, and responsive web applications that enhance user engagement and performance.
Key Takeaways
HTML5 seamlessly integrates with front-end technologies like CSS3 and JavaScript frameworks to enhance user interfaces, support responsive design, and create dynamic, interactive web experiences. It’s essential for modern web development, enabling rich multimedia and app-like functionality in the browser.
8. HTML5 for Mobile Applications

This section covers how HTML5 simplifies building cross-platform mobile applications with ease. Learn more about HTML5’s versatility that extends beyond desktop browsers.
HTML5 has revolutionized mobile application development, enabling developers to create cross-platform mobile apps without the need for native programming languages like Swift (for iOS) or Java (for Android). This section explores how HTML5 empowers mobile app development and highlights the technologies and strategies involved.
1. Cross-Platform Development with HTML5
One of the most significant advantages of HTML5 for mobile app development is its ability to create cross-platform applications. HTML5 apps are built once and can run across multiple platforms, such as iOS, Android, and Windows, significantly reducing development time and costs. Combined with frameworks like PhoneGap (Apache Cordova), HTML5 allows developers to build hybrid mobile apps, blending native features with web technology.
- Hybrid Apps: Hybrid apps are built using HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScript and then wrapped in a native container, allowing them to be distributed via app stores while still having access to device features like the camera or GPS through native APIs.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Developing a single HTML5 app that works across platforms is often cheaper than building separate native apps for each operating system.
2. HTML5 for iOS and Android
HTML5 enables app development for both iOS and Android by leveraging frameworks that allow developers to package HTML5 code into apps that can be run natively on these platforms.
- iOS Compatibility: While iOS prioritizes native apps, HTML5 apps can be run within browsers like Safari or as part of hybrid applications via frameworks like Cordova.
- Android Compatibility: Android is more flexible, with strong browser support for HTML5 features, and provides an excellent environment for both web and hybrid HTML5 apps.
3. HTML5 and Offline Capabilities
One of the key challenges in mobile app development is ensuring that applications work offline. HTML5 addresses this with the Application Cache and Service Workers, enabling apps to store resources and data locally for offline access.
- Application Cache: HTML5’s Application Cache allows developers to store entire web pages locally, so users can continue using the app even when there’s no internet connection.
- Service Workers: Service Workers in HTML5 offer more advanced control over offline capabilities by enabling background sync, caching, and push notifications.
4. Mobile-First Development with HTML5
With the growing importance of mobile devices, adopting a mobile-first strategy is crucial. HTML5, in combination with responsive design techniques, allows developers to design applications primarily for mobile devices, ensuring optimal performance on smartphones and tablets.
- Responsive Design: HTML5 is pivotal in responsive design, allowing apps to adjust their layout and functionality based on the screen size of the device.
- Performance Optimization: HTML5 APIs like Web Workers and Local Storage allow mobile apps to run smoothly and efficiently by handling background tasks and storing data locally.
5. Performance and UX Enhancements
Performance is critical for mobile apps, where resources are often more limited than on desktops. HTML5’s ability to handle multimedia elements (such as audio and video) natively, manage graphics through the Canvas API, and leverage hardware acceleration for animations ensures a smooth and high-quality user experience on mobile devices.
- Multimedia: The native support for multimedia elements like <audio> and <video> in HTML5 allows for smoother, plugin-free playback on mobile.
- Graphics and Animations: HTML5’s Canvas and SVG enable rich visual experiences, including games, infographics, and interactive animations on mobile.
6. HTML5 Game Development for Mobile
HTML5 has become increasingly popular in mobile game development due to its powerful graphics capabilities (Canvas and WebGL), cross-platform nature, and the ability to run directly in mobile browsers or within hybrid apps.
- HTML5 Game Frameworks: Frameworks like Phaser.js, Pixi.js, and Construct 2 make it easy to develop and deploy mobile games using HTML5, allowing developers to focus on gameplay while the framework handles the technical intricacies.
HTML5 offers a versatile and powerful solution for mobile app development, allowing developers to create cross-platform apps that work seamlessly across iOS, Android, and other platforms. From hybrid app development to offline capabilities and performance optimizations, HTML5 is essential for building modern mobile apps that deliver an engaging and responsive user experience.
Key Takeaways
HTML5 offers a robust framework for building cross-platform mobile applications, supporting responsive design, offline functionality, and multimedia integration. It’s a cost-effective solution for developing web apps that work across various devices, including iOS and Android.
9. HTML5 Game Development

HTML5 offers a robust platform for game development, with support for rich graphics and real-time interaction. Learn how HTML5 is being used to build immersive web-based games.
HTML5 has become a powerful platform for game development due to its cross-browser compatibility, open standards, and rich multimedia capabilities. This section explores how developers use HTML5 to create a variety of games, ranging from simple 2D experiences to complex browser-based games that rival native app performance.
1. Why Choose HTML5 for Game Development?
HTML5 is widely chosen for game development because it allows games to run on any modern browser, whether on desktop, tablet, or mobile, without the need for plugins like Flash. Its versatility, paired with robust tools and frameworks, makes it ideal for creating games that are playable across multiple devices.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: HTML5 games can be run on virtually any platform, including Windows, macOS, Android, iOS, and even gaming consoles with web browsers.
- No Need for Plugins: Unlike older technologies like Flash, HTML5 does not require additional plugins to render graphics, making it more secure and user-friendly.
- High Performance: Modern browsers are equipped with powerful engines that optimize HTML5, ensuring smooth gameplay even in more complex games.
2. HTML5 Game Development Frameworks
Several frameworks have been built to streamline game development in HTML5, offering developers the tools to create immersive, high-quality games with less manual coding. Here are some of the most popular:
- Phaser.js: Phaser is one of the most popular 2D game development frameworks for HTML5. It’s highly customizable, supports both WebGL and Canvas, and is packed with features for handling sprites, physics, animations, and input.
- Three.js: For 3D games, Three.js is a powerful library built on top of WebGL. It allows developers to create complex 3D environments and animations, making it ideal for browser-based 3D games.
- Construct 3: A beginner-friendly platform that requires no coding, Construct 3 allows game developers to create HTML5 games visually using drag-and-drop mechanics. It’s ideal for smaller or indie games.
- Pixi.js: Known for its super-fast rendering capabilities, Pixi.js is another top HTML5 framework that excels in 2D graphics and performance. It is often used to create visually rich games with smooth animations.
3. HTML5 Game Elements and APIs
HTML5 offers several key elements and APIs that are particularly useful for game development. These features allow developers to create interactive, visually dynamic games directly in the browser.
- Canvas API: The Canvas element in HTML5 allows developers to draw and manipulate 2D shapes, graphics, and animations in real-time. It’s one of the most crucial elements in building interactive games.
- WebGL: For 3D game development, WebGL (Web Graphics Library) extends the capabilities of the HTML5 Canvas element to handle 3D rendering directly within the browser. It leverages the GPU to deliver hardware-accelerated 3D games.
- Audio API: HTML5’s built-in audio element and the Web Audio API enable developers to incorporate sound effects and background music into games without needing external plugins.
- Gamepad API: The Gamepad API allows HTML5 games to support external game controllers, providing a more traditional console-like gaming experience directly in the browser.
4. Offline HTML5 Games with Service Workers
Thanks to Service Workers in HTML5, developers can build games that work offline or provide seamless online-offline experiences. Service Workers cache game assets and data, enabling gameplay even without an internet connection, which is particularly useful for mobile gaming.
5. Monetizing HTML5 Games
HTML5 games offer several monetization options, whether through in-game advertising, microtransactions, or paid versions. Developers can integrate ads via ad platforms like Google AdSense for games, or build in-app purchases using services like Stripe or PayPal.
- In-Game Ads: Ad networks like AdMob or Unity Ads allow developers to monetize their games by showing banner ads or rewarded video ads during gameplay.
- Freemium Model: Many developers use the freemium model, where the game is free to play but includes microtransactions for purchasing extra content or power-ups.
6. Popular HTML5 Games and Success Stories
HTML5 has been used to build some notable games that have gained wide popularity:
- Cut the Rope: Originally a mobile game, Cut the Rope was rebuilt using HTML5, demonstrating the power of HTML5 to deliver the same high-quality experience in browsers.
- Angry Birds: The HTML5 version of Angry Birds offers the same experience as the original, making it accessible across devices and browsers.
- 2048: This popular tile-based puzzle game was developed entirely in HTML5 and became a viral sensation, proving the potential of simple yet engaging HTML5 games.
HTML5 game development provides a powerful, accessible platform for creating both simple and complex games that can run across multiple devices. With rich APIs like Canvas and WebGL, a variety of development frameworks, and extensive browser support, HTML5 offers a versatile toolkit for modern game developers.
Key Takeaways
HTML5 supports game development through powerful features like the <canvas> element and WebGL for graphics, along with APIs for real-time communication and offline play. It enables creating browser-based games without the need for plugins, offering cross-platform compatibility.
10. HTML5 for Modern Web Applications

