- What is Artificial Intelligence?
- What is Generative AI?
- What is Predictive AI?
- Differences Between Generative AI and Predictive AI
- Generative AI Applications
- Predictive AI Applications
- Benefits and Drawbacks of Generative AI
- Benefits and Drawbacks of Predictive AI
- Choosing Between Generative AI and Predictive AI
- Challenges and Limitations
- Future Trends in AI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become a driving force behind innovation across industries. Among its many forms, Generative AI and Predictive AI stand out for their impact and contrast.
Generative AI focuses on creating new ideas, content, or data, while Predictive AI uses existing data to forecast outcomes and trends. One imagines possibilities, the other anticipates results.
Understanding how these two approaches differ, where they overlap, and how they can work together helps businesses make smarter, faster, and more creative decisions.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence, or AI, is a branch of computer science that aims to make machines think and act like humans. Instead of simply following fixed commands, AI systems can learn from data, recognize patterns, and make decisions on their own.
AI powers many tools we use every day, from voice assistants like Siri and Alexa to recommendation systems on Netflix and Amazon. These systems use algorithms that help them improve over time as they gather more information.
In simple terms, AI helps computers understand, learn, and solve problems. It doesn’t replace human intelligence but works as a partner, handling repetitive, data-heavy tasks and freeing people to focus on creativity and strategy.
What is Generative AI?
Generative AI is a type of artificial intelligence that can create new content instead of just analyzing existing data. It learns patterns, structures, and relationships from large amounts of information, then uses that knowledge to produce something original, like text, images, music, or even code.
For example, tools like ChatGPT, DALL·E, and Midjourney can write essays, draw pictures, or generate designs simply from written prompts. These systems rely on advanced models such as transformers and neural networks to understand context and create outputs that look human-made.
In short, Generative AI doesn’t just process data; it imagines new possibilities based on what it has learned. It’s widely used in content creation, product design, and software development, where creativity and innovation are key.
What is Predictive AI?
Predictive AI is designed to forecast future events or outcomes by studying patterns in past data. Instead of creating new content, it focuses on analyzing what has already happened to predict what’s likely to happen next.
For example, predictive AI helps banks detect fraud, retailers forecast demand, and doctors predict patient risks. It works by feeding large sets of historical data into algorithms like regression models, decision trees, or neural networks, which then identify trends and make data-driven predictions.
In simple terms, Predictive AI helps people and organizations make smarter decisions by turning past information into future insight.
Differences Between Generative AI and Predictive AI
While both Generative AI and Predictive AI use data and machine learning, they serve very different purposes.
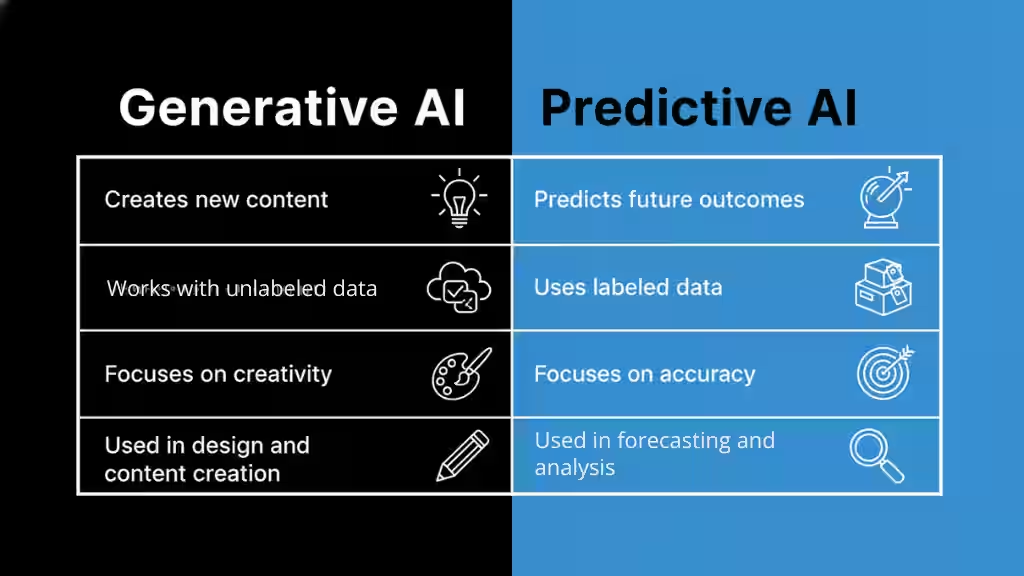
- Goal: Generative AI focuses on creating new things like text, code, or images that didn’t exist before. Predictive AI focuses on forecasting what will happen next based on existing data.
