AI is no longer an experimental add-on to software engineering. It is reshaping how applications are designed, built, tested, and maintained. From AI-assisted coding and automated testing to intelligent deployment pipelines, AI and the future of software development are now deeply intertwined, changing both daily workflows and long-term career paths.
For developers, engineering leaders, and technical educators, this shift brings urgent questions. Which skills will remain essential as AI tools mature? How will roles evolve rather than disappear? And which technologies should teams adopt now to stay competitive rather than reactive?
This guide provides a practical, forward-looking view of AI and the future of software development. You will explore how AI is transforming real-world development processes, what tasks are being augmented or replaced, and how developers can adapt through targeted skill-building and tool mastery. By the end, you will have a clear roadmap to navigate change with confidence and build a career that stays relevant as AI continues to evolve.
How Is AI Changing Software Development Right Now?
AI is transforming software development by automating repetitive tasks, enhancing code quality, and enabling teams to build and maintain software faster. Today’s AI-powered software engineering tools—from code assistants to DevOps automation—help developers focus on design, architecture, and innovation.
- Automated Code Generation: Tools like GitHub Copilot and Google Gemini use large language models (LLMs) to suggest and generate code in real time, directly within integrated development environments (IDEs).
- Testing, Debugging, and DevOps: Machine learning streamlines testing, bug detection, and deployment with predictive analytics and intelligent automation.
- Collaboration, Not Replacement: AI augments developers’ capabilities. While it handles many repetitive tasks, human oversight remains critical for complex problem-solving, creativity, and project leadership.
Traditional vs. AI-Augmented Software Development Workflow
| Workflow Stage | Traditional Approach | AI-Augmented Approach |
| Code Writing | Manual coding | AI-assisted generation & autocompletion |
| Testing & Debugging | Manual/unit testing, hunt for bugs | Automated test case creation, AI bug detection |
| Code Review | Human peer review | AI-powered suggestions, faster feedback |
| Deployment (CI/CD) | Scripted pipelines, manual QA | Automated monitoring, predictive deployment |
| Documentation | Manual docs | Auto-generated doc summaries, code comments |
AI and the Future of Software Development: What It Means for Teams and Careers
AI and the future of software development are inseparable as engineering teams move away from purely manual, code-first workflows toward AI-augmented systems that prioritize speed, quality, and adaptability. AI is no longer just a productivity aid. It is becoming a core part of how modern software is planned, built, and maintained.
Rather than replacing developers, AI is reshaping their role. Repetitive tasks such as boilerplate coding, testing, and documentation are increasingly automated, allowing engineers to focus on higher-value work like system design, architecture, performance optimization, and complex problem-solving.
For businesses, this shift results in faster time to market, more resilient systems, and greater capacity to innovate. For developers, long-term success depends on learning how to work effectively with AI tools, review and validate AI-generated outputs, and apply human judgment where context, ethics, and creativity are essential.
Understanding AI and the future of software development is no longer optional. It is a foundational requirement for building sustainable products, high-performing teams, and careers that remain relevant in a rapidly evolving technology landscape.
How Does AI Automate and Assist Development Tasks?
AI tools automate software development by assisting with code autocompletion, generating functions, spotting bugs, and even writing documentation. These improvements save developers time and reduce errors in everyday workflows.
Key AI-powered tasks include:
- Code Autocompletion: AI predicts and suggests contextually relevant code snippets as you type (e.g., Copilot, Gemini).
- Automated Code Generation: Developers can describe logic in natural language; AI generates working functions, classes, or scripts.
- Error Detection: Real-time issue flagging helps identify security flaws, syntax errors, or logic bugs faster.
- Test Case Creation: AI creates testing scenarios and scripts to validate application behavior.
- Documentation Generation: Code assistants summarize and document code automatically, improving maintainability.
Limitations to note:
- AI sometimes lacks deep context or creativity needed for unique algorithm design.
- Code suggestions may require human review to ensure clarity, safety, and compliance.
AI and DevOps: Optimization Across the SDLC

AI is revolutionizing DevOps by automating pipeline monitoring, accelerating continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD), and enabling predictive maintenance. This leads to greater efficiency and reliability throughout the software development lifecycle (SDLC).
