Human brain has limitations in information processing. When there is plenty of information, it is difficult to process. As a result, some information may take longer to process and some will be missed. The remaining information takes place in our memory. “Cognitive Load Theory” (CLT) covers how the memory stores information. John Sweller developed the theory in 1988.
Based on theory, our memory is divided into three parts. They are- Sensory, Working, and Long Term. “Sensory” memory is the initial & short retention of information.
This type of memory is temporary. It relies on the five senses- auditory, visual, taste, smell, and touch. It filters and keeps the most important information and passes it to the working memory. For example, while visiting an e-commerce site, user sees the visual images, colors, animations, and sounds of the site.
If anything is found scattered or disoriented, the user feels overloaded and later it creates a negative impact on the site. On the other hand, “Working” memory receives the information from sensory memory. It can further process or discard the information. Due to its limited capacity, it can not hold complex information at once. It breaks down the information into chunks (5 to 9 items) and starts processing.
For example, an E-commerce site has a wide range of products with different brands, price ranges, categories, etc. Using sort, filter, and search options makes it easier to find the expected product.
Step by step checkout process helps to stay in the capacity of the working memory of a user. After that, the information is categorized and moves to the “Long-Term” memory.
Consistent branding, logos, and familiar navigation help to reduce cognitive load and influence users to revisit. Here the information is stored in knowledge structures, named ”Schemas”.
In working memory, how this information is processed by humans is called “Cognitive Load”. According to psychologists, “Cognitive Load” refers to the number of attempts required to process information. In UX design, “Cognitive Load” is the mental effort taken to complete a task while interacting with an interface. To enhance the user experience & quality of the product, “Cognitive Load” is the crucial factor for the product & UX enthusiasts.
Types:
Cognitive Load has three types. They are-
i. Intrinsic Cognitive Load
ii. Extrinsic Cognitive Load
iii. Germane Cognitive Load
i. Intrinsic Cognitive Load:
“Intrinsic Cognitive Load” refers to the complexity of the new information. The more complex the information is, the heavier the intrinsic load. It is unavoidable, but it can be solved with proper instruction & intuitive design. For example, many advanced sites with more complex actions, interactions, and contents can make users confused. To sort out this type of problem, walkthroughs, help, and FAQs are used to instruct users with new features.
ii. Extrinsic Cognitive Load:
It refers to the way of presenting information/ tasks in the interface and how easily the users perceive the information. It can vary from person to person. Poorly organized design and irrelevant content can make a simple task into a complex task. Simple, instructional design strategies, infographics, demo videos, or tutorials can reduce the load.
iii. Germane Cognitive Load:
It is the effort of memory and intelligence to use the information into long-term schemas. It extends working memory and helps to learn more difficult information. A well-designed user interface with good user experiences can work as a “Germane Load” to support user goals.
Cognitive Load in QA Brains:
QA Brains is a platform for Quality Assurance enthusiasts, where they can share knowledge, and write blogs through interacting with each other. Implementing “Cognitive Load” in QA Brains platform helps to give a better user experience and reduce cognitive load. As a result, users can focus on the content, follow the instructions, and participate in the community for knowledge sharing. How “Cognitive Load” is implemented in QA Brains platform is discussed below-
1. Mega Menu for Categories (Extrinsic Cognitive Load)
The top navigation menu of QA Brains has “Category” items that represent some QA categories like “Database Testing”, “Cyber Security”, “Mobile App Testing” etc. But whenever a user clicks on the “Category” it directly redirects to the “Category” page. There is no way to view all QA categories at once. Using “Mega Menu” can help to view all categories at once without multiple clicks. Users do not have to visit another page to view all categories. It reduces the mental load to scan and select categories. Besides, minimizing the number of clicks it becomes easier to navigate.
Existing:

Solution:

2. Search bar on landing page (Extrinsic Cognitive Load)
QA Brains landing page does not have any search bar to search blogs, discussions using tags or keywords. Users currently need to visit the inner page to search from the search bar. Adding the search bar on the landing page can reduce the time & effort to visit specific content.
Solution:

3. Clear Interface (Extrinsic Cognitive Load)
- A clear & minimalist interface can help users to have a smooth user experience. Such as “Guest User Landing Page” currently does not have any “Call to Action” (CTA) button on the Hero section to take action like “Sign up”/ “Sign in” to the platform. Clear, concise, and straightforward word is used to give hints to users about what will happen next. For example, CTA button “Join Now” on the Hero section tells users to “Sign up” if the users do not have an account in QA Brains. Already registered users can sign into the account with credentials. After login, users can see CTA buttons “Write Blog” and “Start Discussion” on the Hero section instead of “Join Now “ button.
- As the platform offers both blogs and discussion facilities, a split button dropdown is suggested such as “Write Blog” and “Create Discussion”. Clicking on each will redirect to specific page. Two CTA buttons for Blogs and Discussions are suggested on Hero section and also above the FAQ section while scrolling through the page so that user does not need to scroll up to write blogs or start discussions. Also, other blogs and discussion links are shown with the CTA buttons for user’s convenience.
Existing:

