- What is Responsible AI?
- Responsible AI (RAI) Principles
- Types of Responsible AI
- Responsible AI vs. Trustworthy AI vs. Ethical AI
- How Responsible AI Works
- Responsible AI Development Practices
- Why Is Responsible AI Important?
- Responsible AI Benefits
- Responsible AI Challenges
- Responsible AI Challenges
- Building a Responsible AI Strategy: Best Practices
- Implementing Responsible AI Practices
Imagine you’re a business leader in charge of a tech company that has just launched an innovative AI product designed to improve customer service by automating responses and analyzing customer data. Initially, everything looks great, with customers praising the product for its efficiency. But soon, complaints start rolling in some users feel the AI is making biased decisions, favoring certain demographics over others.
However, there is a solution. “Responsible AI” provides a framework for creating AI systems that are not only powerful but also fair, secure, and aligned with societal values. By following responsible AI principles, your company can avoid pitfalls like bias and discrimination, build trust with your customers, and contribute positively to society.
What is Responsible AI?
Responsible AI is an approach to developing and deploying artificial intelligence (AI) from both an ethical and legal perspective. The goal is to ensure that AI systems are used in a safe, trustworthy, and ethical manner. By using AI responsibly, organizations can increase transparency, promote fairness, and mitigate issues such as AI bias that could otherwise harm individuals or groups.
The core idea behind Responsible AI is to implement AI technologies in a way that aligns with societal values. This includes designing AI systems that are human-centered, interpretable, and explainable. Proponents of Responsible AI believe that establishing a widely adopted governance framework, which outlines AI best practices, helps organizations ensure their AI programming is aligned with ethical principles.
However, the responsibility for ensuring trustworthy AI ultimately lies with the data scientists, software developers, and AI teams who create and deploy the systems. The steps to prevent discrimination, ensure fairness, and promote transparency vary across companies. For instance, the chief analytics officer or a dedicated AI team might oversee the development, implementation, and monitoring of an organization’s Responsible AI framework.
Responsible AI (RAI) Principles
Responsible AI is built on a set of core principles that guide the development and deployment of AI systems in an ethical and transparent manner. These principles are designed to ensure that AI technologies are used to benefit society, avoid harm, and uphold fairness, accountability, and trust.
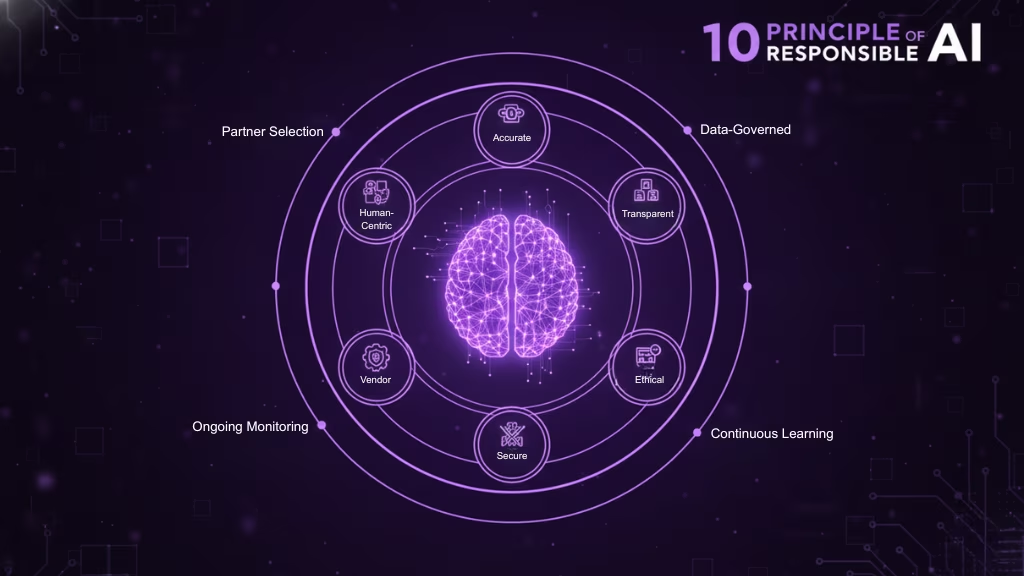
Accurate & Reliable
AI systems should produce accurate and consistent results. They must be tested thoroughly to ensure their outputs are reliable in real-world applications, minimizing errors and maintaining high standards of precision.
