Agentic AI is transforming business operations by enabling AI systems to autonomously perceive, decide, act, and learn within complex enterprise workflows.
Unlike traditional automation, agentic AI adapts in real time and drives measurable impact across industries.
Yet, many leaders struggle to distinguish agentic AI from conventional automation—and to understand how it delivers business value. Businesses face rising workflow complexity, evolving customer demands, and increasing pressure to innovate, but often lack cohesive guidance on practical AI adoption.
This comprehensive guide reveals how agentic AI works for businesses, from architecture to real-world use cases, step-by-step implementation, and governance. By the end, you’ll know precisely what agentic AI is, how it operates in enterprise environments, and how to weigh risks and opportunities for your unique organization.
How Does Agentic AI Actually Work for Businesses? (The Perceive → Reason → Act → Learn Framework)
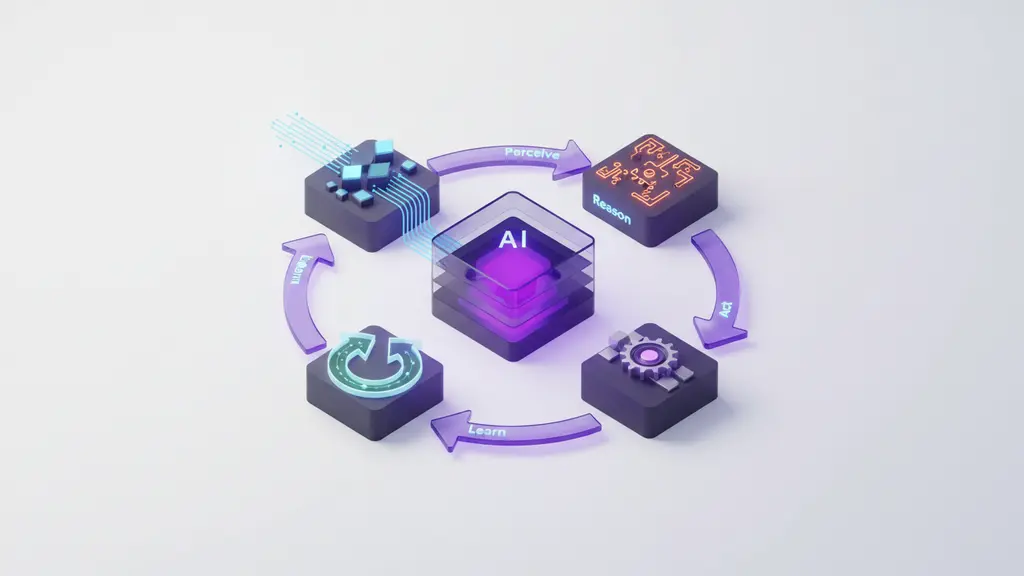
Agentic AI operates on a continuous loop—perceiving business data, reasoning to make decisions, acting on workflows, and learning from outcomes.
This process empowers businesses to automate and optimize complex, dynamic tasks at scale.
Core Steps in the Agentic AI Process:
- Perceive: Ingest and interpret diverse business data sources (e.g., CRM, ERP, IoT).
- Reason: Apply context-aware logic using large language models (LLMs), rules, and analytics.
- Act: Execute tasks across workflows, orchestrating actions across systems.
- Learn: Monitor results and integrate feedback for continuous improvement.
Perceive → Reason → Act → Learn
Example: Automated Customer Support
- Perceive: The AI monitors inbound emails, chat logs, and support tickets from multiple channels.
- Reason: Analyzes language, understands customer intent, and applies policy rules to classify issues.
- Act: Routes the case to the right support queue or triggers automated responses.
- Learn: Collects feedback on resolution time and user satisfaction to refine future actions.
Why this matters:
Agentic AI reduces manual intervention, increases speed, and adapts as business priorities or data change—delivering business workflow automation with intelligence and flexibility.
What Is Agentic AI Architecture? (Single vs. Multi-Agentic Systems)

Agentic AI architecture describes how autonomous agents are deployed, interact, and scale within an enterprise. Businesses can choose between single-agent, multi-agent, or hybrid systems based on complexity and scalability needs.
