AI agent services for smarter business automation are transforming how organizations handle complex workflows, decision-making, and operational efficiency. Unlike traditional automation tools, ai agent services for automation enable systems to act autonomously, adapt to changing inputs, and intelligently coordinate processes across departments.
This guide explains how AI agent services help businesses move beyond rigid automation, reduce manual effort, and build scalable, adaptive operations that deliver measurable business value.
What Are AI Agent Services for Smarter Business Automation?
AI agent services for smarter business automation are enterprise-grade solutions that leverage autonomous or semi-autonomous AI agents to streamline workflows, optimize decisions, and minimize manual intervention across core business processes.
AI agents are distinct from traditional automation in that they operate with self-directed intelligence: they perceive their environment, make decisions, collaborate with other agents, and continuously improve via data-driven learning. Rather than relying on rigid scripts, these agentic AI services orchestrate end-to-end workflows, adapt to new scenarios, and integrate with business systems such as ERP, CRM, or supply chain platforms.
Need Experts For AI Agent Automation?
Example in action:
- A financial compliance agent monitors transactions for suspicious activity, flags irregularities, and triggers escalation workflows without manual intervention.
- In supply chain logistics, a fleet of AI agents forecasts demand, reroutes shipments in real-time, and communicates with vendors to reduce delivery delays.
Agentic automation rises above basic process scripting, enabling smarter business operations through adaptability, real-time insights, and seamless integration.
How Do AI Agents Differ from RPA and Traditional Automation?
AI agents fundamentally outperform RPA and traditional automation by bringing intelligence, adaptability, and autonomy to business processes—whereas RPA excels at repetitive tasks, AI agents handle complexity, learn, and optimize.
| Feature/Capability | Robotic Process Automation (RPA) | Traditional Automation | AI Agent Services (Agentic AI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Task Scope | Rule-based, repetitive | Scripted, transactional | End-to-end, dynamic, data-driven |
| Adaptability | Low | Very low | High (learning from new scenarios) |
| Decision-Making | None (follows rules) | Minimal | Autonomous (contextual, self-optimized) |
| Integration | Surface-level (UI/API) | Basic interfaces | Deep system, API, real-time orchestration |
| Scalability | Linear (bot by bot) | Siloed | Multi-agent, composable, scalable |
| Learning/Improvement | Static, manual updates | Static, slow to change | Self-learning, continuous improvement |
| Best Use Cases | High-volume repetitive tasks | Legacy system automation | Complex workflows, exceptions, insights |
| Limitations | Breaks on process change | Inflexible | Needs data readiness, governance |
| Cost/ROI | Low barrier, quick wins | Mixed | Higher upfront, larger long-term returns |
When to Use Agentic AI vs. RPA:
- Choose RPA for legacy, highly repetitive workflows with little variation (e.g., bulk invoice posting).
- Opt for AI agent services when processes require contextual understanding, real-time adaptation, or decision optimization—such as customer support triage, fraud detection, or multi-step supply chain orchestration.
According to Gartner, organizations increasingly combine RPA and AI agents for best results, but agentic AI is rapidly becoming essential for next-gen, intelligent process automation.
Which Frameworks and Platforms Power Agentic Business Automation?
Agentic business automation is built on advanced AI frameworks and platforms that enable enterprises to orchestrate, scale, and integrate intelligent agents across diverse environments.
The agentic AI platform landscape includes open-source frameworks, cloud-native platforms, and enterprise-scale solutions. Framework selection is critical: it impacts integration, scalability, feature richness, and governance.
| Framework/Platform | Provider | Key Features | Integrations | Best-Fit Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LangChain | Open-source | Multi-agent orchestration, LLM support | Extensive APIs, cloud | Complex multi-agent workflows |
| AutoGPT | Community/OpenAI | Goal-driven autonomous agents, chaining | Python, cloud, REST | Prototyping, process improvement |
| Semantic Kernel | Microsoft | Skill/connector library, memory/persistence | Azure, APIs | Knowledge-driven, scalable agents |
| MetaGPT | Community-driven | Code generation, project agent teams | GitHub, REST APIs | Software dev, automation pipelines |
| BabyAGI | Independent | Rapid task learning, recursive planning | Cloud, scripting | Adaptive, self-improving agents |
| Informatica Agentic Automation | Informatica | Enterprise data automation, governance | Data platforms, SaaS | Data-centric enterprise automation |
Framework Map (infographic concept):
LangChain ←→ AutoGPT ←→ Semantic Kernel ←→ MetaGPT/BabyAGI
↑ | ↑ |
(LLM agents) | (Connectors/Skills) (Auto-code teams)Decision Criteria for Framework Selection:
- Integration depth: Do you need plug-and-play or custom API connectors?