Accountable & Transparent
Organizations must be accountable for the decisions made by AI systems. The processes and reasoning behind AI decisions should be transparent and understandable to users. This allows for oversight and accountability, ensuring that users can trust the decisions being made by the AI.
Fair & Human-Centric
AI systems should be developed with fairness in mind, ensuring they do not discriminate against any group or individual. They should prioritize human welfare, ensuring that the AI enhances human capabilities rather than replacing them. AI should serve the broader public good, reflecting the values and needs of diverse populations.
Safe & Ethical
AI systems must be designed and deployed in ways that minimize risks to individuals and society. They should be safe to use, without unintended harmful consequences, and adhere to high ethical standards that align with societal values.
Secure & Resilient
Security is paramount in the development of AI systems. AI technologies must be protected from adversarial attacks, ensuring they remain resilient and functional in various scenarios. They should also be robust enough to handle unexpected inputs and continue to operate in a secure manner.
Interpretable & Documented
AI systems should be interpretable, meaning their decision-making processes can be understood by humans. Additionally, thorough documentation should be provided to explain how the AI was developed, the data it was trained on, and the rationale behind its decisions.
Privacy-Enhanced & Data-Governed
Responsible AI must prioritize privacy and data protection. AI systems should comply with data privacy regulations, such as GDPR, and ensure that personal data is handled responsibly. AI should be designed to respect users’ privacy and ensure data governance standards are followed.
Vendor & Partner Selection
When working with third-party vendors or external collaborators, organizations must ensure that these parties adhere to the same responsible AI principles. This includes assessing their AI systems for fairness, transparency, and ethical practices before forming partnerships.
Ongoing Monitoring
AI systems require continuous monitoring to ensure they operate within ethical boundaries and continue to meet the standards set during their development. Ongoing evaluation helps identify and address any issues that may arise post-deployment, ensuring that the AI remains reliable and safe.
Continuous Learning & Development
AI systems should evolve over time, adapting to new data and developments in AI ethics. This principle ensures that AI systems are not static but continue to improve and refine their behavior to remain aligned with ethical standards and societal values.
Types of Responsible AI
Responsible AI can be categorized into different types based on the objectives they aim to fulfill, how they approach the design and implementation of AI systems, and the principles they prioritize. Each type addresses unique challenges and societal concerns while ensuring that AI is used ethically and for the benefit of all. Below, we dive deeper into three prominent types of Responsible AI.
