A marketing executive creates campaign ideas using an AI assistant. This tool makes headlines, visuals, and summaries fast. An autonomous system detects a supply chain issue. It reroutes shipments. It updates systems. It alerts stakeholders. All this happens without any human input.
These two moments capture the contrast between Generative AI and Agentic AI. The first creates; the second acts. Generative AI boosts creativity and insight by creating content. Agentic AI achieves goals using its own reasoning and decision-making.
For business leaders, it’s important to see this difference. Generative AI boosts productivity for specific tasks. Agentic AI changes performance overall in processes. Understanding their differences and how they collaborate will boost enterprise competitiveness in 2025 and beyond.
What is Generative AI?
Generative AI describes systems that learn from large datasets. They create new content like text, images, code, or audio that looks like it was made by humans. Generative AI uses large language models (LLMs) and transformer architectures. It predicts what comes next in a sequence. This helps create clear and coherent outputs. Its purpose is to create and synthesize. It answers questions. It drafts content, writes code, and generates designs.
It reacts to user prompts. It processes inputs and generates responses. This makes it a strong tool for creativity, communication, and decision support. However, it’s not meant for autonomous action.
What is Agentic AI?
Agentic AI represents the next stage of AI evolution. It doesn’t just generate it acts. These systems sense their environment. They think about goals, plan multi-step tasks, and carry out actions using various tools and systems. They combine memory, context, and goal persistence. This lets them work continuously and adapt without needing constant help from humans.
Agentic AI acts like a digital agent. It can coordinate workflows, make decisions, and finish tasks from start to finish within set limits.
Fundamental Differences
At the conceptual level, the difference lies in purpose:
- Generative AI answers “What should I create?”
- Agentic AI asks, “What must I accomplish?”
Generative AI produces; Agentic AI performs. The former supports human intent, while the latter pursues it.
Relationship Between the Two
Agentic AI often builds on generative models as core reasoning components. A generative model can create content or suggest actions in a bigger system. This system plans, decides, and carries out tasks. Generative AI is part of Agentic AI’s larger system. One focuses on creativity, while the other emphasizes autonomy.
Architectural and Technical Differences
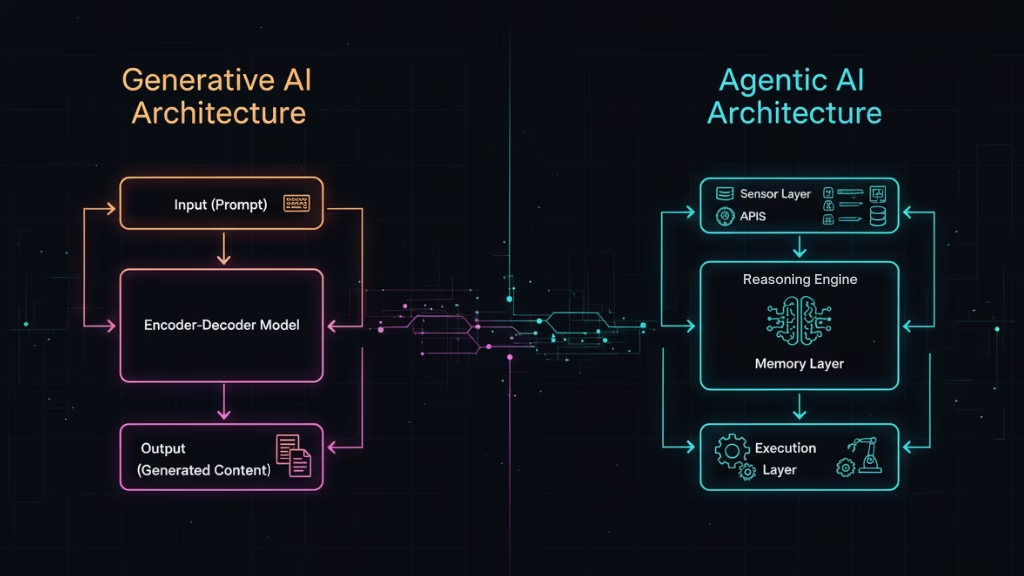
Generative AI Architecture and Mechanisms
Generative AI systems mainly use transformer architectures. They can be encoder-decoder models or decoder-only models. These systems process input and create coherent output. These models use probabilistic pattern recognition. They predict the next word, pixel, or token from previous data.
