Generative AI is triggering a seismic shift in how businesses operate, compete, and innovate, redefining how entire sectors create value. Understanding how generative AI is reshaping industries is no longer optional for leaders, as this technology now enables machines to generate original text, images, code, designs, and insights at scale. According to McKinsey, generative AI could unlock between $2.6 and $4.4 trillion in annual economic value across global industries.
Organizations that grasp how generative AI is reshaping industries can accelerate productivity, shorten time to market, and unlock entirely new business models. Those that delay risk losing relevance as competitors move faster with AI-driven workflows. This article provides expert analysis and a practical roadmap, explaining how generative AI works, where it delivers the most impact across industries, how to adopt it responsibly, and what lies ahead as the technology continues to evolve.
What Is Generative AI and Why Is It Transformative?
Generative AI is a type of artificial intelligence that creates entirely new content—such as text, images, audio, or code—based on patterns it learns from massive datasets. Unlike earlier AI, which mostly classified or predicted, generative AI can generate human-like responses, designs, or solutions at scale.
Key Characteristics of Generative AI
- Foundation Models: Large language models (LLMs) like GPT-4 or Claude are trained on diverse data, enabling them to generate creative outputs.
- Multimodal Capabilities: Generative AI works with text, images, video, and audio, exemplified by tools like DALL-E and Google Gemini.
- Historic Shift: Prior AI focused on recognizing patterns or automating decisions. Generative AI enables creation—powering applications from automated report writing to synthetic image generation.
- Revolution in “Creation”: Its ability to produce drafts, designs, code, and multimedia accelerates workflows across industries.
“Generative AI is the shift from automating repetitive tasks to automating creative and problem-solving processes for the enterprise.” — Clear synthesis of analyst consensus
How Does Generative AI Differ From Traditional AI?
Generative AI differs fundamentally from traditional AI by moving from problem-solving and prediction to creation and synthesis. This leap unlocks new possibilities for automation, personalization, and value generation.
Comparative Overview
| Aspect | Traditional AI | Generative AI |
| Core Function | Predicts, classifies | Creates new content/data |
| Example Tasks | Fraud detection, sorting | Writing reports, designing products |
| Input/Output | Input → label/score | Prompt → original text/image/video |
| Use Cases | Loan approvals, spam | Marketing copy, custom design, chatbots |
| Business Impact | Operational efficiency | Innovation, new products, rapid iteration |
Key distinctions:
- Traditional AI automates structured decisions and tasks by learning rules from existing data.
- Generative AI produces novel content or solutions by learning deeper patterns and relationships—enabling dynamic, personalized, and creative applications at scale.
How Generative AI Is Reshaping Industries?
![How Is Generative AI Reshaping Industries? [2024 Industry Analysis]](https://riseuplabs.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/how-is-generative-ai-reshaping-industries-2024-industry-analysis.webp)
Generative AI is actively transforming sectors by automating content creation, augmenting knowledge, and enabling new business models. Here is a sector-by-sector guide to the most significant industry impacts.
Sector Impact Table
| Industry | Key Use Cases | Benefits | Challenges/Risks |
| Healthcare | Diagnostic automation, personalized care, RAG | Faster diagnoses, tailored care | Accuracy, bias, compliance risks |
| Finance | Fraud detection, report automation, trading | Speed, accuracy, client insights | Data leakage, hallucination, regulation |
| Retail | Chatbots, inventory optimization, personalization | Better CX, inventory agility | Data privacy, over-reliance |
| Manufacturing | Predictive maintenance, gen design, supply chain | Fewer breakdowns, faster prototyping | Data quality, IP, workforce impact |
| Education | AI tutoring, content creation, upskilling | Personalized learning, efficiency | Misinformation, digital divide |
| Legal | Contract analysis, doc summarization | Time savings, reduced errors | Misinterpretation, ethical issues |
| Media | Dynamic content, video generation | Scalability, engagement | Deepfakes, copyright |
| Logistics | Route optimization, demand forecasting | Cost savings, predictability | Data gaps, system complexity |
| Energy | Grid balancing, predictive maintenance | Reliability, operational savings | Regulation, model drift |
Healthcare
Generative AI is accelerating diagnostic workflows, synthesizing patient histories, and personalizing treatment pathways. Models can summarize complex medical records (e.g., using Retrieval-Augmented Generation) and aid in interpreting scans.
