In the world of music, fitness, and health, the term “beats per minute” (BPM) frequently appears. But what exactly does BPM mean, and why is it so important across different fields? This article delves into the concept of BPM, its significance, applications, and how it can be measured and utilized effectively.
What is BPM?
Beats per minute (BPM) is a unit of measure that indicates the number of heartbeats or musical beats occurring in one minute. This measurement is crucial for various applications, ranging from music production to monitoring physical fitness and health.
Besides, BPM stands for various terms such as:
- Business Process Management: Refers to the discipline of managing processes to improve efficiency and effectiveness within an organization.
- Bureau of Political-Military Affairs: A division within the U.S. Department of State responsible for managing security assistance programs.
- Bits Per Minute: A measure of data transfer rate, indicating the number of bits transmitted or processed in one minute.
These are some of the common uses of “BPM” across different domains.
BPM in Music
In the realm of music, BPM is used to describe the tempo of a song. The tempo is the speed or pace of a given piece, and it’s essential for musicians, producers, and DJs to understand and utilize BPM to maintain rhythm and create desired musical effects.
- Creating and Mixing Music: Producers use BPM to synchronize beats and melodies, ensuring smooth transitions and cohesive tracks.
- DJ Performances: DJs rely on BPM to mix songs seamlessly, maintaining a consistent flow on the dance floor.
- Music Genres: Different music genres typically have characteristic BPM ranges. For example, classical music might range between 60-120 BPM, while electronic dance music (EDM) often ranges from 120-150 BPM.
BPM in Fitness
In fitness, BPM is used to measure heart rate, which is an indicator of physical exertion and cardiovascular health.
- Monitoring Exercise Intensity: During workouts, tracking BPM helps individuals ensure they are exercising at the right intensity to achieve their fitness goals.
- Cardiovascular Health: A regular monitoring of heart rate can indicate overall heart health and help in identifying potential health issues early.
- Fitness Apps and Wearables: Modern fitness trackers and smartwatches use BPM to provide real-time data on heart rate, calories burned, and overall activity levels.
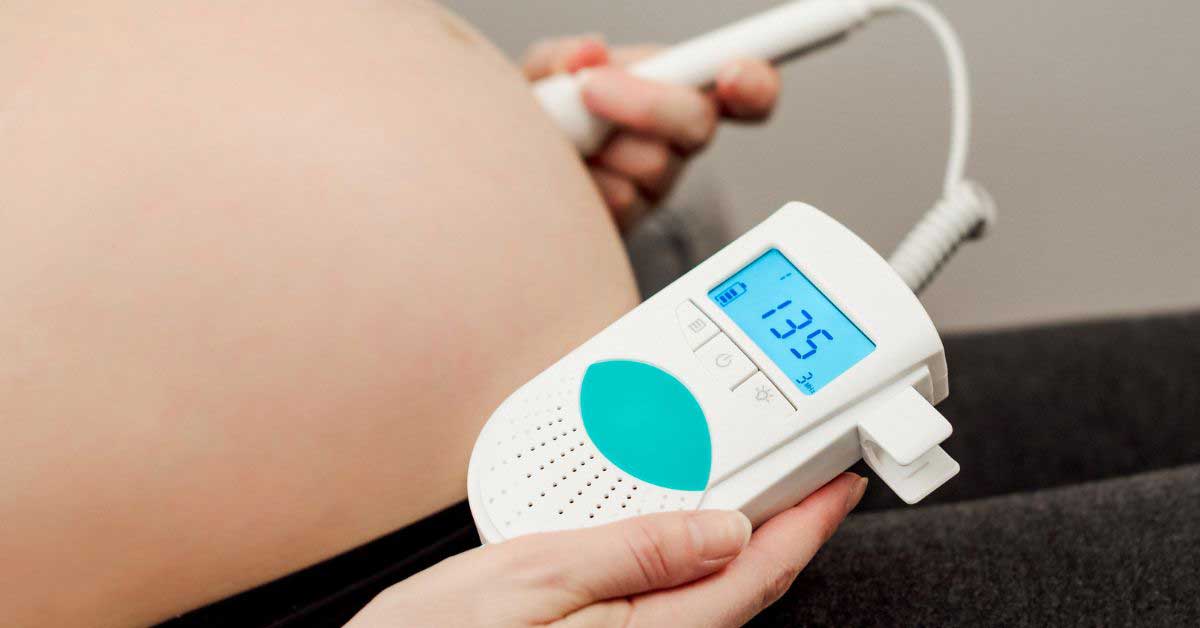
BPM in Healthcare
In healthcare, BPM is a critical measurement for assessing a patient’s heart rate.
- Vital Signs Monitoring: Healthcare providers regularly monitor BPM as part of routine check-ups and during critical care to ensure the heart is functioning properly.
- Detecting Arrhythmias: Abnormal BPM readings can indicate arrhythmias or irregular heartbeats, which may require medical intervention.
- Stress and Recovery: BPM can help monitor stress levels and recovery rates after surgeries or illnesses.
How to Measure BPM
Measuring BPM can be done in several ways, depending on the context:
- Manual Measurement: Using a stopwatch, count the number of beats in 15 seconds and multiply by four to get the BPM.
- Digital Tools: Metronomes, BPM counters, and apps can provide accurate BPM measurements for musicians.
- Fitness Trackers: Wearable devices such as heart rate monitors and smartwatches automatically measure and display BPM.
- Medical Equipment: Electrocardiograms (ECGs) and other medical devices are used in healthcare settings to measure BPM accurately.
The Importance of Understanding BPM
Understanding BPM is crucial for several reasons:
- Improving Performance: In music, fitness, and healthcare, knowing and utilizing BPM can significantly improve performance and outcomes.
- Safety and Health: Monitoring BPM helps in maintaining safe exercise levels and can provide early warnings for health issues.
- Enhancing Enjoyment: For music enthusiasts, understanding BPM can enhance the enjoyment and appreciation of different genres and rhythms.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is a healthy BPM for adults?
A: A normal resting heart rate for adults ranges from 60 to 100 BPM. Athletes may have a lower resting BPM, often around 40-60 BPM.
Q2: How can I measure my BPM accurately during exercise?
A: You can measure BPM during exercise using a heart rate monitor, fitness tracker, or smartwatch. Alternatively, you can manually count your pulse for 15 seconds and multiply by four.
Q3: Why do different music genres have different BPM ranges?
A: Different music genres have varying BPM ranges to evoke specific moods and energies. For example, faster BPMs in genres like EDM create excitement and energy, while slower BPMs in classical music can convey calmness and relaxation.
Q4: How can BPM indicate potential health issues?
A: Abnormal BPM readings, such as consistently high or low heart rates, can indicate potential health issues like arrhythmias, heart disease, or other cardiovascular conditions.
Q5: Can BPM be used to improve fitness?
A: Yes, monitoring BPM during exercise helps ensure you are working out at the right intensity for your fitness goals, whether it’s for burning fat, improving cardiovascular health, or increasing endurance.
Q6: How do musicians use BPM in composing music?
A: Musicians use BPM to set the tempo of a track, ensuring consistency and cohesion throughout a piece. It also helps in aligning different instruments and parts of a composition.
In conclusion, BPM is a versatile and essential measure across various fields. Whether you’re a musician, fitness enthusiast, or healthcare provider, understanding and utilizing BPM can greatly enhance your performance, health, and overall experience.
This page was last edited on 31 July 2024, at 11:01 am
Contact Us Now

Contact Us Now
Start a conversation with our team to solve complex challenges and move forward with confidence.