- What is AI in Product Development?
- How does AI for Product Development Work?
- How AI Transforms Product Development
- Key AI Technologies in Product Development
- Benefits of AI in Product Development
- AI Application Across the Product Development Lifecycle
- Real-World Case Studies
- Risks and Challenges of AI Adoption
- Best Practices to Speed Up Business with AI in Product Development
- The Growing Role of AI Agents
- The Future Outlook
Speed is now one of the strongest competitive advantages in business. Markets shift faster, customer expectations evolve rapidly, and companies that cannot deliver new products quickly risk falling behind. Whether you’re in software, hardware, retail, or digital services, shortening development cycles can directly increase revenue, reduce costs, and unlock new opportunities.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become one of the most transformative enablers for achieving this speed. Rather than optimizing just one stage of the process, AI enhances every part of the product development lifecycle from ideation and design to testing, launch, and continuous optimization. By combining human creativity with AI’s analytical and generative power, businesses can innovate faster and smarter than ever before.
What is AI in Product Development?
AI in product development means using artificial intelligence to improve and speed up the steps involved in creating a product. This includes using tools like machine learning, generative AI, and data analytics to help with tasks such as idea generation, design, prototyping, testing, and launching a product.
With AI, teams can come up with ideas faster, test designs on a computer before building anything, and understand what customers want by analyzing large amounts of data. AI can also predict trends, spot problems early, and automate repetitive tasks. This helps companies bring products to market more quickly and with better quality.
AI also helps after a product is launched. It can monitor how people use the product and suggest improvements. Still, human experts are needed to guide the process, check AI results, and make important decisions.
In simple terms, AI acts like a smart assistant that helps teams work faster, make better choices, and create more innovative products while humans stay in control of strategy and creativity.
How does AI for Product Development Work?
AI for product development works by orchestrating multiple interconnected components and processes within a robust architecture designed to handle diverse data inputs, model training, inference, and user interaction. Here is an in-depth explanation of how it works:
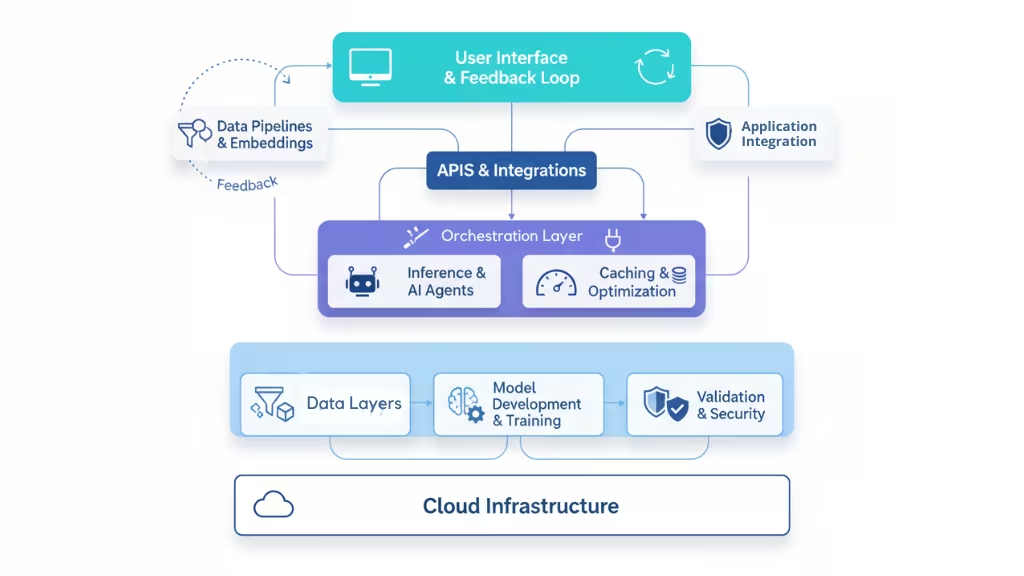
Data Layer: The foundation involves sourcing, validating, and storing data from varied sources critical to product development, such as market research, customer feedback, product performance, sales, and regulatory compliance data. This data is cleaned and preprocessed to ensure quality and relevance for AI consumption.
