- What is End User Management?
- What are EUC Managed Services?
- Definition of End User Management
- Example of End User Management
- Why is End User Management Important?
- History of End User Management
- Origin of End User Management
- Evolution of End User Management
- Current End User Management Trends
- What is the Future of End User Management?
- Benefits of End User Management
- Types of End User Management
- Differences Related to End User Management
- Common Mistakes in End User Management
- End User Management Tools
- How to Handle End User Management
- End User Management Process
- End User Management Skills/Expertise
- End User Management Challenges
- End User Management Risks
- End User Management Strategies
- End User Management Services
- How to Hire an End User Management Vendor
- Recommendations for Business Leaders
- Conclusion
End User Management is crucial for companies’ success in today’s technology-driven business environment. It provides smooth access to computer resources while maintaining security and efficiency, making it fit for enterprises of any size.
As demands increase, end user management services offer the necessary support to streamline operations and optimize productivity.
With the rise of remote work, diverse devices, and cloud-based applications, leveraging end-user management services or end-user managed services is essential to meet evolving business needs.
But how can these end-user managed services transform your business?
In this article, we’ll explore how end user management and EUC managed services can help your organization stay ahead by addressing challenges and opportunities in modern work environment.
| Things to know ↴ |
| Purpose: |
| End-user managed services are designed to support and maintain IT infrastructure, ensuring seamless operation and minimizing downtime for users. |
| Types: |
| Essential services include desktop management, IT help desk support, software updates, hardware management, and user access control. |
| Skills and Qualifications: |
| Professionals in this field typically need IT certifications, a bachelor’s degree in IT-related disciplines, and strong troubleshooting and customer service skills. |
| Control: |
| Managed service providers (MSPs) use specialized tools and processes to monitor and secure end-user devices and systems remotely. |
| Eligibility: |
| Eligibility for end-user managed services depends on company size, IT complexity, and the organization’s specific requirements. |
| Trends: |
| Cloud-based services, automation, AI-driven support, and cybersecurity are key trends driving the future of end-user managed services. |
Explore Related Topics:
Section Outline of End User Management Article:
| Segments | Names |
|---|---|
| Section 1: | About/Concepts |
| Section 2: | Past, Present, and Future |
| Section 3: | Benefits |
| Section 4: | Types and Components |
| Section 5: | Differences |
| Section 6: | Tools & Technologies |
| Section 7: | Strategies, Challenges, and Risks |
| Section 8: | Services |
| Section 9: | Hiring a Company/Vendor |
| Section 10: | Recommendations for Business Leaders |
| Section 11: | FAQs |
Section 1: About End User Management
This section introduces the fundamental concepts, services, and importance of End User Management, setting the foundation for its broader discussion throughout the article.
What is End User Management?
End User Management refers to the strategies, processes, and tools to oversee and improve end users’ experience. End users are the individuals who ultimately use or benefit from a product or service. Effective EUM ensures that these users can operate products efficiently and effectively, resulting in higher satisfaction and productivity.
What are EUC Managed Services?
End-User Computing (EUC) Managed Service is a comprehensive solution that provides organizations with the tools, infrastructure, and support necessary to enable their employees to work effectively and securely from any location. It’s a strategic approach that combines hardware, software, and services to deliver a seamless user experience.
Definition of End User Management
End-user management is the systematic approach to overseeing and supporting the interactions between end users (employees, customers, or clients) and the technology resources they utilize within an organization. This includes managing access to applications, devices, and data while ensuring security, efficiency, and compliance with organizational policies.
According to scholars, “End User Management encompasses the processes and strategies organizations employ to support, guide, and oversee the interaction between end users and the information systems they utilize, ensuring that users have the necessary tools and resources while maintaining system security and compliance.”
Example of End User Management
Examples of End User Management or Managed End User Computing (EUC) services involve outsourcing the management and support of end-user devices and applications. Here are some real-life examples:
Corporate IT Support Services:
Many companies use managed service providers (MSPs) to handle IT support for their employees, including troubleshooting issues with laptops, desktops, mobile devices, and software applications.
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) Solutions:
Organizations deploy VDI solutions where desktop environments are hosted on centralized servers and managed by a service provider. This allows end users to access their desktops remotely from any device.
Device Management for Remote Workforces:
With the rise of remote work, managed EUC services help companies manage and secure devices used by remote employees, ensuring they have secure access to necessary applications and data.
Software as a Service (SaaS) Management:
Managed service providers assist companies in managing and optimizing their SaaS applications, ensuring they are correctly configured, integrated, and secure for end users.
Security and Compliance:
Managed EUC services often include security monitoring, patch management, and compliance enforcement to protect end-user devices and data from security threats and ensure regulatory compliance.
Help Desk and User Support:
Managed service providers offer help desk services to address user queries, troubleshoot issues, and provide technical support for various devices and applications.
Application Virtualization and Streaming:
Companies leverage managed EUC services to virtualize and stream applications to end-user devices, ensuring consistent performance and accessibility across different platforms.
Backup and Disaster Recovery:
Managed EUC services may include backup and disaster recovery solutions to ensure that end-user data is backed up regularly and recoverable in case of data loss or system failure.
These examples illustrate how managed EUC services can enhance operational efficiency, support remote workforces, and ensure the security and reliability of end-user computing environments in various organizations.
Why is End User Management Important?
End User Management is essential for several reasons, as it plays a crucial role in an organization’s overall efficiency, security, and productivity. Here are some of the main reasons why it is essential:
1. Improved Productivity
End-user management ensures that users can access the tools, devices, and support they need to do their jobs efficiently. Streamlining software updates, managing device configurations, and providing prompt IT support minimize downtime, helping employees stay productive.
2. Enhanced Security
End users often represent a significant vulnerability in an organization’s security. So, End User Management helps enforce security policies, such as multi-factor authentication, regular patching, and encryption, to safeguard sensitive data and mitigate the risks posed by cyber threats like phishing, malware, and ransomware.
3. Streamlined IT Operations
By centralizing control over the software, devices, and services that end users rely on, End User Management reduces the complexity of IT operations. It enables IT teams to manage devices and applications remotely, ensuring compliance and uniformity across the organization while reducing IT overhead.
4. Scalability
As organizations grow, End User Management helps scale IT support efficiently. It ensures new users can be onboarded quickly and access appropriate resources and support. This is particularly crucial for companies expanding their workforce or embracing remote work.
5. Cost Efficiency
Effective End User Management can help reduce IT costs by minimizing downtime, optimizing software licensing, and avoiding expensive security breaches. It also supports automation and standardization, which reduces the need for costly, manual IT interventions.
6. User Experience and Satisfaction
They ensure end users have a seamless, consistent experience across their devices and applications, leading to higher job satisfaction. Reliable IT support, smooth access to necessary tools, and minimal disruption are vital to keeping employees focused and motivated.
7. Compliance and Regulatory Adherence
Many industries have strict compliance requirements (e.g., HIPAA, GDPR). End User Management ensures that devices and software comply with these regulations by implementing the necessary safeguards and monitoring systems.
8. Data Management and Backup
End-user management includes ensuring that critical data generated by users is properly managed, backed up, and recoverable in case of a hardware failure or cyberattack. This helps prevent data loss and facilitates business continuity.
9. Support for Remote Work and BYOD
With the rise of remote work and Bring Your Device (BYOD) policies, End User Management ensures that all devices, whether company-issued or personal, are secure, properly managed, and integrated into the organization’s IT environment. This flexibility is crucial for modern, distributed workforces.
10. Risk Mitigation
Organizations can mitigate risks related to unauthorized access, data leaks, and accidental breaches by managing how end users interact with systems and applications. Proper user management helps track and limit what users can access based on their roles, which reduces the likelihood of internal or external security threats.
End User Management is critical because it improves efficiency, supports business growth, enhances security, and helps organizations navigate modern challenges like remote work, data privacy regulations, and digital transformation.
Section 2: Past, Present, and Future