Examples:
- AI-generated clinical summaries cut physician admin time.
- Synthetic patient data supports research while preserving privacy.
Key Risks:
- Model bias may affect diagnosis quality.
- Compliance (HIPAA, GDPR) is critical for patient data.
Finance
Banks and fintechs leverage generative AI for automating financial reports, improving fraud detection, and generating personalized investment insights.
Examples:
- Automated underwriting speeds up loan approvals.
- AI analyzes transaction data for suspicious activity.
Key Risks:
- Hallucinations (confident but false outputs) can cause compliance issues.
- Regulatory scrutiny requires robust data governance.
Retail
Retailers use generative AI for smart chatbots, hyper-personalized marketing, and agile inventory management.
Examples:
- Virtual agents handle customer queries in real time.
- Demand forecasting models reduce stockouts and overstock.
Key Risks:
- Over-reliance on AI can hinder human oversight.
- Customer data privacy must be ensured.
Manufacturing
Generative AI enables predictive equipment maintenance, faster product prototyping, and optimization across the supply chain.
Examples:
- Predictive models prevent unplanned downtime.
- Quick design iteration through AI-generated concepts.
Key Risks:
- Ensuring data accuracy and IP protection.
- Upskilling workforce for AI-integrated processes.
Other Sectors: Education, Legal, Media, Logistics, Energy
Education:
AI creates adaptive tutoring systems and learning content, helping students learn at their own pace. However, teachers must be vigilant about content accuracy.
Legal:
AI streamlines contract review and case research, saving time. Yet, misinterpretation of legal language remains a risk.
Media:
Automated content and video generation fuel rapid multimedia publishing. Safeguards are needed to avoid misinformation and copyright infringement.
Logistics:
AI-driven route and demand optimization cut costs and improve efficiency, but require quality data integration across systems.
Energy:
Generative AI assists with grid load balancing, price forecasting, and maintenance scheduling, contributing to greater reliability and operational efficiency.
What Are the Key Benefits and Opportunities of Generative AI for Business?

Generative AI offers organizations sweeping benefits—from productivity gains to the creation of new business models—making it a pivotal driver of competitive advantage.
Top Benefits
- Productivity and Speed: Automates content creation, rapid reporting, and workflow acceleration.
- Cost Reduction: Reduces operational and labor costs by automating repetitive tasks at scale.
- Personalization: Delivers tailored customer experiences, content, and recommendations.
- Innovation: Enables new products, services, and revenue streams through automated design and ideation.
- Decision Acceleration: Synthesizes and summarizes massive amounts of information for faster insights.
Stat Callout:
Industry estimates forecast a $2.6–$4.4 trillion annual positive impact from generative AI adoption (McKinsey).
What Are the Main Challenges and Risks of Generative AI Adoption?
While generative AI drives value, it also presents challenges that leaders must address to ensure responsible, effective deployment.
Common Challenges and Risks
- Hallucination & Factual Errors: AI may produce convincing but inaccurate outputs.
- Bias and Fairness: Inherited data biases can lead to unfair or discriminatory decisions.
- Security and Data Leakage: Sensitive information may be exposed if AI is not securely managed.
- Intellectual Property Concerns: AI-generated content can raise ownership and copyright questions.
- Regulatory Compliance: Emerging rules (e.g., EU AI Act) demand transparency, documentation, and sector-specific controls.
- Operational Hurdles: Integrating AI at scale requires upskilling staff and updating processes.