Data Pipelines and Embeddings: Preprocessed data is converted into numerical vectors using embedding models, which capture semantic information in a form AI models can understand. These vectors are efficiently stored in vector databases to allow fast querying and retrieval during AI processing.
Model Development and Training Pipelines: AI models including Large Language Models (LLMs) and generative models are developed and trained using scalable compute resources. Automated pipelines manage dataset versioning, model versioning, training, validation, evaluation, and deployment to production.
Orchestration Layer: This layer manages workflow execution and interaction between components. It handles prompt chaining, API calls, contextual data retrieval, memory management across multiple AI calls, and ensures smooth coordination of tasks.
Inference and AI Agents: Users submit queries via product development applications, which are processed through the orchestration layer. AI agents autonomous or collaborative execute specific tasks such as quality monitoring, prototyping, experimentation advising, and personalization. They apply reasoning, planning, tool use, and learning from feedback to enhance product outcomes.
Caching and Performance Optimization: Frequently accessed information is cached to speed up responses using tools like Redis or GPTCache. Continuous monitoring and MLOps tools track AI system performance, logging, and retraining needs to maintain accuracy and scalability.
Validation and Security: Outputs generated by AI models are validated via rule-based guardrails and constraint languages to ensure compliance and dependability. Security measures safeguard sensitive data and maintain privacy throughout the AI workflow.
APIs and Application Integration: AI capabilities are exposed via APIs that integrate seamlessly with business applications, product management platforms, and external services like Zapier or Wolfram that extend functionality.
User Interface and Feedback Loops: Intuitive interfaces present AI-generated insights to users, allowing easy access to design recommendations, market analysis, and strategic guidance. User feedback is captured to iteratively improve AI model outputs and overall system relevance.
Cloud and Infrastructure: The entire system is supported by cloud or on-premise infrastructure, offering scalability, reliability, and compliance with enterprise or industry requirements.
How AI Transforms Product Development
In essence, AI for product development works by leveraging comprehensive, high-quality data; advanced ML models, including LLMs; dynamic orchestration; autonomous agents; and a continuous cycle of feedback and retraining all integrated within a secure, scalable architecture to automate, accelerate, and optimize product ideation, design, testing, and market alignment. This leads to faster innovation, better decision-making, and improved product success outcomes across industries.
AI transforms the product development process by
integrating data-driven insights and automation across the entire lifecycle, leading to significantly faster time-to-market, improved product quality, and enhanced innovation.
Key Transformations
- Data-Driven Ideation and Strategy: AI analyzes vast amounts of data, including customer feedback, social media, and market trends, to identify unmet needs and potential opportunities with a high degree of accuracy. This helps teams make informed decisions and prioritize features based on real-world demand rather than intuition alone.
- Accelerated Design and Prototyping: Generative AI tools can create thousands of design variations and virtual prototypes in minutes based on predefined parameters (e.g., cost, material strength, sustainability targets). This rapid iteration cycle allows designers and engineers to explore a broader range of solutions and identify flaws much earlier in the process, reducing the reliance on costly physical prototypes.
- Enhanced Development and Testing: AI-powered assistants automate repetitive and time-consuming tasks like writing code snippets, generating unit tests, and documenting processes. Machine learning models also analyze code for potential bugs or security vulnerabilities, improving overall software quality and reducing the manual effort required for quality assurance (QA).
- Optimized Manufacturing and Supply Chain: AI optimizes production lines through predictive maintenance (forecasting equipment failures before they occur) and computer vision systems for real-time quality control inspections. It also enhances supply chain management by improving demand forecasting and optimizing logistics, reducing waste and operational costs.