This section explores the historical context, current state, and future direction of End User Management, providing a complete picture of how this vital IT function has developed and what lies ahead for businesses looking to optimize their end-user environments.
History of End User Management
The history of End User Management (EUM) reflects the broader evolution of IT infrastructure and user computing needs over the last several decades.
In the early days of computing, IT departments primarily focused on managing centralized mainframe systems, where users accessed shared resources from a limited number of terminals.
As personal computers became more commonplace in the 1980s and 1990s, the need for managing individual user devices grew.
IT teams were tasked with manually configuring, installing, and troubleshooting desktop machines, often with limited centralized control over software or security updates.
Introducing local area networks (LANs) marked a turning point in End User Management. IT teams could now support multiple users and devices from a central location.
This shift led to the development of early tools for remote desktop management, software deployment, and patch management, laying the foundation for modern EUM practices.
Origin of End User Management
End User Management originated from the growing complexity of managing increasingly distributed computing environments.
In its earliest form, it was limited to providing basic technical support and user assistance, often through on-site visits or individual help desk requests.
As businesses began adopting more personal computing devices, IT departments saw the need for scalable solutions that could manage multiple users and devices simultaneously.
This need gave rise to centralized management systems, which allowed IT teams to gain more control over user devices, applications, and security settings.
The rise of client-server architectures in the late 20th century enabled organizations to connect employees to shared resources and systems, marking the true beginning of structured End User Management practices.
As networks expanded, so did the need for more robust tools to manage, secure, and monitor devices remotely.
Evolution of End User Management
Technological advancements, changes in workplace culture, and the increasing complexity of IT environments have shaped the evolution of End User Management. Key milestones in its evolution include:
1. On-Premise Solutions:
Early End User Management relied heavily on manual processes and on-premise solutions, such as IT staff’s direct installation and configuration of devices. These processes were time-consuming and prone to errors.
2. Remote Management and Automation:
With the rise of networks and the internet, IT teams began using remote desktop tools and automated software distribution systems. Solutions like Mobile Device Management (MDM) and Unified Endpoint Management (UEM) allowed IT teams to automate device configuration, updates, and security measures, saving time and improving efficiency.
3. Cloud Computing:
The shift to cloud-based services dramatically changed End User Management. With cloud computing, organizations can manage users and devices remotely without on-site infrastructure. Software-as-a-service (SaaS) models allow users to access applications from anywhere, leading to more flexible work environments and the need for more robust security protocols.
4. Mobile and BYOD:
The adoption of mobile devices and Bring Your Device (BYOD) policies further complicate end user management. IT departments had to manage a wider variety of devices while ensuring data security and user productivity, leading to the development of advanced endpoint management tools.
5. Remote and Hybrid Work:
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the need for remote and hybrid work environments, making EUM more essential than ever. IT teams had to rapidly adapt to managing employees working from home, often using personal devices, while maintaining corporate security and compliance.
Current End User Management Trends
Today, End User Management is defined by several key trends that are reshaping the way businesses approach user computing:
1. Cloud-Based Management:
Organizations increasingly adopt cloud-based platforms for managing user devices and software. This enables greater flexibility in supporting remote workers and simplifies device provisioning, application deployment, and security updates.
2. Unified Endpoint Management (UEM):
UEM solutions consolidate the management of all devices—whether desktops, laptops, smartphones, or tablets—into a single platform. This unification allows IT teams to streamline operations, enforce security policies consistently, and improve user support across all endpoints.
3. Automation and AI:
Automation tools and AI-powered insights are becoming integral to EUM, helping IT teams predict and resolve issues before they impact users. AI-driven tools can also help optimize device performance, monitor user behavior for security risks, and personalize user experiences.
4. Zero Trust Security:
With increasing cyber threats and a rise in remote work, businesses are adopting Zero Trust security models that continuously verify user identity and device health before granting access to corporate resources. This approach is critical to maintaining security in decentralized work environments.
5. Remote and Hybrid Work Environments:
The ongoing trend of remote and hybrid work has emphasized flexible, user-friendly solutions that allow employees to remain productive regardless of location. EUM must now accommodate seamless access to corporate applications, secure file sharing, and collaboration tools for remote employees.
What is the Future of End User Management?
Several emerging technologies and trends will shape the future of End User Management:
1. AI-Driven Personalization:
Artificial Intelligence will play a more significant role in personalizing the end-user experience. AI-powered systems will predict user needs, optimize device performance, and automate routine IT tasks, reducing user friction and enhancing productivity.
2. Increased Focus on User Experience (UX):
As organizations recognize the importance of IT to employee satisfaction, there will be a growing emphasis on delivering a seamless and intuitive user experience. Self-service IT support, proactive issue resolution, and faster provisioning times will become more common.
3. Enhanced Security and Compliance:
As data privacy regulations become more stringent, future End-User Management solutions will prioritize enhanced security measures, ensuring compliance with global standards like GDPR and CCPA. Advanced security tools will monitor user activity and prevent real-time unauthorized access.
4. Edge Computing and IoT Integration:
The rise of edge computing and the Internet of Things (IoT) will extend End User Management beyond traditional devices to IoT devices and edge-based solutions. IT teams must manage various endpoints, requiring more scalable and agile management tools.
5. Hybrid Cloud Solutions:
As cloud adoption grows, organizations will likely embrace hybrid cloud solutions that allow for flexible scaling and management of both on-premise and cloud-based systems. This will lead to more dynamic EUM platforms integrating multiple environments under a single management framework.
In the future, End User Management will focus on creating more intelligent, automated, and secure environments that empower users while reducing IT complexities. Organizations that invest in these forward-thinking solutions will be well-positioned to support evolving business needs and dynamic workforce models.
Section 3: Benefits
Whether improving operational performance for businesses or offering streamlined access to tools for individuals, the benefits of effective End User Management are far-reaching. This section outlines the specific benefits for different stakeholders.
Benefits of End User Management
Effective End-User Management ensures users have secure and seamless access to the necessary tools and resources, regardless of their role or location.
Organizations can enforce security policies, streamline technical support, and minimize downtime by centralizing control over devices and applications.
The result is improved productivity, enhanced security, and a better overall user experience. Moreover, EUM allows businesses to adapt quickly to changes in the workforce, such as the growing trend of remote work, while maintaining compliance with industry standards and regulations.
Benefits for Businesses
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity: By automating tasks such as software updates, security patches, and device configurations, EUM reduces the time and effort required from IT teams, allowing them to focus on strategic initiatives. Employees also benefit from faster access to tools and resources, minimizing downtime and boosting productivity.
- Enhanced Security: With a centralized system for managing user access and devices, businesses can enforce strict security protocols, including multi-factor authentication and data encryption. This helps protect against cyber threats and ensures compliance with data privacy regulations like GDPR and HIPAA.
- Cost Savings: EUM reduces operational costs by minimizing the need for manual IT intervention and reducing the likelihood of costly security breaches. Cloud-based and automated solutions also help businesses scale their IT operations without significant infrastructure investments.
- Scalability: As businesses grow or adjust to changes like remote work or BYOD policies, EUM provides the flexibility to manage an increasing number of devices and users easily. This scalability ensures that organizations can expand without compromising security or user experience.
- Improved User Experience: A streamlined, user-friendly IT environment increases employee satisfaction. EUM systems prioritize seamless device management, fast issue resolution, and consistent application access, empowering users to focus on their work without technical difficulties.
Benefits for Professionals
- Seamless Access to Resources: End-user management ensures that professionals can access the necessary software, applications, and data anywhere. This is particularly beneficial for remote workers or those who travel frequently, as they can work securely and efficiently from various devices.
- Enhanced Productivity: EUM allows professionals to work without interruptions caused by technical issues or security concerns. Automated updates, quick IT support, and easy access to tools ensure that users can focus on their work rather than dealing with IT complications.
- Increased Security and Privacy: EUM provides robust security measures for professionals handling sensitive information and protecting personal data and work-related files. With advanced encryption and security protocols, professionals can confidently work on corporate systems without fearing data breaches.
- Self-Service IT Solutions: Modern EUM systems often include self-service portals where professionals can resolve common IT issues independently, reducing downtime and enhancing their sense of independence.
Benefits for Job Seekers
- Access to Modern Tools: Many organizations now utilize sophisticated End User Management systems to manage candidate applications, interviews, and assessments. Job seekers benefit from a more streamlined and efficient recruitment process, less downtime, and better communication.
- Improved Job Readiness: As businesses increasingly adopt EUM systems, having familiarity with these tools can enhance a job seeker’s appeal to potential employers. Understanding how to navigate secure, managed work environments can be an advantage in hiring.
- Remote Work Opportunities: Many companies are embracing remote and hybrid work environments. EUM makes it easier for job seekers to apply for and work in jobs that are not geographically restricted. These systems ensure that candidates can access job-related tools securely from anywhere.
- Enhanced Data Security: Job seekers often provide sensitive personal data when applying. Organizations that employ robust EUM systems can protect this information, giving candidates peace of mind about their privacy during the hiring process.
Benefits for Students
- Access to Educational Resources: End-user management helps educational institutions manage student devices and provide easy access to learning materials, software, and digital platforms. This is particularly important for remote or hybrid learning environments, where students need secure access to online courses and assignments from multiple devices.
- Increased Security: With cyber threats becoming more prevalent in educational institutions, EUM ensures that student data is protected through advanced security measures like encryption, malware protection, and secure access protocols. Students can focus on their studies without worrying about data breaches or security risks.
- Optimized Learning Experience: EUM systems support a smooth and user-friendly learning experience by managing device configurations and ensuring the necessary software is up-to-date. This minimizes disruptions and ensures students can concentrate on learning rather than technical difficulties.
- Technical Support: In case of technical issues, EUM provides students with quick access to IT support, ensuring that problems are resolved swiftly. This can be especially valuable in online learning environments where reliable technology is critical to success.
- Preparation for Future Careers: As end-user management becomes increasingly common in workplaces, students familiar with these systems will be better prepared for future careers in industries prioritizing secure, managed IT environments. This hands-on experience with managed services and secure computing can give students a competitive edge in the job market.
Section 4: Types and Components