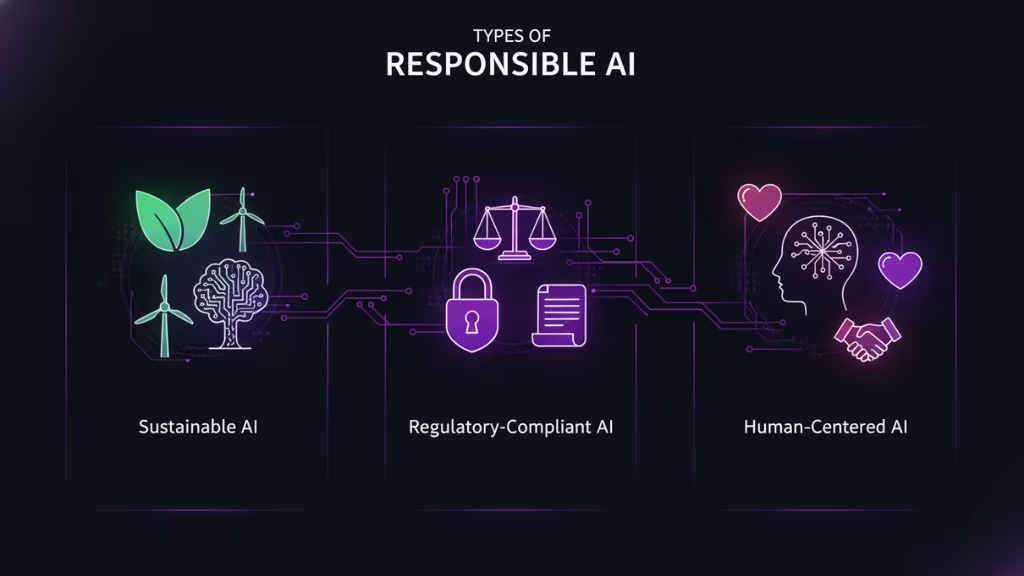
Sustainable AI
Sustainable AI focuses on developing AI systems that have a positive, long-term impact on the environment and society. It emphasizes minimizing the environmental footprint of AI technologies, especially in terms of energy consumption, data usage, and hardware production.
Key Elements:
- Energy Efficiency: AI systems are energy-intensive, especially deep learning models. Sustainable AI aims to reduce energy consumption by optimizing algorithms and hardware, promoting eco-friendly solutions.
- Waste Reduction: Sustainable AI practices encourage reducing electronic waste and ensuring that the lifecycle of AI models and hardware is sustainable.
- Social Responsibility: This type of AI is committed to contributing to the greater good. Sustainable AI looks at the social implications of AI development, ensuring that it supports community-driven projects, health initiatives, education, and environmental preservation.
- Circular Economy: This includes designing AI systems that can be easily recycled or repurposed to avoid creating excessive waste and promoting reuse across industries.
Example: AI models for climate change predictions that use machine learning algorithms to reduce carbon emissions in transportation systems or optimize energy usage in buildings, providing long-term environmental benefits.
Regulatory-Compliant AI
Regulatory-compliant AI ensures that AI systems are developed and deployed in line with legal frameworks and regulations designed to protect individuals and society. It primarily addresses compliance with data protection laws, anti-discrimination rules, and industry-specific guidelines.
Key Elements:
- Legal Compliance: This type of AI complies with national and international regulations like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act), and the emerging EU AI Act. Regulatory-compliant AI ensures that the data used in AI systems is processed and stored legally, with proper consent from individuals.
- Data Privacy: Privacy laws play a critical role in AI, as systems often process sensitive personal data. Regulatory-compliant AI ensures that privacy is maintained by adopting practices such as anonymization, secure data storage, and giving individuals control over their data.
- Fairness and Anti-Discrimination: Regulatory-compliant AI ensures that AI systems do not perpetuate discriminatory practices by adhering to anti-discrimination laws, especially when deploying AI in hiring, lending, or healthcare sectors.
- Auditing and Reporting: Regulatory-compliant AI systems require regular audits to ensure that they align with legal requirements, making auditing and reporting an integral part of their design. This helps organizations avoid penalties and maintain public trust.
Example: A financial institution uses AI to assess loan eligibility. Regulatory-compliant AI ensures that the AI model does not discriminate based on race or gender, complies with anti-discrimination laws, and protects users’ financial data.
Human-Centered AI
Human-centered AI places people at the center of AI design and implementation. This type of AI ensures that technology enhances human well-being, respects human values, and is aligned with societal norms. Human-centered AI prioritizes human oversight and empowerment, ensuring that AI works for people rather than replacing them.
Key Elements:
- Human Oversight: Human-centered AI ensures that humans are always in the loop when it comes to critical decisions, especially in high-stakes fields like healthcare, justice, or finance. The goal is to augment human decision-making, not replace it.