- Scale and control: Is cloud or on-premises preferred?
- Governance: How mature are audit/logging features?
- Ecosystem: Does the platform support third-party or custom modules?
Leading organizations often run proof-of-concept pilots with open frameworks, then scale on enterprise-supported platforms with governance, support, and compliance built-in.
What Are the Core Components of Modern AI Agent Services?
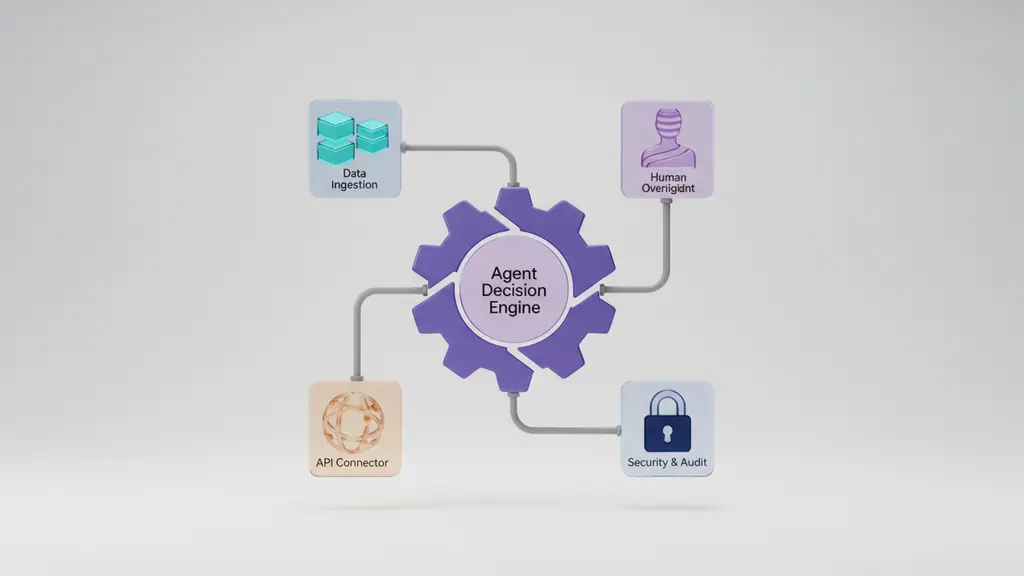
Modern AI agent services consist of modular components that support data ingestion, autonomous decision-making, integration, human oversight, and secure operation—forming the foundation for enterprise adoption and scalability.
Core Components:
- Knowledge & Data Ingestion:
Import, normalize, and contextualize business data from ERP, CRM, SaaS, and IoT sources to fuel agent reasoning. - Decision/Optimization Engines:
Machine learning, reinforcement learning, or rules engines drive process optimization and real-time decisioning. - Integration APIs & Connectors:
Secure APIs, SDKs, and prebuilt connectors enable seamless flow among business systems and external data feeds. - Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) & Governance Layers:
Critical for oversight, exception handling, and aligning agentic automation with policy and compliance needs. HITL ensures that humans intervene or audit key actions as required. - Security & Audit/Logging Modules:
Components managing access controls, activity logging, encrypted data transport, and compliance with regulatory standards (e.g., GDPR).
Example Modern AI Agent Service Architecture:
[User/System] → [Data Ingestion] → [Agent Decision Engine]
↑ ↻ ↓
[Integration Layer] ←→ [Human Oversight & Governance]
↓
[Security & Audit Trail]Enterprises evaluating agentic AI solutions should require visibility into each component, ensuring vendor offerings address integration, control, security, and auditability.
What Are the Top Use Cases for AI Agent Services Across Industries?
AI agent services enable transformative automation across industries by addressing unique business challenges—from real-time compliance in finance to intelligent customer support in retail.