Different types of EUM focus on specific elements such as desktops, mobile devices, applications, and user access. This section explores the fundamental types and components of End User Management, detailing how they contribute to a cohesive and well-managed IT landscape.
Types of End User Management
End-user management can be divided into several categories, each focusing on a different aspect of the IT infrastructure. Together, these types provide a comprehensive approach to handling user devices, software, and access in a secure, scalable, and user-friendly manner.
- Desktop Management
- Mobile Device Management (MDM)
- Application Management
- Access Management

Desktop Management
Desktop Management refers to the tools and practices used to maintain and manage the desktops within an organization. This includes installing, configuring, monitoring, and troubleshooting operating systems, software, and hardware components.
- Software Installation and Updates: IT teams use Desktop Management systems to install and update software on user machines remotely. This ensures that all desktops are running the latest versions, reducing the risk of vulnerabilities or compatibility issues.
- Security Patches and Antivirus: Regular updates and patches are critical for protecting desktops from malware and cyberattacks. Automated patch management tools ensure that all systems remain secure, while antivirus software adds a layer of protection.
- Asset Management: Desktop Management systems often include asset-tracking features that help IT teams manage hardware, software licenses, and other resources. This ensures that the organization maintains proper compliance with licensing agreements and has a clear view of its IT inventory.
- Remote Monitoring and Support: IT administrators can remotely monitor the performance of desktop systems, troubleshoot issues, and provide real-time support to users, reducing downtime and maintaining productivity.

Mobile Device Management (MDM)
Mobile Device Management (MDM) focuses on securing, managing, and monitoring an organization’s mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets. With the rise of Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policies and remote work, MDM has become essential to modern End-User Management strategies.
- Device Security: MDM systems enforce security policies such as password requirements, encryption, and remote wipe capabilities to protect corporate data on mobile devices. This is particularly important for managing the security risks of lost or stolen devices.
- Application Control: MDM allows IT teams to control which applications can be installed or accessed on mobile devices. This prevents users from downloading unauthorized or potentially harmful apps that could compromise security.
- Device Provisioning and Configuration: MDM systems enable IT teams to quickly set up new devices with the necessary settings, applications, and security protocols. This is particularly useful for onboarding new employees or managing a large fleet of mobile devices.
- Monitoring and Compliance: MDM tools monitor device usage, ensuring compliance with corporate policies. Administrators can track device location, data usage, and app activity, enabling swift action in case of suspicious behavior or policy violations.
Application Management
Application Management oversees software applications’ deployment, performance, and security across an organization. It ensures that users can access the necessary applications while controlling licensing, updates, and data integrity.
- Application Deployment: IT teams can deploy software applications remotely to all users or specific groups through centralized management systems. This ensures all employees have the right tools for their roles without manual installation.
- Software Updates and Patches: Application Management systems ensure that all software is updated with the latest patches and versions, reducing security vulnerabilities and improving functionality. This is crucial for preventing downtime and ensuring that applications perform optimally.
- License Management: Application Management tools help track software licenses, ensuring compliance with vendor agreements. This prevents legal issues arising from unauthorized software use and helps organizations manage their software budgets more effectively.
- Application Monitoring: Continuous application performance monitoring is critical to identifying and resolving issues before they affect end users. Application Management systems provide insights into app usage, crashes, and other performance metrics, helping IT teams maintain smooth operations.