Current AI-driven DevOps enhancements:
- Automated Monitoring: Machine learning models detect anomalies in system logs and application performance, triggering alerts or rollbacks if needed.
- Predictive Deployment: AI forecasts deployment risks and optimizes resource allocation during release cycles.
- QA Automation Bots: Intelligent bots handle repetitive testing and regression checks, reducing manual QA workload.
- Enterprise Scale: Large organizations use AI to maintain reliability and uptime, adapting deployment strategies in real time.
Companies integrating AI into DevOps report faster release cycles, improved reliability, and better scalability of their software infrastructure.
What Are AI’s Current Risks, Limitations, and Reliability Concerns?
AI-generated code, while powerful, presents risks that developers and organizations must manage proactively. The most pressing concerns are hallucinations, bias, security risks, and regulatory gaps.
- Hallucinations: AI tools sometimes invent nonexistent APIs, introduce logical errors, or suggest undocumented code patterns.
- Low Explainability: It can be hard to understand why AI made certain recommendations, complicating debugging or audits.
- Security Vulnerabilities: Automatically generated code may not follow security best practices, introducing risks like injection flaws or data leaks.
- Bias in Training Data: AI reflects the biases in its training datasets—potentially leading to unfair, non-compliant, or non-inclusive code.
- Regulatory Compliance: Current legal frameworks struggle to keep up with AI-generated intellectual property and auditability standards.
Mitigation strategies:
- Always perform human review of AI-generated code.
- Use secure code scanning and compliance checks.
- Stay informed about evolving regulatory requirements.
Will AI Replace Software Developers? Exploring Future Scenarios
AI is unlikely to wholly replace software developers in the near term; instead, it will reshape roles and raise expectations for collaboration and expertise. In the coming years, developers can expect new responsibilities, evolving workflows, and a growing need for adaptability.
Outlook by timeline:
| Timeframe | Scenario | Impact on Roles |
| Short Term | Augmentation (2024–2026) | AI boosts productivity; developers lead design and oversight |
| Mid Term | Hybrid Teams (2026–2028) | Human-AI collaboration standard; higher entry bar; new hybrid skills emerging |
| Long Term | Toward AGI? (2028–2030+) | Full automation possible in narrow domains, but complex systems still need humans |
- Force-multiplier effect: According to Gartner and McKinsey, developer hiring remains strong, with human–AI hybrids in demand.
- Roles at risk: Routine coding, junior bug-fix positions, and code maintenance are most vulnerable to automation.
- Roles in demand: Systems architects, AI tool integrators, code reviewers, designers, and product managers.
Snippet-ready:
While AI handles repetitive programming tasks, human developers remain central to creative, strategic, and high-stakes aspects of software engineering.
Human-AI Collaboration: The Future Developer Workflow
The future of software engineering is a partnership, not a replacement. Developers increasingly act as prompt engineers, code reviewers, and integrators—working alongside AI to deliver high-quality software.
Workflow shifts include:
- Writing clear prompts or requirements for AI code assistants.
- Overseeing AI-generated code, correcting errors, and ensuring compliance with project standards.
- Taking on expanded roles—such as integrating AI services, defining architecture, and leading ethical reviews.
Example Week for a Mid-Level Developer:
- Monday: Use AI assistant to scaffold a new feature.
- Tuesday: Review, refactor, and test AI-generated code.
- Wednesday: Collaborate with hybrid team on security audit using AI-powered code scanning.
- Thursday: Design prompts for AI to automate documentation.
- Friday: Mentor peers on integrating new AI tools.
New Career Paths and Evolving Roles
As AI reshapes workflows, it also opens new career opportunities that blend software, data, and product expertise.
Emerging roles include:
- AI Tool Curator: Evaluates and integrates the best AI developer tools for teams.
- Code Reviewer/QA Lead: Specializes in reviewing and validating AI-generated code.
- AI Ethics Reviewer: Ensures that code and processes adhere to ethical and regulatory norms.
- Data-centric Product Managers: Bridge data, AI, and customer needs for smarter product design.