HTML5 is essential for creating modern web applications, especially single-page apps (SPAs) and progressive web apps (PWAs). Discover the full potential of HTML5 for building high-performance web apps.
HTML5 has revolutionized modern web application development by providing tools, APIs, and frameworks that enable developers to create faster, more interactive, and responsive web apps. From enabling offline functionality to building progressive web apps (PWAs) and single-page applications (SPAs), HTML5 has cemented its place at the core of modern web development.
1. Building Single Page Applications (SPAs) with HTML5
Single Page Applications (SPAs) have become popular due to their fast, dynamic, and interactive nature. SPAs load a single HTML page and dynamically update the content as the user interacts with the app. HTML5 plays a vital role in SPA development with features like:
- History API: This allows developers to manipulate the browser history and URL without reloading the entire page, providing seamless navigation in SPAs.
- AJAX and Fetch API: HTML5 supports AJAX and the newer Fetch API, allowing the web app to asynchronously request data from servers without refreshing the page.
Popular JavaScript frameworks like React, Angular, and Vue.js leverage HTML5 to build efficient SPAs.
2. Using HTML5 for Progressive Web Apps (PWAs)
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) combine the best features of native mobile apps and traditional websites, offering offline functionality, push notifications, and better performance. HTML5 is critical in building PWAs, especially for features like:
- Service Workers: A JavaScript API that allows for caching assets and enabling offline capabilities, ensuring that the app works without an internet connection.
- Web App Manifest: A JSON file that gives the app the look and feel of a native mobile app. It includes icons, names, and a splash screen when the app is installed on a user’s device.
PWAs developed using HTML5 offer improved performance, faster loading times, and better user experiences compared to traditional web apps.
3. HTML5 and Offline Support with Service Workers
One of the most significant advances HTML5 brought to modern web applications is offline support. With the Service Worker API, developers can cache HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files, as well as API responses, allowing the app to continue functioning offline or in low-connectivity environments.
- Caching Strategies: Developers can define strategies like “Cache First,” “Network First,” or “Stale While Revalidate” to control how the app fetches and serves content in various network conditions.
- Offline Notifications: HTML5’s Service Workers also enable push notifications to be sent even when the app is not open, enhancing user engagement.
4. HTML5 and Mobile-First Strategy
With more users accessing the web through mobile devices, HTML5 enables a mobile-first strategy by offering responsive design elements and tools that enhance mobile performance. By using Viewport Meta Tags, media queries, and flexible layouts, developers can ensure that HTML5 apps are optimized for different screen sizes and devices.
Key aspects of HTML5 for mobile-first applications include:
- Responsive Design: HTML5, combined with CSS3 media queries, allows for responsive layouts that adapt to different device sizes and resolutions.
- Touch Events: HTML5 provides support for touch-based interactions, essential for mobile devices and tablets.
5. Cross-Platform Compatibility with HTML5
One of the standout features of HTML5 is its cross-platform compatibility. With HTML5, developers can create applications that work seamlessly across different operating systems, browsers, and devices, including desktops, smartphones, and tablets.
- Consistency: HTML5 offers consistent behavior across modern browsers like Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge, reducing development time and effort to handle compatibility issues.
- Device Agnostic: Whether it’s iOS, Android, or desktop, HTML5 allows for a unified codebase that can adapt to different platforms without needing platform-specific code.
6. HTML5 and Web Components
Web Components are reusable, encapsulated HTML5 elements that developers can use to modularize and simplify complex web application development. These components can be custom-built or sourced from libraries, improving code organization and reusability.
- Shadow DOM: HTML5’s Shadow DOM allows for better encapsulation of styles and scripts within components, preventing conflicts with other parts of the app.
- Custom Elements: Developers can create custom HTML tags that encapsulate functionality and content into self-contained units, which improves code maintenance.
7. HTML5 APIs for Web Application Features
HTML5 introduces a wide array of APIs that significantly enhance the interactivity and performance of modern web applications, including:
- Geolocation API: Allows developers to access a user’s geographical location to offer location-based services.
- Web Workers: HTML5’s Web Workers API enables multithreading, allowing intensive tasks like data processing to be offloaded to background threads without affecting the UI performance.
- Web Sockets: HTML5 Web Sockets facilitate real-time, bi-directional communication between the server and the client, making HTML5 ideal for chat applications, live data feeds, and online multiplayer games.
HTML5 has redefined modern web application development by enabling faster, more interactive, and cross-platform compatible applications. Whether it’s creating SPAs, PWAs, or ensuring offline functionality with Service Workers, HTML5 provides the tools and frameworks necessary for building dynamic, responsive web apps for today’s users.
Key Takeaways
HTML5 is essential for modern web applications, offering features like local storage, responsive design, and enhanced multimedia support. These capabilities enable developers to create dynamic, interactive applications that function seamlessly across devices and platforms.
11. HTML5 Web Development Process

A well-structured process is key to efficient HTML5 web development. In this section, we’ll walk through the essential steps, from writing clean code to testing and deployment.
The HTML5 web development process is an organized approach that involves multiple stages, from conceptualization to deployment and maintenance. HTML5, being the foundation of modern web development, follows best practices and modern workflows to build dynamic, responsive, and scalable websites or web applications.
1. Planning and Requirement Gathering
- Understanding Business Needs: The first step in any web development project is understanding the client’s objectives. Businesses need to clarify the purpose of their website or web app, target audience, and specific features or functionalities they require.
- Defining Scope: Based on client discussions, a detailed project scope is created. This includes identifying the type of site (e.g., e-commerce, portfolio, blog) and the functionality that will be built using HTML5, such as multimedia support or interactive elements.
2. Wireframing and Prototyping
- Wireframes: Wireframes act as a blueprint for the website. They outline the structure and placement of elements like navigation menus, images, text, and buttons. Tools like Figma or Adobe XD are commonly used for wireframing.
- Prototyping: A higher-fidelity version of the wireframe, often including the first round of interactivity, is developed. Prototypes allow the client and development team to test user flows and interfaces before actual coding begins.
3. Design and User Experience (UX)
- Responsive Design with HTML5: The design phase involves creating a responsive, mobile-first layout, often using HTML5 in conjunction with CSS3 and frameworks like Bootstrap. The design must adapt to different screen sizes and devices, enhancing the user experience.
- UI/UX Best Practices: HTML5, when combined with CSS and JavaScript, supports intuitive UI elements and user-friendly navigation. HTML5’s semantic elements (like <article>, <header>, <footer>) help structure content logically, enhancing usability and SEO.
4. Front-End Development
- HTML5 Coding: Once the design is approved, front-end developers begin coding the website structure using HTML5. This includes writing clean, semantic HTML5 code, ensuring that the elements are accessible and properly optimized for SEO.
- CSS3 and JavaScript Integration: HTML5 development is often paired with CSS3 for styling and JavaScript for functionality. Developers ensure that the HTML5-based website or app is interactive and visually appealing.
- Cross-Browser Compatibility: Developers test across different browsers (Chrome, Safari, Firefox, etc.) to ensure HTML5 compatibility, checking that the site’s structure and features work as expected on all platforms.
5. Back-End Development
- Server-Side Logic: For more complex web applications, back-end development is integrated with HTML5. Server-side languages like Node.js, PHP, or Python handle data processing, authentication, and database management, while HTML5 provides the interface and content delivery.
- Database Integration: HTML5 web applications often require a database to store and retrieve user data, product details, or other dynamic content. Back-end developers link HTML5 forms and input fields to databases using SQL, NoSQL, or cloud-based databases like Firebase.
6. Testing and Quality Assurance
- Usability Testing: The website is rigorously tested across different devices, browsers, and screen sizes to ensure optimal performance and responsiveness. HTML5’s flexibility makes it possible to build responsive sites that work across mobile, tablet, and desktop.
- Security Testing: HTML5 forms and data inputs are tested for security vulnerabilities, such as XSS (cross-site scripting) and CSRF (cross-site request forgery). HTTPS and SSL certifications are added for secure transmission of sensitive data.
- Performance Optimization: Page load speed, mobile responsiveness, and multimedia playback are tested to ensure the website meets modern performance standards. HTML5 features like lazy loading images and caching help improve website performance.
7. SEO Optimization
- On-Page SEO: HTML5 enables structured markup, which is crucial for SEO. Proper use of semantic tags like <header>, <nav>, and <section> helps search engines better understand the content hierarchy.
- Schema Markup: Integrating structured data or schema.org markup within HTML5 ensures better search engine visibility, helping sites appear as rich snippets in search results.
8. Deployment
- Hosting and Domain Setup: After testing, the site is deployed to a hosting server. Platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, or shared hosting providers are used depending on the size and traffic expectations of the site. The domain is configured, and SSL certificates are implemented for security.
- Version Control: Developers use tools like GitHub or Bitbucket for version control, allowing teams to collaborate efficiently and revert to previous versions if necessary.
9. Maintenance and Updates
- Ongoing Support: HTML5-based websites require regular maintenance, including content updates, security patches, and browser compatibility checks.
- Feature Enhancements: As technology evolves, new features or integrations, such as HTML5 APIs (like Web Workers or WebSockets), can be added to improve the functionality and interactivity of the site.
10. Troubleshooting in HTML5 Development
Troubleshooting is a critical skill in HTML5 web development, enabling developers to identify, diagnose, and resolve issues that may arise during the design and implementation phases. This section outlines common troubleshooting strategies and tips for effective problem-solving in HTML5 projects.
1. Common HTML5 Issues
- Browser Compatibility: One of the most frequent challenges developers face is ensuring that their HTML5 applications work consistently across different web browsers. Variations in support for HTML5 features can lead to inconsistent behavior. Developers should test their applications in multiple browsers, including Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge, to identify and address compatibility issues.
- Invalid Markup: Errors in HTML markup can cause rendering problems and hinder functionality. Developers should validate their HTML using tools like the W3C Markup Validation Service to catch syntax errors and ensure adherence to standards.
- JavaScript Errors: Many HTML5 features rely on JavaScript. Syntax errors or logic errors in JavaScript can lead to unexpected behavior. Utilizing browser developer tools can help in debugging JavaScript code and identifying runtime errors.
- CSS Conflicts: CSS styles can sometimes conflict, resulting in layout issues. Using browser developer tools to inspect elements and their computed styles can help identify conflicting styles and resolve them effectively.
2. Debugging Tools and Techniques
- Browser Developer Tools: Most modern browsers come equipped with developer tools that allow developers to inspect HTML elements, debug JavaScript, and analyze network requests. Familiarizing oneself with these tools is essential for effective troubleshooting.
- Console Logging: Using console.log() statements in JavaScript can help track the flow of execution and identify where errors may be occurring. This technique is invaluable for debugging complex functions and understanding the state of variables.
- Responsive Design Testing: With the increasing importance of responsive design, developers should test their applications on various screen sizes and devices. Emulators and responsive design tools can help simulate different environments and detect layout issues.
3. Documentation and Community Support
- Official Documentation: The HTML5 specification, as well as documentation from libraries and frameworks (like jQuery or Bootstrap), often provide insights into best practices and common pitfalls. Referencing these resources can aid in troubleshooting.
- Online Communities: Forums like StackOverflow and web development communities can be invaluable for troubleshooting. Developers can search for similar issues or ask questions to get help from experienced peers.
4. Best Practices for Troubleshooting
- Isolate the Problem: When encountering an issue, isolate the specific code or feature causing the problem. Commenting out sections of code can help narrow down the source of the issue.
- Stay Updated: Keeping abreast of updates to HTML5 specifications, browser changes, and best practices can prevent issues caused by deprecated features or changes in browser behavior.
- Document Solutions: Maintaining a troubleshooting log can be helpful for future reference. Documenting common issues and their resolutions can save time and effort on subsequent projects.
Key Takeaways
The HTML5 web development process involves planning, designing, coding, testing, and deploying web applications. It emphasizes user-centered design, leveraging HTML5 features for interactivity, ensuring cross-browser compatibility, and maintaining a focus on performance and accessibility.
12. Tips for Writing Clean and Organized HTML5 Code