Access Management
Access Management is the process of controlling who has access to systems, applications, and data within an organization. It plays a critical role in maintaining security by ensuring only authorized users can access sensitive resources.
- Authentication: Access Management systems enforce authentication protocols such as single sign-on (SSO), multi-factor authentication (MFA), and password management to verify user identities before granting access to resources.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): This approach limits access based on the user’s organizational role. IT teams can assign specific permissions to different roles, ensuring that employees only have access to the data and applications they need to perform their jobs.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): IAM systems provide a centralized platform for managing user identities and access permissions. This ensures that access policies are consistent across all systems and can be easily modified as users change organizational roles.
- Audit and Compliance: Access Management tools provide detailed logs of user activity, allowing organizations to audit who accessed what data and when. This is essential to comply with data protection regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA and identify potential security breaches.
Section 5: Differences
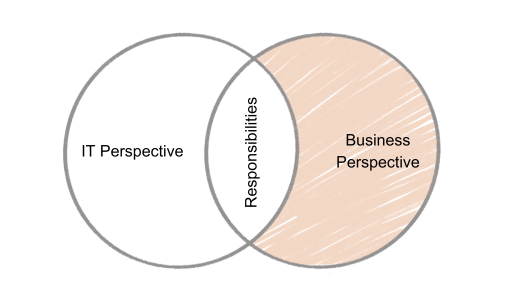
End User Management (EUM) varies significantly depending on the organization’s perspective, the tools and technologies used, and the specific goals of the management strategy. This section discusses the key differences in end user management and highlights common mistakes to help businesses optimize their approach.
Differences Related to End User Management
End-user management is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Differences arise based on the IT perspective, business needs, tools and technologies used, and each organization’s objectives. Recognizing these differences is crucial in developing a customized, effective EUM strategy.
IT Perspective vs. Business Perspective
- IT Perspective: From an IT standpoint, the focus is often on security, compliance, and the seamless integration of technology. IT professionals are concerned with technical performance, protection against cyber threats, and ensuring all systems operate smoothly with minimal disruptions.
- Business Perspective: From a business perspective, the emphasis is more on productivity, cost-efficiency, and user satisfaction. Business leaders focus more on how EUM can support overall business goals, improve employee performance, and foster collaboration.
Tools and Technologies
- IT Tools: IT teams rely on various software solutions for tasks like desktop management, mobile device management (MDM), application management, and access control. These tools focus on streamlining administrative tasks, maintaining security, and monitoring systems in real time.
- Business Tools: On the business side, the focus may be on collaboration tools, customer relationship management (CRM) platforms, and other software that directly contributes to business operations and growth. The tools are chosen for their ability to enhance productivity and ease of use.
Objectives and Goals
- IT Objectives: IT teams aim to maintain system stability, protect data, and ensure the end-user experience is secure and reliable. IT goals include reducing downtime, automating routine tasks, and addressing potential security risks preemptively.
- Business Objectives: Businesses prioritize efficiency and user satisfaction and align IT management with strategic business objectives. The goal is to leverage technology to drive profitability, improve employee performance, and enhance service delivery.
Responsibilities
- IT Responsibilities: IT teams are responsible for deploying, maintaining, and securing the infrastructure that supports end users. This includes everything from system updates, troubleshooting, and network security to access control and compliance management.
- Business Responsibilities: On the other hand, business units ensure users have the tools and resources to meet their goals. Business leaders oversee employee productivity, operational efficiency, and technology support for broader organizational goals.
Metrics and KPIs
- IT Metrics: IT departments often track metrics like system uptime, response time for helpdesk tickets, patching and update rates, and the number of security incidents prevented. These metrics focus on technical efficiency and security.
- Business KPIs: Business leaders look at key performance indicators (KPIs) such as employee productivity, customer satisfaction, cost savings, and return on investment (ROI) from IT systems. These KPIs reflect how well EUM aligns with business objectives and outcomes.
Integration with Business Operations
- IT Integration: From the IT perspective, EUM must seamlessly integrate with existing systems such as enterprise resource planning (ERP), customer relationship management (CRM), and security platforms. This ensures technical compatibility and minimizes disruption.
- Business Integration: For businesses, the focus is on how EUM can be integrated into the daily workflow to improve operational efficiency. The goal is to give users easy access to the necessary tools while enhancing collaboration and streamlining processes.

Common Mistakes in End User Management
While implementing End User Management, organizations often need help with common mistakes that undermine efficiency, security, and user satisfaction. By recognizing and addressing these issues, businesses can improve their EUM strategies and reduce risks.
Lack of Proper User Authentication and Authorization
Failing to implement robust authentication methods such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) can expose systems to unauthorized access. Proper authorization ensures that users have access only to the resources they need, reducing the risk of data breaches.
Not Regularly Reviewing and Updating User Permissions
User roles and responsibilities change over time. Organizations often neglect to review and update user permissions regularly, leaving outdated access rights in place, which can lead to potential security breaches or unauthorized access.
Inadequate User Training and Support
End users need adequate training to effectively use the systems and tools they have available. Organizations often need to pay more attention to this aspect, leading to inefficiencies, mistakes, or even security risks caused by untrained employees misusing systems.
Poor Documentation of User Roles and Responsibilities
Clear documentation of roles and responsibilities is crucial for managing user access and ensuring compliance. Lack of proper documentation can lead to confusion about user privileges and difficulties during audits or security incidents.
Over-Complicating User Interfaces
Complicated user interfaces can frustrate end users, leading to lower productivity or increased errors. Simplifying user interfaces and ensuring intuitive design improves user satisfaction and reduces the need for additional support or training.
Ignoring User Feedback
End users provide valuable insights into the usability of systems and tools. Ignoring user feedback can result in unresolved issues, lowered productivity, and poor user satisfaction. Regularly soliciting and acting on feedback ensures a more user-friendly experience.
Inconsistent Communication of Policies and Guidelines
Effective End User Management requires clear and consistent communication of policies, guidelines, and security protocols. Consistent communication can lead to clarity and compliance with company policies, which may result in security vulnerabilities or operational disruptions.
Inadequate Backup and Recovery Systems
A solid backup and recovery strategy can be beneficial in case of data loss or system failures. Organizations should ensure regular backups and have recovery protocols to minimize downtime and data loss.
Overloading Users with Security Requirements
While security is critical, overloading users with too many security requirements, such as frequent password changes or cumbersome authentication processes, can lead to frustration. A balance must be struck between security and usability.
Lack of Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Role-based access control (RBAC) allows organizations to assign permissions based on user roles. Without RBAC, users can easily have unnecessary access to sensitive data or systems, increasing the risk of insider threats or data breaches.
Not Addressing Shadow IT
Shadow IT refers to end users using unauthorized systems or applications. Failing to address this issue can lead to security vulnerabilities, data leaks, and compliance breaches. Organizations should monitor and regulate all IT assets used by employees.
Section 6: Tools and Processes
Effective End User Management (EUM) depends on the right combination of tools, processes, and expertise. This section outlines the various tools used to manage end users, explains how organizations can handle EUM, and provides a framework for the necessary skills and processes to streamline operations.
End User Management Tools
End-user management tools ensure smooth operations, security, and efficiency in managing IT infrastructure and users. These tools automate tasks, provide real-time monitoring, and enhance user experience by offering personalized and secure access to the systems they need.
- Desktop Management Tools: Solutions like Microsoft Endpoint Manager and VMware Horizon help IT teams monitor, update, and troubleshoot user devices remotely. These tools ensure that desktop environments are kept secure, up-to-date, and running efficiently.
- Mobile Device Management (MDM) Tools: With the increase in mobile and remote work, MDM tools like Jamf and MobileIron are essential. They allow IT teams to manage mobile devices, enforce security policies, and ensure compliance with corporate standards, even when devices are off-premises.
- Application Management Tools: Microsoft Intune and Citrix Workspace simplify application deployment, management, and security. These platforms ensure that users can access suitable applications while maintaining high control over software distribution and usage.
- Access Management Tools: Identity and access management (IAM) solutions like Okta, OneLogin, and Azure Active Directory are critical for controlling who can access what data and systems. These tools enforce strong authentication, manage user permissions, and ensure secure platform access.
- Collaboration Tools: Platforms like Slack, Microsoft Teams, and Zoom improve communication and collaboration among end users, ensuring efficient workflows and engagement regardless of geographical location.