- Input and Output: Generative AI uses large, often unlabeled data to learn patterns and produce new outputs. Predictive AI uses labeled data (with known outcomes) to make accurate predictions or classifications.
- Learning Style: Generative AI often uses unsupervised or semi-supervised learning, while Predictive AI relies mainly on supervised learning.
- Use Cases: Generative AI is popular in creative and design tasks, while Predictive AI dominates fields like business forecasting, healthcare, and risk analysis.
In short, Generative AI creates, and Predictive AI anticipates. When used together, they form a powerful combination, one inventing possibilities, the other guiding them with data-driven foresight.
Generative AI Applications
Generative AI is widely used across industries to speed up creation, design, and development. It helps automate creative work while still producing original, human-like results. Below are some of its most common applications.
Code Generation and Completion
Generative AI can write and improve code automatically. Tools like GitHub Copilot and ChatGPT help developers by suggesting code snippets, completing functions, or fixing errors. This makes programming faster, reduces mistakes, and lets engineers focus on problem-solving instead of repetitive typing.
Data Augmentation
In data science, Generative AI is used to create synthetic data, realistic but artificial datasets used to train machine learning models. This is useful when real data is limited, sensitive, or expensive to collect. Synthetic data improves model accuracy while protecting privacy.
Writing
Generative AI can produce blogs, emails, reports, and marketing copy in seconds. It helps content creators brainstorm ideas, rewrite drafts, or tailor messages for different audiences. Businesses use it to save time and maintain a consistent tone across communication.
Speech and Music Generation
AI systems like Jukebox and Murf can compose music or generate realistic speech in multiple voices and languages. These tools are transforming industries such as entertainment, gaming, and education by offering low-cost, customizable sound creation.
Video and Image Generation
Generative models can create images, animations, and even videos from simple text prompts. Tools like DALL·E, Runway ML, and Pika Labs are used by designers, advertisers, and filmmakers to visualize ideas instantly without needing full production teams.
Generative AI’s ability to produce unique, high-quality outputs makes it a key driver of creativity and innovation in today’s digital world.
Predictive AI Applications
Predictive AI helps organizations make smarter decisions by using data to anticipate trends, risks, and opportunities. It’s widely used across industries where forecasting and planning are crucial.
Financial Services
In banking and finance, predictive AI analyzes customer behavior, market data, and transaction patterns to detect fraud, assess credit risk, and forecast market trends. For example, it can predict which customers might default on loans or identify unusual spending that signals fraud.
Retail
Retailers use predictive AI to forecast demand, optimize pricing, and personalize product recommendations. By analyzing shopping patterns, seasonal trends, and customer preferences, stores can reduce overstocking, prevent shortages, and improve customer satisfaction.
Healthcare
In healthcare, predictive AI supports early disease detection, treatment planning, and patient monitoring. It can predict which patients are at higher risk for certain conditions or complications, helping doctors act before problems become serious.
Supply Chain
Predictive AI improves logistics, production, and inventory management. It helps businesses predict delays, manage stock levels, and adjust operations in real time. For example, shipping companies use AI to forecast delivery times and avoid disruptions.