Agentic AI Architecture Types:
| Architecture Type | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Single Agent | One AI agent manages a defined workflow or domain. | Simple, siloed processes |
| Multi-Agent System | Several agents collaborate, each specialized (e.g., supervisor/worker model). | Complex, cross-functional operations |
| Hybrid/Supervisor-Worker | One agent oversees and coordinates multiple “worker” agents for orchestration. | Large-scale, multi-step business flows |
Integration Patterns
- APIs connect agentic AI to enterprise systems like CRM, ERP, or cloud platforms.
- Cloud-based architectures enable flexible deployment and scalability.
- Schematic Diagram Example:
[Business Data] --> [Perceive Agent]
|
[Reasoning Engine]
|
[Actuator Agents]
|
[Feedback Loop]
When to Use Each Architecture
- Start with a single agent for automating focused tasks (e.g., appointment scheduling).
- Adopt multi-agent systems for end-to-end process orchestration (e.g., supply chain, IT incident response).
- Hybrid models are ideal for environments where coordination and oversight are necessary.
Key takeaway:
Agentic AI architecture determines the level of autonomy, adaptability, and scalability your solution can achieve.
How Is Agentic AI Different from Traditional AI or Automation?
Agentic AI is fundamentally different from traditional rule-based automation and standard AI models due to its autonomy, adaptability, and continuous learning.
| Feature | Agentic AI | Traditional AI / Automation |
|---|---|---|
| Autonomy | High – agents initiate and adapt | Low – process needs human trigger |
| Learning | Continuous (feedback-driven) | Static, requires manual updating |
| Adaptation | Dynamic, handles novel situations | Fixed workflow, rigid rules |
| Decision Making | Context-aware, multi-step | Linear, pre-programmed decisions |
Example Scenario:
- Traditional Automation: An RPA bot extracts invoices, performs pre-coded steps, and stops if an exception occurs.
- Agentic AI: An agent monitors all invoices, identifies anomalies, reasons about best resolution steps, requests missing information, and learns from exceptions to handle them better next time.
How Agentic AI Works for Businesses in Real Enterprise Workflows
Agentic AI delivers direct impact across multiple business functions. From IT to HR, finance to customer operations, agentic agents automate, optimize, and adapt in real time.
Industry Use Case Grid
| Industry/Function | Agentic AI Application | Key Benefits | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| IT Operations | Automated incident response | Faster resolution, 24/7 monitoring | Exabeam SecOps |
| HR & Employee Support | Onboarding workflow agents | Reduced manual effort, faster start | Chatbot agents |
| Finance & Risk | Fraud detection and reporting | Real-time alerts, risk reduction | Transactional AI |
| Customer Service | Self-service resolution, escalation | Shorter response time, higher CSAT | Virtual agents |
| Cybersecurity | Threat detection & response agents | Proactive defense, less downtime | AWS security AI |
Sample Agentic AI Use Cases
- IT: Automated ticket triage and resolution, reducing average incident resolution time.
- HR: Intelligent onboarding assistants delivering personalized guidance to new employees.
- Finance: Real-time fraud monitoring—flagging, investigating, and reporting anomalies faster than manual processes.
- Customer Service: 24/7 virtual agents handling 80%+ of common requests before handoff.
- Cybersecurity: Continuous monitoring and response to emerging threats without human delay.
Metrics:
According to consulting leaders like BCG, organizations report productivity lifts of 20–30% and cost reductions of up to 25% in processes where agentic AI is fully implemented.
What Are the Core Benefits of Agentic AI for Businesses?
Agentic AI offers businesses significant efficiency gains, adaptability, and value that outstrip legacy automation solutions.
Key Agentic AI Benefits:
- Efficiency & Productivity: Automates multi-step workflows, freeing staff for higher-value tasks.
- Error Reduction: Minimizes manual mistakes by standardizing and optimizing decision paths.
- Continuous Adaptation: Learns from feedback and adjusts to new data or rules in real time.
- 24/7 Operation: Agents work round-the-clock, delivering continuous business workflow automation.
- Scalability: Multi-agent systems grow with organizational needs, supporting expansion without exponential cost.
- Innovation: Enables new digital products and internal processes not possible with traditional IT tools.
Case Metrics:
– Productivity improvements of 20–30%.
– Significant reduction in operational bottlenecks and manual handoffs (sources: McKinsey, BCG).