How Can Companies Adopt Generative AI? A Stepwise Framework
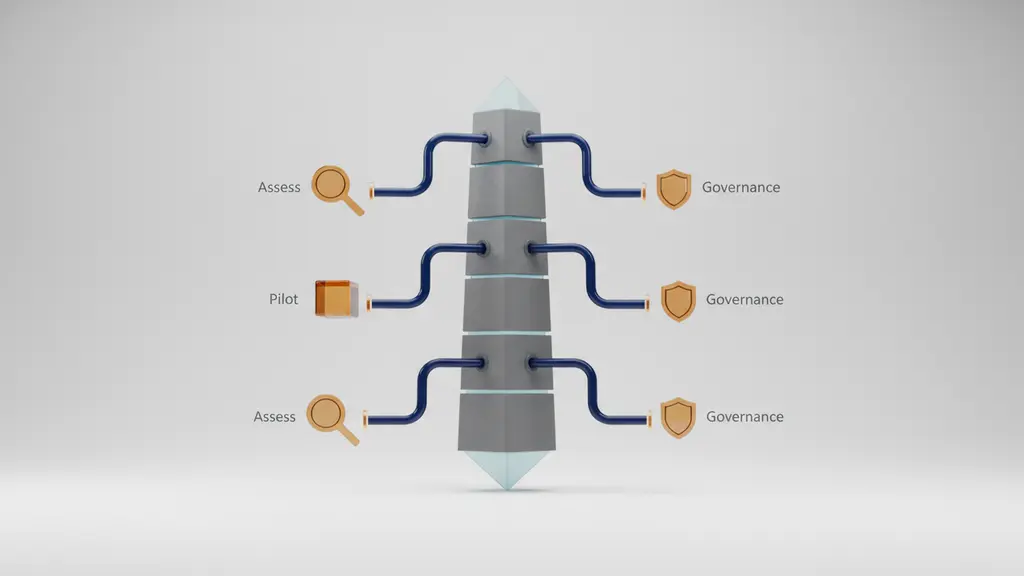
A structured approach maximizes generative AI’s benefits—while containing risk. Here’s a clear, actionable adoption roadmap for business leaders.
Stepwise Adoption Framework
- Assess Business Needs & Data Readiness
Identify use cases where generative AI adds the most value. Examine data quality, privacy, and accessibility. - Pilot Projects & Quick Wins
Launch contained experiments in high-impact areas (e.g., report generation, customer service bots). - Measure ROI & Impact
Set clear goals and metrics. Track productivity, cost savings, and outcome quality. - Upskill Teams & Change Management
Invest in staff training and foster a culture of responsible AI use and innovation. - Responsible AI Governance
Implement explainability, transparency, and ethical guardrails aligned with regulations. - Integrate with Existing Processes
Ensure AI complements human workflows and technology systems.
Visualize this as your “Generative AI Adoption Journey”—from scoping to scaling, with checkpoints for governance and learning.
What Future Trends Will Shape Generative AI and Industry Transformation?
Generative AI is rapidly evolving. Several key trends will define its business impact and operational realities in the years ahead.
Emerging Trends
- Agentic AI: Autonomous systems capable of reasoning, planning, and acting—beyond simple chat or copy tasks.
- Multimodal Models: AI integrating text, images, audio, and video for richer, context-aware applications.
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG): Directly connects AI with live databases and proprietary knowledge, enhancing relevance and accuracy.
- Domain-Specific & Proprietary Models: Customized large language models tailored for industry or organizational needs.
- Regulatory Evolution: Heightened standards (e.g., EU AI Act) will make transparency, risk management, and documentation core to compliance.
- Workforce Transformation: New job roles, upskilling, and AI-assisted workflows will reshape organizational talent strategies.
