- What is an AI Agent?
- What is Agentic AI?
- Core Architectural Differences
- Key Capability Comparisons
- Behavioral and Operational Distinctions
- Real-World Use Cases and Applications
- Technical Frameworks and Innovations
- Governance, Risks, and Ethical Considerations
- Market Trends and Future Outlook
- When to Use Which
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has changed a lot over the years. In the past, AI systems used simple rules to make decisions. But now, with advances in machine learning and deep learning, AI is much more powerful and is used in almost every industry to automate tasks, help make decisions, and provide insights. Two important types of AI today are AI agents and Agentic AI. While they may sound similar, they are actually very different in how they work and what they can do.
In this article, we will explain the main differences between AI agents and Agentic AI. We will look at how they are built, what they can do, and the kinds of problems they are best at solving. By the end, you will know when to use each type of AI and how they can help in different industries.
What is an AI Agent?
An AI agent is a software program designed to perform specific tasks on behalf of users, responding to inputs with either predetermined behaviors or behaviors learned from experience. In many ways,
AI agents are like digital assistants that excel at completing tasks within certain boundaries. They interact with their environment by receiving inputs, processing that information, and then executing actions to achieve a particular goal.
The term “agent” suggests that these systems act on their own, but in reality, AI agents have limited autonomy. They are programmed to follow specific instructions, whether they are simple rules or complex decision trees learned from data.
For example, a customer service chatbot is a classic AI agent: it can understand and respond to customer queries by searching knowledge bases and giving answers, but it cannot independently redesign the customer experience or proactively reach out to customers on its own.
How AI Agents Work
AI agents typically work in a reactive way, meaning they only respond when prompted by a user or a change in their environment. While they can learn from data and experience, they are not independent thinkers. Instead, they follow a set of predefined rules or models that dictate their actions.
Here’s how an AI agent generally works:
- Input: The agent receives some form of data, whether it’s a customer’s question, an email to process, or market data to analyze.
- Processing: The AI agent analyzes the input using its predefined algorithms or trained models to decide what action to take. It might use techniques like natural language processing (NLP), machine learning, or a decision tree to figure out how to respond.
- Output: The agent performs an action. This could be answering a customer question, recommending a product, or sending a report.
Despite their ability to process and respond intelligently, AI agents can only act within fixed parameters. They cannot go beyond the tasks they were programmed for unless they are updated with new instructions or data.
Examples of AI Agents
AI agents are increasingly common in our daily digital experiences. Here are some common examples:
- Chatbots and Virtual Assistants: From Siri to enterprise-level customer service bots, these agents interpret user queries and execute simple commands. They use NLP to understand language, match user requests to predefined intents, and deliver responses. However, they can’t change their own behavior or take on tasks outside their programming.
- Recommendation Engines: Services like Netflix and Amazon use AI agents to analyze your behavior and suggest content or products. These agents match patterns from your previous activity to predict what you might like. However, they don’t innovate new recommendation strategies on their own they simply execute what they’ve been trained to do.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA) Bots: RPA bots automate repetitive tasks like data entry, form processing, and generating reports. They follow predefined workflows very efficiently but can’t reimagine the processes they work within.
- Trading Bots: In financial markets, trading bots execute buy and sell orders based on market signals and strategies set by humans. They react to market conditions quickly, but they do not develop new trading strategies without human intervention.
- Email Filters: Spam detection systems are AI agents that classify emails into categories like “spam” or “important” based on learned patterns. These systems improve their accuracy over time as they get more feedback, but they don’t look for new types of spam on their own unless reprogrammed.
What is Agentic AI?
Agentic AI is a type of artificial intelligence that goes beyond simple tasks. While AI agents are designed to handle specific, straightforward tasks (like answering questions or filtering emails), Agentic AI uses multiple agents working together to solve more complex problems.
Think of it as a team of robots or systems that each handle a different part of a bigger job, and they all work together to get things done.
How Agentic AI Works
Instead of reacting only when something happens, like AI agents, Agentic AI can make decisions on its own. It can plan out how to achieve a goal, adjust its plans as needed, and even solve problems without human intervention.
For example, in a business setting, an Agentic AI system could manage an entire supply chain. One agent might keep track of inventory, another could predict demand, and another could coordinate shipping. These agents work together, making decisions, sharing information, and adapting to changes as needed. If there’s a delay in a shipment, the system might automatically adjust the schedule or find alternative suppliers without anyone having to tell it what to do.
