When it comes to web development, choosing the right tools can be a game-changer. With so many options available, developers often face the challenge of navigating a sea of choices. The wrong tool can slow down your workflow, cause unnecessary frustration, and even jeopardize the success of a project. On the flip side, the right tools can streamline development, boost productivity, and lead to cleaner, more maintainable code.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through the essential web development tools. Whether you’re a front-end developer, back-end engineer, or full-stack professional, understanding the best tools to use for each part of your development workflow is crucial.
We’ll break down the factors you need to consider when choosing tools, provide detailed comparisons, and help you future-proof your stack with the latest and most effective tools available.
What Are Web Development Tools?
Web development tools are software programs, libraries, frameworks, and platforms that assist developers in building, testing, deploying, and maintaining websites and web applications. These tools streamline the development process, improving productivity and ensuring the final product is efficient, functional, and scalable.
Key Functions and Tool Types
Web development tools can be categorized into various types, each serving a unique purpose throughout the development cycle:
- Code Editors & IDEs (Integrated Development Environments): These are essential for writing and editing code. Popular examples include Visual Studio Code, Sublime Text, and WebStorm. They offer syntax highlighting, debugging, and sometimes built-in Git integrations.
- Frontend Frameworks: Frameworks like React, Vue.js, and Angular help developers build user interfaces more efficiently by providing pre-written components, state management, and routing.
- Backend Frameworks: Tools like Node.js, Django, and Laravel simplify server-side logic, making it easier to handle databases, authentication, and other critical backend operations.
- Version Control Systems (VCS): Git and platforms like GitHub and GitLab are crucial for tracking changes in code, managing multiple contributors, and maintaining the integrity of a codebase.
- Testing & Debugging Tools: Tools such as Selenium, Postman, and Chrome DevTools allow developers to test code, debug errors, and optimize performance.
- CI/CD & DevOps Tools: Jenkins, Docker, and Kubernetes help automate and streamline the testing, integration, and deployment processes, ensuring that updates to code are quickly and reliably delivered.
- Design & Prototyping Tools: Platforms like Figma, Adobe XD, and Sketch enable developers and designers to collaborate on creating user interfaces, wireframes, and prototypes before coding begins.
- Project Management Tools: Tools such as Jira, Trello, and Asana help development teams organize tasks, track progress, and communicate effectively throughout a project.
- AI-assisted Tools: Tools like GitHub Copilot and ChatGPT are changing the way developers write code, offering suggestions, code snippets, and even entire functions to improve efficiency.
- DevOps and CI/CD Tools: The rise of Docker and Kubernetes enables developers to automate the deployment process, manage containers, and ensure that code runs seamlessly across various environments.
- Prototyping Tools: The role of prototyping tools such as Figma, Adobe XD, and Sketch has become increasingly important. These tools help developers and designers work together to create and visualize the user experience before coding begins, ensuring the end product meets user expectations.
What Factors Should You Consider Before Choosing a Tool?
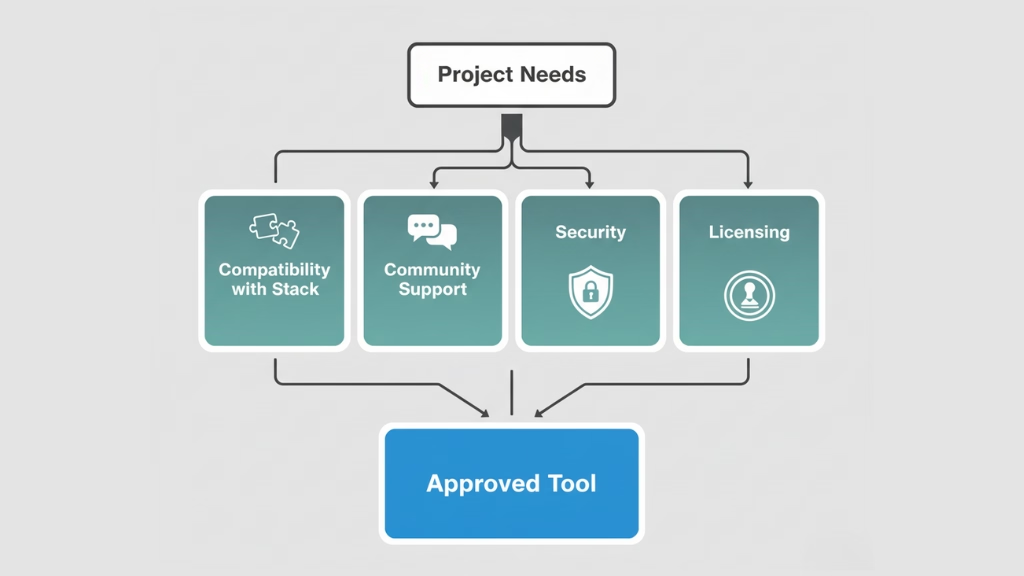
When selecting web development tools, it’s important to consider several key factors that will influence both the efficiency and the success of your project. Choosing the wrong tool can lead to wasted time, frustration, and unnecessary complexity. Here’s what to keep in mind when evaluating your options:
Compatibility with Existing Tech Stack
The tools you choose should integrate well with your existing development environment. A tool that fits seamlessly into your stack will reduce the learning curve and allow for smoother collaboration among your team. For example, if your team is already using Node.js for backend development, a JavaScript-based framework like React or Vue.js would be an ideal choice for frontend development.