Generative AI’s smarts come from its base model. This model is usually trained on terabytes of text or other data types. It performs a single-pass operation: take a prompt → generate a response. Some models can keep a little context, but they are still stateless. This means every interaction is separate. This design allows for wide generalization. But it limits long-term thinking and tracking goals.
Agentic AI Architecture: Layers and Components
Agentic AI systems adopt a layered and modular design, combining reasoning, memory, and execution. A typical architecture includes:
- Perception Layer – Collects data from multiple inputs (APIs, databases, sensors, user interactions) and translates them into machine-readable form.
- Reasoning Engine – Uses LLMs combined with symbolic reasoning and planning algorithms to interpret goals, evaluate alternatives, and make decisions.
- Memory Layer – Maintains context across time, storing both short-term and long-term information to enable continuity, learning, and adaptation.
- Execution Layer – Interfaces with external systems, invoking APIs, running code, or triggering workflows to complete objectives.
This architecture allows Agentic AI to operate through continuous perceive–reason–act loops rather than single-pass responses.
Memory and Context Handling in Agentic AI
Unlike generative AI, which forgets previous interactions once a task is complete, agentic systems maintain persistent memory.
- Working memory stores the immediate context for current reasoning.
- Episodic memory records historical events and outcomes for learning.
- Knowledge base memory stores domain-specific facts, policies, and rules.
This persistent context enables long-horizon tasks, personalization, and self-improvement capabilities that generative models alone cannot achieve.
Underlying Technologies Supporting Each AI Type
- Generative AI depends mainly on LLMs, diffusion models, and transformers for prediction-based generation.
- Agentic AI combines multiple technologies:
- LLMs for reasoning
- Planning algorithms for multi-step task execution
- Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) for factual grounding
- Tool use frameworks for API integration and automation
- Memory systems for context management
- Orchestration layers for coordinating multiple agents or workflows
- LLMs for reasoning
In short, Generative AI is a model, while Agentic AI is a system one that embeds models within an autonomous decision-making and execution framework.
Functionality and Task Scope
Focus and Primary Tasks of Generative AI
Generative AI shines in tasks that are creative and knowledge-heavy. It works best when these tasks can be done in one go. Its strength lies in spotting patterns and putting content together. It turns data into text, visuals, or code. Typical use cases include:
- Writing articles, emails, or reports
- Generating code snippets or documentation
- Creating visual or audio content
- Summarizing documents or datasets
Each task is self-contained, requiring a human to interpret the output, make decisions, and initiate the next step. This makes generative AI ideal for augmenting individual creativity and productivity rather than replacing end-to-end workflows.
Focus and Primary Tasks of Agentic AI
Agentic AI operates at a different level of goal-oriented execution. Instead of responding to prompts, it perceives situations, reasons about the objective, plans multi-step strategies, and executes them autonomously.
For instance, in a business context, an agentic system might:
- Diagnose customer issues, apply policies, and resolve tickets end-to-end
- Analyze inventory levels, forecast demand, and automatically place orders
- Monitor cybersecurity threats, isolate anomalies, and trigger responses
- Manage multi-stage marketing or financial operations workflows
These systems combine reasoning with action, turning high-level goals into measurable outcomes.
Workflow Complexity and Execution Differences
The distinction is clear:
- Generative AI performs single-step tasks → output is the end product.
- Agentic AI performs multi-step tasks → output is goal completion.
Where generative AI stops at suggestion, agentic AI continues until success, looping through perception, reasoning, and action cycles to reach defined objectives.
Autonomy and Human Interaction: Reactive vs Autonomous
Generative AI is reactive: it waits for input and requires ongoing human direction. Agentic AI is autonomous. It acts on its own, anticipates what’s next, and only escalates issues when exceptions occur.
This difference defines their roles in business. Generative AI supports human operators. Agentic AI takes on tasks and manages workflows that used to need constant human help.
Use Cases and Applications
Generative AI Use Cases
1. Content Creation and Creative Assistance
Generative AI automates tasks for content creation and creative help.It can write marketing copy, blog articles, and ad scripts. It also helps create visual assets.