How to Handle End User Management
Successfully handling End User Management involves more than just implementing the right tools. It requires a well-defined strategy, collaboration across departments, continuous user needs, and system performance assessment.
- Develop Clear Policies: Establish clear IT policies for users, including guidelines for acceptable use, security protocols, and software access. These policies should be regularly communicated and updated to align with evolving technology and security threats.
- Centralize Management: Use centralized management tools that allow IT teams to oversee all devices, applications, and users from a single dashboard. This reduces the complexity of managing multiple platforms and ensures that all users are treated consistently.
- Ensure Regular Audits and Updates: Regularly audit user accounts, device statuses, and permissions to ensure everything runs smoothly and securely. Automatic updates to systems and applications should be a priority to minimize vulnerabilities.
- User Support and Training: Offer end users comprehensive training and ongoing support. Proper training reduces downtime and ensures employees can use the tools provided effectively. Establishing an IT helpdesk or user support service is crucial for addressing issues promptly.
End User Management Process
The End User Management process encompasses the lifecycle of users within the organization, from onboarding to offboarding. A structured approach helps ensure users have the necessary tools and access while maintaining security and compliance.
- User Onboarding: When a new employee joins, they must be provided with the appropriate tools, applications, and permissions. This process involves setting up new user accounts, provisioning devices, and granting access to necessary systems.
- Monitoring and Support: Once users are onboarded, continuous monitoring is essential. IT teams must track device performance, application usage, and potential security threats. This allows for proactive troubleshooting and maintenance, minimizing disruptions.
- Security Management: Implementing robust authentication methods, monitoring access rights, and ensuring that devices are secure are all critical components of EUM. This step helps prevent unauthorized access and ensures compliance with data protection regulations.
- User Offboarding: When an employee leaves the organization, it’s crucial to deactivate their accounts, revoke access to systems, and reclaim company devices. The offboarding process ensures that former employees can no longer access sensitive data, reducing the risk of insider threats.
- Continuous Improvement: The EUM process should be revisited regularly to identify inefficiencies and areas for improvement. User feedback and system audits help refine policies and tools, ensuring the management process evolves with the organization’s needs.
End User Management Skills/Expertise
Managing end users requires specific technical and soft skills. IT professionals responsible for EUM must be proficient in technology while also understanding the broader business implications of user management. Key skills include:
- Technical Expertise: IT teams must understand the tools and platforms used to manage devices, applications, and access. This includes knowledge of desktop and mobile management software, security protocols, and user authentication systems.
- Security Knowledge: Given the increasing prevalence of cyber threats, IT professionals must be well-versed in security best practices, including encryption, multi-factor authentication, and network security.
- Communication Skills: End users often have varying levels of technical proficiency. IT professionals must effectively communicate with users, offering clear instructions and solutions without overwhelming them with technical jargon.
- Problem-Solving: Handling day-to-day user issues requires quick thinking and strong problem-solving abilities. IT teams must be capable of diagnosing problems and implementing fixes efficiently to minimize downtime.
- Project Management: Managing large-scale EUM initiatives, such as company-wide software upgrades or onboarding processes, requires strong project management skills. IT professionals should be adept at coordinating teams, managing timelines, and ensuring that projects are completed on schedule.
- User-Centered Focus: Successful end user management prioritizes user satisfaction and productivity. IT professionals must adopt a user-centered approach, providing tools and solutions that enhance user experience and help achieve business goals.
Section 7: Challenges, Risks, and Strategies
End User Management (EUM) is crucial in modern IT infrastructure. Still, it comes with its own set of challenges and risks. This section explores the common challenges, associated risks, and key strategies organizations can employ to overcome these issues.
End User Management Challenges
As businesses become more reliant on technology, managing end users becomes increasingly complex. IT teams must navigate various technical, security, and compliance-related challenges to ensure the smooth functioning of the organization.
1. Complexity of Managing Diverse Devices
Managing multiple platforms has become more difficult with the proliferation of devices—from desktops to laptops, tablets, and smartphones. IT departments face challenges in standardizing device management while supporting a broad range of hardware and operating systems.
- Key Challenge: Ensuring consistent security protocols and user experiences across diverse devices.
- Solution: Implementing Unified Endpoint Management (UEM) solutions to centralize control and automate device management.
2. User Compliance and Security Fatigue
Many end users experience fatigue when constantly being asked to follow security protocols such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) or frequent password changes. This can lead to non-compliance, creating vulnerabilities within the organization’s systems.
- Key Challenge: Balancing security requirements with user convenience to avoid user frustration and lapses in compliance.
- Solution: Simplifying user authentication processes through biometrics or single sign-on (SSO) solutions.
3. Scalability Issues
As organizations grow, managing a more extensive and more geographically dispersed user base becomes increasingly difficult. Scaling end user management practices to accommodate hundreds or thousands of users can strain IT resources and existing systems.
- Key Challenge: Expanding EUM practices without sacrificing efficiency or security.
- Solution: Cloud-based management platforms can enable scalability and flexibility in managing large numbers of users.
4. Limited IT Resources
Smaller organizations or IT departments with limited staff may need help managing end users effectively, especially when faced with increasing demands for support, security, and compliance.
- Key Challenge: Meeting EUM needs with a small IT staff or limited budget.
- Solution: Automation tools and managed service providers can help offload routine tasks and provide additional support.
5. Resistance to Change
Users may need to be more active in adopting new tools, software, or processes, which can hinder the effective implementation of EUM practices. Resistance can stem from a lack of understanding or fear of losing control over how they use technology.
- Key Challenge: Convincing users to embrace new EUM processes, policies, or tools.
- Solution: Offering clear training, demonstrations, and ongoing support to ease the transition to new systems.