Writing clean HTML5 code ensures your site is easy to maintain and performs well. This section covers some best practices for keeping your code structured, readable, and scalable.
Writing clean and well-organized HTML5 code is essential for maintaining readability, ease of collaboration, scalability, and ensuring that web pages perform optimally. Proper structure and formatting also make your code more accessible to search engines and assistive technologies, improving SEO and user experience. Here are some essential tips to follow when developing HTML5 websites:
1. Use Semantic HTML5 Elements
- HTML5 introduced several semantic elements like <article>, <section>, <header>, <footer>, and <nav>. These elements clearly define the structure of your content and make it easier for both developers and search engines to understand the page’s layout.
- Example: Instead of using multiple <div> tags for sections, use:
<article>
<header>
<h1>Article Title</h1>
</header>
<section>
<p>Article content goes here...</p>
</section>
<footer>
<p>Author information...</p>
</footer>
</article>2. Maintain Proper Indentation and Spacing
- Consistent indentation makes your code easier to read and debug. Use two or four spaces for indentation, and avoid using tabs to maintain consistency.
- Best Practice: Use an editor with auto-indentation features like Visual Studio Code, Sublime Text, or Atom.
3. Follow Naming Conventions
- Use meaningful, readable names for your class and ID attributes. Avoid cryptic or overly abbreviated names, and use hyphens to separate words in class names (e.g., main-navigation, article-content).
- Avoid: cls123, foo-bar
- Better: main-header, nav-bar
4. Use Comments Wisely
- Comments are essential for documenting complex sections of code, but avoid excessive or redundant comments. Clear code should largely explain itself, but well-placed comments improve collaboration and future maintenance.
- Example:
<!-- Main navigation for the website -->
<nav class="main-navigation">
...
</nav>5. Avoid Inline CSS and JavaScript
- Keep your HTML, CSS, and JavaScript separate. Inline styles or scripts clutter HTML and make it harder to maintain and scale your project.
- Avoid:
<p style="color: blue;">Hello World</p>- Better: Link to an external stylesheet or JavaScript file:
<link rel="stylesheet" href="styles.css">
<script src="scripts.js"></script>6. Use External Libraries Sparingly
While frameworks and libraries like Bootstrap or jQuery can speed up development, avoid over-reliance on them. Use only what you need to keep the page lightweight and reduce load times. HTML5 already provides many features natively.
7. Validate Your HTML5 Code
- Regularly check your code with the W3C HTML Validator to ensure it follows best practices and is free from syntax errors. Properly validated HTML5 code improves compatibility across browsers and platforms.
- Validator Link: W3C Validator
8. Optimize Images and Media
- Use proper <img> attributes, such as alt, and provide responsive image sizes. Leverage HTML5’s <picture> element for adaptive images based on screen sizes, and use appropriate formats like WebP for optimized performance.
- Example:
<picture>
<source srcset="image-small.webp" media="(max-width: 600px)">
<source srcset="image-large.webp" media="(min-width: 601px)">
<img src="image-large.jpg" alt="Example image">
</picture>9. Accessibility Best Practices
- Use accessible HTML attributes like aria-labels, and ensure all interactive elements, like buttons or form inputs, are keyboard navigable. Label form elements properly and use semantic elements to improve accessibility for users with disabilities.
- Example:
<button aria-label="Submit Form">Submit</button>10. Use Consistent HTML5 Doctype
Always start your HTML5 document with the proper doctype declaration to ensure browsers render the page in standards mode:
<!DOCTYPE html>Key Takeaways
To write clean and organized HTML5 code, use proper indentation and semantic elements, comment your code for clarity, and maintain a consistent naming convention. These practices enhance readability, facilitate collaboration, and simplify maintenance.
13. HTML5 Performance Optimization

Optimizing HTML5 for performance is critical for faster load times and a better user experience. This section covers techniques to enhance speed and efficiency in your HTML5 projects.
Optimizing performance is a key consideration in web development, and HTML5 offers several built-in features and best practices that can significantly improve the speed, efficiency, and overall performance of web applications. In this section, we’ll explore different strategies to enhance performance while developing HTML5 websites and web applications.
1. Minimizing HTTP Requests
- Reducing the number of HTTP requests a page makes can drastically improve load times. Combining JavaScript and CSS files, using image sprites, and minimizing the number of external resources help limit these requests.
- Best Practices:
- Combine multiple CSS files into one.
- Use inline SVGs instead of separate image files for small, simple graphics.
2. Leveraging HTML5’s Built-in Features
- HTML5 provides native multimedia support for audio and video, eliminating the need for external plugins like Flash, which adds extra load to web pages. Using HTML5’s <audio> and <video> tags reduces resource load and improves performance, especially on mobile devices.
- Example:
<video controls>
<source src="video.mp4" type="video/mp4">
Your browser does not support the video tag.
</video>3. Implementing Lazy Loading
- Lazy loading defers the loading of non-critical resources, such as images, until they are needed. HTML5 has a built-in attribute loading=”lazy” for images and iframes that helps improve page load speed by loading only the visible content.
- Example:
<img src="image.jpg" alt="example" loading="lazy">4. Using the <picture> Element for Responsive Images
- The <picture> element allows you to load different images depending on the viewport size. This means lower resolution images are served to mobile devices, while higher resolution images are reserved for larger screens. This technique reduces bandwidth usage and improves load times for mobile users.
- Example:
<picture>
<source media="(max-width: 600px)" srcset="small.jpg">
<source media="(min-width: 601px)" srcset="large.jpg">
<img src="default.jpg" alt="Responsive Image">
</picture>5. Web Storage and Caching
- HTML5’s Web Storage API (including localStorage and sessionStorage) allows websites to store data in the user’s browser. This enables faster access to data without the need to fetch it repeatedly from the server. Storing session data or preferences can improve the user experience and decrease server load.
- Example:
localStorage.setItem("username", "JohnDoe");
let user = localStorage.getItem("username");6. Reducing DOM Size
- A large Document Object Model (DOM) increases the time taken by browsers to parse HTML. Keeping the DOM size small by removing unnecessary divs and elements improves rendering performance.
- Best Practices:
- Use semantic tags efficiently to avoid bloating the DOM.
- Avoid deeply nested elements, which slow down page rendering.
7. CSS and JavaScript Minification
- Minifying CSS and JavaScript files involves removing unnecessary characters (such as whitespace, comments, and line breaks) from the code without affecting functionality. Minified files are smaller in size and thus faster to download.
- Best Practices:
- Use tools like UglifyJS for JavaScript and CSSNano for CSS minification.
8. Asynchronous Loading of JavaScript
- When JavaScript is loaded synchronously, it blocks the page rendering process until the entire script is loaded. By using the async or defer attributes on the <script> tag, the browser can load JavaScript files without blocking the rest of the page.
- Example:
<script src="script.js" async></script>9. Gzip Compression
- Compressing files using Gzip reduces the size of your HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files, speeding up their delivery to the client’s browser. Most modern browsers and servers support Gzip compression.
- Best Practices:
- Enable Gzip compression on your server to reduce file sizes.
10. Using Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
- CDNs store copies of your website’s static assets (CSS, JavaScript, images) on servers across the world, ensuring users can download resources from the server closest to their location, improving load times.
- Best Practices:
- Use popular CDNs like Cloudflare or AWS CloudFront to host static assets.
By following these performance optimization techniques, developers can ensure that their HTML5 websites deliver a smooth and fast user experience, leading to better engagement and higher conversions.
Key Takeaways
HTML5 optimizes performance through efficient coding practices, reduced page load times, and the use of asynchronous loading for scripts. Implementing features like lazy loading for images and leveraging browser caching further enhances the user experience by delivering faster, more responsive web applications.
HTML5 and Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is a critical aspect of web development that ensures a website ranks well in search engine results, improving visibility and organic traffic. HTML5 offers several features that contribute to better SEO performance.
1. Semantic Markup for Improved Crawling
- HTML5 introduces semantic elements like <header>, <footer>, <article>, and <section>, which help search engines understand the structure and content of a webpage better. This semantic clarity improves the website’s crawlability and enhances how search engines interpret the relevance of your content.
- Example:
<article>
<header>
<h1>HTML5 and SEO Benefits</h1>
</header>
<section>
<p>SEO is crucial for any website’s success, and HTML5 helps by offering semantic markup...</p>
</section>
<footer>Author: John Doe</footer>
</article>2. Faster Page Load Speed
- Speed is a ranking factor in SEO. HTML5 improves page load times by allowing native multimedia support (reducing reliance on external plugins) and enabling optimizations like lazy loading of images. Faster websites generally rank higher in search engines.
- Example:
<img src="image.jpg" alt="SEO Tips" loading="lazy">3. Mobile-Friendliness with Responsive Design
- With mobile-first indexing, search engines prioritize websites that are optimized for mobile devices. HTML5 facilitates responsive design through the use of the <meta name=”viewport”> tag and media queries in CSS3, improving the user experience across devices and contributing to better SEO.
- Example:
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">4. Enhanced Accessibility for SEO
HTML5’s support for accessibility features like ARIA (Accessible Rich Internet Applications) improves how search engines understand content. When websites are accessible, they tend to rank higher, as search engines recognize them as user-friendly.
Key Takeaways
HTML5 enhances SEO by promoting semantic markup, which helps search engines better understand content structure. Features like improved multimedia handling and faster load times also contribute to higher search rankings, making HTML5 vital for optimizing web visibility.
HTML5 and Web Analytics
Web analytics allows developers and businesses to track visitor behavior and make data-driven decisions. HTML5 contributes to better data tracking by integrating well with web analytics tools and offering features that enhance data collection.
1. Improved User Interaction Tracking
HTML5 APIs, such as the History API, enable websites to track user interactions more accurately without needing to reload the entire page, especially in Single Page Applications (SPAs). This provides better insight into user behavior, which is essential for analytics.
2. Custom Data Attributes for Tracking
- HTML5’s data-* attributes allow developers to add custom, trackable data to elements. This can be extremely useful for web analytics platforms, enabling tracking of specific user interactions.
- Example:
<button data-product-id="12345" data-action="click">Buy Now</button>3. Session Management with Web Storage API
HTML5’s Web Storage API (localStorage and sessionStorage) allows for more sophisticated session management and tracking. By storing information locally on the client-side, web analytics tools can access and monitor session data without needing to rely on cookies alone.
4. Tracking Engagement through Multimedia
HTML5’s native support for multimedia elements such as <video> and <audio> makes it easier to track user engagement with rich media content. Analytics tools can easily monitor how long users watch videos or interact with audio on the site.
Key Takeaways
HTML5 improves web analytics by facilitating richer data collection through advanced APIs and user interaction tracking. This capability allows developers to gather insights on user behavior and engagement, enabling informed decisions for enhancing user experience and optimizing content.
14. HTML5 in Specialized Applications