- Personalized User Experiences: AI enables the creation of hyper-personalized products and user interfaces by analyzing individual user preferences and behaviors in real-time. This adaptive approach, famously used by companies like Netflix for content recommendations, increases user satisfaction, engagement, and brand loyalty.
- Continuous Improvement Post-Launch: After a product launch, AI systems continuously monitor performance and analyze user behavior and sentiment from various channels. These insights feed directly back into the development cycle, allowing for rapid, data-backed iterations and ongoing product evolution to meet changing customer needs.
In essence, AI acts as a strategic partner and a powerful automator, allowing human teams to focus on creativity, strategy, and complex problem-solving, fundamentally reshaping the product development process into a faster, more efficient, and customer-centric endeavor
Key AI Technologies in Product Development
To accelerate product development end-to-end, businesses rely on a set of powerful AI technologies that automate work, generate ideas, predict failures, and coordinate complex workflows. These technologies form the backbone of modern, AI-enhanced product lifecycle management.
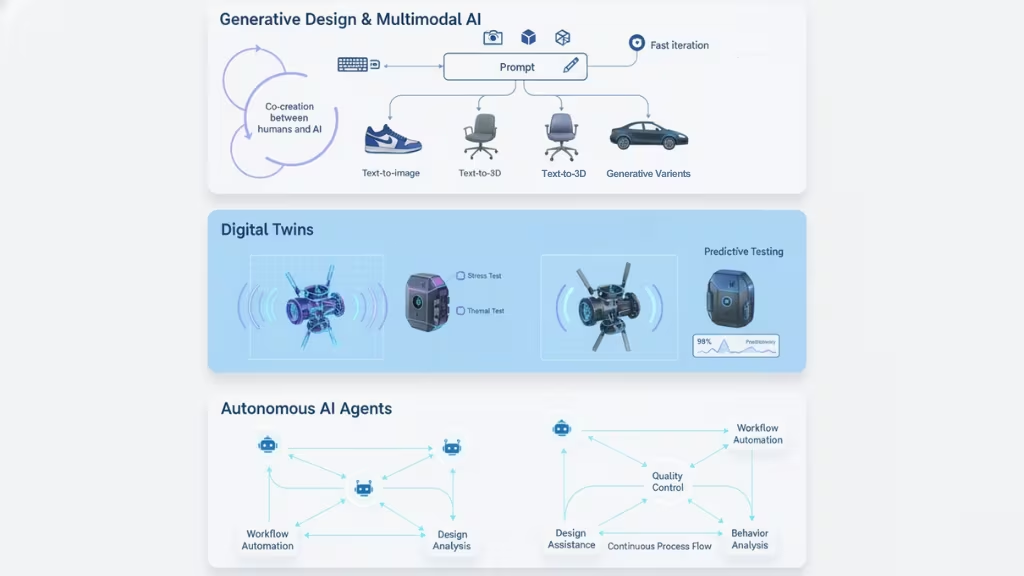
1. Generative Design & Multimodal AI Models
Generative AI transforms how teams ideate and create:
- It generates multiple product variants from simple text prompts.
- Produces design alternatives based on constraints like material, cost, durability, or aesthetics.
- Multimodal models (text + image + 3D) can produce sketches, renders, and even 3D models from verbal descriptions.
This enables rapid co-creation between humans and AI, drastically speeding up the early phases of development.
2. Digital Twins
Digital twins are virtual replicas of physical products or systems. They allow teams to:
- Simulate real-world performance.
- Run stress tests, thermal tests, and failure predictions.
- Identify design flaws before creating physical prototypes.
- Test multiple scenarios faster than any physical lab could.
Digital twins reduce risk, optimize product reliability, and cut prototyping costs.
3. Autonomous AI Agents
AI agents are emerging as key productivity drivers across product development. These agents can:
- Manage workflows (task automation, scheduling).
- Perform quality control checks.
- Generate design options or marketing content.
- Automate user behavior analysis.
- Support product lifecycle management with minimal human input.