Education is evolving: Coding bootcamps and CS curricula increasingly focus on AI literacy, prompt engineering, and responsible machine learning use.
What Skills Will Software Developers Need in the Age of AI?
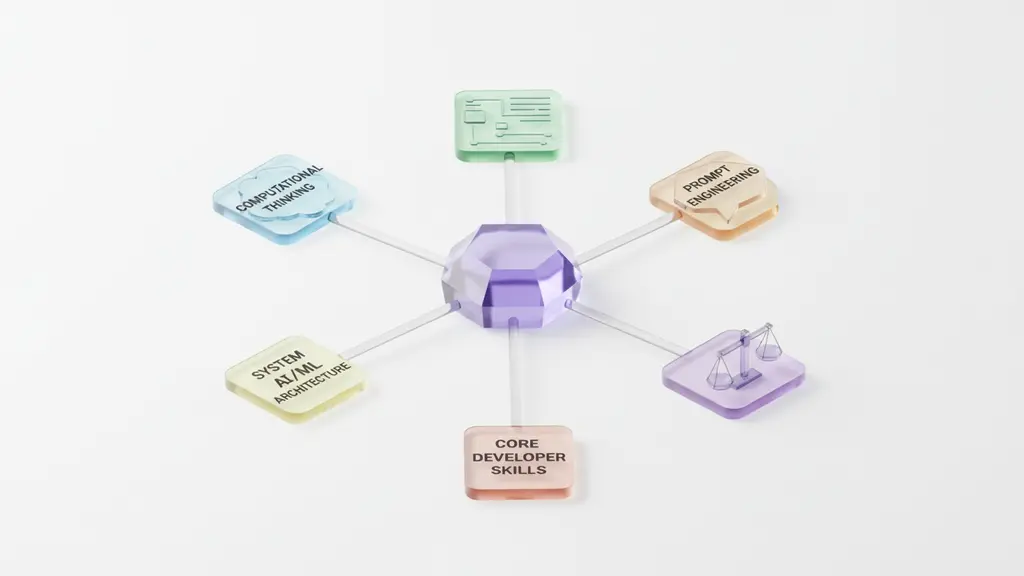

Developers will need a mix of traditional computer science fundamentals, AI/ML basics, and new skills in prompt engineering, risk management, and communication. Continuous learning will be essential for career resilience.
Top 5 Skills for Developers in the Age of AI:
- Computational Thinking: Ability to break down complex problems—still foundational even as AI assists with implementation.
- System Design and Architecture: Understanding scalable, resilient systems that go beyond code snippets.
- AI/ML Literacy: Grasping concepts like data labeling, LLMs, and model limitations (even for non-specialists).
- Prompt Engineering: Ability to interact effectively with generative AI, crafting queries and reviewing outputs.
- Soft Skills: Communication, creativity, domain expertise, and ethical judgment for hybrid team success.
AI Skills Roadmap for Developers
| Skill | Why It Matters | How to Build It | Useful Resources |
| System Design | Drives app scalability | Study case studies, practice | “Designing Data-Intensive Applications” |
| AI/ML Fundamentals | Informs tool selection | AI bootcamps, online courses | Coursera ML Specialization, DataCamp |
| Prompt Engineering | Optimizes AI assistance | Experiment, reference guides | GitHub Copilot Labs, OpenAI docs |
| Code Review/Audit | Ensures code safety | Peer reviews, code scanning | SonarQube, Snyk, JetBrains AI |
| Lifelong Learning | Keeps skills current | Micro-certifications, side projects | Udemy, Coursera, company L&D |
How to Upskill: Education, Bootcamps, and On-the-Job Strategies
Upskilling for AI-driven development is accessible, with flexible options ranging from online courses to company-sponsored programs.
Top strategies for AI upskilling:
- Attend AI-focused bootcamps: Programs from CMU, DataCamp, Coursera, and others now offer AI/ML and prompt engineering tracks.
- Build real-world projects: Try personal side projects using AI APIs or integrating Copilot into workflow—maintain a portfolio illustrating practical experience.
- Pursue micro-certifications: Short, stackable credentials keep skills sharp and demonstrate commitment.