End User Management Risks
Poorly managed end user environments can expose an organization to significant risks, both in terms of security and compliance. IT leaders must proactively mitigate these risks to avoid costly disruptions and breaches.
1. Data Breaches and Cybersecurity Threats
As cyberattacks become more sophisticated, the risk of data breaches rises. Poorly managed user devices or lax security policies can provide entry points for attackers.
- Key Risk: Loss of sensitive information due to unauthorized access.
- Mitigation: Implementing strong encryption, multi-factor authentication, and endpoint security to minimize attack surfaces.
2. Unauthorized Access and Insider Threats
Insider threats, either malicious or accidental, pose a significant risk. Employees or contractors may access confidential information they shouldn’t have, intentionally or through weak access controls.
- Key Risk: Internal users accessing or sharing sensitive data improperly.
- Mitigation: Enforcing role-based access control (RBAC) and regularly auditing access privileges.
3. Device Loss or Theft
Lost or stolen devices pose a severe risk if they contain sensitive information or provide access to the organization’s systems. Unsecured mobile devices, in particular, are vulnerable to breaches.
- Key Risk: Data exposure due to missing devices.
- Mitigation: Ensuring devices are encrypted and employing remote wipe capabilities for lost or stolen equipment.
4. Compliance and Legal Risks
Many industries are subject to stringent regulations around data privacy and security (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA). Failing to comply with these regulations can lead to legal actions, fines, and reputational damage.
- Key Risk: Non-compliance with data protection regulations leading to legal repercussions.
- Mitigation: Regularly reviewing and updating policies to meet current legal and compliance standards.
5. Downtime and System Outages
Inadequate user management can lead to system outages, impacting productivity and revenue. Downtime caused by poor monitoring or inefficient support can disrupt business operations.
- Key Risk: Lost productivity and revenue due to system failures.
- Mitigation: Monitoring tools and proactive maintenance ensure high system availability.

End User Management Strategies
To address the challenges and risks outlined above, organizations must adopt comprehensive strategies that enhance their end-user management practices’ security, efficiency, and scalability.
1. Implement Identity and Access Management (IAM)
IAM solutions enable organizations to manage user identities, authenticate users securely, and control system access. These tools ensure that only authorized users can access specific data and systems.
- Strategy: Deploying IAM solutions such as Okta or Microsoft Azure Active Directory to enhance security.
- Benefit: Ensures that only the right individuals can access sensitive data and systems.
2. Adopt a Zero-Trust Security Model
The Zero-Trust model assumes that no one, whether inside or outside the organization, should be trusted by default. This model enforces continuous verification of every user and device that attempts to access resources.
- Strategy: Implementing Zero-Trust security models to mitigate unauthorized access risks.
- Benefit: Enhances security by assuming that every access request is potentially malicious.
3. Automation of User Provisioning and Deprovisioning
Automation tools can streamline user account creation, modification, and deletion. This reduces the risk of human error and ensures that users always have appropriate access.
- Strategy: Using tools like Microsoft Intune to automate user account creation and deletion.
- Benefit: Reduces errors and ensures timely access changes as users join or leave the organization.
4. Unified Endpoint Management (UEM) Solutions
UEM solutions provide a centralized platform for managing all user devices, whether desktop, mobile, or tablet. These tools offer a consistent device management, security, and monitoring approach.
- Strategy: Implementing UEM platforms like VMware Workspace ONE to manage devices across multiple platforms.
- Benefit: Simplifies device management and ensures security protocols are uniformly applied.
5. Ongoing Security Awareness Training
End users are often the weakest link in security. Regular training ensures that users know current threats, understand the importance of security policies, and learn how to respond to potential breaches.
- Strategy: Conduct regular security training sessions and phishing simulations for users.
- Benefit: Reduces the likelihood of security incidents caused by human error or negligence.
Section 8: Services

Effective End User Management (EUM) encompasses a variety of services that ensure users have the necessary tools, support, and security to perform their tasks efficiently. This section outlines the key services involved in EUM and how they contribute to enhanced user productivity and organizational performance.
End User Management Services
EUM services are designed to address the diverse needs of end users while streamlining IT operations. These services include IT support, software management, data backup and recovery, cloud management, security management, network management, remote training management, digital asset management, and user experience improvement.
1. IT Support Services

IT support services assist end users in resolving technical issues related to hardware, software, and network connectivity.
This support can be delivered through various channels, including help desks, ticketing systems, and on-site support.
- Service Overview: IT support teams assist users with troubleshooting problems, guide them through technical difficulties, and ensure that IT systems function smoothly.
- Benefit: Enhances user satisfaction and productivity by quickly resolving issues hindering work performance.
2. Software Management Services

Software management involves installing, configuring, and maintaining applications used by end users. This service ensures users can access the latest software versions while managing licensing and compliance.
- Service Overview: Software management includes monitoring software usage, applying updates, and managing licenses to ensure compliance with legal requirements.
- Benefit: Keeps software up to date, reducing vulnerabilities and enhancing user productivity.
3. Data Backup and Recovery Services

Data backup and recovery services protect an organization’s data from loss due to accidental deletion, hardware failures, or cyberattacks. These services ensure that critical information is securely backed up and can be restored quickly.
- Service Overview: Regular backups are performed, and recovery plans are established to restore data in case of loss.
- Benefit: Minimizes downtime and data loss, ensuring business continuity.
4. Cloud Management Services

Cloud management services oversee the deployment, maintenance, and optimization of cloud-based applications and resources. These services help organizations leverage cloud technology while managing costs and ensuring security.
- Service Overview: Cloud management includes managing virtual machines, storage, and cloud services to optimize performance and costs.
- Benefit: Provides scalability and flexibility while minimizing the complexities associated with cloud infrastructure.
5. Security Management Services

Security management services focus on protecting end-user devices and organizational data from cyber threats. This includes implementing security policies, monitoring threats, and conducting regular security assessments.
- Service Overview: Security management involves deploying antivirus software, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems, as well as conducting security training for users.
- Benefit: Reduces the risk of data breaches and enhances overall organizational security.
6. Network Management Services

Network management services ensure the reliable operation of an organization’s network infrastructure. This includes monitoring network performance, troubleshooting connectivity issues, and maintaining network devices.
- Service Overview: Network management includes configuring routers, switches, and firewalls and ensuring optimal network performance.
- Benefit: Enhances user experience by ensuring stable and fast network connectivity.
7. Remote Training Management Services

Remote training management services provide end users with training and resources to use technology and software tools effectively. This can be especially valuable for remote workers or organizations with distributed teams.
- Service Overview: Remote training includes webinars, online tutorials, and personalized training sessions to enhance users’ skills and confidence.
- Benefit: Improves user competency and adoption of technology, leading to increased productivity.
8. Digital Asset Management Services
Digital asset management services help organizations organize, store, and retrieve digital assets such as documents, images, and videos.
These services ensure that users can easily access the resources they need.
- Service Overview: Digital asset management includes establishing a centralized repository, implementing tagging and categorization systems, and ensuring proper access controls.
- Benefit: Streamlines access to information and enhances collaboration among users.
9. User Experience Improvement Services

User experience improvement services focus on enhancing end users’ overall satisfaction with the tools and systems they use.
This includes gathering feedback, analyzing user behavior, and making necessary adjustments to improve usability.
- Service Overview: Improving user experience may involve user surveys, usability testing, and iterative design processes to enhance interfaces and workflows.
- Benefit: Increases user satisfaction and productivity by providing a seamless experience with technology.
Section 10: Hiring a Company