By turning data into foresight, Predictive AI enables businesses to act proactively rather than reactively, saving time, money, and resources.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Generative AI
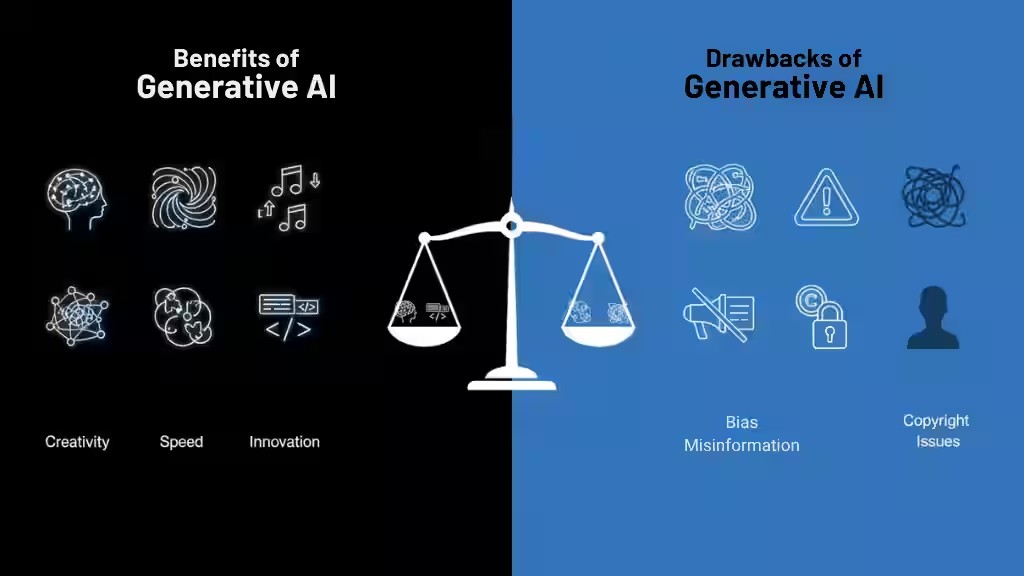
Generative AI offers exciting possibilities, but it also comes with important challenges. Understanding both sides helps users apply it responsibly and effectively.
Benefits
- Creativity and Innovation: Generative AI can produce new ideas, designs, and solutions in seconds, helping artists, writers, and engineers work faster and explore more options.
- Time and Cost Efficiency: It automates repetitive creative tasks like content drafting or image editing, saving both time and money.
- Personalization: Businesses can use it to create customized marketing content, chat responses, or product designs for individual users.
- Accessibility: Generative AI tools make professional-level creation easier for non-experts, lowering skill barriers in design, music, and coding.
- Data Generation: It can create synthetic data to train other AI systems safely, improving privacy and accuracy.
Drawbacks
- Inaccuracy and Hallucination: Generative models sometimes produce wrong or misleading information that sounds correct.
- Copyright and Ownership Issues: AI-generated content can unintentionally copy or resemble copyrighted material, creating legal risks.
- Bias and Ethical Concerns: If trained on biased data, outputs can reinforce stereotypes or misinformation.
- High Resource Costs: Training large generative models requires huge amounts of data, energy, and computing power.
- Security Risks: Generated content, like fake images or text, can be misused to spread false information.
Generative AI is powerful and creative, but it works best when used thoughtfully with human oversight and ethical safeguards in place.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Predictive AI
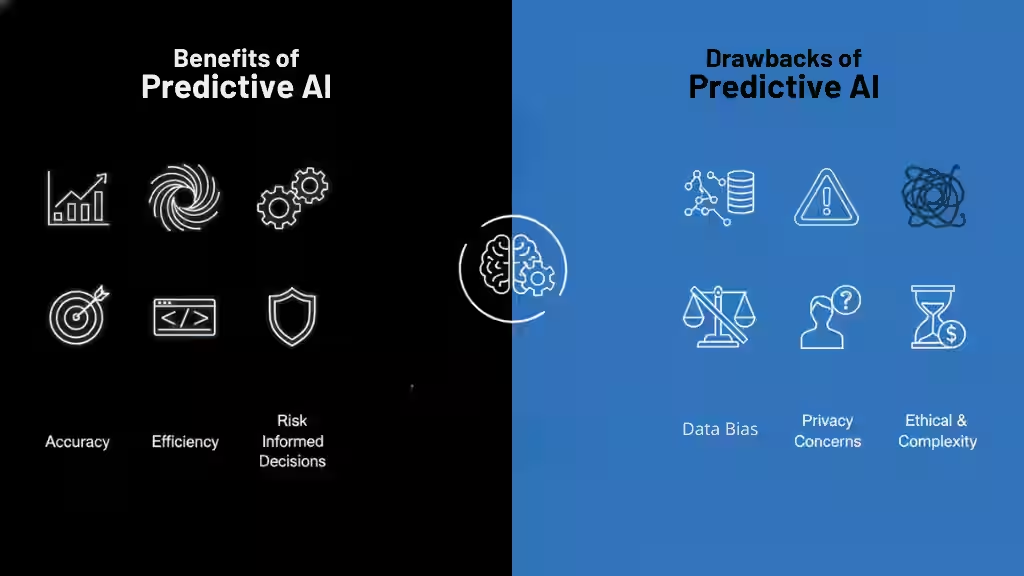
Predictive AI helps organizations make informed, data-driven decisions, but it also has limitations that must be managed carefully.