- Transparency and Explainability: Human-centered AI systems must be interpretable, meaning that users can understand how decisions are made. This helps users trust the AI and empowers them to make informed decisions. For example, in healthcare, doctors need to understand why an AI recommends a particular treatment.
- Ethical Alignment: Human-centered AI aligns with ethical standards by incorporating diverse perspectives in its design and ensuring fairness and inclusivity. It must be designed to respect and reflect human values such as privacy, equity, and dignity.
- Empowerment and Control: This approach empowers users by giving them control over how AI interacts with them. It also ensures that AI systems are accessible and understandable to all individuals, regardless of their background or technical expertise.
Example: AI-based health diagnostics tools that assist doctors in diagnosing diseases, but ensure that medical professionals have the final say in patient care. The AI model would be designed to explain its reasoning, allowing the healthcare provider to make informed decisions in the best interest of the patient.
Responsible AI vs. Trustworthy AI vs. Ethical AI
Understanding the differences between Responsible AI, Trustworthy AI, and Ethical AI is essential for navigating the complex landscape of AI development. While these terms are often used interchangeably, they each emphasize different aspects of AI’s relationship with society and its responsible deployment.
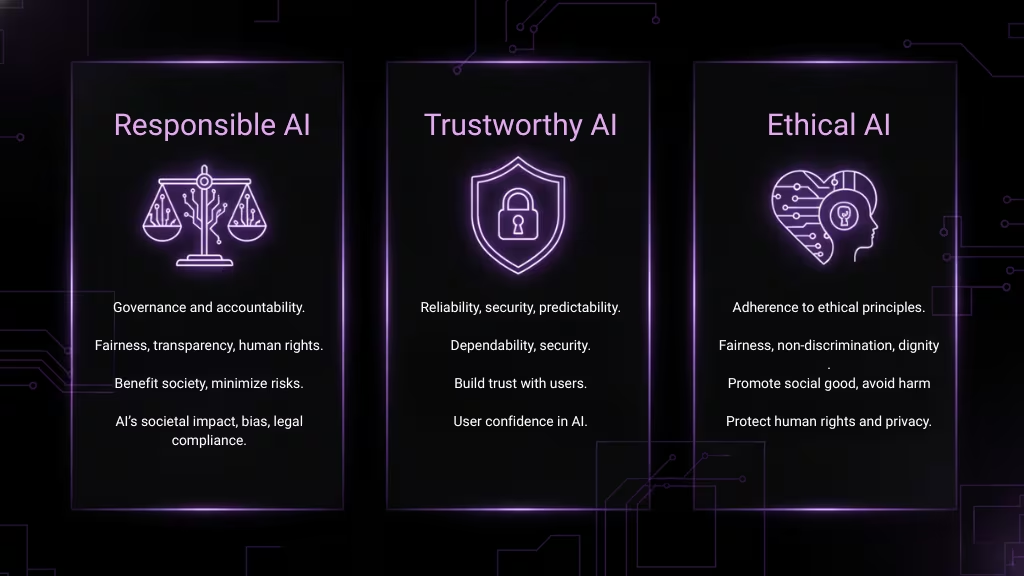
Here’s the comparison in table format for clearer understanding:
| Aspect | Responsible AI | Trustworthy AI | Ethical AI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Focus | Governance, accountability, and ethical considerations. | Ensuring reliability, security, and predictability. | Adherence to moral principles (fairness, privacy, etc.). |
| Key Elements | Fairness, transparency, accountability, human rights. | Dependability, security, predictable behavior. | Non-discrimination, respect for human dignity, fairness. |
| Goal | Ensure AI benefits society and minimizes risks. | Build systems that users can trust for accurate outcomes. | Design systems that promote social good and avoid harm. |
| Key Concerns | AI’s impact on society, legal compliance, bias reduction. | Building user confidence in AI decisions. | Protecting human rights, fairness, and privacy. |
| Example | AI governance frameworks, oversight, and compliance. | Ensuring AI systems are secure and consistently perform. | Ensuring AI decisions are ethical and respect social norms. |
How Responsible AI Works
Responsible AI integrates ethical principles throughout the entire AI development lifecycle, from planning to deployment and ongoing monitoring. It ensures that AI systems are designed and used in a way that aligns with societal values, minimizes harm, and fosters trust among users.