HTML5’s versatility allows it to be used in specialized applications, from e-commerce platforms to educational tools. This section explores how HTML5 adapts to a wide range of industry needs.
HTML5 has proven itself to be a versatile and powerful tool, not just for traditional web development, but also for a wide range of specialized applications across industries. This section highlights how HTML5 is applied in various sectors, including e-commerce, education, enterprise, and digital marketing.
HTML5 for E-commerce and Online Sales
HTML5 has had a significant impact on the e-commerce landscape by enabling the creation of fast, responsive, and secure online stores. Here’s how HTML5 benefits e-commerce businesses:
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: HTML5 allows e-commerce websites to perform seamlessly across multiple devices, from desktops to smartphones and tablets. This is vital for online stores, where mobile commerce is growing rapidly.
- Improved User Experience (UX): With HTML5’s rich media support (video, audio, and interactive elements), e-commerce websites can offer a better shopping experience by including product demos, tutorials, and virtual tours.
- Offline Capabilities for Shopping Apps: The HTML5 Service Worker API can be used to enable offline functionality in Progressive Web Apps (PWAs), allowing customers to browse products and add items to carts even when they’re offline.
Key Takeaway: HTML5 enables responsive, feature-rich e-commerce websites that enhance user engagement and streamline the purchasing process, whether on a desktop or mobile device.
HTML5 for Digital Marketing
HTML5 is a powerful tool for creating interactive and engaging digital marketing campaigns. Here’s how it impacts this field:
- Interactive Ads: HTML5 allows for the creation of rich, animated advertisements that can capture attention without relying on external plugins like Flash. Marketers can create interactive ads that adapt to different devices and screen sizes.
- Personalized Experiences: Using HTML5 APIs, marketers can tailor web content dynamically based on user behavior, location, and preferences, enhancing personalization in marketing strategies.
- Cross-Device Campaigns: HTML5 ensures that marketing content, from banners to videos, works consistently across all platforms, allowing for unified digital marketing strategies.
Key Takeaway: HTML5 helps marketers build immersive, interactive digital campaigns that offer personalized experiences and engage users across multiple devices.
Building HTML5 Email Templates
HTML5 is transforming email marketing by enabling developers to create dynamic, engaging email templates that work across devices. Key benefits include:
- Responsive Emails: HTML5 ensures that emails are fully responsive, adjusting their layout based on the user’s device, improving click-through rates and user engagement.
- Interactive Elements: Marketers can embed interactive elements like image carousels, forms, and even video directly into emails without users needing to visit an external website.
- Lightweight Code: HTML5 email templates often result in cleaner, faster-loading emails, which can improve deliverability and engagement rates.
Key Takeaway: HTML5 allows businesses to design interactive, responsive, and dynamic email campaigns, making email marketing more engaging and effective.
HTML5 for Education and E-learning
HTML5 is reshaping the education and e-learning sector by making it easier to deliver interactive and multimedia-rich content. Key applications include:
- Interactive Learning Modules: HTML5 supports the creation of interactive lessons with features like drag-and-drop activities, quizzes, and multimedia content that make learning more engaging.
- Cross-Platform Learning: E-learning platforms built with HTML5 can be accessed across devices, ensuring students can learn anywhere, anytime, on any device.
- Offline Learning: By utilizing Service Workers, HTML5-based learning apps can offer offline access, allowing students to download and access course content without an internet connection.
Key Takeaway: HTML5 empowers educators and developers to create cross-platform, interactive e-learning solutions that cater to modern learners’ needs, both online and offline.
Building Interactive Storytelling Websites with HTML5
HTML5’s ability to handle multimedia and complex interactions makes it ideal for creating interactive storytelling websites. Whether for entertainment, education, or journalism, HTML5 enhances the user experience with:
- Multimedia Integration: By embedding audio, video, and images, HTML5 allows for a rich, multimedia storytelling experience. Websites can include interactive timelines, video backdrops, and animations that guide users through a narrative.
- Enhanced User Engagement: HTML5’s animation capabilities, combined with CSS3 and JavaScript, enable developers to create immersive storytelling environments that captivate audiences.
- Mobile-Friendly Storytelling: Since HTML5 is fully responsive, stories presented through this technology are accessible and visually stunning across all devices.
Key Takeaway: HTML5 brings stories to life with interactive multimedia elements, providing engaging and immersive storytelling experiences that work across devices.
HTML5 in Enterprise Applications
In the enterprise sector, HTML5 is used to develop robust, scalable applications for business operations, employee management, and client relations:
- Cross-Platform Enterprise Apps: HTML5 enables the development of cross-platform enterprise apps that work seamlessly across different operating systems and devices, allowing businesses to run unified systems.
- Streamlined Collaboration Tools: HTML5’s real-time communication capabilities (via WebSockets) enhance collaboration tools, enabling faster and more efficient communication across global teams.
- Data-Intensive Applications: HTML5, with its Web Storage API and offline capabilities, can support the development of enterprise-grade data management applications, ensuring reliable performance even with large datasets.
Key Takeaway: HTML5 provides the backbone for creating scalable, data-driven enterprise applications that operate efficiently across platforms.
These specialized applications demonstrate HTML5’s flexibility and capacity to cater to diverse business needs beyond basic web development.
Key Takeaways
HTML5 excels in specialized applications such as e-commerce, digital marketing, and education by providing interactive features and multimedia support. Its capabilities enhance user engagement and functionality, making it ideal for creating tailored solutions across various industries.
15. HTML5 for Business and Strategy

HTML5 offers significant business benefits, from reducing development costs to improving user engagement. This section will show you how to align your business strategy with HTML5’s capabilities for maximum impact.
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, HTML5 has emerged as a pivotal technology for businesses looking to innovate and stay competitive. This section explores how businesses can leverage HTML5 to drive growth, enhance customer experiences, and optimize their digital strategies.
HTML5 for Business Growth and Marketing
HTML5 plays a crucial role in enhancing marketing strategies and driving business growth. Here’s how:
- Rich User Experiences: HTML5 enables businesses to create visually engaging and interactive websites and applications. By utilizing features like animations, multimedia, and responsive design, companies can capture and retain users’ attention, leading to higher conversion rates.
- Cost-Effective Development: HTML5 allows for a single codebase to be used across multiple platforms (web, mobile, and desktop), reducing development time and costs. Businesses can save resources by developing once and deploying everywhere, rather than creating separate applications for different platforms.
- Improved Analytics and Feedback: HTML5’s capabilities allow for enhanced tracking and analytics integration. Businesses can gather valuable insights on user behavior, enabling data-driven decisions to optimize marketing strategies and product offerings.
Key Takeaway: HTML5 empowers businesses to create engaging, cost-effective solutions that drive growth and provide actionable insights through improved analytics.
Choosing the Right HTML5 Development Partner for Businesses
Selecting the right development partner is critical for businesses looking to implement HTML5 solutions. Consider the following factors:
- Expertise and Experience: Look for a partner with a proven track record in HTML5 development. They should have a portfolio showcasing their ability to build responsive, interactive applications tailored to your industry.
- Understanding of Business Needs: The ideal development partner should prioritize understanding your business goals and target audience, ensuring that the HTML5 solutions align with your overall strategy.
- Post-Launch Support: Choose a partner that offers ongoing support and maintenance after the launch. This ensures that any issues are promptly addressed and that your applications remain updated with the latest HTML5 features and best practices.
Key Takeaway: Finding a knowledgeable and reliable HTML5 development partner is essential for businesses to successfully implement and sustain their digital strategies.
In-House vs. Outsourcing HTML5 Development
Deciding whether to build an in-house team or outsource HTML5 development is a significant consideration for businesses:
- In-House Development:
- Pros: Greater control over the development process, easier communication, and alignment with company culture.
- Cons: Higher overhead costs, longer recruitment times, and potential skills gaps if the team lacks specific HTML5 expertise.
- Outsourcing Development:
- Pros: Access to a broader talent pool, cost savings, and the ability to scale development efforts quickly. Outsourcing can provide access to specialized skills without the long-term commitment of hiring full-time staff.
- Cons: Potential communication challenges, time zone differences, and less direct control over the development process.
Key Takeaway: Businesses must weigh the pros and cons of in-house versus outsourced HTML5 development to determine which approach best aligns with their goals and resources.
The ROI of HTML5 for Businesses
Understanding the return on investment (ROI) associated with HTML5 initiatives is crucial for justifying development costs:
- Increased Efficiency: HTML5’s ability to enable cross-platform compatibility can lead to reduced development times and costs, contributing to overall business efficiency.
- Higher Conversion Rates: Engaging and interactive web experiences facilitated by HTML5 can lead to improved user engagement and higher conversion rates, directly impacting revenue.
- Long-Term Sustainability: As technology evolves, HTML5’s adaptability ensures that businesses can continue to innovate without needing complete overhauls of their existing systems, providing long-term cost savings.
Key Takeaway: The ROI from HTML5 investments can be substantial, driven by efficiencies, increased engagement, and long-term adaptability to changing market needs.
HTML5 in Digital Transformation for Businesses
HTML5 is a fundamental component of digital transformation strategies. Here’s how it contributes:
- Modernizing Legacy Systems: HTML5 allows businesses to update or replace outdated systems with modern web applications, improving functionality and user experience without starting from scratch.
- Enabling Omnichannel Experiences: HTML5 facilitates the creation of seamless omnichannel experiences, allowing customers to interact with a brand across various platforms and devices without losing continuity.
- Driving Innovation: With its robust features, HTML5 encourages experimentation and innovation. Businesses can develop new applications and services that meet emerging customer needs and market trends.
Key Takeaway: HTML5 is vital for businesses undergoing digital transformation, providing the tools needed to modernize, innovate, and create cohesive customer experiences across platforms.
Key Takeaways
HTML5 empowers businesses by enhancing user engagement, improving accessibility, and reducing development costs through cross-platform compatibility. Its strategic implementation can drive growth, streamline operations, and strengthen online presence, making it a valuable asset for modern business strategies.
16. Security, Privacy, and Compliance in HTML5