Core Architectural Differences
AI Agents Architecture
AI agents are typically single, task-focused systems that operate within clear, predefined boundaries. Their architecture is simple, with each agent designed to perform a specific job. The design of these agents typically follows a basic cycle: they receive input (data or a request), process the input based on a set of rules or patterns, and then take action based on their programming. The task could be something like answering a question or sorting emails, but the agent is limited to only what it has been programmed to do.
AI agents are modular, meaning that they consist of different parts, like a perception module (which receives data), a reasoning module (which decides how to act), and an action module (which carries out the task). However, all these parts work independently to handle only a single task, and the agent does not interact much with other agents. It’s a standalone system.
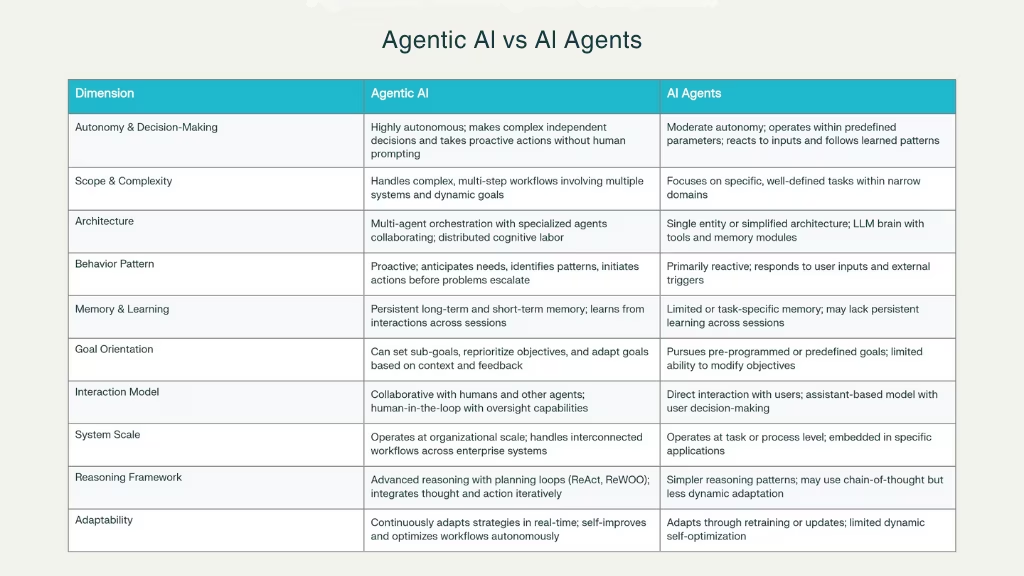
Agentic AI Architecture
Agentic AI, on the other hand, is much more complex. Instead of a single agent, it involves multiple specialized agents that collaborate to solve problems. These agents can have different roles within the system. One might be responsible for gathering data, another for analyzing it, and another for taking action based on that analysis. The key difference is that these agents don’t work alone they coordinate and share information to achieve larger, more complex goals.
One of the most important features of Agentic AI is the orchestration layer. This layer is responsible for coordinating how the agents communicate with each other, delegate tasks, and adjust their actions based on real-time information. It’s like the manager in a team, ensuring that all the agents are working together toward the same goal, but each one is handling a different part of the process.