Below are the key steps in how Responsible AI is implemented:
Defining Ethical Principles
The first step in building Responsible AI is establishing clear ethical guidelines. These principles guide every stage of development, ensuring that the AI systems being created are fair, transparent, and accountable.
Ethical principles like fairness, privacy, and transparency should be defined upfront and embedded into the design process.
Data Collection and Preparation
Responsible AI begins with the data that trains the models. The data used must be diverse, unbiased, and representative of all relevant groups.
This step also involves ensuring that the data is collected ethically and with the consent of those whose data is being used. Data privacy laws, such as GDPR, must be adhered to.
Model Development and Testing
During the development phase, AI models are created based on the defined principles. These models are rigorously tested to identify any biases or unfair treatment toward certain groups. Developers ensure that the models are interpretable and that their decision-making processes can be understood by humans.
Rigorous testing also checks that the model meets safety, reliability, and ethical standards.
Deployment and Monitoring
Once the AI system is deployed, Responsible AI principles continue to apply. Continuous monitoring is crucial to ensure that the AI performs as expected and does not cause harm.
This involves setting up ongoing evaluations of the AI’s decisions, checking for potential biases, and ensuring that the system remains aligned with ethical principles over time.
Feedback and Improvement
Responsible AI is a continuous process. Feedback loops are established to learn from AI system performance and user experience.
This feedback informs adjustments to the system, ensuring that it evolves in line with ethical standards, user needs, and changing societal expectations. Regular audits and compliance checks ensure that the AI continues to meet regulatory and ethical standards.
Responsible AI Development Practices
Developing Responsible AI requires a set of best practices that guide the creation of ethical, transparent, and fair AI systems. These practices focus on ensuring AI models are free from biases, secure, interpretable, and aligned with societal values. Below are some key development practices for Responsible AI:
Assessing Model Training Data
The first step in developing a responsible AI model is ensuring that the data used for training is representative, unbiased, and diverse. Data scientists must assess the training data for any hidden biases that could lead to unfair outcomes, particularly in areas like hiring, criminal justice, or healthcare.
Causal Analysis
Causal analysis helps in understanding the relationship between different variables in AI models. This practice ensures that AI models are not merely identifying patterns but are making decisions based on a true understanding of cause and effect. This is especially important for ensuring fairness and avoiding discriminatory outcomes.
Counterfactuals Analysis
Counterfactual analysis involves comparing what would have happened if different decisions were made. It helps identify and mitigate bias by checking how different demographic groups are treated under different conditions, ensuring that decisions are not based on discriminatory variables.
Fairness in Machine Learning
Fairness is a core principle of Responsible AI. Developers must regularly check for fairness in AI models by ensuring that outcomes are equally distributed across different demographic groups. Techniques such as fairness constraints or re-weighting data can be used to prevent discrimination and ensure equitable treatment.
Model Error Assessment
Responsible AI also involves regularly assessing the errors that AI models make. By identifying and analyzing errors, developers can refine models to reduce unintended consequences and ensure that the system’s performance improves over time. This includes both false positives and false negatives.
Model Interpretability
AI models should be interpretable, meaning that their decision-making process is understandable to humans. This is crucial for building trust in AI systems. Techniques such as feature importance scores or decision trees can help make models more transparent, allowing users to see how specific inputs lead to certain outputs.
Why Is Responsible AI Important?
Responsible AI is vital because it ensures that artificial intelligence benefits society while minimizing potential risks and harms. As AI becomes more embedded in everyday decisions from healthcare to finance to employment, it’s crucial that these systems operate transparently, fairly, and ethically. Without proper oversight, AI can unintentionally amplify bias, erode trust, and cause real-world harm.