Security is paramount in web development, and HTML5 introduces several features to help. This section explores how HTML5 improves security while ensuring compliance with privacy standards.
As HTML5 becomes a fundamental technology for web applications, addressing security, privacy, and compliance issues is paramount. This section delves into the security features of HTML5, best practices for safeguarding data, and compliance with regulations.
HTML5 Security Best Practices
Ensuring the security of web applications developed with HTML5 requires a comprehensive approach. Here are the essential best practices:
- Use HTTPS: Always serve HTML5 applications over HTTPS to encrypt data in transit. This protects against man-in-the-middle attacks and ensures the integrity and confidentiality of user data.
- Input Validation and Sanitization: Validate and sanitize all user inputs to prevent common vulnerabilities like Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) and SQL Injection attacks. HTML5 provides form validation features that can be utilized for input checks.
- Content Security Policy (CSP): Implementing a Content Security Policy helps prevent XSS attacks by specifying which sources of content are trusted. This reduces the risk of unauthorized scripts being executed on your web pages.
Key Takeaway: Adopting best practices such as using HTTPS, validating inputs, and implementing CSP is crucial for securing HTML5 applications.
Security Benefits for Businesses Using HTML5
HTML5 offers several built-in security features that benefit businesses:
- Sandboxing: HTML5 provides the ability to create sandboxed environments for web applications, isolating them from the rest of the browser and limiting their access to system resources. This enhances security by containing potential threats.
- Same-Origin Policy: This policy restricts how documents or scripts loaded from one origin can interact with resources from another origin, helping to prevent malicious activities.
- Web Cryptography API: HTML5 includes APIs that allow developers to implement cryptographic functions, enabling secure data storage and transmission. Businesses can leverage this for encrypting sensitive information.
Key Takeaway: HTML5’s built-in security features, such as sandboxing and the Web Cryptography API, provide businesses with enhanced protection for their web applications.
HTML5 for Secure Forms and Transactions
When it comes to handling forms and online transactions, HTML5 offers tools to enhance security:
- Secure Input Types: HTML5 introduces new input types such as email, URL, and password, which help enforce proper formatting and security measures automatically.
- Form Validation: HTML5’s form validation features allow for real-time feedback on user inputs, reducing the risk of submission errors and enhancing security by ensuring that data meets specified criteria before being sent to the server.
- Tokenization: For sensitive transactions, HTML5 can be used in conjunction with tokenization methods to replace sensitive data with unique identifiers, minimizing the risk of data breaches.
Key Takeaway: HTML5 provides robust features for securing forms and online transactions, including secure input types and real-time validation.
Ethics and Privacy in HTML5 Web Development
With increasing concerns about user privacy, ethical considerations in HTML5 web development are more important than ever:
- User Consent: It’s essential to obtain explicit user consent before collecting or processing their personal data. This aligns with regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
- Data Minimization: Collect only the data necessary for the application’s functionality. Limiting data collection reduces risks associated with data breaches and misuse.
- Transparency: Clearly communicate how user data will be used, stored, and protected. This builds trust with users and enhances compliance with privacy regulations.
Key Takeaway: Ethical practices in HTML5 development, including obtaining user consent and data minimization, are vital for maintaining privacy and compliance.
Compliance with Regulations
Businesses must ensure that their HTML5 applications comply with relevant regulations to avoid legal issues and penalties:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): This regulation requires businesses operating in the EU or handling EU citizens’ data to follow strict data protection protocols. HTML5 applications must be designed to facilitate user rights such as access, rectification, and erasure of personal data.
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA): Similar to GDPR, CCPA gives California residents specific rights regarding their personal data. HTML5 applications should implement mechanisms to comply with these rights.
- Accessibility Standards: Compliance with accessibility standards, such as the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG), ensures that HTML5 applications are usable by individuals with disabilities, promoting inclusivity.
Key Takeaway: Compliance with data protection regulations like GDPR and CCPA is essential for businesses using HTML5, as is ensuring accessibility for all users.
By addressing security, privacy, and compliance proactively, businesses can build trust with their users while creating robust and secure HTML5 applications.
Key Takeaways
HTML5 enhances security through features like sandboxing for iframes and secure context requirements for sensitive APIs. However, developers must also implement best practices for data privacy and comply with regulations, ensuring user data protection and building trust in web applications.
17. Cutting-Edge Technologies and HTML5
HTML5 works alongside JavaScript APIs and libraries that enable technologies such as VR, AR, AI, and blockchain on the web, opening new possibilities for the web. This section explores how HTML5 is driving innovation in the digital space.
HTML5 remains a foundational component of modern web development, enabling developers to create modern, interactive, and immersive applications. This section explores how HTML5 integrates with cutting-edge technologies to enhance user experiences and drive innovation.
HTML5 and Data Visualization
Data visualization is a powerful tool for interpreting complex information. HTML5 offers several features that facilitate effective data presentation:
- Canvas Element: The <canvas> element allows developers to draw graphics on the fly using JavaScript. This is ideal for creating dynamic charts and graphs that can update in real-time based on user interactions or incoming data.
- SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics): SVG is a markup language for describing two-dimensional graphics. Modern browsers support SVG alongside HTML5.
- Integration with Libraries: JavaScript libraries such as D3.js and Chart.js operate on HTML and SVG elements, which provide powerful tools for creating complex and interactive data visualizations.
Key Takeaway: HTML5 enhances data visualization capabilities, making it easier to create dynamic and interactive representations of complex data sets.
HTML5 and Virtual/Augmented Reality (VR/AR)
Virtual and augmented reality technologies are revolutionizing how users interact with digital content, and HTML5 plays a significant role in this evolution:
- WebXR API: The WebXR API, accessed via JavaScript, enables immersive VR and AR experiences in the browser. This API provides a unified interface for accessing VR and AR devices, simplifying the development process.
- Interactive Environments: HTML5’s multimedia capabilities allow for the integration of audio, video, and graphics, creating rich and engaging environments for VR and AR applications.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: By leveraging HTML5, developers can create VR and AR experiences that are accessible across various devices and platforms without the need for additional installations or downloads.
Key Takeaway: HTML5 provides the structural layer for VR and AR experiences delivered through WebXR and JavaScript APIs, broadening the scope of interactive applications available on the web.
HTML5 and Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI-powered web applications use JavaScript-based machine learning libraries that operate within HTML5-based interfaces, allowing for smarter, more personalized experiences:
- Machine Learning Libraries: HTML5 can be used in conjunction with JavaScript libraries like TensorFlow.js to implement machine learning models directly in the browser. This allows developers to build intelligent applications that can learn from user interactions.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Web applications built with HTML5 interfaces can integrate AI-driven NLP services to enhance user interfaces, enabling features like chatbots, voice recognition, and sentiment analysis.
- Data-Driven Insights: HTML5 applications can utilize AI to analyze user data and behavior, allowing businesses to tailor content and experiences to individual preferences, thus improving engagement and satisfaction.
Key Takeaway: HTML5 empowers developers to create intelligent applications by integrating AI technologies, enhancing user experiences through personalization and data-driven insights.
HTML5 and the Internet of Things (IoT)
As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to expand, HTML5 is increasingly used to connect devices and enable seamless interactions:
- WebSockets: Web applications can use WebSockets via JavaScript to enable real-time IoT communication, which facilitates real-time, two-way communication between devices and servers. This is crucial for IoT applications that require instant data exchange.
- Device Access: Browser APIs allow web applications to access device capabilities, with HTML5 providing the interface layer.
- Data Visualization for IoT: HTML5’s data visualization features allow developers to present IoT data in a user-friendly manner, making it easier to monitor and analyze information from connected devices.
Key Takeaway: HTML5 serves as a vital component in the development of IoT applications, enabling real-time communication and enhancing the interconnectivity of devices.
HTML5 and Blockchain Technology
The integration of blockchain technology with HTML5 opens up new possibilities for secure and transparent web applications:
- Decentralized Applications (dApps): HTML5 can be used to build dApps that run on blockchain networks. These applications offer enhanced security and transparency, as they operate on a decentralized ledger.
- Smart Contracts: HTML5 applications can interact with smart contracts, enabling automated and self-executing agreements. This streamlines transactions and reduces the need for intermediaries.
- Tokenization: HTML5 can facilitate the development of applications that leverage tokenization for digital assets, enhancing security and enabling new business models.
Key Takeaway: HTML5 is instrumental in the development of blockchain-based applications, providing secure, decentralized, and innovative solutions for various industries.
Key Takeaways
HTML5 integrates seamlessly with cutting-edge technologies like WebAssembly, AI, and IoT, enabling developers to create high-performance applications and interactive experiences. Its adaptability fosters innovation, making it a crucial framework for future web advancements and smart technologies.
18. Tools and Best Practices in HTML5 Development

Efficient development requires the right tools and practices. In this section, we’ll introduce popular tools and frameworks that simplify HTML5 development and ensure high-quality results.
HTML5 web development has evolved into a robust field, thanks to a plethora of tools and best practices that streamline the development process. This section covers essential tools for HTML5 development and best practices to ensure code quality, maintainability, and performance.
HTML5 Development Tools and Frameworks
Using the right tools can significantly enhance productivity and efficiency in HTML5 web development. Here are some of the most popular development tools and frameworks:
- Text Editors and IDEs:
- Visual Studio Code: A widely used code editor that supports HTML5 development with extensions for linting, syntax highlighting, and integrated terminal support.
- Sublime Text: Known for its speed and responsiveness, Sublime Text offers a distraction-free writing mode and numerous packages for HTML5 development.
- Atom: An open-source editor developed by GitHub that provides a hackable environment for customizing your HTML5 development experience.
- Frameworks and Libraries:
- Bootstrap: A front-end framework that simplifies responsive web design using HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScript components.
- jQuery: A JavaScript library that simplifies DOM manipulation, event handling, and AJAX calls, making it easier to work with HTML5 elements.
- React, Angular, and Vue.js: These modern JavaScript frameworks facilitate building dynamic web applications by enabling the development of reusable components.
- Version Control Systems:
- Git: Essential for tracking changes in your HTML5 codebase, Git allows for collaboration among developers and helps manage project versions efficiently.
- GitHub and GitLab: Platforms that host Git repositories, offering additional features like issue tracking, code reviews, and CI/CD pipelines.
Key Takeaway: Utilizing robust development tools and frameworks enhances productivity and code quality in HTML5 web development.
HTML Editors
HTML editors provide a focused environment for writing and editing HTML5 code. The choice of editor can impact the development workflow:
- WYSIWYG Editors:
- Adobe Dreamweaver: A popular WYSIWYG editor that offers visual design capabilities alongside code editing, allowing developers to see the impact of changes in real-time.
- Microsoft Expression Web: Another WYSIWYG editor that supports HTML5 development, providing design tools and CSS styling features.
- Code-Focused Editors:
- Brackets: An open-source code editor specifically designed for web development, featuring live preview capabilities for HTML5 changes.
- Notepad++: A lightweight code editor that supports multiple programming languages and provides essential features for HTML5 development.
Key Takeaway: Choosing the right HTML editor can streamline the coding process, whether through WYSIWYG features or advanced code editing capabilities.
Automated Testing for HTML5
Automated testing is crucial for ensuring the quality and functionality of HTML5 applications. Here are key tools and practices:
- Unit Testing Frameworks:
- Jest: A delightful JavaScript testing framework for testing UI components, making it suitable for HTML5 applications built with libraries like React.
- Mocha: A flexible testing framework that supports asynchronous testing, ideal for testing HTML5 features and APIs.
- End-to-End Testing Tools:
- Selenium: A widely used tool for automating web browsers, enabling testing of HTML5 applications across different browsers and devices.
- Cypress: A modern end-to-end testing framework that provides fast and reliable testing for web applications, with an easy-to-use interface.
- Performance Testing Tools:
- Lighthouse: An open-source tool from Google that helps assess the performance, accessibility, and SEO of HTML5 applications.
- WebPageTest: A tool that allows you to test the performance of your HTML5 applications in various browsers and devices, providing detailed reports on load times and resource usage.
Key Takeaway: Implementing automated testing ensures the functionality and performance of HTML5 applications while reducing manual testing efforts.
Versioning HTML5 Standards
Maintaining awareness of HTML5 standards and best practices is crucial for developers. Here’s how to manage versioning effectively:
- Stay Updated with W3C and WHATWG: Follow the latest developments and changes to HTML5 specifications from the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) and the Web Hypertext Application Technology Working Group (WHATWG).
- Use Semantic Versioning: Implement semantic versioning (SemVer) for your HTML5 projects to communicate changes clearly. This includes major, minor, and patch updates to signal backward-incompatible changes, new features, or bug fixes.
- Documentation and Changelog: Maintain thorough documentation and changelogs for your HTML5 projects to track changes over time, making it easier for team members to understand modifications.
Key Takeaway: Keeping abreast of HTML5 standards and utilizing semantic versioning enhances project organization and clarity.
Continuous Deployment and Automation in HTML5
Continuous deployment and automation can greatly streamline the HTML5 development process:
- CI/CD Tools:
- Jenkins: An open-source automation server that supports continuous integration and continuous deployment for HTML5 applications.
- CircleCI: A cloud-based CI/CD tool that automates the testing and deployment process, integrating seamlessly with GitHub repositories.
- Build Tools:
- Webpack: A module bundler that packages JavaScript applications, optimizing resources for HTML5 applications and improving load times.
- Gulp: A task runner that automates repetitive tasks such as minification, compilation, and image optimization, enhancing the development workflow.
Key Takeaway: Leveraging CI/CD tools and build automation streamlines the development process, improving efficiency and deployment speed for HTML5 applications.
Key Takeaways
Effective HTML5 development relies on tools like code editors, version control systems, and testing frameworks. Following best practices such as using semantic markup, optimizing performance, and ensuring cross-browser compatibility leads to cleaner code, enhanced collaboration, and improved user experiences.
19. HTML5 Web Development Books