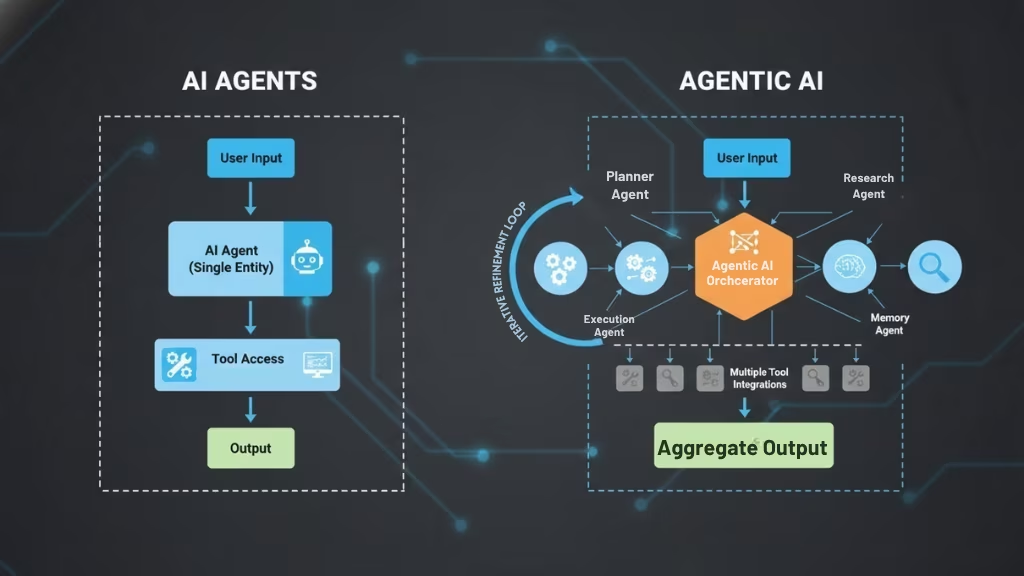
Key Capability Comparisons
Autonomy and Decision-Making
AI agents are reactive. This means they only take action when something triggers them, like when a user asks a question or when a system alert goes off. They follow specific instructions and perform tasks based on pre-programmed rules. For example, a chatbot answers customer questions but doesn’t make decisions on its own, like sending a follow-up email or deciding when to remind customers about a service.
Agentic AI, however, has higher autonomy. It doesn’t just wait for someone to tell it what to do it can set its own goals and make decisions to achieve them. For instance, if an Agentic AI system is managing a supply chain, it can decide to reroute shipments if there’s a delay, without needing instructions from a human. Agentic AI can take action based on long-term goals and learn from past outcomes to make better decisions in the future. This ability to plan ahead and act independently makes Agentic AI much more powerful than traditional AI agents.
Scope and Complexity of Tasks
AI agents are designed to handle simple, specific tasks. They are great at doing one thing at a time like answering customer questions, making recommendations, or filtering emails. But they are limited to the task they’ve been programmed for. For example, a recommendation engine can suggest products based on a user’s past shopping behavior, but it can’t change its strategy to solve bigger business challenges like increasing customer loyalty.
On the other hand, Agentic AI is designed to manage complex tasks that require multiple steps and coordination between different agents. These tasks might involve many interconnected systems. For example, in a business, Agentic AI could handle everything from tracking inventory to optimizing delivery routes. The system can divide tasks among different agents, each specialized in one part of the process, and they work together to solve larger problems. Agentic AI handles complexity by allowing different agents to collaborate and make decisions on their own, tackling much bigger challenges than a single AI agent could.
Learning and Adaptation Approaches
AI agents can learn over time, especially with the help of machine learning. For instance, a customer service chatbot might improve by learning from past conversations. However, it usually needs to be retrained by humans if the task or data changes. For example, if a new type of customer query becomes common, the chatbot needs a programmer to update its rules and instructions to handle it.
Agentic AI, on the other hand, is designed to learn continuously and adapt. It doesn’t need to be retrained by humans. It can adjust its behavior based on new experiences and data. For example, an Agentic AI managing business operations might learn from past mistakes, like delays in deliveries, and adjust its future decisions to avoid those problems. This ability to adapt and improve over time makes Agentic AI much more flexible and capable of handling unexpected challenges.
Memory Systems
AI agents typically have limited memory. For example, a chatbot might remember a user’s question during the current conversation but forget everything once the conversation ends. These agents focus on short-term tasks and don’t keep long-term knowledge.
In contrast, Agentic AI can use persistent memory. This means it can remember important information over a long period of time and use that memory to make better decisions in the future. For example, an Agentic AI in a supply chain system might remember that certain suppliers were frequently late and use that information to adjust future orders or find better alternatives. By sharing memory across different agents, Agentic AI can learn and improve continuously, building a better understanding of how to achieve its goals.
Proactivity vs. Reactivity
AI agents are mostly reactive; they act only when prompted. For example, a chatbot will only reply to a customer’s message when the customer reaches out. It won’t act unless there’s an input or trigger, like a question or a request.