How Do You Implement Agentic AI in Your Organization? (Roadmap & Checklist)
Implementing agentic AI requires a structured approach—from initial assessment through integration and scaling.
Clear steps, best practices, and a readiness checklist drive successful outcomes.
Step-by-Step Agentic AI Implementation:
- Assess Needs & Opportunities: Identify high-impact workflows where agentic AI can deliver value.
- Evaluate Vendors & Solutions: Compare platforms based on architecture, interoperability, and controls.
- Build a Pilot: Select a controlled environment to test agentic AI performance and ROI.
- Integrate Systems: Connect agentic AI to existing software via APIs (CRM, ERP, IoT, etc.).
- Monitor & Measure: Track performance with clear KPIs (e.g., time reduction, error rates).
- Iterate & Scale: Apply learnings from pilots to wider processes and departments.
Agentic AI Readiness Checklist:
- Clear business case defined
- Data sources mapped and accessible
- Integration plan for existing systems
- Governance and oversight in place
- ROI metrics and KPIs established
- Pilot and scaling roadmap agreed
Best Practice Tips:
- Engage end-users early to ensure adoption.
- Start small with targeted pilots, building organizational learning.
- Secure executive sponsorship and IT alignment to overcome silos.
What Are the Main Risks, Controls, and Governance Practices?
Adopting agentic AI introduces new risks—bias, operational drift, explainability gaps, and compliance issues—but these can be managed with strong governance and technical safeguards.
Top Agentic AI Risk Categories:
- Bias in Decision Making: Agents can perpetuate or amplify bias if training data is unbalanced.
- Model Drift: Over time, AI may deviate from intended outcomes as business data evolves.
- Lack of Explainability: Complex agents may become “black boxes,” complicating audits or compliance.
- Compliance Violations: Automated decisions could breach industry or legal standards.
Governance Best Practices:
- Define clear ethical guidelines and transparency requirements.
- Implement explainability methods—dashboards, audit trails, or interpretable models.
- Use human-in-the-loop designs for critical decisions (humans approve or override agent actions).
- Regularly review, test, and update agentic AI logic.
Risk to Controls Table
| Risk | Control/Practice |
|---|---|
| Bias | Diverse training data, human oversight |
| Drift | Continuous monitoring, retraining |
| Explainability gap | Model interpretability, audit trails |
| Compliance issues | Alignment with standards, regular audits |
Bottom line:
Robust agentic AI governance ensures safety, compliance, and stakeholder trust as organizations automate more business processes.
Real-World Case Studies & Benchmarks
Real-world deployments illustrate the measurable impact of agentic AI across sectors.
Mini-Case Study Summaries
Financial Services:
Challenge: Fraud detection was manual and slow.
Outcome: Agentic AI now monitors transactions in real-time, reducing false positives and improving detection rates.
IT Operations:
Challenge: Incident response was hindered by ticket backlogs.
Outcome: Automation agents triage, prioritize, and resolve low-complexity tickets, cutting mean time to resolution by 25%.
Customer Service:
Challenge: High volume of routine requests overwhelmed staff.
Outcome: Virtual agents resolve over 80% of inquiries without escalation, boosting customer satisfaction.
Comparative Table: Agentic AI Benchmarks
| Sector | Use Case | Metric | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Finance | Fraud detection | False positives | -30% (fewer) |
| IT/Ops | Incident response | MTTR | -25% reduction |
| Customer Service | Self-service agents | CSAT score | +15 points (improved) |
Expert Quote:
“Organizations that embed agentic AI into their core workflows report faster innovation cycles and meaningful cost savings.” — BCG, “How Agentic AI Is Transforming Enterprise Platforms”
What Are the Key Challenges—and How Can Businesses Overcome Them?
Agentic AI adoption is not without hurdles—ranging from data and integration issues to organizational readiness and skills gaps.
With foresight and targeted action, these challenges can be mitigated.
Common Agentic AI Challenges & Solutions:
- Data Quality & Access:
– Challenge: Incomplete or siloed data hinders agent performance.
– Solution: Establish data governance, improve integration and hygiene. - Integration Complexity:
– Challenge: Legacy or fragmented systems complicate agent deployment.