Community Support, Security, and Licensing
- Community Support: A strong community is crucial for troubleshooting, updates, and finding solutions to common problems. Popular tools like React or Visual Studio Code benefit from large, active communities, making it easier to find resources, tutorials, and plugins.
- Security: Make sure the tools you choose adhere to industry standards for security. This is especially important for tools that handle sensitive data, like backend frameworks (e.g., Django, Laravel) or CI/CD platforms.
- Licensing: Understand the licensing model of the tools you’re considering. Many tools, like Visual Studio Code or Node.js, are open-source, which can be advantageous for cost-conscious teams. However, for enterprise solutions, you may need to consider the licensing fees for tools like WebStorm or Jira.
U.S. Relevance: Tools Supported by Top U.S. Tech Employers
When selecting web development tools, it’s also important to consider the tools used by leading tech companies, especially if you are targeting the U.S. job market or planning to scale within the U.S. These tools are often selected for their scalability, reliability, and developer-friendly features. For instance:
- React.js, developed by Facebook, is widely adopted in U.S.-based companies for its component-based architecture and speed.
- Node.js and Express are frequently used in scalable backend applications, with major employers like Netflix and LinkedIn utilizing them.
- Git and platforms like GitHub and GitLab are industry standards for version control across U.S. tech companies.
Understanding what tools are popular in the U.S. can help you make informed decisions, whether you’re looking to hire developers or choose tools that are in demand by employers.
Which Top Web Development Tools Every Developer Should Know?
Choosing the right tools for your specific development needs, whether for the frontend, backend, or full-stack, is crucial for ensuring the success of your project. Below, we explore the best tools for each area of web development, helping you identify the right fit based on your use case and team needs.
Frontend Development Tools Every Developer Should Know
Frontend development is essential for creating the part of the website or web application that users interact with. Below are the key tools that every frontend developer should be familiar with:
- Code Editors (VS Code, WebStorm)
Code editors are an integral part of any developer’s workflow. Visual Studio Code (VS Code) is a free, lightweight, and highly customizable editor that supports a wide variety of languages and extensions. WebStorm, on the other hand, is a premium IDE developed by JetBrains, known for its advanced features, especially for JavaScript and TypeScript development. Both editors are popular choices for frontend developers, with VS Code being favored for its extensibility and WebStorm for its deep out-of-the-box functionality.
- CSS Frameworks (Bootstrap, Tailwind)
CSS frameworks help streamline the process of styling websites. Bootstrap is one of the most popular and widely used frameworks, offering a mobile-first approach and a grid system for responsive layouts. Tailwind CSS, a utility-first CSS framework, allows developers to quickly build custom designs by applying utility classes directly in the HTML. Tailwind has gained popularity for its flexibility and ease of customization compared to more opinionated frameworks like Bootstrap.
- Browser Dev Tools
Every developer should be proficient with browser developer tools (DevTools) built into browsers like Google Chrome and Firefox. These tools provide powerful features for debugging, inspecting HTML and CSS, analyzing performance, and testing JavaScript. Whether you’re fixing layout issues, inspecting the DOM, or tracking network requests, browser dev tools are indispensable for frontend debugging.