This section outlines the steps to consider when hiring an EUM vendor, helping organizations navigate the selection process, and establishing a partnership that aligns with their goals.
How to Hire an End User Management Vendor/Agency/Company
When hiring an EUM vendor, a systematic approach is essential to ensure that you find a partner who meets your organization’s unique requirements and standards. Here are the key steps to follow:
1. Define Your Requirements
Before you begin the vendor selection process, clearly defining your EUM needs is essential. This includes identifying the specific services you require, such as IT support, software management, or security services.
- Considerations: Outline the scope of work, key performance indicators (KPIs), and any regulatory or compliance requirements.
- Benefit: A well-defined set of requirements helps streamline the selection process and ensures you find a vendor that meets your needs.
2. Research Potential Vendors
Conduct thorough research to identify potential EUM vendors that align with your organization’s requirements. This may involve searching online, seeking recommendations, and reviewing industry directories.
- Sources: Use platforms like LinkedIn, industry forums, and trade shows to gather a list of reputable vendors.
- Benefit: A comprehensive list of vendors allows for a more informed comparison during selection.
3. Evaluate Vendor Expertise and Experience
Assess each potential vendor’s expertise and experience about your specific requirements. Look for vendors with a proven track record in delivering EUM services.
- Evaluation Criteria: Consider their industry experience, client portfolio, and any case studies or success stories they can provide.
- Benefit: Choosing a vendor with relevant experience increases the likelihood of successful project outcomes.
4. Assess Security and Compliance
Security is a critical aspect of EUM. Evaluate each vendor’s security practices, protocols, and compliance with industry standards and regulations.
- Key Aspects: Inquire about their data protection measures, incident response protocols, and compliance with regulations such as GDPR or HIPAA.
- Benefit: Ensuring a vendor has robust security practices protects your organization from potential data breaches.
5. Ask About Customization and Flexibility
Different organizations have unique needs, so assessing whether potential vendors can offer customizable solutions is essential.
- Discussion Points: Inquire about the vendor’s ability to tailor their services to meet your specific requirements and adapt to changes in your business.
- Benefit: A flexible vendor can better accommodate your evolving needs over time.
6. Evaluate Support and Training
Support and training are essential components of successful EUM services. Evaluate the level of support each vendor offers and the training resources available to your end users.
- Support Channels: Inquire about support options (e.g., phone, email, chat) and the availability of training materials or programs for users.
- Benefit: Comprehensive support and training enhance user satisfaction and adoption of EUM services.
7. Cost and Pricing Models
Understand the cost structure and pricing models of potential vendors. This includes evaluating their pricing for various services and any additional fees that may apply.
- Considerations: Compare pricing models (e.g., per user, flat fee) and ensure transparency regarding all costs involved.
- Benefit: A clear understanding of costs helps prevent budget overruns and ensures that the selected vendor fits your financial constraints.
8. Request for Proposal (RFP)
Once you’ve narrowed your options, consider issuing a Request for Proposal (RFP) to gather detailed information regarding their services and pricing from each vendor.
- RFP Components: Include your requirements, evaluation criteria, and response deadlines in the RFP.
- Benefit: An RFP provides a structured way to gather consistent information for comparison.
9. Test and Pilot Programs
Conduct test or pilot programs with shortlisted vendors to evaluate their services. This can provide valuable insights into how well the vendor meets your needs.
- Pilot Evaluation: Monitor the vendor’s performance during the pilot phase and gather user feedback.
- Benefit: Testing allows for a real-world assessment of the vendor’s capabilities before making a long-term commitment.
10. Review Contracts and SLAs
Carefully review contracts and Service Level Agreements (SLAs) with the selected vendor. Ensure that all terms and conditions, including support levels and response times, are clearly defined.
- Key Aspects: Consider the agreement’s termination clauses, liability limitations, and performance metrics.
- Benefit: A well-drafted contract protects your interests and establishes clear expectations for both parties.
11. Finalize the Selection
After completing the evaluation and negotiation process, finalize your vendor selection. Communicate your decision to the chosen vendor and establish a timeline for implementation.
- Next Steps: Set up a kickoff meeting to discuss the implementation process and establish communication channels.
- Benefit: A clear start to the partnership ensures a smooth transition into the EUM services.
Section 11: Recommendations
End User Management Recommendations for Businesses
Business leaders are pivotal in establishing strategies and practices that support end users while aligning with organizational goals. This section outlines key recommendations for business leaders to enhance their EUM initiatives.
1. Prioritize User-Centric Solutions
Adopting a user-centric approach means designing and implementing solutions that focus on the needs and preferences of end users. This includes considering user feedback during the selection of tools and processes.
- Action Steps: Conduct user surveys, focus groups, or interviews to gather insights into users’ experiences and needs. Use this data to inform decision-making regarding tools and processes.
- Benefit: Prioritizing user needs increases adoption rates and overall satisfaction with EUM services.
2. Implement Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Identity and Access Management (IAM) systems ensure users have secure access to the resources they need while minimizing the risk of unauthorized access.
- Action Steps: Deploy IAM solutions that include features like single sign-on (SSO), multi-factor authentication (MFA), and role-based access control (RBAC).
- Benefit: IAM enhances security by controlling user access and helps ensure compliance with data protection regulations.
3. Invest in Device and Endpoint Management
Effective device and endpoint management is vital for maintaining productivity and security. This includes deploying management solutions that support various devices, including desktops, laptops, and mobile devices.
- Action Steps: Implement Unified Endpoint Management (UEM) tools that provide a centralized approach to managing devices, software updates, and security patches.
- Benefit: Investing in device management reduces vulnerabilities and streamlines operations, allowing IT teams to focus on more strategic tasks.
4. Focus on User Data Security and Compliance
User data security is paramount in today’s threat landscape. Business leaders must prioritize practices that protect user data and ensure compliance with relevant regulations.
- Action Steps: Develop and enforce data protection policies, conduct regular security audits, and ensure employee training on data security best practices.
- Benefit: Prioritizing data security protects the organization from breaches and helps build trust with users and clients.
5. Leverage Automation for Efficiency
Automation can significantly enhance the efficiency of EUM processes by reducing manual tasks and improving response times for support requests.
- Action Steps: Identify repetitive tasks that can be automated, such as user provisioning and de-provisioning, software updates, and incident responses. Implement automation tools to streamline these processes.
- Benefit: Automation improves operational efficiency and allows IT teams to focus on complex issues.
6. Adopt a Proactive Support Model
Moving from a reactive to a proactive support model involves anticipating user needs and addressing issues before they escalate.
- Action Steps: Monitor system performance, analyze user behavior, and establish regular check-ins with users to identify potential issues early.
- Benefit: A proactive approach minimizes downtime and enhances the user experience by ensuring readily available support.
7. Engage in Continuous Feedback and Improvement
Creating a culture of continuous improvement involves regularly seeking feedback from users and adjusting EUM practices based on their input.
- Action Steps: Establish feedback mechanisms, such as user satisfaction surveys or regular check-ins, to gauge the effectiveness of EUM initiatives and identify areas for improvement.
- Benefit: Engaging with users fosters a sense of ownership and partnership, leading to better alignment between EUM services and user needs.
Section 12: FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
End User Management FAQs
This section addresses common questions about EUM to clarify its importance, tools, and future directions.
When did End User Management start?
End-user management began to evolve in the late 1990s and early 2000s, alongside the rapid adoption of personal computers in the workplace. As organizations started to rely more on technology, the need for structured management of end users and their devices became evident.
Which tools are used in End User Management?
Standard tools used in EUM include:
- Unified Endpoint Management (UEM) solutions
- Identity and Access Management (IAM) tools
- Mobile Device Management (MDM) software
- Application Performance Monitoring (APM) tools
- Remote Desktop Support software
How can businesses benefit from End User Management?
