If you’re diving into full-stack JavaScript development, chances are you’ve heard of the MEAN stack and for good reason. It’s one of the best ways to build modern, scalable, and cloud-ready applications using just JavaScript. But with all the different technologies out there, it can be hard to know where to begin.
That’s where this guide comes in. We’re going to show you how to make the most of the MEAN stack from MongoDB and Express.js to Angular and Node.js. By using JavaScript across the board, you’ll be able to streamline your coding process, cut down on the learning curve, and speed up your development.
Whether you’re new to the stack or looking to level up your skills, this guide will give you all the insights, tips, and examples you need to get started on your first cloud-ready application. Let’s dive in and make building apps easier, faster, and more fun!
What is the MEAN Stack?
The MEAN stack is a popular collection of open-source technologies used to build dynamic, scalable web applications. It comprises four main components: MongoDB, Express.js, Angular, and Node.js.
These technologies are all JavaScript-based, allowing developers to use a single language for both the front-end and back-end development. This makes MEAN stack applications highly efficient, as developers don’t need to switch between multiple programming languages or deal with the complexity of integrating different technologies.
Key Components of the MEAN Stack
The MEAN stack is a powerful set of technologies that work together to build dynamic and scalable web applications. It combines MongoDB, Express.js, Angular, and Node.js, providing an end-to-end solution using JavaScript. Let’s take a closer look at each of these key components.
MongoDB is a powerful NoSQL database that stores data in flexible, JSON-like documents. It is ideal for managing large volumes of unstructured data and provides excellent scalability as your applications grow.
Express.js is a minimal and flexible Node.js framework that simplifies back-end development. It handles routing, middleware, and HTTP requests, making it easy to connect the front-end with the database seamlessly.
Angular is a feature-rich front-end framework developed by Google for building dynamic single-page applications (SPAs). It enables interactive and responsive UIs with capabilities like two-way data binding and reusable components.
Node.js is a server-side JavaScript runtime that uses an event-driven, non-blocking I/O model. It enables the development of fast, scalable server applications that integrate effortlessly with both MongoDB and Angular.
Why Choose the MEAN Stack?
The MEAN stack is a popular choice for building dynamic, scalable web applications. By using JavaScript for both front-end and back-end, it offers a unified development environment and a seamless workflow. Let’s explore why developers choose the MEAN stack for their projects:
Unified Development: The MEAN stack uses JavaScript across both the front-end and back-end, enabling developers to work in one language throughout the entire application. This reduces the learning curve, streamlines development, and promotes code consistency.
Scalability: Thanks to MongoDB’s flexible data model and Node.js’s non-blocking, event-driven architecture, the MEAN stack is ideal for handling high volumes of traffic and large datasets. This makes it perfect for building applications that need to scale as they grow.
Cost-Effective: All technologies in the MEAN stack are open-source, which means you can build powerful applications without the costs associated with proprietary software. This makes it a budget-friendly option for startups and small businesses.
Real-Time Capabilities: The non-blocking I/O model of Node.js and the dynamic, real-time updates provided by Angular make the MEAN stack an excellent choice for applications requiring real-time functionality, such as chat applications or live dashboards.
How the MEAN Stack Works
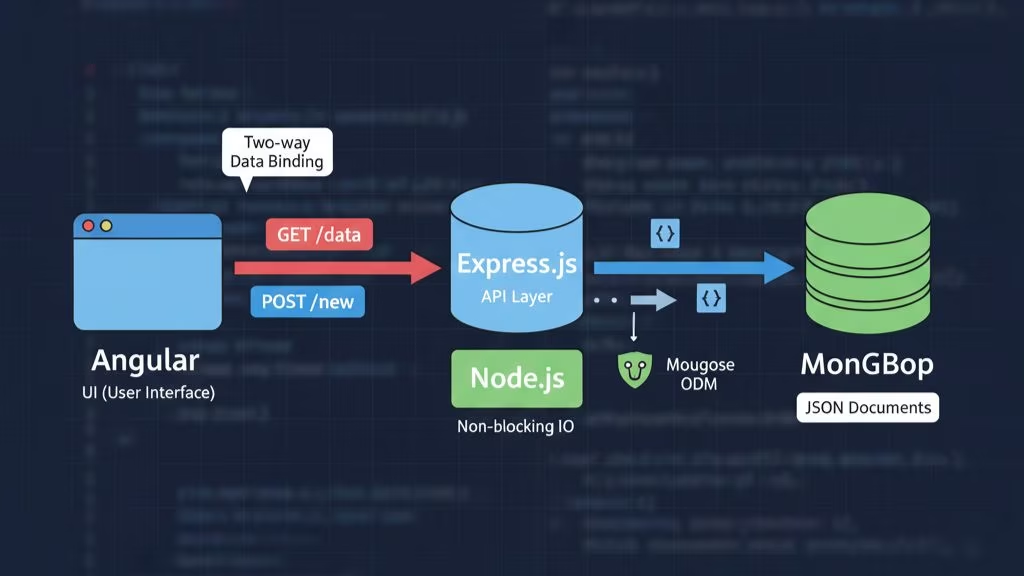
The power of the MEAN stack lies in how its components work seamlessly together. Understanding the flow of data between the client, server, and database is key to unlocking the full potential of this stack.