Backend Tools and Server-Side Frameworks
Backend development focuses on the server-side logic, databases, and APIs. Below are the most commonly used backend tools and frameworks:
- Node.js: A runtime built on Chrome’s V8 engine, Node.js allows developers to use JavaScript for both frontend and backend development. Its non-blocking, event-driven architecture makes it ideal for scalable applications that require real-time data.
- Laravel: Laravel is a PHP framework known for its elegant syntax and robust features like routing, authentication, and ORM (Object-Relational Mapping). It’s an excellent choice for building modern web applications with PHP.
- Django: A high-level Python framework that follows the “batteries-included” philosophy, Django comes with many built-in features, such as an admin panel, authentication, and database management, making it a go-to for rapid development.
- Express.js: A minimalist framework for Node.js, Express is essential for building APIs and server-side web applications. It’s fast, flexible, and minimal, allowing for scalable web apps with minimal configuration.
Database Management, Testing Libraries
Effective backend development relies heavily on database management and testing. Some essential tools include:
- Databases: Tools like MongoDB (NoSQL) and PostgreSQL (SQL) are commonly used for handling and storing data.
- Testing Libraries: Backend testing libraries like Mocha, Chai, and Jest are important for ensuring that your server-side code runs correctly and reliably.
DevOps, Version Control, and Collaboration Tools
In modern development, collaboration and automation are crucial. Here are some tools to enhance your workflow:
- GitHub: A platform for version control and collaboration, GitHub is indispensable for managing code changes, collaborating with team members, and deploying code. It integrates well with other tools like Jenkins and GitLab.
- Docker: A tool that automates the deployment of applications inside lightweight containers, Docker simplifies the process of building, testing, and deploying applications in any environment.
- Kubernetes: Often used in conjunction with Docker, Kubernetes helps manage containerized applications, providing orchestration for large-scale deployments and ensuring that they run smoothly.
- CI/CD Pipelines: Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Deployment (CD) tools like Jenkins, Travis CI, and CircleCI automate the process of testing and deploying code, ensuring that updates are delivered faster and with fewer errors.
Project Management (Jira, Asana, Trello)
Effective project management is essential for keeping development teams organized and productive. Tools like Jira, Asana, and Trello provide task management, backlog tracking, sprint planning, and more. Jira, in particular, is a popular tool for agile teams and software development, while Trello is known for its simplicity and ease of use.
Prototyping, Design, and Accessibility Tools
Collaboration between designers and developers is critical to creating a great user experience. Below are the essential tools for design and accessibility:
- Figma: A powerful web-based design tool, Figma allows teams to collaboratively create wireframes, prototypes, and high-fidelity designs. Its real-time collaboration features make it a favorite among design and development teams alike.
- Adobe XD: Adobe XD is another popular design and prototyping tool, providing an intuitive interface for creating interactive prototypes and wireframes. It integrates well with other Adobe products and offers cross-platform collaboration.
- Accessibility Checkers: Ensuring your website is accessible is crucial. Tools like Axe and WAVE help identify accessibility issues in your web application, ensuring compliance with WCAG standards.
Tools for Responsive Design and Cross-Device UX
As mobile-first design becomes increasingly important, tools that help ensure responsive design are a must. Bootstrap, Tailwind CSS, and Media Queries are essential for ensuring that your website or app provides a seamless user experience across devices, from mobile phones to desktops.
AI & No-Code/Low-Code Tools Shaping the Future
The future of web development is also being shaped by AI and no-code/low-code platforms, which allow developers and even non-developers to build sophisticated applications without writing extensive code.
- GitHub Copilot: Powered by OpenAI, GitHub Copilot assists developers by suggesting code snippets and solutions, significantly speeding up development time.
- Webflow: A no-code platform that allows users to design, build, and launch responsive websites visually, Webflow is a powerful tool for designers and developers looking to quickly create websites without writing code.
- ChatGPT: Integrated into coding environments, ChatGPT offers developers assistance with debugging, code generation, and explanations, making it a versatile AI-powered tool.
- StackBlitz: A cloud-based IDE, StackBlitz allows developers to quickly prototype and deploy web apps directly in the browser, making development more accessible and efficient.