Businesses can benefit from EUM by improving productivity, enhancing user satisfaction, reducing support costs, ensuring data security, and achieving better compliance with regulations. Effective EUM can lead to a more streamlined IT operation, ultimately supporting the organization’s goals.
Who are the end users?
End users interact with an organization’s technology and systems to perform their job functions. This can include employees, contractors, and even customers who utilize digital services provided by the organization.
How does EUM improve productivity?
EUM improves productivity by ensuring end users have the right tools, applications, and support to perform their tasks efficiently. Users can focus more on their work by minimizing downtime and streamlining access to necessary resources.
Why is user feedback important in EUM?
User feedback is essential in EUM, providing insights into user experiences, challenges, and preferences. This information helps organizations make informed decisions about tools, processes, and support strategies, ultimately improving user satisfaction and engagement.
How does EUM support remote work?
EUM supports remote work by providing users with secure access to necessary resources and applications, ensuring that IT support is available remotely, and maintaining communication and collaboration tools that facilitate teamwork regardless of location.
What is proactive support in EUM?
Proactive support involves anticipating user needs and potential issues before they arise. This includes regular system monitoring, user training, and feedback collection to improve user experiences and reduce the number of support requests.
How has EUM evolved over time?
EUM has evolved from basic desktop support in the early days of computing to a comprehensive approach that includes mobile device management, cloud services, and a focus on user experience. Technology advancements have driven this evolution, leading to more integrated and user-centric management practices.
Why is security important in EUM?
Security is vital in EUM, as end users often have access to sensitive data and systems. Adequate security measures help safeguard the organization and its users against data breaches, unauthorized access, and other cyber threats.
What is the role of automation in EUM?
Automation plays a significant role in EUM by streamlining repetitive tasks, such as user provisioning and software updates. This increases efficiency and allows IT teams to focus on strategic initiatives rather than routine operational tasks.
How can businesses implement EUM effectively?
Businesses can implement EUM effectively by assessing user needs, selecting appropriate tools, providing training, and establishing clear policies and procedures. Regular feedback loops and continuous improvement practices also contribute to successful implementation.
What are the benefits of user-centric design in EUM?
User-centric design in EUM leads to improved user satisfaction, higher tool adoption rates, and reduced support requests. Organizations can enhance productivity and foster a more positive work environment by designing systems and processes with the user in mind.
How does EUM impact brand loyalty?
Effective EUM contributes to brand loyalty by ensuring users have positive experiences with a company’s products and services. Satisfied users are more likely to remain loyal and advocate for the brand, enhancing its reputation and market presence.
What is desktop management in EUM?
Desktop management involves managing the physical and virtual desktop environments end users use. This includes software installation, configuration, updates, and troubleshooting to ensure optimal performance.
How does mobile device management fit into EUM?
Mobile Device Management (MDM) is a subset of EUM focused on securing, monitoring, and managing mobile devices used within an organization. MDM solutions help enforce security policies, manage applications, and support mobile users.
What role does user training play in EUM?
User training is essential in EUM as it equips end users with the knowledge and skills to use the tools and resources available effectively. Proper training reduces the likelihood of errors, enhances productivity, and increases user satisfaction.
What is application management in EUM?
Application management involves overseeing the software applications used by end users, including installation, configuration, performance monitoring, and troubleshooting. It ensures that users have access to the necessary tools for their work.
How can EUM reduce support costs?
EUM can reduce support costs by streamlining processes, automating repetitive tasks, and providing practical user training. Organizations can lower the volume of support requests by minimizing issues and improving user self-sufficiency.
What is access management in EUM?
Access management involves controlling user access to resources and systems based on their roles and permissions. It ensures that users have appropriate access while protecting sensitive information from unauthorized individuals.
How do AI and machine learning enhance EUM?
AI and machine learning enhance EUM by automating repetitive tasks, predicting user needs, and identifying potential security threats. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data to improve decision-making and support strategies.
How can businesses gather valuable user feedback in EUM?
Businesses can gather user feedback through surveys, focus groups, regular check-ins, and feedback tools integrated into applications. Encouraging open communication and actively seeking input helps organizations identify areas for improvement.
Why is continuous improvement significant in EUM?
Continuous improvement is essential in EUM as it allows organizations to adapt to changing user needs, emerging technologies, and evolving security threats. Regularly reviewing and refining EUM practices ensures that they remain practical and relevant.
How does EUM contribute to better product development?
EUM contributes to better product development by ensuring end users have the necessary tools and support. This leads to more efficient workflows and enhanced feedback loops. This user-focused approach can result in more successful products that align with user needs.
What are the benefits of proactive support in EUM?
Proactive support helps identify and resolve potential issues before they escalate, reducing downtime and enhancing user satisfaction. This approach fosters a more efficient IT environment and strengthens user trust in the organization’s support capabilities.
How can augmented reality be used in EUM?
Augmented reality (AR) can be used in EUM for training, troubleshooting, and remote support. By overlaying digital information in the real world, AR can enhance user understanding and improve the effectiveness of support initiatives.
What is the role of monitoring in EUM?
Monitoring in EUM involves tracking user activities, system performance, and security events to identify and resolve issues quickly. Effective monitoring enables organizations to maintain optimal performance and enhance user satisfaction.
How does effective communication enhance EUM?
Effective communication enhances EUM by ensuring users receive timely information, support, and updates. Clear communication fosters a positive relationship between users and IT teams, promoting collaboration and user engagement.
What are some common tools used in EUM for remote support?
Common tools for remote support in EUM include remote desktop software, screen-sharing applications, and helpdesk ticketing systems. These tools enable IT teams to assist users regardless of physical location, improving support efficiency.
How can businesses ensure user data security in EUM?
Businesses can ensure user data security in EUM by implementing robust security policies, using encryption, conducting regular security audits, and providing user training on best practices for data protection.
How can end users provide feedback on their experiences?
End users can provide feedback through surveys, suggestion boxes, direct communication with IT support, or feedback tools integrated into applications. Encouraging users to share their experiences helps organizations identify areas for improvement.
What is the role of technical proficiency in EUM?
Technical proficiency is crucial in EUM. It enables IT professionals to manage user needs effectively, troubleshoot issues, and implement solutions. A strong technical foundation helps ensure that EUM practices are efficient and effective.
How does EUM support hybrid work environments?
EUM supports hybrid work environments by providing flexible access to tools and resources, ensuring security measures are in place, and offering user support regardless of location. This approach facilitates collaboration and productivity for all users.
Conclusion
End-user management (EUM) plays a critical role in today’s technology-driven workplaces, ensuring that employees have the tools and support they need to succeed.
Organizations can enhance productivity and user satisfaction while reducing costs by prioritizing user-centric solutions, investing in security and compliance, and leveraging automation.
Effective EUM practices will foster a positive user experience and maintain operational efficiency as businesses adapt to remote and hybrid work environments.
Understanding the importance of EUM and the skills required for effective management empowers business leaders and professionals to make informed decisions that align with organizational goals.
As the work landscape evolves, embracing continuous improvement and leveraging technology will be crucial for staying ahead of challenges and harnessing opportunities in End User Management.
Organizations can create a more engaged, productive, and secure workforce that drives long-term success by prioritizing these elements.
This page was last edited on 23 December 2025, at 4:46 pm
Contact Us Now

Contact Us Now
Start a conversation with our team to solve complex challenges and move forward with confidence.