Platforms like Jasper and Canva AI let marketers and designers build campaigns in minutes instead of days.
2. Software Development and Code Generation
Tools like GitHub Copilot and Amazon CodeWhisperer use generative models to suggest, complete, and document code. They accelerate development cycles, improve consistency, and assist with testing and debugging.
3. Customer Service Support and FAQ Generation
Generative AI chat assistants draft replies, summarize tickets, and generate knowledge base articles. While these models don’t take full action, they empower human agents to respond faster and more accurately.
4. Marketing, Design, and Scientific Research
In marketing and design, generative AI produces images, layouts, and campaign ideas. In research, it aids in hypothesis generation, report drafting, and even molecule or material design through pattern recognition in scientific data.
In essence, Generative AI boosts creativity, speeds up repetitive content tasks, and supports informed decision-making, but leaves final judgment and execution to humans
Agentic AI Use Cases
1. Workflow Automation and Multi-step Task Execution
Agentic AI autonomously executes workflows across multiple systems. For example, a finance agent can extract invoice data, reconcile payments, and update ledgers without human oversight.
2. Customer Service Issue Resolution and Escalation
Beyond drafting responses, agentic systems like Bank of America’s Erica or H&M’s virtual assistant handle customer issues end-to-end, analyzing the problem, taking corrective actions, and escalating only exceptions.
3. Supply Chain Optimization and Financial Trading
Enterprises deploy agentic systems to predict demand, adjust logistics, and optimize procurement automatically. In finance, AI trading agents continuously analyze markets and execute transactions based on real-time data.
4. Healthcare Treatment Planning and Cybersecurity
In healthcare, agents analyze medical records, cross-reference research, and adapt treatment plans. In cybersecurity, systems like Darktrace autonomously detect, isolate, and neutralize threats in real time.
5. Predictive Maintenance and Autonomous Operations
Industrial firms use agentic AI to monitor equipment, forecast failures, and schedule maintenance automatically, achieving near-continuous uptime.
Agentic AI thus extends AI from insight generation to autonomous execution, turning complex, data-heavy operations into self-managing systems.
Limitations and Challenges
Generative AI Limitations
1. Hallucinations and False Outputs
Generative AI models often produce plausible but incorrect information, a phenomenon known as hallucination. Since these systems generate responses based on probability rather than verified truth, factual reliability remains a core challenge, particularly in regulated or high-stakes industries.
2. Knowledge, Currency, and Data Freshness
Most generative models are trained on static datasets with defined cut-off dates. Without real-time data access or retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), outputs may reflect outdated or incomplete knowledge, limiting utility in fast-evolving fields like finance or cybersecurity.
3. Context and Memory Constraints
Even advanced models have limited context windows. They process only a finite amount of information at once, which restricts their ability to manage long documents, sustain context across interactions, or maintain continuity in complex workflows.
4. Over-reliance and Automation Bias
Users often place excessive trust in AI outputs without adequate validation. This “automation bias” can lead to poor decisions or unchecked dissemination of inaccuracies, especially when AI-generated outputs are treated as authoritative without human oversight.
Agentic AI Limitations
1. Security and Ethical Risks
Agentic AI introduces new attack surfaces. Autonomous systems capable of executing actions pose risks if compromised or poorly governed. Studies show over 60,000 successful prompt injection attempts across enterprise AI setups, exposing sensitive data or bypassing controls.
2. Explainability and Transparency Issues
Because agentic systems operate through complex reasoning and planning layers, their decisions can be opaque. This lack of explainability challenges compliance and auditability, especially in sectors like healthcare or finance that require clear accountability trails.
3. Operational Failures and Governance Challenges
Real-world deployments reveal mixed performance. While some agents achieve over 90% success rates, others underperform due to poor data quality or misaligned objectives. Enterprises often underestimate the governance complexity of monitoring, restricting, and auditing agentic actions across systems.
4. Reliability and Vendor Ecosystem Concerns
“Agent washing” has become common vendors rebranding chatbots as “AI agents.” Of thousands of solutions marketed as agentic, only a small fraction demonstrate true autonomous capability. Immature tooling and inconsistent standards increase the risk of operational failure or integration breakdowns.