Ethical Imperatives for Businesses and Governments
Businesses and governments hold immense responsibility in shaping how AI impacts people’s lives. Implementing Responsible AI practices ensures that decisions made by machines align with human values and rights. For organizations, this means going beyond compliance to prioritize fairness, transparency, and accountability in every AI initiative. Governments, in turn, must establish regulatory frameworks and oversight mechanisms to safeguard against unethical or discriminatory use of AI.
Responsible AI also helps organizations avoid reputational and legal risks. A single instance of AI misuse such as biased hiring algorithms or unethical data usage can severely damage public trust and brand credibility. By embedding ethical principles from the start, organizations can demonstrate integrity and build confidence with their stakeholders.
Societal Expectations for Ethical Technology Use
Today’s consumers expect technology to operate ethically. People want to know that AI-driven systems are fair, unbiased, and protect their privacy. Companies that fail to meet these expectations face growing public scrutiny and loss of consumer trust. Responsible AI ensures that organizations remain transparent about how AI works, how data is used, and how decisions are made.
Moreover, as AI continues to shape critical societal systems like education, healthcare, and law enforcement, ethical implementation becomes not just a competitive advantage, but a social necessity. Responsible AI ensures that innovation benefits everyone, not just a select few, and that technology remains aligned with human values.
Responsible AI Benefits
Responsible AI offers both ethical and practical advantages. It helps organizations innovate safely while earning public trust, maintaining compliance, and driving long-term business success. Here are the key benefits of adopting Responsible AI practices:
Competitive Advantage
Organizations that prioritize responsible AI stand out as leaders in ethics and innovation. As customers, investors, and partners increasingly value transparency and accountability, companies with responsible AI frameworks gain a stronger reputation and competitive edge.
Cost Savings and Efficiency
By embedding responsibility into AI development early on, companies reduce the risks of costly errors, rework, or regulatory fines. Responsible AI also promotes efficient workflows by detecting problems such as bias or model drift before they escalate into major issues.
Enhanced Brand Trust
Transparency and fairness foster trust among customers, employees, and the public. When people understand how an AI system makes decisions and see that it does so ethically they are more likely to engage with and support it. This trust strengthens long-term brand loyalty.
Improved Decision-Making
Responsible AI ensures that AI systems are accurate, explainable, and free from bias. This leads to better, data-driven decisions that align with business goals while protecting individuals and communities from unfair outcomes.
Risk Mitigation
Ethical and regulatory compliance are central to Responsible AI. Organizations that proactively monitor and govern their AI systems are less likely to face lawsuits, data breaches, or reputational crises. Responsible practices help identify and mitigate potential risks before they cause harm.
Responsible AI Challenges
While the benefits of Responsible AI are clear, putting it into practice presents several real-world challenges. These obstacles often stem from technical, organizational, and regulatory complexities that make responsible implementation difficult but essential.
AI Bias: Identification and Mitigation
Bias remains one of the most persistent challenges in AI. Since AI models learn from historical data, they can inherit and amplify existing biases, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes. Detecting these biases requires diverse data sources, fairness audits, and continuous retraining. However, defining what counts as “fair” in every context can be complex, as fairness varies across cultures, industries, and social settings.
AI Governance: Ensuring Ethical Compliance
Many organizations struggle to establish clear governance frameworks for AI. Responsible AI demands cross-functional collaboration between data scientists, legal teams, ethicists, and executives. Yet, few companies have structured oversight systems in place. Without governance, AI risks becoming a “black box” where no one is accountable for its outcomes.
Regulatory Compliance and Standardization
Global regulations for AI are still evolving. Countries and regions are introducing different laws like the EU AI Act or emerging U.S. AI regulations, each with unique requirements. This lack of standardization makes compliance challenging for organizations operating across borders. Companies must constantly adapt to changing policies to ensure their AI systems meet local and international ethical standards.