Instead of one massive AI model, companies increasingly deploy multiple specialized agents working together to accelerate development.
Benefits of AI in Product Development
AI doesn’t just streamline workflows it fundamentally transforms how fast and efficiently products can be brought to market. Here are the core benefits businesses gain by integrating AI into their product development process:
1. Reduced Time to Market
AI accelerates the slowest and most resource-heavy phases of development:
- Automated design generation shortens concept creation.
- Rapid prototyping tools reduce iteration cycles.
- AI-driven simulations eliminate the need for multiple physical prototypes.
- Automated testing identifies issues long before manual QA would.
The result: products move from idea to launch weeks or months faster, giving companies a powerful competitive edge.
2. Improved Decision-Making
AI processes massive amounts of data far beyond human capability to help teams:
- Predict user needs and behavior.
- Identify market trends.
- Analyze technical feasibility.
- Forecast potential risks.
With predictive analytics, product managers can make smarter, data-backed decisions, reducing guesswork and uncertainty.
3. Higher Product Quality
AI improves quality at every stage:
- Automated defect detection catches issues early.
- ML-powered simulations predict failures before production.
- QA automation expands test coverage.
- Continuous monitoring flags anomalies in real time.
This translates to fewer bugs, fewer recalls, and fewer customer complaints.
4. Cost Reduction
AI cuts costs by:
- Reducing physical prototyping needs.
- Minimizing development errors.
- Automating repetitive tasks that otherwise require large teams.
- Shortening R&D cycles and reducing time wasted on manual workflows.
Fewer mistakes and faster development = significant cost savings.
5. Increased Innovation Capacity
AI allows companies to explore more ideas in less time:
- Generative models create hundreds of design variants instantly.
- AI tools support ideation with market insights and creative prompts.
- Teams iterate faster, unlocking more possibilities.
With AI, creativity becomes scalable, enabling organizations to innovate at a pace that wasn’t possible before.

AI Application Across the Product Development Lifecycle
AI doesn’t just improve one part of product development it enhances every stage. Here’s how AI accelerates the full lifecycle from idea to launch and beyond.
1. Ideation and Problem Definition
Using AI to Analyze Market Trends & Customer Feedback
AI tools scan massive data sources reviews, social media, forums, competitor releases to uncover:
- unmet customer needs
- emerging market patterns
- pain points
- trending features
This gives product teams a data-backed starting point instead of guesswork.
Generating Hypotheses & Creating Structured Requirements
AI can:
- summarize user problems,
- cluster recurring themes,
- turn insights into early feature hypotheses,
- draft structured product requirement documents (PRDs) from raw inputs.
This dramatically speeds up the strategic planning phase.
2. Design and Prototyping
Automating Design Variations & Interactive Prototypes
Generative design tools instantly produce:
- multiple UI/UX variations
- mechanical or industrial design alternatives
- layout experiments
- architecture options (for software or hardware)
This allows rapid iteration before committing engineering time.
AI Image Generators for Renders & Marketing Materials
Multimodal AI can create:
- realistic product renders
- 3D concept art
- packaging designs
- marketing visuals
Teams no longer wait weeks for designers or photo studios during early concept validation.
3. Development
AI-Assisted Coding, Bug Detection & Unit Test Automation
AI tools now write a significant portion of routine code:
- boilerplate generation
- component scaffolding
- API integration
- database schema suggestions
AI also:
- identifies vulnerabilities,
- flags risky functions,
- and generates unit & integration tests automatically.
This reduces development cycles and improves code quality from day one.
4. Quality Assurance & Experimentation
Comprehensive Test Scenario Generation & Edge Case Identification
AI expands QA coverage by:
- generating thousands of test cases, including rare edge scenarios
- simulating user journeys
- predicting where failures are likely to occur
- automatically analyzing logs for anomaly detection
This leads to fewer regressions and faster debugging.