Integration and Convergence of Agentic AI and Generative AI
How Generative AI Powers Agentic AI
Generative AI often serves as the creative and reasoning core within an agentic system. While the agent determines what needs to be done, the generative model determines how to express or construct it. For example, during a workflow, an agent might rely on a generative model to:
- Draft customer communications
- Generate code or scripts for task automation
- Summarize findings or create reports for human review
In this way, generative AI provides linguistic, creative, or analytical outputs that the agentic system integrates into broader, goal-directed execution.
Multi-step Orchestration and Tool Integration
Agentic systems coordinate multiple generative and analytical components to achieve complex objectives. A single agent may use text generation for documentation, image generation for design tasks, and data analysis models for decision support, combining them through tool orchestration and API integration.
This layered integration turns isolated generative models into parts of a cohesive, end-to-end automation framework capable of perceiving, reasoning, and acting autonomously.
Quality Control and Self-Improvement via Agentic Layers
Agentic AI introduces feedback and evaluation loops around generative models. Agents can assess generated outputs, detect inconsistencies, request re-generation, or cross-verify information against databases.
Over time, this self-correcting mechanism improves both accuracy and reliability, reducing the risk of hallucinations that plague standalone generative systems.
Collaborative Human-AI Workflows
In practical enterprise settings, the two paradigms coexist through shared responsibility frameworks:
- Generative AI produces creative or analytical outputs for human validation.
- Agentic AI autonomously manages execution but escalates to humans for exceptions, ethical decisions, or creative judgment.
This “human-in-the-loop” model ensures efficiency without losing oversight.
Emerging Protocols for Agent Communication and Security
As multi-agent ecosystems grow, efforts are starting to standardize how agents communicate, ensure safety, and manage access control. Frameworks like LangChain, AutoGen, and OpenDevin focus on secure tools and safe communication. They also ensure controlled autonomy. This way, collaboration stays transparent and secure.
Together, these developments signal the fusion of generative intelligence with agentic autonomy, creating systems that not only produce high-quality content but also act upon it intelligently, bridging creativity and execution within unified AI ecosystems.
Future Trends and Developments
Increasing Convergence and Unified Workflows
The next phase of enterprise AI will blur the lines between generative and agentic systems. Organizations are shifting to unified workflows.
Generative models in these systems create:
- Asset reports
- Communications
- Code
Then, agentic layers automatically validate, deploy, and act on these outputs. This integration turns AI into an active partner in full business processes, not just a passive helper.
Enhanced Accuracy and Reasoning in Agentic Systems
Future agentic AI will use hybrid reasoning models. It will mix large language models with structured logic and symbolic planning. It will also use real-time data retrieval. These systems will cut down on hallucinations. They do this by linking generative outputs to verified knowledge. Then, they reason about context before taking action.
Proactive and Predictive Autonomous Systems
Modern agentic systems mainly respond to goals or prompts. The next generation will be proactive and predictive. They will identify risks or opportunities before humans can. An AI-driven operations agent can spot supply chain delays. It can reroute shipments on its own and alert leadership before disruptions occur.
Creative Autonomy: From Ideation to Execution
Generative and agentic intelligence will come together. This will create AI systems that can think creatively and act on their ideas. Future systems could do more than create designs or campaign drafts. They might also launch, test, and optimize campaigns on their own. This blends creativity with real-time execution.
Emerging Standards and Governance Frameworks
As autonomy grows, strong governance and ethics frameworks will be vital. Industry groups and regulators are creating standards. They focus on agent behavior. They also cover explainability and fail-safe mechanisms. Find clear audit trails for autonomous decisions. Use standard APIs for teamwork among agents. Improve accountability models for AI results.
AI is clearly changing. It is moving from generative help to autonomous orchestration. The systems of tomorrow won’t just create, they’ll operate, decide, and continuously improve. Enterprises need to make sure their autonomy is trustworthy and can be audited. It should also align with human intent.
Strategic Implications for Organizations
Leveraging Generative AI for Quick Productivity Wins
Generative AI offers the fastest path to visible results.
Organizations can use it for:
- Marketing
- Customer support
- Software development
- Operations
It speeds up content creation, automates documentation, and improves communication.
These low-risk, high-impact use cases boost internal AI knowledge. They also show clear productivity improvements.
Early adoption helps teams with:
- Prompt engineering
- Data governance
- Quality assurance
This learning boosts their skills and efficiency.