- Leverage workplace learning: Seek out peer learning, mentorship, and company-sponsored training.
Popular resources for developer upskilling:
| Method | Examples |
| Bootcamps | CMU AI Bootcamp, Springboard |
| Online Courses | Coursera, DataCamp, Udacity |
| Certifications | Google Cloud ML, AWS AI, IBM AI |
| Project Platforms | GitHub, Kaggle, OpenAI Playground |
| Community Mentorship | Developer meetups, LinkedIn groups |
Which AI Tools and Platforms Are Shaping Software Engineering?
Dozens of AI developer tools are streamlining workflows, from autocompletion to CI/CD integration. Choosing the right tool depends on project needs, team size, and safety requirements.
Comparison of Leading AI Developer Tools
| Tool | Main Function | Usage | Pros | Cons |
| Copilot | Code autocompletion | IDE plugin (VS Code, etc.) | Fast, language support | Context limits, paid tier |
| Gemini | Code generation, QA | Google Cloud, select IDEs | Multi-modal, Google API stack | Limited IDE support (as of 2024) |
| JetBrains AI | IDE-native AI assistant | JetBrains IDEs | Deep integration, context-rich | Mostly JetBrains ecosystem |
| TensorFlow, PyTorch | ML modeling, deployment | Python/ML workflows | Open source, powerful | Learning curve, not for beginners |
| Watsonx | Enterprise AI platform | Custom, large-scale SDLC | Scale, collaboration, security | Enterprise pricing, setup |
Tool selection criteria:
- Reliability and accuracy of code suggestions
- Security and explainability of outputs
- Support for preferred programming languages and workflows
- Community support and documentation
Real-World Case Studies: AI Tool Integration and ROI
Organizations large and small are reaping benefits from AI tools—but only when integration is strategic and workflows are adapted.
Case Study: SME vs. Enterprise Adoption
- SME (Small Team): Adopted Copilot for Python and JavaScript workflows. Within three months, saw a 25% reduction in time spent on repetitive coding tasks, though manual code reviews remained essential.
- Enterprise: Integrated JetBrains AI with CI/CD and QA pipelines. Reported faster bug detection but faced challenges training teams and customizing AI models for legacy codebases.
Key metrics reported:
- Time saved: Faster prototyping and code documentation
- Bug rate: Slight initial increase in errors, mitigated through stricter reviews
- ROI: Positive where AI adoption was paired with training and workflow updates
Common failure points:
- Over-trusting AI-generated code without human oversight
- Lacking clear guidelines for tool use and code review
What Are the Main Risks, Limitations, and Ethics of AI in Software Development?
AI in software development introduces security, ethical, and compliance risks. Proactive risk management and transparent processes are critical for safe adoption.
Key risks and ethical challenges:
- Security Vulnerabilities: Generated code may include insecure patterns or expose sensitive data.
- Compliance Gaps: Arriving code can conflict with internal standards or upcoming regulations (e.g., the EU AI Act, NIST AI Risk Management Framework).
- Intellectual Property: Source and originality of AI-generated code can be unclear, posing copyright risks.
- Bias and Fairness: Models can perpetuate or amplify bias from training data.
- Transparency & Accountability: Hard-to-audit decision-making processes raise issues for traceability and governance.
Best practice checklist for safe AI integration:
- Always review and scan AI-generated code for vulnerabilities.
- Document sources, prompt decisions, and code reviews for compliance audits.
- Stay aligned with evolving global standards (EU AI Act, NIST guidelines).
- Build human-in-the-loop processes for critical projects.
- Assign clear accountability for reviewing and releasing production code.
The Next 5 Years in Software Engineering (2025–2030)
- AI will augment, not replace, most software engineers: Human creativity, oversight, and design remain vital.
- New roles and team structures will emerge: Hybrid teams, AI tool specialists, and ethics reviewers are on the rise.
- Developer skills will shift: Focus on system design, AI literacy, prompt engineering, and continuous learning.
- Tool adoption must be strategic and safe: Vet tools for explainability, security, and regulatory alignment.
- Organizational and personal adaptability is key: Agile learning, upskilling, and ethical leadership will define career advancement.