Agentic AI, however, is proactive. It continuously monitors its environment and takes action without being asked. For example, an Agentic AI managing customer service might reach out to customers who are likely unhappy, even before they contact the company. This proactive approach allows Agentic AI to handle ongoing situations and solve problems before they become bigger issues, improving efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Goal Flexibility and Workflow Decomposition
AI agents have fixed goals. They are programmed to perform a specific task, like answering a question or recommending a product. These tasks stay the same unless the agent is updated by a human. For instance, a recommendation engine’s sole goal is to suggest products based on past behavior, and it can’t shift focus to other business needs like customer retention without human input.
Agentic AI, on the other hand, is much more flexible. It can break down a broad goal into smaller, actionable tasks and work on several goals at once. For example, in a large company, Agentic AI might be tasked with improving both inventory levels and customer satisfaction. It can split these tasks into smaller parts, like analyzing customer feedback or adjusting stock levels, and prioritize them based on new information. This ability to adapt and reorganize tasks as needed gives Agentic AI a major advantage in managing complex, multi-step processes.
Behavioral and Operational Distinctions
AI Agents as Specialized, Task-Focused Executors
AI agents are designed to handle specific tasks and work within clear limits. They are specialized in one area and follow a set of rules or instructions to get the job done. For example, a chatbot may only answer customer service questions, and a recommendation engine might suggest products based on user behavior. These agents do their job well, but they can’t go beyond their assigned task.
AI agents are reactive, meaning they only act when something triggers them like a customer asking a question or a user clicking a button. They can’t think for themselves or make decisions outside of the tasks they were programmed to do. They are best for jobs that are simple and straightforward, like answering questions or suggesting products, but they can’t handle more complex problems.
Agentic AI as Adaptive, Strategic Orchestrators
Agentic AI, on the other hand, is much more flexible and adaptive. It’s designed to handle more complex tasks that require planning and adjustments over time. Instead of just following simple rules, Agentic AI can adapt to new information and adjust its actions to achieve larger goals.
For example, an Agentic AI system used for supply chain management can do much more than just track inventory. It could also adjust delivery schedules, find new suppliers, and optimize routes based on real-time data. If the system detects a potential problem, like a delay in shipping, it can take action to solve it without waiting for a human to intervene. This makes Agentic AI more proactive, meaning it tries to solve problems before they become bigger issues.
Collaboration Within Agentic AI vs. Independent Operation in AI Agents
Another important difference is how AI agents and Agentic AI work with other systems. AI agents usually work alone. For example, a customer service chatbot can answer questions, but it won’t talk to other systems or share information with them. It simply completes the task it’s given, following its rules.
In contrast, Agentic AI systems involve multiple agents working together. These agents may specialize in different areas, but they communicate and coordinate their actions to achieve a common goal. For instance, one agent might handle inventory management, another focuses on customer satisfaction, and a third takes care of orders. By working together, the agents within an Agentic AI system can improve the overall process and make smarter decisions.
Examples Illustrating Behavioral Differences
- AI Agent Example: A recommendation engine on an online store looks at a user’s previous purchases and suggests products they might like. The system doesn’t change unless a programmer updates it. It reacts to data but doesn’t try to predict what a user might want next or adjust its recommendations without human intervention.
- Agentic AI Example: An Agentic AI system in a customer service department could look at user feedback and automatically suggest improvements. If it sees that customers are often unhappy with delivery times, the system might change delivery routes, find better suppliers, or send out follow-up emails all on its own.
Real-World Use Cases and Applications
AI Agents in Action
AI agents are already used in many aspects of our daily digital lives. They are best at handling simple, repetitive tasks that don’t require much creativity or complex decision-making. Here are some examples of how AI agents are used:
- Customer Support: AI agents like chatbots are often used to answer customer questions or solve simple problems. For example, a chatbot can check the status of an order or provide basic troubleshooting tips. However, when a problem is more complex, such as a product defect or refund requests, humans need to step in.
- Recommendation Engines: Services like Netflix, Amazon, and Spotify use AI agents to recommend movies, products, or music based on what you’ve liked in the past. These agents analyze your behavior and suggest similar items, but they don’t change how they make recommendations without human updates.
- Email Filters and Spam Detection: Email filtering agents sort incoming emails into different categories, like inbox, spam, or promotions. These agents look for patterns in the email to decide if it’s spam. Over time, they get better at this, but they still work within fixed rules to filter emails.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): RPA bots automate repetitive office tasks like filling out forms, entering data, or processing invoices. They follow specific instructions to complete the tasks, saving time for employees. However, these bots can’t adapt to new processes unless reprogrammed.