Benefits
- Better Decision-Making: Predictive AI turns historical data into clear insights, helping businesses forecast sales, demand, and customer behavior with greater accuracy.
- Cost and Time Savings: By predicting problems early, such as equipment failures or supply delays, companies can act before issues become expensive.
- Improved Efficiency: Automation of analysis allows teams to focus on strategy rather than manual data crunching.
- Risk Management: Financial institutions, healthcare providers, and manufacturers use predictive models to detect fraud, prevent losses, and manage operational risks.
- Personalization: Predictive analytics helps tailor recommendations, ads, and services to individual users, improving engagement and satisfaction.
Drawbacks
- Data Bias: If past data is biased or incomplete, the predictions will reflect those same problems, sometimes leading to unfair or inaccurate outcomes.
- Overfitting: Predictive models can become too focused on training data and fail to perform well with new information.
- Limited Interpretability: Complex models, like deep neural networks, may be hard to understand or explain to non-technical users.
- Dependence on Historical Data: Predictive AI struggles when facing new or unexpected events not seen in past data (for example, market shocks or pandemics).
- Maintenance Needs: Models degrade over time and need regular updates to stay accurate as real-world conditions change.
Predictive AI offers strong practical value, but it must be carefully trained, monitored, and tested to remain fair, accurate, and reliable.
Choosing Between Generative AI and Predictive AI
Choosing the right type of AI depends on what you want to achieve. Both Generative and Predictive AI are powerful, but they serve different goals.
When to Use Generative AI
Use Generative AI when your focus is on creating or designing something new.
It’s ideal for:
- Writing, designing, or coding from scratch
- Generating marketing content, visuals, or product ideas
- Creating synthetic data for testing or model training
- Building chatbots and creative assistants that interact naturally
Generative AI shines in creative, design, and innovation-driven fields, where originality and personalization matter most.
When to Use Predictive AI
Use Predictive AI when your goal is to forecast, plan, or make data-based decisions.
It’s best suited for:
- Predicting demand, sales, or market trends
- Detecting fraud and managing financial risk
- Diagnosing health conditions or predicting equipment failures
- Optimizing logistics and resource use
Predictive AI excels in operations, planning, and analysis, where accuracy and foresight lead to better outcomes.
Using Both Together
Many businesses now combine both to gain a competitive edge. Generative AI can create content or ideas, while Predictive AI analyzes how well those ideas might perform. Together, they enable smarter automation and more informed creativity.
Challenges and Limitations
Even with their impressive capabilities, both Generative AI and Predictive AI face important challenges that limit their reliability and scalability. Recognizing these helps users apply AI more responsibly.
1. Data Quality and Bias
AI models depend heavily on data. If the training data contains errors or biases, the output will too. For example, biased data can cause unfair decisions in hiring, lending, or healthcare predictions. Ensuring clean, diverse, and unbiased data is essential.
2. Lack of Transparency
Both AI types, especially complex neural networks, can act like black boxes, providing results without clear explanations. This makes it hard for users to understand or trust why a certain output or prediction was made.
3. Ethical and Legal Issues
Generative AI raises copyright and ownership concerns, while Predictive AI can impact privacy and fairness. Questions like “Who owns AI-created work?” or “Who’s responsible for a wrong prediction?” remain unresolved in many regions.
4. High Costs and Resource Demands
Training and maintaining large AI models require powerful hardware, massive datasets, and significant energy consumption. Smaller companies may struggle to afford these resources, slowing adoption.