Scalability of Ethical AI Practices
Implementing responsible AI principles in one project is manageable, but scaling them across an entire organization is much harder. As AI adoption grows, maintaining consistent ethical oversight across multiple products, departments, and geographies requires strong governance tools, cultural change, and continuous education.
Building a Responsible AI Strategy: Best Practices
Building a Responsible AI strategy means turning ethical principles into concrete actions that guide how AI is developed, deployed, and monitored. A strong strategy ensures that AI systems align with business goals while upholding fairness, transparency, and accountability. Below are best practices for creating a solid Responsible AI framework.
Define Responsible AI Principles
Start by clearly defining what Responsible AI means for your organization. Establish a set of guiding principles such as fairness, transparency, and privacy that align with your company’s mission, values, and industry standards. These principles serve as the foundation for every AI project, ensuring consistent ethical direction across teams.
Establish Governance and Oversight
Create a governance structure that defines roles, responsibilities, and accountability for AI initiatives. This may include forming an internal AI ethics board, assigning Responsible AI officers, or integrating ethical reviews into project workflows. Governance ensures that ethical concerns are addressed before systems are deployed.
Embed Ethics in the AI Lifecycle
Responsible AI must be integrated into every stage of development from data collection and model design to deployment and monitoring. Teams should perform bias checks, conduct fairness testing, and ensure explainability throughout the lifecycle. Embedding ethics early reduces the risk of unintended harm later.
Measure and Monitor Continuously
Responsible AI is not a “set and forget” process. Continuous monitoring ensures that AI systems remain compliant, fair, and accurate as data and conditions evolve. Regular audits, bias testing, and feedback loops help maintain alignment with ethical and regulatory standards over time.
Promote Transparency and Explainability
Make AI systems understandable to users, stakeholders, and regulators. Provide clear explanations of how decisions are made, what data is used, and how potential risks are managed. Transparent communication builds trust and strengthens accountability.
Foster a Culture of Responsibility
Ethical AI starts with people. Train employees on AI ethics and create awareness programs that promote responsible practices across departments. Encourage open discussions about AI risks and make ethical decision-making part of your company’s culture.
Collaborate Externally
Work with regulators, industry peers, and academic experts to share knowledge and best practices. External collaboration helps ensure your organization stays aligned with global ethical standards and emerging regulations.
Implementing Responsible AI Practices
Putting Responsible AI into action requires translating principles into daily operations. Implementation involves practical steps that ensure AI systems are ethical, transparent, and accountable throughout their lifecycle. Below are key practices organizations should adopt to embed responsibility into every stage of AI development and deployment.
Define Responsible AI Principles
Begin by setting a clear ethical framework tailored to your organization’s goals and industry. These principles, such as fairness, accountability, transparency, and privacy, should guide all AI projects. Document them clearly so that every team member understands how to apply them in practice.
Educate and Raise Awareness
Training and education are essential for successful implementation. All stakeholders, developers, executives, and end users should understand AI’s ethical risks and best practices. Regular workshops and ethics training sessions help teams identify potential biases and ensure responsible behavior in design and deployment.
Integrate Ethics Across the AI Development Lifecycle
Ethical considerations must be woven into every phase of AI development, from data collection and model design to deployment and maintenance. This means conducting fairness audits, testing for bias, ensuring explainability, and establishing feedback mechanisms to address ethical issues as they arise.
Protect User Privacy
Responsible AI requires strict data governance. Organizations should collect only the data they truly need, protect it through encryption and anonymization, and comply with privacy regulations like GDPR or CCPA. Transparent communication about data use helps build user trust and reinforces accountability.
Facilitate Human Oversight
AI systems should not operate in isolation. Human oversight is essential for interpreting results, identifying potential errors, and making final decisions. Building mechanisms for human review especially in critical areas like healthcare or hiring ensures accountability and prevents harmful automation.