Top Industry Use Cases
| Industry | Use Case | How Agentic AI Delivers Value |
|---|---|---|
| Banking | Compliance, Fraud Detection | Agents continuously monitor, analyze, and flag anomalous transactions for regulatory reporting and fraud mitigation. |
| Retail/Ecommerce | Inventory & Customer Care | AI agents forecast demand, manage inventory, and route customer inquiries to achieve personalized, rapid service. |
| HR | Candidate Screening, Onboarding | Automates CV parsing, shortlist generation, and coordinates interviews with hiring managers, freeing HR teams for higher-value tasks. |
| Supply Chain | Demand Forecasting, Logistics | Multi-agent networks optimize logistics routes, predict supply chain disruptions, and coordinate supplier communications. |
| Customer Service | Ticket Triage, Self-Service | Conversational AI agents resolve Tier 1–2 queries instantly, escalate complex issues, and increase customer satisfaction. |
Mini Case Snapshots:
- Supply Chain Leader: Deployed AI agents for logistics that reduced delivery lead times by up to 30%, according to recent industry surveys.
- Large Bank: Automating KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML (Anti-Money Laundering) checks through agentic AI resulted in ~50% time reduction and fewer regulatory errors.
These real-world examples showcase the scalable, adaptive power of AI agent services to drive smarter business automation across verticals.
Benefits and ROI Benchmarks of Agentic AI Automation
Agentic AI automation drives measurable improvements in efficiency, cost, error reduction, and decision speed—offering superior ROI compared to legacy approaches.
Key Performance Metrics
- Operational Efficiency: Reduce manual effort and process cycle times (e.g., processing claims or invoices 40–70% faster).
- Cost Reduction: Decrease in FTE (Full-Time Equivalent) needs, lowered error-related losses, and fewer compliance penalties.
- Error Rate: AI agents catch and resolve exceptions, dramatically cutting manual mistakes.
- Agility & Insight: Real-time analytics, continuous learning, and scalability enable organizations to respond faster to change.
- Time-to-Value: Rapid pilot deployment (often weeks, not months) and early measurement of impact.
Sample ROI Calculation
| Approach | Year 1 Cost | % Process Automated | Error Rate | Time Saved | ROI (Yr 1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manual | $0 | 0% | High | Baseline | N/A |
| RPA | $100K | ~30–40% | Medium | 2–5x | ~20–40% |
| Agentic AI | $250K | ~70–90% | Low | 5–10x | 50–150%+ |
Value Beyond Hard Savings:
- Enhanced compliance outcomes
- Improved customer experience
- Better alignment of human talent to creative, high-value work
How Do You Deploy AI Agent Services from Pilot to Enterprise Scale?
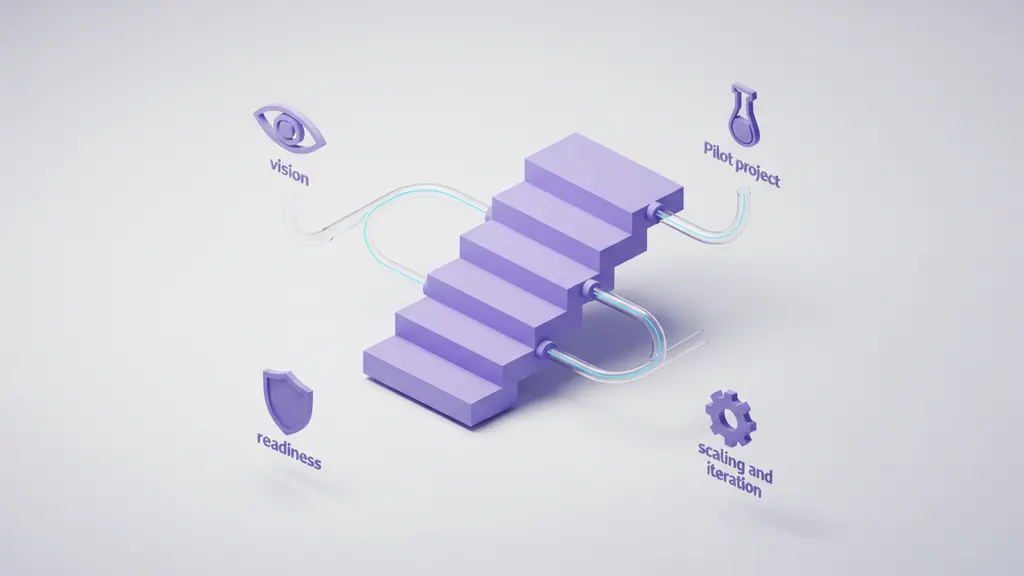
Successful AI agent service deployment follows a structured, stepwise journey—starting from vision alignment through to enterprise integration, training, and scaling.