Agentic AI in Action
While AI agents are useful for specific tasks, Agentic AI is designed to handle larger, more complex problems. It can make decisions across multiple areas, adapting as needed. Here are some examples of how Agentic AI is used:
- Supply Chain Management: An Agentic AI system could optimize an entire supply chain. It can manage inventory, forecast demand, adjust deliveries, and find new suppliers all in real time. For example, if a shipment is delayed, Agentic AI can automatically reroute it or order extra stock if sales are higher than expected. The system doesn’t just react to problems, it anticipates them and makes adjustments before they become bigger issues.
- Healthcare: Agentic AI can improve patient care by coordinating between departments, predicting patient needs, and adjusting care plans. For instance, it could monitor patient data, alert doctors to high-risk cases, and suggest treatments. It can also ensure smooth communication between medical staff, reducing errors and improving efficiency.
- Financial Operations: In banking, Agentic AI can help with fraud detection, risk assessment, and regulatory compliance. It monitors transactions in real time, spotting unusual patterns. If something suspicious happens, it can take action by freezing an account or notifying authorities all while making sure the system follows financial regulations.
- IT Operations: Agentic AI can be used to automate IT tasks. For example, if a server goes down, the system could switch to a backup server and fix the problem automatically. It can handle most IT support tasks on its own, which frees up IT staff to focus on more important work.
- Smart Environments: In smart homes or cities, Agentic AI can manage systems like traffic lights, power grids, and public transportation. It coordinates between different agents, like monitoring traffic flow or energy usage, and adjusts as needed. These systems learn from their environment and adapt, making cities more efficient and responsive.
Comparative Impact on Efficiency and Complexity Handling
The real strength of Agentic AI is its ability to handle complex tasks that involve many steps and require collaboration between different agents. While AI agents are great at automating simple tasks, Agentic AI can manage multiple interconnected tasks, adjusting and learning as it goes.
For example, in supply chain management, an AI agent might only be in charge of managing inventory. But with Agentic AI, the system can handle inventory, analyze sales trends, adjust delivery schedules, and even negotiate with suppliers without needing constant human input. This ability to handle multiple tasks at once and to learn and adapt over time makes Agentic AI much more powerful in today’s fast-changing world.
Technical Frameworks and Innovations
ReAct and Alternative Reasoning Frameworks for Agentic AI
One of the key innovations behind Agentic AI is its ability to reason and act simultaneously. The ReAct framework, which stands for Reasoning + Acting, is a popular approach used in Agentic AI. In this model, agents reason about a problem, take action, and then reflect on the outcome before adjusting their strategies. This cycle of reasoning, action, and reflection allows Agentic AI systems to learn, adapt, and improve over time, enabling them to handle complex tasks and continuously optimize their performance.
For instance, in a customer service application, an Agentic AI system using the ReAct framework might first reason about the best way to resolve a customer’s issue, take action to resolve it (like providing a solution or escalating the problem), and then reflect on whether the action worked or needs adjustment. This ability to loop through reasoning and action repeatedly allows Agentic AI to adjust its approach based on real-time results.
While ReAct is one of the most popular frameworks for reasoning and acting, there are also alternative approaches. ReWOO (Reasoning Without Observations) is another framework that focuses on pre-planning actions without waiting for immediate feedback. This can be useful in situations where constant feedback is unnecessary, or when decisions must be planned in advance and then executed in a sequence.