For those looking to deepen their understanding of HTML5, numerous books offer valuable insights. This section explores essential reads for mastering HTML5 web development.
Books remain one of the best resources for learning and mastering HTML5 web development. Whether you’re a beginner looking to grasp the fundamentals or an experienced developer seeking to deepen your knowledge, the following titles offer valuable insights, practical examples, and comprehensive guidance on HTML5 and its applications.
1. “Web Development & Design Foundations With HTML5” by Dr. Terry Ann Felke-Morris
This ever-popular book, now in its 10th edition, is one of the most popular courses on web development. It includes chapters on Responsive Page Layout, up-to-date coverage of HTML5 elements and attributes, code samples, case studies, and various web resources. Furthermore, this book has a companion website that includes a page for each chapter with the links for the URLs shared in the textbook. Thus, Web Development & Design Foundations With HTML5 by Dr. Terry Ann Felke-Morris is widely used in the classroom.
2. “Introduction to Web Development Using HTML 5” by Kris Jamsa
Introduction to Web Development Using HTML5 is a book that offers a practical approach that empowers novice web developers to craft their very first web pages while enabling seasoned professionals to swiftly grasp the intricacies of HTML5. Packed with numerous real-world examples, this resource begins by familiarizing readers with standard HTML and its application in building classic websites. Throughout this journey, the book guides developers in formatting and styling their pages using Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and introduces automation techniques with JavaScript and jQuery.
3. “HTML5 and CSS3 All-in-One For Dummies” by Andy Harris
This accessible guide combines HTML5 and CSS3 in one comprehensive resource. It includes step-by-step instructions, examples, and tips for developing responsive web applications. The “For Dummies” series is known for its friendly, approachable style, making it suitable for readers of all skill levels.
4. “HTML5: Up and Running” by Mark Pilgrim
Mark Pilgrim’s book offers a quick introduction to the new features of HTML5. It’s great for developers who are already familiar with previous HTML versions and want to get up to speed with HTML5. The book covers practical applications, including offline web applications and the use of various APIs.
5. “HTML5 Cookbook” by Christopher Schmitt and Sarah Horton
This book is structured as a collection of recipes for solving common web development problems using HTML5. It covers a wide range of topics, from building forms to integrating multimedia and using APIs, making it a practical reference for developers looking for quick solutions.
6. “Pro HTML5 with Visual Studio 2015” by Bruce Johnson
Aimed at developers familiar with Visual Studio, this book focuses on leveraging HTML5 with the IDE. It covers everything from building mobile applications to using new HTML5 features effectively within the Visual Studio environment, making it ideal for those in the Microsoft ecosystem.
7. “HTML5: The Definitive Guide” by Chuck Musciano and Bill Kennedy
This comprehensive guide serves as a reference for experienced developers. It delves deeply into the intricacies of HTML5, providing insights into its features, APIs, and best practices. The book is ideal for those looking to master HTML5 in a professional context.
8. “HTML5 for Web Designers” by Jeremy Keith and Rachel Andrew
This book is geared toward web designers who want to understand HTML5 without diving deep into programming. It emphasizes the design aspects of HTML5 and includes practical tips for using new elements and attributes effectively.
9. “HTML5: The Missing Manual” by Matthew MacDonald
This book is a part of the well-known Missing Manual series and is ideal for beginners. It covers everything from basic HTML5 structure to advanced features, including multimedia, APIs, and forms. MacDonald’s clear explanations and practical examples make it easy to understand and apply the concepts.
10. “Learning Web Design: A Beginner’s Guide to HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and Web Graphics” by Jennifer Niederst Robbins
A comprehensive guide for those new to web design, this book covers not only HTML5 but also CSS and JavaScript. Robbins provides clear explanations, hands-on exercises, and practical tips for creating visually appealing and functional web pages.
20. Enhancing User Experience with HTML5

User experience is at the heart of modern web development, and HTML5 provides the tools to enhance it. This section covers how HTML5 features help create seamless, intuitive user interactions.
User experience (UX) is a critical aspect of web development, directly impacting how users interact with a website or application. HTML5 offers a wealth of features that can significantly enhance UX, making it more engaging, accessible, and interactive. This section explores various strategies and techniques for improving user experience using HTML5.
HTML5 and Micro-Interactions
Micro-interactions are small, subtle animations or design elements that enhance the user’s experience by providing feedback and guiding interactions. Here’s how HTML5 supports micro-interactions:
- CSS Transitions and Animations: HTML5 allows developers to use CSS for creating smooth transitions and animations, which can be applied to buttons, forms, and other UI elements. This visual feedback can make actions feel more responsive and engaging.
- JavaScript Event Listeners: By utilizing JavaScript to handle events, developers can create dynamic interactions, such as hover effects or notifications, that react to user inputs in real-time.
- User Feedback: Micro-interactions can inform users about successful actions (e.g., form submissions) or errors (e.g., invalid inputs), improving the overall clarity of the interface.
Key Takeaway: Micro-interactions enhance user experience by providing feedback and creating a more engaging and interactive interface through HTML5’s animation and event capabilities.
HTML5 and Web Accessibility Initiatives (WAI)
Accessibility is a crucial component of user experience, ensuring that web content is usable by individuals with disabilities. HTML5 includes several features that facilitate accessibility:
- Semantic Elements: HTML5 introduces semantic elements (e.g., <header>, <footer>, <article>) that help screen readers and assistive technologies better understand the structure and meaning of web content.
- ARIA (Accessible Rich Internet Applications) Roles: Developers can use ARIA roles and attributes to enhance the accessibility of dynamic content and user interface components, making them more navigable for users relying on assistive technologies.
- Keyboard Navigation: HTML5 enables the implementation of keyboard shortcuts and navigation, ensuring that all users, including those who cannot use a mouse, can access the website’s features.
Key Takeaway: HTML5 enhances web accessibility through semantic elements and ARIA roles, ensuring a more inclusive user experience for all individuals.
Personalization in E-commerce with HTML5
Personalization improves user experience by tailoring content and interactions to individual preferences. HTML5 supports various strategies for creating personalized experiences in e-commerce:
- User Data Storage: HTML5’s Web Storage API allows developers to store user preferences and session data on the client side, enabling personalized content delivery without requiring server requests.
- Dynamic Content Loading: With AJAX and the Fetch API, HTML5 applications can load personalized content dynamically based on user behavior, enhancing engagement and reducing load times.
- Recommendation Systems: By leveraging data analytics, developers can implement recommendation systems that suggest products or content based on users’ past behavior, creating a more relevant shopping experience.
Key Takeaway: HTML5 supports personalization in e-commerce by enabling user data storage and dynamic content loading, resulting in a tailored shopping experience.
HTML5 and Responsive Web Design
Responsive web design (RWD) ensures that websites function well across a variety of devices and screen sizes. HTML5 plays a vital role in creating responsive designs:
- Flexible Grid Layouts: HTML5 combined with CSS3 enables developers to create fluid grid layouts that adjust seamlessly to different screen sizes, ensuring optimal display on desktops, tablets, and smartphones.
- Media Queries: CSS media queries allow developers to apply different styles based on device characteristics, such as screen width or resolution, ensuring that users have a consistent experience across all devices.
- Viewport Meta Tag: The viewport meta tag helps control the layout on mobile browsers, allowing developers to set the scaling and dimensions of web content to improve readability and usability on smaller screens.
Key Takeaway: HTML5 enhances responsive web design by enabling flexible layouts and media queries, ensuring a consistent user experience across all devices.
Key Takeaways
HTML5 significantly enhances user experience by offering interactive features, responsive design, and multimedia support. These capabilities create engaging, intuitive interfaces that improve usability, accessibility, and overall satisfaction, making web applications more appealing and user-friendly.
21. Future of HTML5 Web Development