Full-Stack: Tools for End-to-End Development
Full-stack development involves both the frontend and backend, so selecting tools that work well together is crucial for efficiency and scalability. The following tools are ideal for full-stack development:
- MERN Stack (MongoDB, Express.js, React, Node.js): This full-stack JavaScript framework is extremely popular for building modern web applications. Since all components are based on JavaScript, the MERN stack allows for a seamless development experience and easy data sharing between frontend and backend.
- LAMP Stack (Linux, Apache, MySQL, PHP): A traditional, open-source stack that has been the foundation of many web applications. PHP is commonly used for server-side logic, MySQL for databases, and Apache for web serving.
- Django + React: A powerful combination where Django handles backend logic and database management, while React takes care of the dynamic frontend. This pairing is ideal for developers who want a robust backend with a fast, interactive frontend.
Each of these tools has its strengths, and the best choice depends on factors like project size, team experience, and performance requirements. By selecting the right tools for both frontend and backend development, you’ll set your project up for success from the start.
Local Development Environments
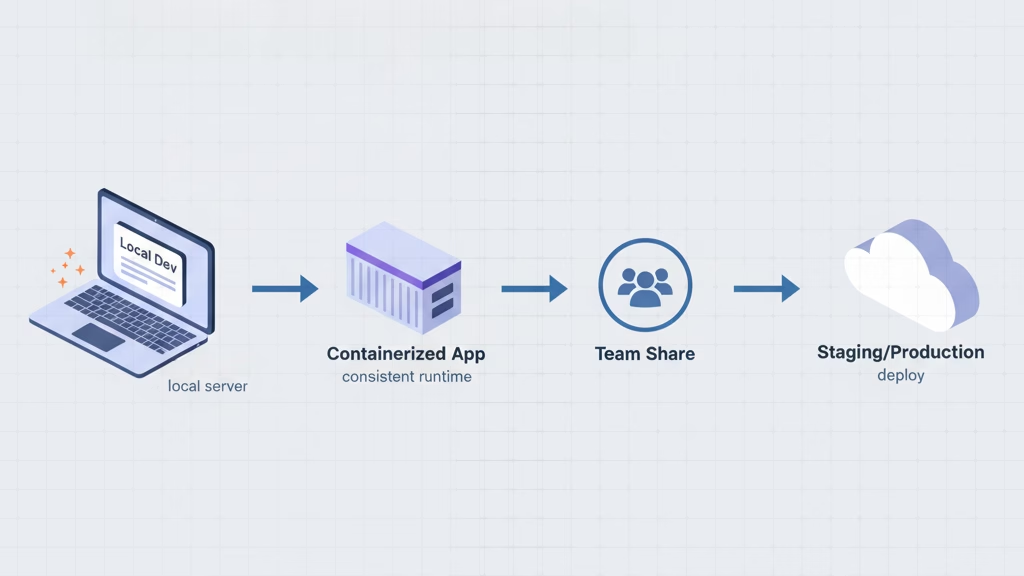
Before deploying any web project, developers rely on local development environments to build and test applications in a safe, isolated setting. These tools simulate real-world server conditions on your own computer, allowing developers to experiment, debug, and iterate without affecting live websites.
A proper local setup ensures faster development, easier troubleshooting, and seamless collaboration between team members.
Popular Local Development Tools:
- XAMPP / WAMP / MAMP: Ideal for PHP-based projects, these tools bundle Apache, MySQL, and PHP, providing a full local web server environment out of the box.
- Local by Flywheel: A user-friendly tool tailored for WordPress development with features like one-click site creation and SSL support.
- Node.js + Vite or Live Server: For JavaScript and frontend developers, Node.js combined with tools like Vite or Live Server allows real-time reloading and testing of dynamic web applications.
- Docker Desktop: Goes beyond local servers by containerizing applications, ensuring that your project runs the same way across different machines and production environments.
Package Managers: npm, Yarn, and Composer
Package managers are essential tools that simplify how developers install, manage, and update software dependencies. Instead of manually downloading libraries or frameworks, developers use package managers to automate and track dependencies, ensuring projects stay organized and up to date.
- npm (Node Package Manager): The default package manager for Node.js, npm powers most modern JavaScript applications. It provides access to over a million open-source packages, making it the backbone of the JavaScript ecosystem.