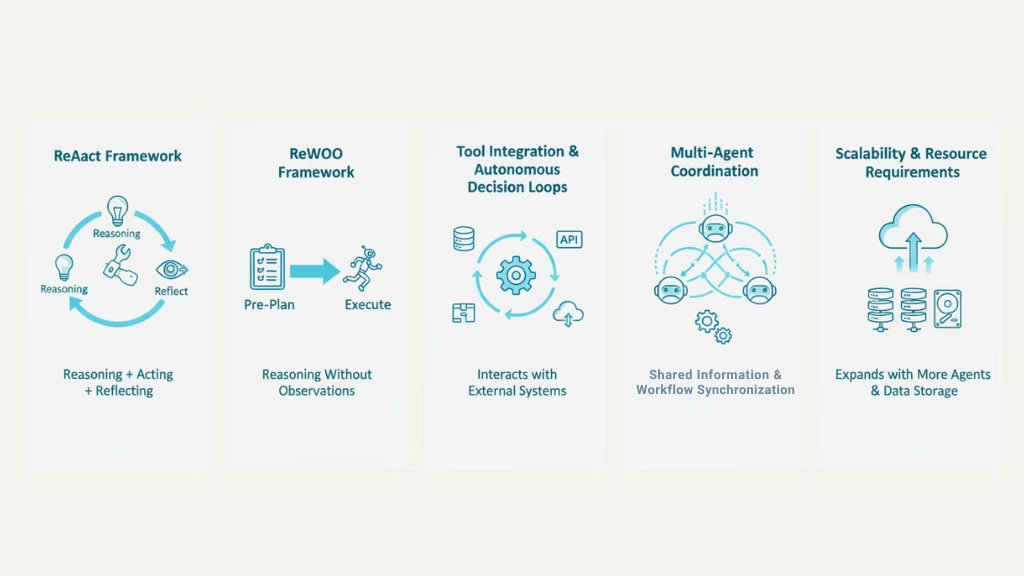
Tool Integration and Autonomous Decision Loops
Agentic AI systems also rely on tool integration to enhance their capabilities. These tools, such as APIs, databases, and external systems, allow Agentic AI agents to interact with the real world, collect data, and perform actions in environments beyond their internal systems. For example, an Agentic AI system managing a company’s sales might integrate with customer relationship management (CRM) software to retrieve customer data or use external tools to automate email marketing.
What makes Agentic AI systems truly autonomous is the decision loop they use. These systems don’t just follow pre-set instructions they make decisions on their own, continuously analyzing data, adjusting strategies, and taking action based on what they learn. This autonomous decision-making process is essential for handling complex tasks that require continuous adjustments, such as supply chain optimization, financial monitoring, or IT systems management.
Multi-Agent Coordination Protocols and Orchestration Platforms
Agentic AI systems rely heavily on multi-agent coordination to manage the interaction between various specialized agents. Each agent in an Agentic AI system focuses on a specific task, but they need to work together seamlessly to achieve broader goals. This is where multi-agent coordination protocols come in. These protocols define how agents communicate, share information, and coordinate actions to ensure that they are all working toward the same objective.
For example, in a large-scale logistics operation, one agent might track inventory, while another handles delivery schedules. If there’s a delay, these agents need to communicate with each other and adjust their actions accordingly to minimize disruption. The coordination protocols ensure that the agents are synchronized, avoiding confusion or conflicting actions.
Orchestration platforms help manage these multi-agent systems. These platforms provide a framework for coordinating and monitoring the actions of different agents. They make sure that each agent knows what task to focus on, when to act, and how to share information with other agents. Without orchestration, managing multiple agents working on a complex task would be chaotic and inefficient.
Resource Requirements and Scalability Considerations
While Agentic AI offers powerful capabilities, it also comes with higher resource demands. Because these systems rely on multiple agents that need to communicate and coordinate with each other, the infrastructure required to run them is more complex and resource-intensive than the infrastructure for AI agents. For example, Agentic AI systems might require more computing power to handle multiple agents working in parallel, as well as advanced data storage systems to manage large amounts of historical data that these agents rely on.
However, one of the advantages of Agentic AI is its scalability. As the complexity of tasks grows, Agentic AI systems can be expanded by adding more specialized agents to the system. These agents can be trained or programmed to handle new tasks without disrupting the existing system. For example, if a business needs to add a new function, like managing customer feedback, they can simply add an agent that specializes in that area. The ability to scale up in this way makes Agentic AI particularly attractive for businesses with growing needs or those that require flexibility.
When to Use Which
Choosing between AI agents and Agentic AI depends on the complexity of the tasks you need to automate and how much autonomy you want the system to have. Here are some guidelines to help you decide which one is right for your business:
AI Agents: When to Use Them
AI agents are best suited for situations where the tasks are simple, repetitive, and well-defined. If your business needs to automate basic processes that don’t require complex decision-making, AI agents are the way to go. They are great for tasks like:
- Customer service chatbots: Answering frequently asked questions or guiding users through basic processes.
- Email filtering: Automatically sorting messages into folders based on rules.
- Product recommendations: Suggesting items to users based on their past behavior.
- Data entry and processing: Automating repetitive tasks like filling out forms or organizing information.
These tasks are often predictable and don’t change much over time, making AI agents a great solution. They are cost-effective and easy to implement for businesses that want to automate specific, straightforward tasks without requiring significant changes or constant oversight.