5-Year Forecast Table
| Scenario | Impact | Action for Developers |
| Augmentation | Most devs use AI assistants | Upskill in prompt engineering |
| Hybrid Teams | Human-AI pair programming is standard | Emphasize collaboration, review |
| New Developer Roles | AI tool/ethics reviewers in every org | Pursue AI/ML micro-credentials |
| Regulatory Focus | Compliance and audit skills in demand | Learn relevant frameworks |
| Automation Plateau | AI excels at standard tasks; humans lead complex projects | Grow system architecture expertise |
Frequently Asked Questions: AI, Careers, and Software Development
Will AI replace software developers?
AI will not replace all software developers in the foreseeable future. While AI in software development automates routine coding and repetitive tasks, humans remain essential for system design, complex problem solving, architecture decisions, and strategic leadership.
What skills do future software developers need in the age of AI?
Future developers need a balanced skill set that complements AI in software development, including computational thinking, system architecture, AI and ML literacy, prompt engineering, code auditing, and strong communication skills for working in hybrid human–AI teams.
What are the most advanced AI tools for developers?
Leading tools shaping AI in software development include GitHub Copilot, Google Gemini, JetBrains AI Assistant, TensorFlow, PyTorch, and IBM Watsonx. Each supports different workflows, from code generation and review to machine learning deployment.
Is AI-generated code reliable and safe?
AI-generated code can significantly improve productivity, but within AI in software development, it must always be reviewed for security, accuracy, and compliance. Human oversight combined with automated scanning tools is essential to ensure safe production use.
How does AI automate tasks in the SDLC?
AI in software development automates many stages of the SDLC, including code writing, error detection, test case generation, CI/CD monitoring, and documentation. This allows developers to focus on higher-level design, architecture, and optimization work.
What are the limitations of AI in programming?
Despite its strengths, AI in software development has limitations such as limited deep context understanding, risk of hallucinated outputs, potential bias, low explainability, and evolving legal and compliance challenges.
Will AI affect entry-level or junior developer jobs?
Entry-level roles focused on repetitive coding are most impacted by AI in software development. However, junior developers can future-proof their careers by learning AI tools, prompt engineering, code review practices, and system design fundamentals.
How can software engineers future-proof their careers?
To stay relevant as AI in software development evolves, engineers should invest in AI literacy, continuous learning, system design expertise, ethical development practices, and strong collaboration skills with AI-powered tools.
What is the impact of AI on DevOps and CI/CD?
AI in software development enhances DevOps and CI/CD through predictive maintenance, intelligent monitoring, automated testing, and faster feedback loops, resulting in more reliable and efficient deployments.
Are there regulations for AI-generated code?
Yes. As AI in software development becomes more widespread, regulations such as the EU AI Act and the NIST AI Risk Management Framework are shaping governance and compliance. Developers should stay informed and build audit-ready development processe
Conclusion
AI is reshaping the future of software development in fundamental ways, changing how software is built, maintained, and scaled. This shift brings both opportunity and responsibility. Teams that understand where AI adds value, where human judgment remains essential, and how to integrate AI tools thoughtfully will be best positioned to succeed.
For developers and technology leaders, long-term relevance depends on adaptability. Strengthening core engineering fundamentals, building AI literacy, and embracing continuous learning are now as important as mastering any single programming language. When AI is used as a collaborator rather than a shortcut, it becomes a powerful force for higher-quality software, faster innovation, and sustainable career growth.
The future of software development will not belong to AI alone. It will belong to professionals and organizations that know how to work with it effectively, responsibly, and strategically.
Key Takeaways
- AI is rapidly shifting software development tasks and workflows.
- Developers will remain central—but must enhance skills in system design, AI literacy, and team collaboration.
- Tool adoption should be paired with vigilant code review and compliance.
- Continuous learning is essential: embrace bootcamps, certifications, and side projects.
- Proactive adaptation positions engineers and organizations for lasting success.
This page was last edited on 2 February 2026, at 5:55 pm
Contact Us Now

Contact Us Now
Start a conversation with our team to solve complex challenges and move forward with confidence.