Planning for Agentic AI Adoption in Complex Domains
Agentic AI requires a strategic and staged approach. Enterprises should begin with contained domains, customer service workflows, IT operations, or logistics before expanding to enterprise-wide automation. Successful adoption depends on:
- Data readiness: clean, structured, and accessible data across systems
- Clear boundaries: defined rules for agent autonomy and escalation
- Governance frameworks: audit trails, approval checkpoints, and security protocols
Agentic AI’s value multiplies when integrated across ecosystems but so do its risks. Establishing control structures early prevents governance failures later.
Skill Development: Prompt Engineering and Agentic System Design
The convergence of generative and agentic AI introduces new roles and skill requirements. Organizations will need:
- Prompt engineers who translate intent into effective AI instructions
- AI architects who design multi-agent systems and orchestration layers
- Governance specialists who ensure transparency and ethical compliance
- Human-AI collaboration managers who define when and how humans stay in the loop
Upskilling teams in these areas will be key to scaling AI responsibly.
Balancing Human Oversight with Increasing Autonomy
Enterprises must strike a balance between efficiency and control. The most effective AI strategies follow a “human-in-command” model:
- Generative AI assists human creativity.
- Agentic AI executes autonomously but escalates edge cases.
This hybrid approach ensures productivity gains without sacrificing accountability or ethical compliance.
Timeline Expectations and Success Factors
Generative AI projects can yield results in weeks, but agentic AI initiatives typically require 6–12 months for data preparation, integration, and governance alignment before measurable ROI appears.
Key success factors include:
- Starting small with high-value, automatable processes
- Building strong data and API integration foundations
- Implementing continuous monitoring and learning loops
- Maintaining transparent decision logs for auditability
Organizations that manage this evolution deliberately will move from AI-assisted productivity to AI-driven transformation, positioning themselves for competitive advantage as autonomy matures.
Conclusion
Generative AI and Agentic AI represent two different stages in smart systems. One focuses on creation. The other emphasizes doing things on its own.
Generative AI boosts productivity. It helps people work faster, think more widely, and communicate better. It boosts human skills. This leads to more creativity and efficiency in many industries.
Agentic AI, in contrast, redefines how work gets done. It turns static outputs into active systems. These systems can think, plan, and act toward specific goals with little help from people. Where generative AI supports human performance, agentic AI extends it.
For organizations, the strategic path forward isn’t about choosing between the two it’s about integration. Generative AI helps a lot. It automates tasks and generates insights quickly. Agentic AI creates lasting change by automating whole workflows. They create a range of abilities: from smart help to self-directed management.
Winners in the next decade will be those who build responsibly. They will mix creativity, autonomy, and governance into one AI operating model. This model must be productive, explainable, and aligned with human values.
FAQs
How do Generative AI and Agentic AI differ?
Generative AI focuses on creating content text, images, code based on input prompts. Agentic AI, on the other hand, focuses on goal achievement by autonomously executing complex, multi-step processes without constant human oversight.
Can Agentic AI replace Generative AI?
No, Agentic AI does not replace Generative AI. They complement each other. Generative AI creates content and provides insights, while Agentic AI acts on that content and carries out tasks autonomously.
Which offers a higher ROI?
Generative AI tends to provide quicker ROI through productivity boosts in tasks like content creation, while Agentic AI offers long-term, transformational ROI by automating end-to-end processes, though it requires more upfront investment and preparation.
How can organizations deploy both effectively?
Organizations should start with Generative AI to build productivity and AI fluency, then move to Agentic AI for more complex, autonomous process automation. Combining both allows businesses to optimize creativity and execution across workflows.
What are the key risks of Generative and Agentic AI?
Generative AI risks include inaccuracies and hallucinations in its outputs. Agentic AI introduces risks around autonomy and security, such as the potential for unauthorized actions or lack of transparency in decision-making.
How long does it take to adopt Agentic AI?
Adopting Agentic AI typically takes 6–12 months, involving data preparation, system integration, and establishing governance frameworks before full deployment.
This page was last edited on 2 December 2025, at 5:09 pm
Contact Us Now

Contact Us Now
Start a conversation with our team to solve complex challenges and move forward with confidence.