Stepwise Playbook for Deployment
- Define Vision & Objectives:
Clarify automation goals, value drivers, and success KPIs. Engage executive stakeholders early. - Assess Readiness & Vendor Selection:
Evaluate data maturity, integration landscape, and security needs. Shortlist compatible agentic AI frameworks or enterprise platforms. - Pilot Project:
Choose high-impact, low-risk process as a testbed. Deploy pilot with clear metrics and human-in-the-loop for oversight. - Integration & Iteration:
Expand agent integration with core systems (ERP, CRM), collect learnings, and address edge cases using iterative cycles. - Scale & Optimize:
Broaden scope across departments or geographies. Formalize governance, change management, and ongoing support processes.
Change Management Best Practices
- Training: Upskill employees on new workflows, AI collaboration, and exception handling.
- Human-in-the-Loop: Ensure human control for sensitive, high-risk tasks.
- Stakeholder Communication: Maintain open, ongoing communication to manage impact and adoption.
Deployment Readiness Checklist
- Is your data accessible, high-quality, and sufficiently labeled?
- Do you have API access or integration options for core systems?
- Are executive sponsors and key business users aligned?
- Is the organization culturally ready for automation-driven change?
Common Pitfalls: Skipping pilot phases, underestimating change management, lack of ongoing governance, or neglecting compliance requirements.
What Are the Key Challenges and Risks in Agentic AI Automation?
While agentic AI enables transformative automation, enterprises face tangible challenges in integration, data readiness, governance, and compliance.
Top Challenges & Risks
- Data Readiness: Poor data quality, fragmented systems, or lack of standardized processes hinder agent deployment.
- Integration Complexity: Connecting AI agents to legacy, ERP, or CRM systems can be resource-intensive and require robust API management.
- Compliance & Regulation: Navigating evolving regulations (e.g., GDPR, data residency), especially across geographies, is critical.
- Security & Privacy Risks: Improper handling of sensitive data or weak access controls can expose businesses to cyber threats.
- Scalability: Scaling from pilot to production often reveals architectural bottlenecks or need for enhanced monitoring.
Mitigation Strategies:
- Conduct comprehensive data audits before rollout.
- Prioritize platforms with proven integration blueprints.
- Implement layered security and proactive compliance monitoring.
- Foster a culture of continuous improvement and governance.
How Do You Ensure Compliance, Security, and Governance with AI Agents?
Enterprises must embed robust compliance, security, and governance controls within AI agent automation to safeguard data, ensure regulatory adherence, and foster enterprise trust.
Governance Framework Essentials
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Restrict agent permissions by job function or data domain.
- Audit Trails: Every agent action is logged for traceability, reporting, and post-event review.
- Fail-Safes & Intervention: Define thresholds and constraints where agents must seek human validation.
Data Handling and Privacy
- Geographic Data Controls: Ensure data processing aligns with local regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA).
- Data Retention & Deletion: Automate lifecycle management for sensitive or regulated data.
Compliance Playbook: Steps to Pass Audit
- Map Data Flows: Document how and where data moves within agent-driven workflows.
- Establish Controls: Set up automated and manual checks for regulated activities.
- Monitor & Report: Use dashboards to review agent outcomes, anomalies, and compliance status regularly.
- Continuous Training: Regularly update agent decision logic to reflect new policies or risks.
What Are the Top Trends Shaping the Future of Agentic Business Automation?
Emerging trends such as multi-agent autonomy, real-time decision automation, and self-adapting agent ecosystems are shaping the next phase of business automation.