5. Go-to-Market Launch
AI-Driven Content Creation & User Onboarding Personalization
AI accelerates launch preparation by creating:
- landing page copy
- app store descriptions
- demo scripts
- user manuals
- video storyboards
Meanwhile, personalization engines tailor onboarding flows to increase early adoption and reduce bounce rates.
6. Continuous Optimization
User Behavior Analysis for Improvement & Churn Prediction
Post-launch, AI continues improving the product by:
- analyzing session data
- flagging drop-off points
- predicting churn
- recommending feature improvements
- running automated A/B tests
This ensures products evolve in lockstep with real-world user behavior.
Real-World Case Studies
Here are some concrete examples of how leading companies across industries use AI to accelerate product development, improve quality, and deliver better user experiences faster.
1. Automotive: BMW’s AI-Enhanced Assembly, QA & Predictive Testing
BMW integrates AI throughout its manufacturing and product engineering processes:
- Assembly Communication: Vision-based AI systems monitor assembly lines and detect misalignments or incorrect part placements in real time, reducing human error.
- Quality Assurance: AI-powered vision systems inspect parts with micron-level precision far faster and more accurately than manual inspection.
- Predictive Testing: Digital twins simulate thousands of failure scenarios before physical prototypes exist, shrinking testing cycles significantly.
Impact: Higher product consistency, fewer defects, faster ramp-up for new vehicle models.
2. Consumer Electronics: Faster Launch Cycles with Generative AI
Leading electronics brands use AI to accelerate competitive product launches:
- Trend Analysis: AI analyzes global customer feedback, reviews, and buying patterns to identify must-have features.
- Rapid Concepting: Multimodal generative models produce industrial design variations outer shells, button layouts, screen styles within minutes.
- Simulation-Based Testing: AI predicts overheating, stress, battery performance, and durability before building physical prototypes.
Impact: Months shaved off R&D timelines, increased hit-rate of successful product launches.
3. Entertainment: Netflix’s AI-Driven Personalization & Rapid Prototyping
Netflix uses AI extensively across its product lifecycle:
- Personalized Recommendations: Machine Learning models drive ~80% of the content users watch.
- A/B Experimentation: AI orchestrates large-scale multivariate tests to optimize thumbnails, previews, and UI flows.
- Rapid Prototyping: AI models help design and simulate new interface changes and test them with synthetic user groups.
Impact: Massive engagement uplift and ability to roll out UI improvements weekly.
4. Retail & Fashion: Stitch Fix’s AI-Powered Personalization & Inventory Optimization
Stitch Fix blends human stylists with AI systems for end-to-end product creation and curation:
- Inventory Optimization: Predictive models determine which clothing types will sell and in what quantities.
- Hyper-Personalized Styling: AI matches items to customer profiles, boosting satisfaction and retention.
- Demand Forecasting: Algorithms predict trend cycles, allowing better planning for seasonal inventory.
Impact: Reduced stock waste, fewer returns, and a highly personalized customer experience.
Risks and Challenges of AI Adoption
While AI accelerates product development, it also introduces risks that businesses must manage carefully. Moving too fast without the right checks can create bottlenecks, inaccuracies, or even reputational damage. Here are the key challenges teams must be aware of:
1. Overconfidence in AI-Generated Concepts Without Human Validation
AI can produce highly convincing designs, ideas, and analyses but convincing does not mean correct.
Common pitfalls include:
- designs that look feasible but are impossible to manufacture,
- requirements that sound logical but don’t meet customer needs,
- data insights based on incorrect assumptions.
Human review must remain mandatory at every major decision point.
2. Potential Biases & Inaccuracies in AI Outputs
If the underlying data is biased, incomplete, or outdated, the AI will:
- misinterpret market signals,
- generate flawed designs,
- or recommend features irrelevant to real users.
This can lead to product–market misalignment or alienation of customer segments.
Quality data + human oversight = crucial.