5. Model Drift and Accuracy Loss
Predictive models can become less accurate as real-world conditions change, a problem known as model drift. Generative models can also lose quality over time if not updated regularly.
6. Misinformation and Misuse
AI-generated images, videos, and text can be used to create deepfakes or fake news, spreading misinformation online. Without proper safeguards, this can damage trust and cause real harm.
Despite these limitations, ongoing research focuses on improving explainability, fairness, and efficiency, helping AI evolve into a more reliable and ethical tool.
Future Trends in AI
AI is evolving faster than ever, and both Generative and Predictive AI are shaping the next wave of technology. The future will bring smarter, faster, and more connected systems that combine creativity with intelligence.
1. Multimodal AI
AI models are becoming multimodal, meaning they can understand and generate across several forms of data text, images, video, and sound. This will enable richer, more natural human–machine interactions.
2. Real-Time and Edge AI
Future AI systems will work in real time and closer to where data is produced, known as edge computing. This reduces delays and allows instant decision-making in areas like self-driving cars, robotics, and IoT devices.
3. AI Personalization
Generative and Predictive AI will merge to create hyper-personalized experiences from tailored learning content to custom shopping recommendations and healthcare plans unique to each person.
4. Neuro-Symbolic and Explainable AI
To build trust, new models are focusing on explainability, showing how AI makes its choices. Hybrid “neuro-symbolic” systems mix deep learning with logical reasoning to make outputs both accurate and understandable.
5. Ethical and Sustainable AI
There’s a growing focus on responsible AI, reducing carbon emissions from model training, ensuring fair use of data, and preventing bias. Governments and companies are creating stronger AI governance frameworks to guide safe innovation.
6. AI Collaboration
Instead of replacing humans, future AI will act as a collaborator, enhancing creativity, productivity, and decision-making. Generative AI will imagine possibilities, while Predictive AI will evaluate their success, forming a balanced partnership between imagination and insight.
The future of AI lies in integration and responsibility, combining human creativity with machine intelligence to solve problems faster and more fairly.
Conclusion
Generative AI and Predictive AI represent two powerful sides of modern artificial intelligence, one focused on creating, the other on forecasting.
Generative AI drives creativity by producing new ideas, designs, and solutions. Predictive AI delivers clarity by analyzing data to anticipate future outcomes. Each has its strengths, but the real potential appears when they work together, combining imagination with insight.
As technology advances, the line between the two continues to blur. Future systems will generate ideas and instantly test their likely success, creating a continuous loop of innovation and prediction.
In the end, the smartest organizations won’t choose one over the other; they’ll use both, responsibly and strategically, to shape a more intelligent, creative, and data-driven world.
FAQs
What is the main difference between Generative AI and Predictive AI?
Generative AI creates new content such as text, images, or music, while Predictive AI forecasts future outcomes based on existing data. In short, Generative AI creates, and Predictive AI predicts.
Can Generative AI and Predictive AI work together?
Yes. Generative AI can create new ideas or synthetic data, while Predictive AI can analyze and forecast which of those ideas are most likely to succeed. Together, they make AI systems more complete and effective.
Which industries use Generative AI the most?
Generative AI is widely used in marketing, design, entertainment, and software development, helping teams create visuals, code, and content faster and more efficiently.
Where is Predictive AI most useful?
Predictive AI is most valuable in finance, healthcare, retail, and supply chain management, where forecasting and risk analysis help improve decision-making and efficiency.
Is Generative AI safe to use?
Yes, but it must be used carefully. Users should check for accuracy, bias, and copyright issues. Human review is always recommended before publishing or sharing AI-generated content.
Will AI replace human jobs?
AI will automate some repetitive tasks, but it’s more likely to change jobs than completely replace them. People will focus more on creativity, problem-solving, and decision-making, while AI handles routine work.
What’s next for AI technology?
The future of AI lies in combining Generative and Predictive capabilities, creating systems that both imagine and reason, supporting humans in making faster, smarter, and more ethical decisions.
This page was last edited on 6 November 2025, at 5:12 pm
Contact Us Now

Contact Us Now
Start a conversation with our team to solve complex challenges and move forward with confidence.