Industry-by-Industry Generative AI Impact Table [Summary Grid]
| Industry | Key Use Cases | Benefits | Challenges/Risks |
| Healthcare | Medical imaging analysis, RAG for records | Rapid diagnosis, personalized care | Bias, data privacy, compliance |
| Finance | Automated reporting, fraud detection | Speed, accuracy, customer insights | Hallucinations, regulation |
| Retail | Virtual agents, inventory AI, marketing | Better CX, agility, cost control | Data privacy, over-reliance |
| Manufacturing | Predictive maintenance, gen design prototypes | Fewer failures, quick innovations | IP, data integrity, upskilling |
| Education | AI tutoring, content gen, upskilling | Personalized pace, efficiency | Misinformation, digital divide |
| Legal | Contract review, research acceleration | Time-saving, lower costs | Interpretation errors, bias |
| Media | Content and video generation | Scalability, engagement growth | Deepfakes, copyright risk |
| Logistics | Route planning, demand AI, optimization | Cost savings, predictability | Data gaps, complexity |
| Energy | Grid optimization, failure prediction | Efficiency, reliability | Regulation, data integration |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ): Generative AI and Industry Transformation
What is generative AI and how is it different from predictive AI?
Generative AI creates new content, such as text, images, or code, while predictive AI focuses on forecasting outcomes or classifications based on existing data. Generative AI’s ability to synthesize content makes it transformative for business innovation.
Which industries are most impacted by generative AI?
Healthcare, finance, retail, manufacturing, education, legal, and media are among the sectors experiencing significant transformation through automation, personalization, and new service models enabled by generative AI.
How is generative AI used in healthcare, finance, retail, and manufacturing?
In healthcare, it speeds diagnosis and summarizes patient data; in finance, it automates reporting and enhances fraud detection; in retail, it powers chatbots and demand forecasting; in manufacturing, it drives predictive maintenance and rapid prototyping.
What are the main benefits of generative AI for businesses?
Generative AI boosts productivity, cuts costs, enables hyper-personalization, accelerates innovation, and helps leaders make faster, data-driven decisions.
What challenges do businesses face in implementing generative AI?
Key challenges include potential for biased or inaccurate outputs, data security risks, regulatory compliance demands, and the need for new skills and ethical governance.
How can companies get started with generative AI adoption?
Start by assessing use cases and data readiness, launch focused pilot projects, measure impact, upskill teams, implement responsible governance, and integrate AI with business processes.
What are the risks of generative AI (bias, hallucination, data security)?
Risks include AI-generated misinformation (“hallucinations”), embedded bias, potential data leakage, intellectual property questions, and evolving compliance requirements.
How does generative AI affect jobs and the workforce?
Generative AI automates some repetitive tasks but also creates new roles—especially in AI oversight, prompt engineering, and ethical management—requiring workforce reskilling and adaptation.
What future trends should businesses watch for in generative AI?
Agentic AI, multimodal systems, Retrieval-Augmented Generation, new regulatory frameworks, and specialized AI models are set to drive industry change in the next few years.
What best practices support responsible and ethical generative AI use?
Follow transparent governance, validate model accuracy, ensure explainability, monitor for bias, protect data, comply with regulations, and foster ongoing education.
Conclusion: Preparing for the GenAI-Powered Future
Generative AI is not a passing trend—it is a fundamental shift that is already reshaping industries, unlocking new business models, and redefining the future of work. By understanding how generative AI operates, where it adds the greatest value, and embedding responsible governance, forward-thinking organizations can secure a long-term competitive edge. The time to act is now: assess your readiness, pilot strategically, and invest in the skills and safeguards that will define tomorrow’s leaders.
Ready to begin your generative AI journey? Connect with our experts for a tailored assessment or an executive workshop on responsible AI adoption.
Key Takeaways
- Generative AI drives sector-wide transformation, offering $2.6–$4.4 trillion in annual value.
- Healthcare, finance, retail, and manufacturing are early leaders in adoption and impact.
- Key benefits include productivity, cost savings, personalization, and innovation.
- Risks—such as bias, errors, and compliance—require strong governance.
- A stepwise adoption approach maximizes impact and minimizes disruption.
This page was last edited on 2 February 2026, at 9:19 am
How can we help you?

