3. Need for Skilled Oversight to Integrate AI Results Effectively
AI doesn’t replace:
- product managers
- designers
- engineers
- QA analysts
Instead, it augments them.
Teams must learn how to:
- prompt AI effectively,
- validate outputs,
- integrate AI artifacts into real workflows,
- and maintain cross-functional communication.
Companies lacking AI fluency risk slower adoption and inconsistent outcomes.
4. Balancing Automation with Human Creativity
AI is exceptional at:
- generating options,
- detecting patterns,
- automating repetitive work.
But it cannot:
- understand emotional nuance,
- make strategic trade-offs,
- evaluate ethics or brand alignment,
- replace intuitive leaps of human creativity.
The biggest danger is letting automation override innovation. The most successful companies use AI to amplify human creativity, not replace it.
Best Practices to Speed Up Business with AI in Product Development
To unlock the true speed benefits of AI, companies must adopt it strategically not chaotically. These best practices ensure faster development cycles without sacrificing quality or creativity.
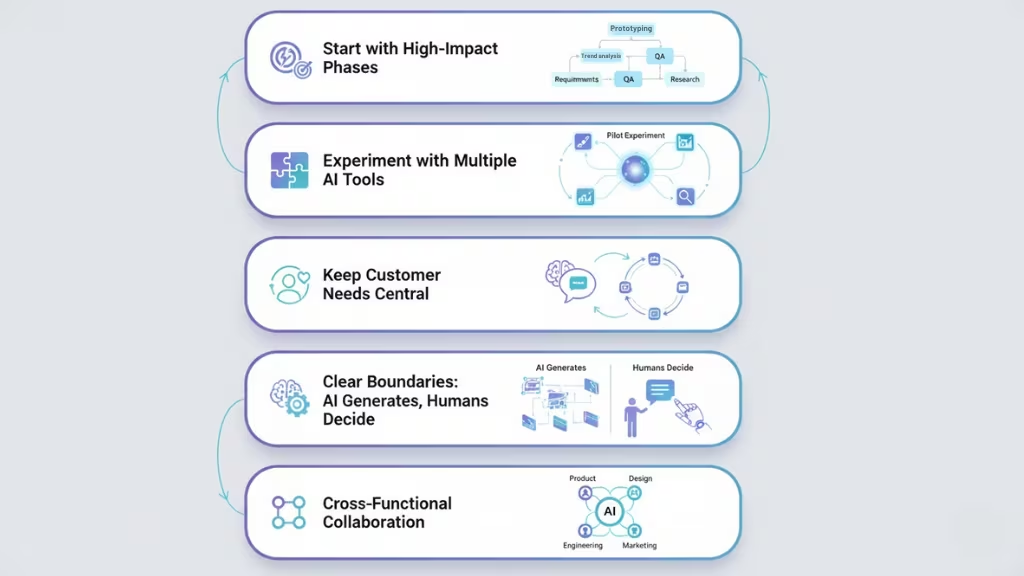
1. Start Strategically With High-Impact, High-Effort Phases
Not all stages of product development provide the same ROI from AI.
The fastest gains usually come from:
- Prototyping & design variation
- User research summarization
- QA & automated testing
- Requirement generation
- Market trend analysis
Begin with the phases that slow you down the most. Then expand AI adoption across the lifecycle.
2. Experiment With Multiple AI Tools While Staying Flexible
Different tools excel at different tasks. For example:
- One AI may generate better UI layouts,
- another may produce more accurate technical documentation,
- and another may excel at automated test coverage.
Run small pilots. Compare outcomes. Stay flexible and avoid early tool lock-in AI evolves quickly.
3. Keep Customer Needs at the Center of AI-Driven Innovation
AI can provide:
- ideas,
- design choices,
- marketing content,
- data summaries.
But only customers validate whether those ideas matter.
Use AI to speed up how you build, never replace why you build which should always come from real user needs.