Encourage External Collaboration
Responsible AI extends beyond internal teams. Partnering with external organizations, academic institutions, and policymakers helps maintain alignment with global ethical standards. Collaboration also encourages knowledge sharing and helps organizations stay ahead of regulatory changes.
Conclusion
Responsible AI is more than a compliance checklist it’s a long-term commitment to building trust, fairness, and accountability into every aspect of artificial intelligence. As AI continues to influence how people live, work, and make decisions, organizations must ensure that their systems not only perform efficiently but also uphold ethical values and societal well-being.
By embedding Responsible AI principles such as transparency, fairness, and human oversight, organizations can reduce bias, protect privacy, and prevent unintended harm. It also enables businesses to gain a competitive edge by fostering user trust, meeting regulatory expectations, and strengthening their brand reputation.
The journey toward Responsible AI is ongoing. It requires continuous learning, collaboration, and monitoring to adapt to new technologies and global standards. Companies that take this path position themselves as ethical innovators, driving progress that benefits both business and society.
FAQs: Responsible AI
What is Responsible AI?
Responsible AI refers to the practice of developing and deploying artificial intelligence systems that are ethical, transparent, fair, and accountable. It ensures that AI technologies benefit people and society while minimizing potential harm, bias, or misuse.
Why is Responsible AI important?
Responsible AI builds trust between organizations and users. It helps prevent bias, discrimination, and privacy violations while ensuring AI systems comply with laws and ethical standards. It also protects brand reputation and promotes sustainable innovation across industries.
What are the key principles of Responsible AI?
The core principles include accuracy and reliability, accountability and transparency, fairness and human-centered design, safety and ethics, privacy and data governance, and ongoing monitoring with continuous learning. Together, these principles guide organizations in creating AI systems that are safe, equitable, and trustworthy.
How can a company implement Responsible AI?
Organizations can implement Responsible AI by defining clear ethical guidelines, training teams on AI ethics, and integrating these principles into each stage of AI development. Establishing governance frameworks, conducting audits, and ensuring human oversight help maintain accountability and transparency in AI systems.
What challenges do organizations face in adopting Responsible AI?
Common challenges include identifying and mitigating bias, keeping up with changing regulations, ensuring collaboration across departments, and scaling ethical practices across global operations. Overcoming these challenges requires continuous monitoring, cross-functional coordination, and leadership commitment.
How is Responsible AI different from Ethical AI or Trustworthy AI?
Responsible AI focuses on governance and accountability. Ethical AI emphasizes moral principles such as fairness and privacy. Trustworthy AI centers on reliability and user confidence. Together, they create a holistic framework for safe, human-aligned AI systems.
What are the benefits of adopting Responsible AI?
Adopting Responsible AI strengthens brand trust, ensures regulatory compliance, improves decision-making accuracy, reduces risk, and supports sustainable innovation. It also helps organizations build long-term credibility by aligning technology with ethical and social values.
Who is responsible for enforcing Responsible AI in an organization?
Responsibility is shared across executives, data scientists, compliance officers, and AI ethics teams. Some organizations appoint a Chief AI Ethics Officer or create an AI Governance Committee to oversee policy enforcement and ethical compliance.
How does Responsible AI impact consumers?
Responsible AI ensures that consumers interact with systems that are fair, secure, and respectful of their rights. It promotes transparency, allowing users to understand how AI decisions are made and ensuring that their data is used responsibly.
What is the future of Responsible AI?
The future of Responsible AI lies in global collaboration, standardized governance frameworks, and continuous learning. As AI technology evolves, so will the ethical standards and regulations that ensure it benefits humanity in a transparent and equitable way.
This page was last edited on 2 December 2025, at 4:53 pm
Contact Us Now

Contact Us Now
Start a conversation with our team to solve complex challenges and move forward with confidence.