Agentic AI: When to Use It
Agentic AI, on the other hand, is designed for more complex, dynamic environments where tasks are interconnected, changing, and require strategic decision-making. If your business needs a system that can handle multiple tasks at once, adapt to new situations, and make decisions on its own, Agentic AI is the right choice. It’s ideal for scenarios like:
- Supply chain management: Managing inventory, predicting demand, and optimizing delivery schedules especially when things can change rapidly, like with shipping delays or changes in customer demand.
- Healthcare systems: Coordinating patient care, predicting patient needs, and adjusting treatment plans in real-time.
- Smart city management: Monitoring and controlling traffic, energy usage, and public transportation to ensure smooth operation and adaptability to changing conditions.
- Financial operations: Detecting fraud, adjusting investment strategies, or automating regulatory compliance in real-time.
These systems require a lot of flexibility and the ability to handle multiple objectives. They can learn from data and adapt based on real-time feedback. While more expensive and complex to implement, Agentic AI can dramatically improve efficiency and enable new levels of automation for businesses facing dynamic, interconnected problems.
Cost-Benefit Considerations and Infrastructure Implications
When deciding between AI agents and Agentic AI, you should also consider the cost and infrastructure needs. AI agents are generally less expensive to implement and require less complex infrastructure. They are ideal for automating simple tasks with clear rules and expectations.
On the other hand, Agentic AI requires more advanced infrastructure to support multiple agents, continuous learning, and real-time decision-making. It also requires more resources to set up and manage, making it a larger investment. However, for companies that need to automate complex workflows or processes across different systems, the investment in Agentic AI can pay off in the long run by increasing efficiency and reducing the need for human oversight.
Examples of Appropriate Selection
- AI Agent Example: A small e-commerce store might use an AI agent for a recommendation engine that suggests products to customers based on their past browsing and purchases. The task is simple and doesn’t require constant changes, so a single AI agent would be sufficient.
- Agentic AI Example: A large retail chain with multiple stores across different regions might use Agentic AI to manage its supply chain, inventory levels, delivery schedules, and customer feedback. The system would coordinate between several specialized agents, adjusting plans based on real-time data and long-term goals, making it much more effective for large-scale operations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, AI agents and Agentic AI serve different purposes, each suited to specific tasks and business needs. AI agents are perfect for automating simple, repetitive tasks that are well-defined and predictable. On the other hand, Agentic AI is designed to handle more complex, multi-step processes that require strategic decision-making, adaptability, and continuous learning. For straightforward tasks, AI agents are the go-to choice, but for tasks that require coordination, complex decision-making, and adaptation, Agentic AI offers a whole new level of automation.
Understanding these differences will allow organizations to make informed decisions about which type of AI to implement, ensuring that the system they choose aligns with their business goals, infrastructure, and future growth plans.
FAQs
What is the main difference between AI agents and Agentic AI?
AI agents handle specific, simple tasks independently, while Agentic AI uses multiple agents to work together on complex tasks, making decisions and adapting autonomously.
Can AI agents learn from experience?
Yes, they can learn within specific tasks, but their learning is limited compared to Agentic AI, which can adapt across multiple tasks over time.
When should I use an AI agent instead of Agentic AI?
Use AI agents for simple, repetitive tasks. Use Agentic AI for complex, multi-step workflows or tasks that require coordination and adaptation.
How much does it cost to implement Agentic AI?
Agentic AI is more expensive to implement due to its complexity and infrastructure requirements, but it offers long-term benefits for large, complex operations.
Can AI agents and Agentic AI work together in the same system?
Yes, they can work together, with AI agents handling simple tasks and Agentic AI coordinating complex workflows.
Is Agentic AI more secure than AI agents?
Agentic AI systems are more complex and require robust security measures to ensure safe operation, especially since they are autonomous.
What are some real-world examples of Agentic AI?
Examples include supply chain optimization, healthcare coordination, and smart city management, where multiple agents work together to achieve larger goals.
How do I start using Agentic AI in my business?
Identify complex tasks that require coordination and invest in the right infrastructure and partners to build a tailored Agentic AI solution.
This page was last edited on 1 January 2026, at 12:02 pm
Contact Us Now

Contact Us Now
Start a conversation with our team to solve complex challenges and move forward with confidence.