Client-Side Interaction: AngularJS (or Angular)
Angular handles the presentation layer and communicates with the back-end using HTTP requests. It uses two-way data binding to ensure that changes in the user interface are immediately reflected in the underlying data model and vice versa.
Server-Side Processing: Express.js on Node.js
When Angular sends a request (such as a GET or POST request) to the server, Express.js receives this request, applies business logic, and interacts with MongoDB to retrieve or manipulate data. After the data is processed, Express sends it back to Angular in a format that Angular can easily display.
Database Interaction: MongoDB
Express.js communicates with MongoDB using Mongoose (a popular MongoDB object modeling tool for Node.js). Data is sent to MongoDB in JSON format, ensuring seamless communication across the stack. MongoDB’s flexible schema allows for easy modification and quick scaling as your application grows.
Response to Client: Angular’s Dynamic Update
Angular takes the data returned by the server and updates the view accordingly, ensuring the application remains responsive and interactive.
The Unifying Factor: JavaScript Everywhere
Since MongoDB, Express, Angular, and Node.js all use JavaScript (or are JavaScript-compatible), developers can work with a single language across the entire application. This minimizes context switching and reduces development time, making the stack easier to learn and maintain.
MEAN vs MERN: A Side-by-Side Comparison
When deciding between the MEAN and MERN stacks, it’s important to understand how their differences impact the performance, scalability, and suitability for various types of applications. Below, we’ll compare the two stacks based on key factors, helping you decide which one is best for your project.
| Aspect | MEAN Stack | MERN Stack |
|---|---|---|
| Front-End | Angular – Full-featured framework for SPAs | React.js – Lightweight, flexible UI library |
| Structure | Opinionated and structured, guiding development | Flexible, customizable, with more control |
| Performance | Slightly slower due to two-way data binding | Faster, optimized with virtual DOM updates |
| Data Binding | Two-way data binding for synchronized updates | One-way data binding, promoting better performance |
| Learning Curve | Steeper due to complexity and structure | Easier to learn, with a focus on simplicity |
| Best For | Enterprise-grade, large-scale applications | Interactive, dynamic apps and real-time interfaces |
| Scalability | Highly scalable and consistent, suitable for large apps | Scalable and modular, ideal for smaller teams/projects |
| Ecosystem | Rich built-in tools (Angular CLI, etc.) | Extensive third-party library support (e.g., npm) |
When to Choose MEAN vs MERN?
Choose MEAN if:
- You need a comprehensive, structured framework to guide your development.
- Your project is enterprise-grade, requiring high consistency and the ability to scale smoothly.
- You prefer a complete, end-to-end solution, with all technologies working seamlessly from front-end to back-end.
Choose MERN if:
- Your project demands high interactivity, like real-time applications or content-heavy platforms.
- You value flexibility and want more control over the front-end architecture.
- You’re looking to leverage React’s fast rendering and lightweight nature for dynamic, responsive interfaces.
Common Use Cases for the MEAN Stack
The MEAN stack is incredibly versatile and ideal for a wide variety of web applications. Below, we explore some of the most common use cases where MEAN shines, helping you decide when it’s the perfect fit for your next project.
1. Single-Page Applications (SPAs)
Angular makes building Single-Page Applications (SPAs) seamless, offering smooth transitions and dynamic content updates. On the backend, Node.js handles real-time requests efficiently, ensuring your app performs well even under heavy traffic.
Example:
Apps like Gmail, Facebook, and Twitter are prime examples of SPAs, where users can interact with the app without needing to refresh the page.
2. E-commerce Platforms
For e-commerce platforms that require scalability and fast response times, the MEAN stack is a go-to solution. MongoDB’s flexible data model and Node.js‘s ability to handle many simultaneous connections make it easy to build a scalable and high-performance e-commerce site.
Example:
A scalable e-commerce platform where users can browse products, see real-time pricing updates, and interact with the system in a seamless shopping experience.
3. Real-Time Applications
Real-time apps require constant, uninterrupted communication between the client and server. The MEAN stack‘s Node.js handles real-time data processing, while MongoDB ensures fast data retrieval, making it ideal for real-time apps.
Example:
Applications like Slack and Trello, where users collaborate and receive instant updates in real-time.