4. Establish Clear Boundaries: AI Generates Options, Humans Decide
AI is best used for:
- generating alternatives
- proposing variations
- identifying insights
- automating analysis
Humans remain responsible for:
- final decisions
- prioritization
- ethical considerations
- creative direction
- strategic alignment
This balance prevents missteps and maintains product integrity.
5. Prioritize Collaboration & Cross-Functional Integration
AI is most powerful when:
- product,
- design,
- engineering,
- marketing,
- and data teams
…use it together.
Successful companies:
- share AI outputs openly,
- maintain consistent workflows,
- align teams on how AI should be interpreted,
- and train staff to use the same set of tools.
Cross-functional AI integration = faster, smoother product cycles.
The Growing Role of AI Agents
AI agents are emerging as one of the most transformative forces in modern product development. Unlike traditional AI tools that operate only when prompted, AI agents can work autonomously, executing tasks, coordinating workflows, and making micro-decisions to accelerate delivery.
These specialized agents act like digital team members each responsible for a specific function and together they can significantly speed up the product lifecycle.
1. Autonomous Agents Executing Key Product Development Tasks
AI agents can now independently perform tasks such as:
- Insight mining: Analyzing customer feedback, market trends, and competitor changes to create real-time reports.
- Rapid prototyping: Generating UI layouts, component variations, renders, and even initial 3D models.
- Quality assurance: Running test suites, detecting anomalies, and summarizing bug clusters.
- Launch enablement: Drafting launch content, creating marketing visuals, and preparing onboarding flows.
- Personalization: Tailoring recommendations, onboarding, or user flows based on real-time user data.
These agents reduce manual workload and compress timelines dramatically.
2. Specialized AI Agents Working Together to Accelerate the Lifecycle
Instead of one giant model, companies are using multiple agents that collaborate:
- A Research Agent pulls insights →
- A Design Agent generates concepts →
- A Development Agent builds scaffolds or code →
- A QA Agent tests them →
- A Marketing Agent prepares launch content →
- A Personalization Agent optimizes user behavior post-launch.
This creates an AI-driven assembly line, where each agent pushes work to the next just like a real team.
The result?
A product cycle that once took months can shrink into weeks or even days.
3. Human Oversight Remains Essential
Even the most advanced agents require:
- supervision,
- ethical review,
- constraint setting,
- strategic guidance,
- and final approvals.
Humans define what the agents should accomplish.
Agents handle the “how” and “when.”
This balance ensures:
- creativity stays human-led,
- AI stays aligned with brand direction,
- and automation never becomes a bottleneck.
The Future Outlook
The future of product development is not just faster it’s fundamentally more intelligent, adaptive, and proactive. AI is evolving from a supportive tool into a core driver of innovation, reshaping how teams build, test, and scale products.
Here’s what the next era looks like:
1. AI-Powered Humans Driving Innovation Beyond Traditional Limits
Human creativity + AI capability = a new standard of innovation.
In the near future:
- Product managers will ideate with AI copilots that understand markets instantly.
- Designers will sketch, prototype, and refine concepts in minutes rather than weeks.
- Engineers will develop complex systems with AI handling most repetitive coding tasks.
- Marketers will launch campaigns guided by real-time AI insights.
Humans remain the visionaries AI becomes the accelerator.
2. Continuous Metrics Tracking for Sustained Success
Product development will shift from: reactive → predictive.
AI will continuously track:
- user behavior,
- feature performance,
- market movements,
- anomaly patterns,
- churn drivers,
- customer sentiment.
These insights will inform every iteration, making product updates faster, smarter, and more aligned with user needs.
Teams won’t wait for problems to arise AI will flag them in advance.
3. Predictive Product Development Becomes the Norm
Instead of building based on historical data, AI will enable teams to build based on:
- forecasted demand,
- predicted failures,
- anticipated user preferences,
- future trend simulations.
Digital twins and predictive models will allow teams to “see the future” of a product before building it.
This means:
- fewer costly mistakes,
- better resource allocation,
- higher product success rates.