HTML5 continues to evolve, with new updates and emerging trends shaping the future of web development. This section explores what lies ahead for HTML5 and the web so you can be stay ahead of the curve.
The landscape of web development is continually evolving, and HTML5 remains at the forefront of this transformation. As technology advances, HTML5 is expected to adapt and grow, leading to new possibilities for developers and users alike. This section explores anticipated trends, emerging technologies, and the future direction of HTML5 web development.
Trends in HTML5 Web Development
As HTML5 continues to mature, several trends are shaping its future, impacting how developers approach web projects:
- Increased Adoption of Progressive Web Apps (PWAs): PWAs, which combine the best of web and mobile applications, are becoming increasingly popular. HTML5 plays a critical role in enabling offline capabilities, push notifications, and responsive design, making PWAs a viable alternative to traditional native applications.
- Focus on Performance Optimization: With user experience as a top priority, there will be a greater emphasis on optimizing HTML5 applications for speed and performance. Techniques such as code splitting, lazy loading, and minimizing resource sizes will become standard practices.
- Rise of WebAssembly: WebAssembly (Wasm) is emerging as a game-changer in web development. It allows developers to run code written in languages like C, C++, and Rust alongside HTML5, enabling performance-intensive applications (e.g., games and complex simulations) to run directly in the browser.
Key Takeaway: The future of HTML5 web development will see increased adoption of PWAs, a focus on performance optimization, and the integration of WebAssembly for enhanced application capabilities.
HTML5 and WebAssembly
WebAssembly is set to revolutionize web development by providing a way to run high-performance code in the browser. This technology complements HTML5 by:
- Enabling Performance-Intensive Applications: WebAssembly allows developers to write computationally heavy applications that run efficiently in browsers, making it possible to create complex games, 3D rendering, and scientific simulations using HTML5.
- Interoperability with JavaScript: WebAssembly modules can be seamlessly integrated with HTML5 and JavaScript, allowing developers to leverage existing libraries and frameworks while improving performance.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: WebAssembly provides a consistent execution environment across different browsers and devices, making it easier to deliver high-performance applications that work seamlessly for all users.
Key Takeaway: The integration of WebAssembly with HTML5 will enable developers to build high-performance applications that leverage the capabilities of both technologies, expanding what is possible on the web.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in HTML5 Development
AI is becoming increasingly prevalent in web development, offering new opportunities to enhance user experiences and automate processes:
- AI-Powered Tools: Developers can leverage AI-driven tools for code completion, debugging, and performance optimization, allowing for more efficient HTML5 development workflows.
- Personalized User Experiences: AI can analyze user behavior and preferences, enabling developers to create highly personalized experiences within HTML5 applications, such as tailored content recommendations and adaptive user interfaces.
- Chatbots and Virtual Assistants: HTML5 can be used to create interactive chatbots and virtual assistants that provide customer support or guidance on websites, enhancing user engagement and satisfaction.
Key Takeaway: The incorporation of AI into HTML5 web development will lead to more efficient workflows and personalized user experiences, transforming how users interact with web applications.
HTML5 and Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) is another area where HTML5 is likely to play a significant role:
- Web Interfaces for IoT Devices: HTML5 provides a user-friendly interface for controlling and monitoring IoT devices, allowing users to interact with their devices through web applications.
- Real-Time Data Visualization: HTML5 can be used to create dashboards that display real-time data from IoT devices, enhancing user understanding and engagement.
- Cross-Device Compatibility: HTML5’s responsive design capabilities ensure that web interfaces for IoT devices function seamlessly across various platforms and screen sizes.
Key Takeaway: HTML5 will continue to facilitate the development of web interfaces for IoT devices, enabling real-time data visualization and enhancing user interactions with smart technologies.
Future of Web Browsers and HTML5
As web browsers evolve, so too will their support for HTML5 features:
- Continued Standardization: Organizations like W3C and WHATWG will continue to refine HTML5 specifications, ensuring that web standards keep pace with technological advancements and developer needs.
- Enhanced Browser Features: Future browser updates will likely include improved support for HTML5 APIs and features, allowing developers to create even more sophisticated web applications.
- Browser Performance Improvements: Ongoing enhancements in browser performance will further optimize the execution of HTML5 applications, leading to faster load times and improved user experiences.
Key Takeaway: The future of web browsers will support the evolution of HTML5, enabling developers to leverage new features and improved performance for more advanced web applications.
Key Takeaways
The future of HTML5 web development is promising, with ongoing enhancements and broader adoption of APIs and frameworks. Emerging technologies like WebAssembly and AI integration will further expand HTML5’s capabilities, enabling developers to create even more dynamic, responsive, and feature-rich applications.
22. Common HTML5 Development Challenges and Solutions