Top 5 Trends for 2025–2026
- Multi-Agent Autonomy:
Teams of AI agents collaborate to handle complex, dynamic business environments—enabling higher levels of orchestration and resiliency. - Composable Enterprise Architectures:
Modular, API-driven platforms empower rapid assembly and reconfiguration of automation workflows. - Explainable, Self-Adapting AI:
Advances in transparency and AI ethics foster trust and regulatory alignment. - Low-Code/No-Code Automation Tools:
Business users increasingly configure and manage agentic processes without deep coding expertise. - AI as-a-Service:
Consumption-based, cloud-native agentic automation services lower the barrier to enterprise adoption, enabling rapid scaling.
Automation Maturity Curve (Infographic Concept)
- Level 1: Manual processes
- Level 2: RPA & Scripted Automation
- Level 3: Intelligent (Agentic) Automation
- Level 4: Autonomous, Real-Time Decisioning
Staying ahead requires continuous review of emerging frameworks, evolving architectures, and changing regulatory landscapes.
Frequently Asked Questions about AI Agent Services for Business Automation
What are AI agent services for business automation?
AI agent services for automation are software solutions that use autonomous or semi-autonomous AI agents to automate, optimize, and orchestrate business processes. These services enable smarter, more adaptive operations compared to traditional rule-based automation.
How do agentic AI services differ from RPA?
While RPA focuses on repetitive, rule-based tasks, ai agent services for automation leverage intelligent agents that can learn, adapt, and make context-aware decisions. This allows organizations to automate more complex workflows with greater flexibility and resilience.
Which enterprise frameworks support AI agent deployments?
Frameworks such as LangChain, AutoGPT, Semantic Kernel, MetaGPT, and Informatica’s Agentic Automation platform are widely used to build and manage ai agent services for automation, offering varying levels of orchestration, integration, and governance support.
What are the main benefits and KPIs of agentic AI automation?
Key benefits of ai agent services for automation include faster process cycle times, reduced operational costs, lower error rates, improved agility, and real-time decision support. Common KPIs include ROI, automation coverage, time-to-value, and error reduction rates.
How do organizations ensure compliance and governance with AI agents?
Organizations ensure compliance by embedding governance controls into ai agent services for automation, such as role-based access, audit trails, data privacy safeguards, and automated compliance monitoring aligned with regulations like GDPR.
What industries benefit most from agentic AI automation?
Industries such as banking, retail, HR, supply chain, logistics, and customer service benefit most from ai agent services for automation due to their complex, high-volume, and compliance-driven workflows.
What are common challenges in implementing agentic AI services?
Common challenges include data readiness, legacy system integration, security risks, regulatory compliance, and scaling ai agent services for automation from pilot projects to enterprise-wide deployment.
Can AI agents integrate with legacy business systems?
Yes, modern ai agent services for automation integrate with legacy systems through APIs, connectors, and middleware, although the level of effort depends on system architecture and data accessibility.
How long does it take to deploy enterprise AI agent services?
Pilot implementations of ai agent services for automation can be deployed within weeks, while full enterprise rollouts typically take several months depending on workflow complexity, data maturity, and organizational readiness.
What are the key trends in agentic AI for business automation?
Key trends shaping ai agent services for automation include multi-agent collaboration, composable automation platforms, explainable AI, low-code development, and AI-as-a-service delivery models.
Conclusion
AI agent services are reshaping how organizations approach business automation by enabling intelligent, adaptive, and autonomous workflows. Instead of relying on rigid rules and manual oversight, businesses can use agent-driven systems to orchestrate processes in real time, respond to change faster, and unlock measurable efficiency gains.
Organizations that adopt AI agent services with a clear strategy, strong governance, and a focus on real business outcomes are better positioned to scale operations, reduce complexity, and stay competitive as automation continues to evolve.
Key Takeaways
- AI agent services deliver smarter business automation by blending autonomous decision-making, adaptive workflows, and deep system integration.
- Agentic AI outperforms RPA in complex, dynamic, and exception-driven processes—boosting efficiency and ROI.
- Choosing the right framework depends on integration, governance, and scalability needs; leading platforms include LangChain and Semantic Kernel.
- Success requires robust data readiness, compliance strategy, stepwise deployment, and ongoing change management.
- Staying current with agentic AI trends positions organizations to future-proof operations and drive competitive advantage.
This page was last edited on 2 February 2026, at 9:08 am
Contact Us Now

Contact Us Now
Start a conversation with our team to solve complex challenges and move forward with confidence.