4. AI Agents Evolving Into Fully Autonomous Product Teams
Over time, AI agents will:
- operate 24/7,
- manage entire workflows,
- execute sprints automatically,
- integrate feedback loops,
- coordinate between stages of the lifecycle.
Human leaders will guide strategy; AI agents will handle execution.
This will mark the shift from AI-assisted development to AI-orchestrated development.
5. A Future Where Product Development Never Sleeps
As AI becomes embedded across tools and processes, product development becomes:
- continuous,
- always optimizing,
- constantly learning,
- ever-evolving.
Products will improve themselves based on real-time data automatically.
The businesses that win will be those that:
- integrate AI deeply,
- adopt agents early,
- and maintain strong human oversight to steer creativity and ethics.
Conclusion
AI is transforming product development from a slow, linear process into a dynamic, data-driven, and highly automated lifecycle. Businesses that adopt AI early gain the power to innovate faster, reduce development costs, and continuously adapt to customer needs. From generative design and autonomous AI agents to predictive analytics and digital twins, AI empowers teams to move with unprecedented speed without sacrificing quality.
The future of product development belongs to organizations that embrace human–AI collaboration. Humans provide creativity, vision, and strategic direction, while AI accelerates execution, insight generation, and optimization. By combining the strengths of both, companies can build better products, deliver them faster, and stay ahead in an increasingly competitive market.
FAQs: AI in Product Development
How does AI speed up product development?
AI automates the most time-consuming steps, including design iteration, prototyping, testing, and data analysis. This reduces manual effort and compresses development cycles from months to weeks.
Is AI replacing product managers or designers?
No. AI enhances their abilities by generating options, summarizing data, and automating repetitive tasks. Humans still make the strategic, creative, and final decisions.
What are the best use cases of AI in product development?
The most effective use cases include generating design variations quickly, analyzing customer feedback to identify needs, creating rapid prototypes, automating coding and bug detection, running large-scale testing with AI-generated scenarios, predicting product performance through simulations, personalizing user experiences after launch, and using data insights to guide product improvements. These applications help teams move faster, reduce errors, and build better products with less effort.
What are the risks of using AI in product development?
The main risks include relying too much on AI-generated ideas that may be inaccurate or biased, using poor-quality data that leads to misleading results, and missing important human insights or customer context. Without skilled oversight, AI can produce errors or impractical suggestions, and teams may make decisions based on faulty outputs. Human review and strategic judgment are essential to avoid these issues.
Do small businesses benefit from AI in product development?
Absolutely. AI tools lower the cost of prototyping, design, and testing giving small teams enterprise-level capabilities without large R&D budgets.
How do AI agents impact product development?
AI agents automate workflow steps like insight mining, QA, onboarding personalization, and content generation. Multiple agents can collaborate to accelerate the full lifecycle.
What skills are needed to integrate AI into product development?
Teams need skills in understanding and interpreting AI outputs, basic prompt engineering to get useful results, data literacy to work with insights and analytics, and the ability to validate and refine AI-generated ideas. It’s also important for teams to know how to integrate AI tools into existing workflows, collaborate across functions, and maintain human oversight to ensure accuracy, creativity, and alignment with product goals.
Can AI improve already-launched products?
Yes. AI continuously analyzes user behavior, predicts churn, identifies bottlenecks, and recommends iterative improvements enabling ongoing optimization post-launch.
What industries benefit most from AI in product development?
Major adopters include automotive, consumer electronics, software, retail, healthcare, and entertainment but any business that builds products can benefit.
What’s the future of AI in product development?
AI will evolve from a support tool into an orchestration engine running autonomous agents, predicting market shifts, and optimizing products in real time. Human creativity + autonomous AI execution will define the next generation of product innovation.
This page was last edited on 29 January 2026, at 2:43 pm
Contact Us Now

Contact Us Now
Start a conversation with our team to solve complex challenges and move forward with confidence.