HTML5 development can come with its share of challenges, from browser compatibility issues to performance bottlenecks. This section aims to share the solutions to common problems developers face.
While HTML5 has revolutionized web development with its array of features and capabilities, developers often face challenges when utilizing this powerful technology. Understanding these challenges and implementing effective solutions can enhance the development process and ensure the successful deployment of HTML5 applications. This section outlines some common challenges encountered in HTML5 development and provides practical solutions.
Browser Compatibility Issues
Despite HTML5 being supported by most modern browsers, discrepancies still exist in how various browsers interpret and render HTML5 features. This can lead to inconsistent user experiences across different platforms.
Solutions:
- Use Feature Detection: Tools like Modernizr can help detect support for specific HTML5 features in users’ browsers, enabling developers to implement fallbacks or polyfills when necessary.
- Cross-Browser Testing: Regularly testing applications across different browsers (e.g., Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge) can identify compatibility issues early in the development process. Using tools like BrowserStack or Sauce Labs can streamline this process.
- Graceful Degradation and Progressive Enhancement: Design applications that work on older browsers while gradually adding enhanced features for modern browsers. This approach ensures that all users have a functional experience.
Key Takeaway: Browser compatibility issues can be mitigated through feature detection, cross-browser testing, and adopting graceful degradation or progressive enhancement strategies.
Performance Optimization Challenges
HTML5 applications can suffer from performance issues, particularly when dealing with heavy multimedia content, complex animations, or large data sets. Slow load times and lagging interactions can lead to poor user experiences.
Solutions:
- Minimize HTTP Requests: Reduce the number of elements that require separate HTTP requests by combining CSS and JavaScript files, and using image sprites where appropriate.
- Lazy Loading: Implement lazy loading techniques for images and other resources to enhance initial load speed. This ensures that content is only loaded when it enters the viewport.
- Optimize Resources: Compress images and minify CSS and JavaScript files to decrease file sizes and improve load times. Tools like ImageOptim and UglifyJS can help automate this process.
Key Takeaway: Performance optimization challenges can be addressed through strategies such as minimizing HTTP requests, implementing lazy loading, and optimizing resources.
Security Concerns
With the rise of web applications, security threats such as cross-site scripting (XSS), cross-site request forgery (CSRF), and data breaches have become increasingly common. HTML5 applications can be vulnerable to these risks if not properly secured.
Solutions:
- Input Validation and Sanitization: Ensure that all user inputs are validated and sanitized to prevent XSS attacks. Use frameworks that automatically escape data and provide built-in security features.
- Implement Content Security Policy (CSP): A CSP helps prevent XSS attacks by specifying which sources of content are trusted. By implementing CSP headers, developers can restrict the sources from which content can be loaded.
- Use HTTPS: Ensure that your HTML5 application is served over HTTPS to protect data in transit and prevent man-in-the-middle attacks.
Key Takeaway: Security concerns in HTML5 development can be mitigated through proper input validation, implementing CSP, and using HTTPS for secure data transmission.
Learning Curve for Developers
While HTML5 simplifies many aspects of web development, the sheer breadth of features and APIs can present a steep learning curve for new developers. Understanding best practices and utilizing the latest features can be daunting.
Solutions:
- Comprehensive Training Resources: Utilize online courses, tutorials, and documentation to provide developers with a solid foundation in HTML5. Websites like MDN Web Docs and W3Schools offer valuable resources for learners.
- Join Developer Communities: Participating in forums, discussion groups, and social media platforms can help developers learn from others, share knowledge, and stay updated on industry trends.
- Start with Projects: Hands-on experience is invaluable. Encourage developers to work on small projects that utilize HTML5 features, gradually increasing complexity as they become more comfortable with the technology.
Key Takeaway: Address the learning curve associated with HTML5 by utilizing training resources, engaging with developer communities, and encouraging hands-on project experience.
Integration with Other Technologies
HTML5 development often involves integrating with various other technologies, such as CSS, JavaScript frameworks, and server-side languages. Ensuring seamless integration can be challenging.
Solutions:
- Understand the Ecosystem: Developers should familiarize themselves with the technologies they plan to integrate with HTML5, including popular frameworks like React, Angular, or Vue.js, to ensure compatibility and efficient workflows.
- Utilize APIs: HTML5 offers several APIs (e.g., Web Storage, Geolocation) that can enhance functionality. Learning how to effectively use these APIs can improve integration and streamline development.
- Documentation and Collaboration: Maintain clear documentation for integration points and encourage collaboration among team members to address integration challenges early in the development process.
Key Takeaway: Successful integration of HTML5 with other technologies can be achieved by understanding the ecosystem, utilizing available APIs, and fostering collaboration among team members.
By recognizing these common challenges and implementing effective solutions, developers can optimize their HTML5 web development processes, resulting in robust, secure, and high-performing applications that deliver exceptional user experiences.
Key Takeaways
HTML5 development poses challenges such as inconsistent browser support, performance issues, and accessibility concerns. Solutions include using polyfills for compatibility, optimizing code for performance, and adhering to accessibility standards, ensuring a seamless experience across devices and users.
23. Conclusion
As we conclude this comprehensive guide to HTML5 web development, it’s clear that HTML5 is a transformative technology that has significantly shaped the landscape of web applications. Its robust features, combined with the evolving web ecosystem, offer developers powerful tools to create rich, interactive, and user-friendly experiences.
Throughout this guide, we’ve explored various aspects of HTML5, including its history, benefits, core concepts, advanced features, and the challenges developers may encounter. HTML5 empowers businesses to build responsive and engaging websites, while also supporting the development of modern web applications that are critical in today’s digital world.
Moreover, the continuous advancements in HTML5, including its integration with cutting-edge technologies like AI, WebAssembly, and IoT, signal a promising future for web development. As developers adapt to these changes, they can leverage HTML5 to create innovative solutions that meet the demands of users and businesses alike.
In summary, investing in HTML5 web development is not just about adopting a new standard; it’s about embracing the future of the web. By understanding the capabilities and best practices of HTML5, developers can enhance their skill sets, optimize performance, and deliver exceptional web experiences that keep pace with technological advancements.
24. FAQs on HTML Web Development
Here are some frequently asked questions (FAQs) about HTML web development, covering a range of topics from basic concepts to advanced features. This section aims to clarify common queries and provide insights for developers and businesses interested in HTML5.
1. General HTML5 Questions
What is HTML5 in web development?
HTML5 is the latest version of the Hypertext Markup Language, designed to create and structure content on the web. It introduces new elements, attributes, and APIs that enhance multimedia support and improve web application functionality.
Is HTML5 different from HTML?
Yes, HTML5 offers significant enhancements over previous versions of HTML, including new semantic elements, improved support for audio and video, and various APIs for web applications, making it more suitable for modern web development.
Does HTML5 still work?
Yes, HTML5 is widely supported by all modern web browsers, and it remains a core technology for web development, enabling the creation of rich and interactive web experiences.
Is HTML5 still a thing?
Absolutely! HTML5 continues to be a foundational technology for web development and is actively used for creating websites and applications. Its ongoing updates ensure its relevance in the ever-evolving web landscape.
How do I start learning HTML5?
To start learning HTML5, you can access numerous online resources, such as tutorials, courses, and documentation. Begin with the basics of HTML syntax, then gradually explore HTML5-specific features and best practices through hands-on projects.
Can I learn HTML5 without learning HTML?
While you can try to learn HTML5 with minimal HTML knowledge, a solid understanding of HTML is essential for effectively utilizing HTML5’s features. Familiarity with basic HTML will greatly enhance your learning experience.
Should I start with HTML or HTML5?
It’s advisable to start with basic HTML concepts before diving into HTML5. Understanding foundational HTML will make it easier to grasp the new features and functionalities introduced in HTML5.
What is the disadvantage of HTML5?
One disadvantage of HTML5 is its varying level of support across different browsers, which may lead to compatibility issues. Additionally, certain features may not work as expected in older browsers, necessitating the use of polyfills or fallback solutions.
What is the best program for HTML5?
Several programs and text editors support HTML5 development, including Visual Studio Code, Sublime Text, Atom, and Adobe Dreamweaver. These tools provide features like syntax highlighting, code completion, and built-in debugging to streamline the development process.
What does “::before” mean in HTML?
The “::before” pseudo-element in CSS is used to insert content before an element’s actual content. It allows developers to style or add decorative elements without altering the HTML markup, enhancing the design flexibility.
2. HTML5 Development and Learning
How do I start HTML5?
To start learning HTML5, you can begin by reading online tutorials and guides that cover the fundamentals of HTML syntax and structure. Create simple web pages using HTML5 features, and gradually incorporate CSS and JavaScript to enhance your skills. Many platforms also offer interactive coding exercises to practice your knowledge.
How many hours does it take to learn HTML5?
The time it takes to learn HTML5 varies based on your prior experience and the depth of understanding you wish to achieve. On average, you can gain a basic proficiency in HTML5 within a few weeks of dedicated study and practice, while mastering advanced features may take several months.
Is HTML5 hard to learn?
HTML5 is generally considered easy to learn, especially for beginners. Its syntax is straightforward, and many resources are available to help you grasp the concepts. However, mastering the more advanced features may require additional time and practice.
Is it difficult to learn HTML5?
Learning HTML5 is typically not difficult, particularly for those with some prior exposure to web technologies. The language is designed to be user-friendly, making it accessible for individuals new to coding.
Can I learn HTML in 3 days?
While you may grasp the basics of HTML within three days, becoming proficient and comfortable with creating full web pages will take more time. Continuous practice and exploration of more complex concepts will be necessary to fully understand HTML5.
Should I learn HTML5 or Python?
Your choice depends on your goals. If you want to focus on web development, learning HTML5 is essential. If you’re interested in backend development, data analysis, or machine learning, Python might be a better choice. Both languages have their own strengths and applications.
Should I learn HTML5 or CSS first?
It’s beneficial to learn HTML first, as it forms the structure of web pages. Once you have a solid understanding of HTML, you can dive into CSS to learn how to style and layout those pages effectively.
Is HTML easier than JavaScript?
Yes, HTML is generally considered easier to learn than JavaScript. HTML is a markup language used for structuring content, while JavaScript is a programming language that involves more complex concepts like logic and interactivity.
Should I write all HTML before CSS?
It’s a common practice to write your HTML first to create the structure of your web page. Once the HTML is in place, you can then style it using CSS. This approach allows you to see how your content is organized before applying design elements.
Do you need a CSS page for each HTML page?
No, you don’t need a separate CSS file for each HTML page. You can link a single CSS stylesheet to multiple HTML pages, allowing for consistent styling across your website. This method promotes efficiency and maintainability in your code.
3. HTML5 in Practice
Can you make a website with HTML5?
Yes, you can definitely create a website using HTML5. Its robust features allow you to build modern, interactive web pages that include multimedia elements like audio and video, as well as support for complex applications.
How to create a website in HTML5 step by step?
To create a website in HTML5, follow these steps:
1. Plan your website: Define its purpose, structure, and content.
2. Set up your development environment: Choose a text editor (like Visual Studio Code or Sublime Text) and set up a local folder for your project.
3. Create an HTML file: Start with a basic HTML5 template that includes the declaration.
4. Add content: Use HTML elements to create headings, paragraphs, links, images, and other content.
5. Style your website: Use CSS to enhance the appearance of your website.
6. Test your website: Open it in different browsers to check compatibility.
7. Publish your website: Choose a hosting provider to make it accessible online.
Can I make my own website using HTML?
Absolutely! HTML provides the foundational structure for web pages. By using HTML along with CSS for styling and JavaScript for interactivity, you can create a fully functional website.
How do I turn my HTML into a real website?
To turn your HTML into a real website, you need to host it on a web server. This involves selecting a web hosting provider, uploading your HTML files, and setting up a domain name to make your website accessible to users.
How do I make my own website totally free?
You can create a website for free by using platforms that offer free hosting services, such as GitHub Pages, Netlify, or WordPress.com. Many of these platforms allow you to build and publish simple HTML websites without incurring costs.
Can I host an HTML website for free?
Yes, several services allow you to host your HTML website for free. Options like GitHub Pages, Netlify, and Firebase Hosting provide free hosting solutions, although they may have limitations on storage and bandwidth.
How much does it cost to host an HTML website?
The cost to host an HTML website can vary widely based on the hosting provider and the level of service. Basic shared hosting plans typically start at around $2 to $10 per month, while premium services can cost significantly more depending on features and support.
How much is a simple HTML website?
The cost of a simple HTML website can range from free (using a free hosting provider) to a few hundred dollars if you choose to register a domain and pay for hosting services. Custom development may increase the cost further.
What is the simplest way to host HTML?
The simplest way to host HTML is to use a free service like GitHub Pages, where you can upload your HTML files and publish them directly from a GitHub repository. Alternatively, you can use services like Netlify or Vercel that offer easy deployment options.
Is HTML5 good for Progressive Web Apps (PWAs)?
HTML5 is used as part of the foundation for PWAs, alongside CSS, JavaScript, and web APIs like Service Workers. While HTML alone does not create a PWA, it provides the structure needed for building installable, offline-capable web applications.
4. HTML5 and Browsers
What browser uses HTML5?
All modern web browsers support HTML5, including Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Safari, Microsoft Edge, and Opera. These browsers have integrated HTML5 features, allowing developers to create rich web applications and multimedia experiences.
Which browsers support HTML5?
HTML5 is supported by the latest versions of major browsers:
1. Google Chrome (desktop and mobile)
2. Mozilla Firefox (desktop and mobile)
3. Apple Safari (desktop and mobile)
4. Microsoft Edge (desktop and mobile)
5. Opera (desktop and mobile)
Older versions of some browsers may not fully support HTML5 features, so it’s essential to keep your browser updated for the best experience.
How do I run HTML5 in Chrome?
To run HTML5 in Google Chrome, simply create an HTML file using a text editor, save it with a .html extension, and open the file in Chrome. You can also use Chrome’s Developer Tools (accessible via F12 or right-clicking on a page) to test and debug your HTML5 code directly in the browser.
How do you tell if a website is using HTML5?
To determine if a website is using HTML5, you can:
1. Inspect the Page Source: Right-click on the page and select “View Page Source” or “Inspect.” Look for the declaration, which indicates HTML5 usage.
2. Check for HTML5 Elements: Look for elements unique to HTML5, such as <header>, <footer>, <article>, <section>, <video>, and .
3. Use Online Tools: Various online tools and validators can analyze a website and report on its HTML5 compliance.
How do I add HTML5 to my Google Site?
To add HTML5 elements to a Google Site, you can use the HTML Box feature:
1. Open your Google Site and navigate to the page where you want to add HTML5 content.
2. Click on the “Insert” menu and choose “Embed.”
3. Select the “Embed Code” option and paste your HTML5 code into the box.
4. Save your changes, and your HTML5 content will be displayed on the site.
5. HTML5 vs Other Technologies
Should I learn Python before HTML and CSS?
While learning Python can be beneficial, it is not necessary to learn it before HTML and CSS. HTML and CSS are foundational technologies for web development, essential for creating and styling web pages. Python, on the other hand, is primarily used for backend development. It can complement your skills in web development, particularly if you’re interested in web frameworks like Django or Flask, but starting with HTML and CSS provides a solid grounding in web technologies. Learning the basics of HTML and CSS first will help you understand how the front end of a web application works before diving into backend programming with Python.
Is HTML easier than JavaScript?
Yes, HTML is generally considered easier to learn than JavaScript. HTML is a markup language focused on structure and content, whereas JavaScript is a programming language that adds interactivity and dynamic behavior to websites. HTML uses simple tags and attributes, making it more straightforward for beginners. JavaScript requires an understanding of programming concepts such as variables, functions, and control flow, which can be more complex for newcomers. However, both are essential skills for web development, and mastering them will enhance your capabilities as a developer.
Is it OK to learn JavaScript without HTML and CSS?
While you can technically learn JavaScript without first learning HTML and CSS, it is not advisable. HTML provides the structure for web pages, and CSS styles them; understanding these technologies is crucial for effectively using JavaScript to manipulate web content. Learning JavaScript in isolation may lead to confusion when you want to apply your skills to real-world web development scenarios. A solid foundation in HTML and CSS will enhance your JavaScript learning experience, making it easier to grasp concepts such as the Document Object Model (DOM) and event handling.
Can you get a job just doing HTML and CSS?
While having skills in HTML and CSS is valuable, most web development jobs require a broader skill set that includes JavaScript and potentially backend languages. Many positions, especially in front-end development, expect familiarity with frameworks and libraries such as React, Angular, or Vue.js, in addition to HTML and CSS. However, entry-level positions, such as web content editors or UI/UX designers, may focus more on these skills. In summary, while it’s possible to find a job with just HTML and CSS skills, expanding your knowledge to include JavaScript and other technologies will greatly improve your job prospects.
What can replace HTML and CSS?
HTML and CSS are foundational technologies for web development, and while there are alternatives, they generally work in conjunction with HTML and CSS rather than replace them entirely. Technologies like Markdown allow for simple formatting of text, and various front-end frameworks (such as React or Vue.js) abstract some HTML/CSS into components. However, these technologies still rely on HTML and CSS under the hood. Additionally, tools like WYSIWYG editors (What You See Is What You Get) can simplify web design, but they ultimately produce HTML and CSS code. For web development, mastering HTML and CSS remains essential, as they form the backbone of all web content.
6. HTML5 Installation and Availability
Is HTML5 free?
Yes, HTML5 is completely free to use. As a markup language, HTML5 is an open standard maintained by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) and is available for anyone to use without any licensing fees. You can create, modify, and distribute HTML5 documents freely, making it an accessible choice for developers worldwide.
Can I download HTML5 for free?
You don’t need to download HTML5 itself, as it is a specification rather than a software package. However, you can download various resources, tools, and libraries that support HTML5 development. Many text editors (such as Visual Studio Code, Atom, and Sublime Text) and frameworks (like Bootstrap) are available for free and provide functionalities to help you work with HTML5 efficiently.
Do I have to install HTML5?
No, you do not have to install HTML5. HTML5 is not software that requires installation; it is a set of standards and rules for creating web content. You can start using HTML5 immediately by writing HTML code in a text editor and opening it in any modern web browser. Browsers automatically interpret HTML5 code, enabling you to view and test your web pages without additional installations.
This page was last edited on 21 December 2025, at 10:58 am
Contact Us Now

Contact Us Now
Start a conversation with our team to solve complex challenges and move forward with confidence.