- Yarn: Developed by Meta (Facebook), Yarn offers faster installs, better caching, and more reliable dependency management than traditional npm setups, a favorite for large-scale or enterprise projects.
- pnpm: A lightweight and performance-optimized alternative to npm and Yarn, known for its disk space efficiency.
- Composer: The go-to package manager for PHP developers, Composer handles dependencies in frameworks like Laravel and Symfony.
Website Testing & Performance Tools

No web project is complete without thorough testing. Website testing tools help developers ensure that sites function properly, perform efficiently, and deliver a seamless user experience across browsers and devices. These tools are key to catching issues before deployment and maintaining long-term performance quality.
- Google Lighthouse: A built-in Chrome tool that audits your site for performance, accessibility, best practices, and SEO, providing actionable improvement scores.
- BrowserStack: Allows developers to test their websites across hundreds of browsers, operating systems, and devices without maintaining physical hardware.
- GTmetrix: Offers detailed load time analysis, page speed insights, and optimization recommendations to improve web performance.
- Pingdom & WebPageTest: Useful for uptime monitoring, speed testing, and identifying bottlenecks in web delivery.
- Axe Accessibility Checker: Helps ensure compliance with accessibility standards (WCAG), identifying potential usability issues for users with disabilities.
Conclusion
When selecting web development tools, focus on those that align with your project’s long-term goals. It’s tempting to chase trends, but the best tools are those that fit your team’s workflow and project requirements. Whether working on front-end, back-end, or full-stack, the right tools enhance productivity, streamline collaboration, and support scalability.
The most effective tools aren’t always the newest or most popular, they should integrate seamlessly into your tech stack. The right combination leads to faster development cycles, fewer bugs, and more efficient workflows.
Key Takeaways
- Align tools with goals: Focus on tools that support long-term scalability and needs.
- Avoid chasing trends: Ensure tools fit your team’s workflow, not just popularity.
- Select for each area: Front-end, back-end, and full-stack tools should complement each other.
- Prioritize integration: Choose tools that work well together within your existing stack.
- Future-proof: Consider scalability, security, and support to ensure longevity.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Here are some of the most common questions developers ask about web development tools. These answers will help you choose the right tools, improve your workflow, and stay updated with the latest trends.
What are the best tools for web developers?
The best tools for web developers are those that fit your project’s needs. Popular choices include React.js, Node.js, GitHub, VS Code, and cloud-based tools like GitHub Codespaces.
Which tools do professional U.S. developers use most?
U.S. developers widely use tools like Git, React.js, Node.js, Docker, Jira, and VS Code due to their scalability, community support, and integration capabilities.
Is GitHub Copilot worth using for front-end dev?
GitHub Copilot can be a huge time-saver for front-end development by providing AI-assisted code suggestions and generating code snippets, making it a valuable tool for many developers.
What is the difference between a library and a framework?
A library is a collection of functions and tools you can call in your code. A framework, on the other hand, provides a more structured approach to building applications, often dictating the architecture of the project.
Can I build a website without a code editor?
It is technically possible to build a website without a code editor, but it’s highly impractical. Code editors like VS Code provide features that speed up coding, error checking, and testing, making them essential for efficient development.
What tools do companies like Google or Meta use?
Large companies like Google and Meta use a variety of tools, including React.js, Node.js, Django, Kubernetes, and GitHub for managing their large-scale projects.
Are paid tools better than free ones?
Paid tools often offer more advanced features, better customer support, and security. However, many free tools like VS Code, Git, and React are powerful and widely used in the industry, especially for smaller teams or individual developers.
How do I know if a tool is beginner-friendly?
Beginner-friendly tools often have a simple, intuitive interface, extensive documentation, and community support. Tools like VS Code, React, and Bootstrap are great examples for beginners.
What web dev tools are cloud-native?
Cloud-native web development tools include GitHub Codespaces, Replit, and StackBlitz, which allow developers to code and deploy directly from the cloud without needing local setups.
Is Docker necessary for all developers?
While Docker is essential for DevOps and teams deploying large-scale applications, it may not be necessary for smaller projects or individual developers. However, it is a valuable tool for ensuring that code runs consistently across environments.
This page was last edited on 28 October 2025, at 9:52 am
How can we help you?
