4. Content Management Systems (CMS)
With its dynamic front-end capabilities and powerful backend architecture, the MEAN stack is perfect for Content Management Systems (CMS). You can easily manage and scale content while providing a rich, engaging experience for users.
Example:
A news website or blog platform where admins can quickly create, update, and manage articles, images, and videos, while maintaining a dynamic user interface.
5. Social Media Platforms
For building social media platforms, the MEAN stack excels in handling high data loads and frequent user interactions. Its ability to scale and provide real-time features like chat, status updates, and notifications makes it a great choice.
Example:
A social media platform like Facebook or Instagram, where users can post, comment, and interact in real time.
6. Real-Time Dashboards
Real-time dashboards require quick data processing and seamless updates, both of which are efficiently handled by the MEAN stack. With its ability to handle continuous data flow, it’s perfect for displaying live metrics.
Example:
A financial dashboard that shows real-time stock prices, company performance metrics, or server health, where the data is continuously updated.
7. Collaborative Tools
The MEAN stack is an excellent choice for developing collaborative tools, allowing multiple users to interact with data in real-time. Its powerful front-end updates, combined with real-time server interaction, make collaboration smooth and efficient.
Example:
Platforms like Google Docs or Microsoft Teams, where users collaborate on documents or projects, making live edits and updates.
How to Get Started with MEAN Stack Development
Getting started with the MEAN stack involves setting up a development environment and understanding the tools you’ll be using. Follow this step-by-step guide to set up your MEAN stack application, and you’ll be building modern, scalable web applications in no time!
1. Prerequisites
Before diving into development, ensure you’re familiar with the basics of JavaScript, web development, and NoSQL databases like MongoDB. Understanding RESTful APIs will also be helpful.
Key prerequisites:
- JavaScript (ES6+) knowledge
- Basic understanding of RESTful API concepts
- Familiarity with NoSQL databases, especially MongoDB
2. Installing Node.js and npm
Node.js is essential for running JavaScript on the server-side, and npm (Node Package Manager) helps you manage dependencies and libraries.
How to Install Node.js and npm:
To verify the installation, open your terminal and run the following commands: node -v # Check Node.js version npm -v # Check npm version
Visit the Node.js official website and download the latest stable version of Node.js.
npm will automatically be installed alongside Node.js.
3. Installing MongoDB
MongoDB is the database used in the MEAN stack. To get started, you need to install MongoDB locally or use a cloud-based service like MongoDB Atlas.
How to Install MongoDB Locally:
1. Go to the MongoDB download center
2. Follow the installation instructions for your operating system.
3. Once installed, you can start the MongoDB server by running mongodb in your terminal.
Alternatively, you can sign up for MongoDB Atlas
4. Installing Angular CLI
Angular CLI is a powerful command-line tool that simplifies the process of creating, managing, and serving Angular applications during development.
Steps to Install Angular CLI:
- Open your terminal and install Angular CLI globally by running the following command:
npm install -g @angular/cli - After the installation, verify that it’s installed correctly by checking the Angular CLI version:
ng --version - Once the Angular CLI is installed, you can create your first Angular project by running:
ng new my-mean-app
5. Setting Up Express.js and Node.js
Now, let’s configure the back-end using Node.js and Express.js. Express simplifies routing and handling HTTP requests, making it easy to create APIs and connect your front-end with the database.
Steps to Set Up Express.js:
- Navigate to your Angular project’s root folder and initialize a new Node.js application by running:
npm init -y # Creates the package.json file - Install Express.js:
npm install express - Create a new file named
server.jsin the root folder and set up a basic server:const express = require('express'); const app = express(); const port = 3000; app.get('/', (req, res) => res.send('Hello, MEAN Stack!')); app.listen(port, () => { console.log(`Server is running at http://localhost:${port}`); }); - Run the server by executing:
node server.js
6. Connecting Angular with Express and MongoDB
To make your Angular front-end interact with the Express.js back-end and MongoDB, you’ll need to set up API routes on the server to fetch data from MongoDB and send it to the front-end. Here’s how you can set up the API communication:
How to Set Up API Communication:
- In Express, create routes to handle CRUD operations (Create, Read, Update, Delete). Here’s an example of a route to retrieve data from MongoDB:
app.get('/api/data', (req, res) => { // MongoDB query to fetch data db.collection('yourCollection').find({}).toArray((err, data) => { if (err) { return res.status(500).send('Error retrieving data'); } res.json(data); // Send the fetched data to the client }); }); - In Angular, use the HttpClient module to send HTTP requests to your Express API. This will allow you to fetch data from the server and display it in the Angular app. First, ensure you’ve imported HttpClient into your Angular service or component:
import { HttpClient } from '@angular/common/http'; constructor(private http: HttpClient) {}Then, create a method to make a GET request to the Express API:fetchData() { this.http.get('http://localhost:3000/api/data') .subscribe(data => { console.log(data); // Handle the response here }, error => { console.error('Error fetching data', error); // Handle errors }); }
7. Running Your MEAN Stack Application
Once your Angular front-end and Express back-end are set up, you can run them both simultaneously for full-stack development.