– Solution: Use standard APIs, phased integration, and middleware. - Talent & Skills Gaps:
– Challenge: Limited in-house AI/automation expertise.
– Solution: Upskill teams, leverage external partners, pilot with vendor support. - Change Management:
– Challenge: Resistance to process change or job redesign.
– Solution: Prioritize communication, involve stakeholders, and highlight quick wins. - Governance Maturity:
– Challenge: Unclear controls can allow drift or compliance lapses.
– Solution: Embed AI governance frameworks and human-in-the-loop protocols.
Expert Perspective:
“Pilot projects and cross-functional teams are essential for building trust and demonstrating agentic AI’s effectiveness before scaling enterprise-wide.” — AWS, “What is Agentic AI?”
The Future of Agentic AI in Business: Trends to Watch
Agentic AI is evolving rapidly, setting new standards for enterprise automation and innovation.
Key Trends (2025–2026):
- Multi-Agent & Event-Driven Architectures:
Enable even more dynamic, collaborative workflows across the business. - Democratization through Low-Code Platforms:
SMBs and line-of-business teams can now deploy agentic AI with minimal coding. - Responsible AI & Ethics:
Compliance, transparency, and explainability requirements are shaping future solutions. - Next-Gen Human-AI Collaboration:
Agents and humans increasingly work together—“human-in-the-loop” design as mainstream.
FAQ: Everything Businesses Need to Know About Agentic AI
What is agentic AI and how does it work for businesses?
Agentic AI refers to AI systems capable of perceiving data, reasoning, taking autonomous actions, and learning from feedback—empowering businesses to automate, adapt, and optimize complex workflows.
How is agentic AI different from traditional AI or automation?
Unlike static, rules-based automation, agentic AI adapts to data changes, learns from outcomes, and can make context-aware decisions without constant human scripting or intervention.
What are typical business use cases for agentic AI?
Common applications range from IT operations (incident response) and HR (onboarding bots), to finance (fraud monitoring), customer service (virtual agents), and cybersecurity (threat response).
What are the core steps in an agentic AI process?
Agentic AI follows a loop: perceive (gather data), reason (decide), act (execute), and learn (optimize).
How do businesses implement agentic AI systems?
Implementation involves assessing needs, selecting solutions, piloting, integrating with current systems, monitoring performance, and scaling with governance.
What are the main benefits of agentic AI for enterprises?
Key benefits include increased efficiency, reduced errors, faster adaptation to change, 24/7 operation, and greater scalability.
What risks should businesses be aware of with agentic AI?
Risks include potential bias, decision drift, lack of explainability, and compliance gaps—but these can be managed with strong controls.
How do you ensure governance and compliance with agentic AI?
Implement transparent processes, explainability tools, human oversight, regular audits, and alignment with regulations and ethics standards.
What industries benefit most from agentic AI?
Industries with complex, high-volume workflows—such as IT, finance, HR, customer service, and cybersecurity—see the most significant gains.
Can agentic AI integrate with legacy systems and existing software?
Yes, leading agentic AI platforms are designed to connect via APIs and middleware for seamless integration with both legacy and modern enterprise systems.
Conclusion: Key Takeaways & Next Steps
Agentic AI is reshaping how businesses automate, orchestrate, and innovate. By understanding its core mechanisms (perceive, reason, act, learn), optimal architectures, and practical applications, organizations can begin their automation journey with confidence.
To get started, assess your workflows and pinpoint high-impact opportunities for agentic AI. Use the readiness checklist, consult with IT/AI advisors, and pilot responsibly to unlock long-term value.
Key Takeaways
- Agentic AI enables businesses to automate complex, adaptive workflows via autonomous agents that perceive, reason, act, and learn.
- Flexible architectures (single, multi-agent, hybrid) support everything from focused tasks to end-to-end enterprise orchestration.
- Use cases span IT, finance, HR, customer service, and cybersecurity—delivering measurable productivity and innovation benefits.
- Implementation success requires integration planning, governance controls, and change management.
- Future trends include multi-agent collaboration, democratized AI, and deeper human-AI teamwork.
This page was last edited on 2 February 2026, at 5:54 pm
Contact Us Now

Contact Us Now
Start a conversation with our team to solve complex challenges and move forward with confidence.