How to Run the Angular App:
- Navigate to your Angular project directory and run:
ng serve - This will start your Angular application, which will be available at:
http://localhost:4200.
How to Run the Express App:
- Ensure your Express server is running by executing:
node server.js - The Express back-end will be accessible at: http://localhost:3000.
8. Deployment Considerations
Once your MEAN stack application is ready, you can deploy it to the cloud using platforms like Heroku, AWS, or DigitalOcean.
Steps for Cloud Deployment:
- Set up a cloud account on a platform like AWS, Heroku, or any other of your choice.
- Deploy your Angular front-end by pushing it to a hosting service like Firebase Hosting or Netlify.
- Deploy your Express back-end to a platform like Heroku or AWS EC2.
Conclusion
The MEAN stack is a powerful, full-stack JavaScript solution that allows developers to build scalable, dynamic web applications. By using MongoDB, Express.js, Angular, and Node.js together, the MEAN stack simplifies development with a single language throughout the entire application. Here’s a quick recap of the key takeaways:
Key Takeaways
- Unified JavaScript Development
- Scalability and Performance
- Cost-Effective
- Real-Time Capabilities
- Developer Support & Ecosystem
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Here are some of the most frequently asked questions about the MEAN stack, designed to address common queries and concerns that both developers and businesses may have when working with this technology.
1. What is the MEAN stack?
The MEAN stack is a collection of JavaScript technologies used for building dynamic web applications. It includes MongoDB (a NoSQL database), Express.js (a web application framework for Node.js), Angular (a front-end framework), and Node.js (a runtime environment for executing JavaScript on the server).
2. What are the advantages of using the MEAN stack?
Some key benefits of the MEAN stack include:
1. Single language for front-end and back-end: JavaScript is used throughout the entire application, making development more consistent and easier to manage.
2. Scalability: MongoDB is designed for scalability, making it suitable for applications that need to grow over time.
3. Cost-effectiveness: All components of the MEAN stack are open-source, reducing the cost of development and deployment.
4. Real-time capabilities: Node.js is well-suited for real-time applications like chat apps or live data dashboards.
3. How does the MEAN stack differ from the MERN stack?
The primary difference between the MEAN and MERN stacks is the front-end framework. MEAN uses Angular, while MERN uses React. Angular is a full-fledged framework, whereas React is a JavaScript library that focuses on building user interfaces. The choice between MEAN and MERN depends on the project’s requirements for flexibility, performance, and team expertise.
4. Can I use the MEAN stack for mobile app development?
While the MEAN stack is primarily used for web applications, it can also be used in mobile App development through tools like Ionic or React Native (with the MERN stack). Ionic allows you to build mobile apps using web technologies (Angular, Node.js, and Express) that run natively on mobile devices.
5. Is MongoDB the best choice for all applications?
MongoDB is a great choice for applications with flexible data models and requirements for rapid development. However, it may not be the best option for applications requiring complex relationships or transactions, where SQL databases like MySQL or PostgreSQL are often preferred.
6. How do I deploy a MEAN stack application?
To deploy a MEAN stack application, you typically deploy the front-end (Angular) and back-end (Node.js/Express) separately. The front-end can be deployed to platforms like Firebase Hosting or Netlify, while the back-end can be hosted on platforms like Heroku, AWS, or DigitalOcean. MongoDB can be hosted locally or on cloud-based services like MongoDB Atlas.
7. What are some common challenges when using the MEAN stack?
1. Learning curve: While JavaScript is a familiar language, learning how to work with all the components of the MEAN stack (especially Angular and MongoDB) can be challenging for beginners.
2. Performance with large datasets: MongoDB’s performance can degrade if it’s not properly indexed or if you’re handling very large datasets, so optimizations are necessary.
3. Complexity with scaling: As your application grows, managing all the different components of the MEAN stack can become complex, requiring careful architecture and design.
8. How can I become proficient in the MEAN stack?
To become proficient in the MEAN stack, you should:
1. Learn JavaScript thoroughly, including ES6+ features.
2. Understand the fundamentals of Node.js, Express.js, Angular, and MongoDB.
3. Build small projects using the MEAN stack to gain hands-on experience.
4. Refer to online resources, tutorials, and documentation from the official websites of Angular, Node.js, and MongoDB.
This page was last edited on 29 December 2025, at 2:33 pm
Contact Us Now

Contact Us Now
Start a conversation with our team to solve complex challenges and move forward with confidence.