Solution:



4. Content Categorization (Intrinsic Cognitive Load)
- The landing page currently has the categories section. But there is no trending, popular level-wise section. Even after login, the user does not get personalized content categories like user-generated content like blogs and discussions section. Categorization helps users to find content according to their needs and choices.
- Besides, unnecessary & irrelevant content can be omitted. Initially, relevant information can be presented with the expand or view more details option for further needs.
Existing:

Solution:

5. Guidance & instructions (Germane Cognitive Load)
- Users can get a short overview in infographics of the platform after onboarding the landing page both for guest users and logged in state. This helps specially new users about the purpose and how to contribute to the community.
- Besides, to write blogs or start discussions, tips are included so that effective blogs can be written or discussions can be participated easily. Once the user gets to know about the procedure, they become familiar with it. They can store it in their long-term memory and later they can easily perform any difficult task without any hassle.
Existing:

Solution:


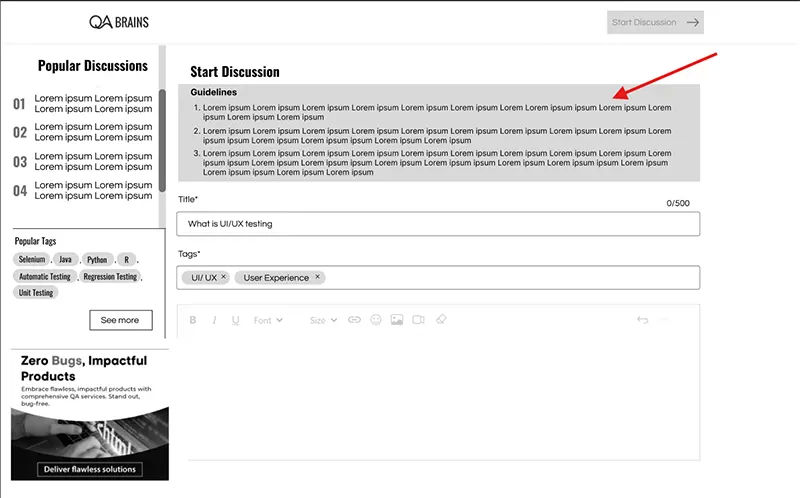
6. Visual Hierarchy (Extrinsic Cognitive Load)
- Visual Hierarchy helps to draw the attention of users and increase user engagement. It is about creating a clear and logical way of representing the information to navigate the users.
- Additional features of QA Brains like Discussions, Tags List, Discussion Comments List, and other visual hierarchies are maintained just like the existing features. Elements like texts, alignments, font sizes, icons, primary, and secondary buttons, etc. represent important information to the users. For example, the “Discussions” page has a primary button named “Start Discussion” which will prompt the user to start a new discussion. Total number of discussions presented in blod & large font so that user can know the discussion counts at a glance. In the discussions list, minimal information is kept to reduce to “Intrinsic Cognitive Load”. Discussion title is in bold and bigger size whereas the description is in normal font and smaller size. For detailed descriptions, they can click on the respective discussion details page. The list page kept limited information to not make it overwhelming.
- As the discussion can be created from blogs as well, an identifier is suggested to get information about which discussion is created from blogs or which is just only discussion.
- If one or multiple tags are used in the discussion, they will be shown in the list. They are represented in different texts, colors, shapes, and sizes.
- Filtering and sorting options are suggested to optimize user’s time. As a result, the user does not have to scroll through the whole list to find his desired discussion.
- While looking at the discussion list page, some data is a must for the user like who created the discussion, how many views it has got, how many users have voted, and number of comments or replies. This covers the overall discussion summary on this page.
Solution:

7. Consistency (Extrinsic Cognitive Load)
Consistency is one of the 10 Usability Heuristics. It defines the same patterns, behaviors, and elements throughout a website. Using the same visuals, layouts, and interactions creates a better user experience. It eliminates user’s confusion, and frustrations leading to a better user journey. Consistent Layout is maintained throughout the other pages of QA Brains. While developing QA Brains, consistency is considered. Font style, action button style, size, header, navigation menu, error message, etc. are kept same as the existing platform. So that users do not face navigation issues and confusion.
Conclusion:
Cognitive Load is important for user-centered design process. The less cognitive load is, the easier it becomes for users to understand the product. It creates more user engagement resulting in user happiness, satisfaction, and retention. In a nutshell, it can be said that Cognitive Load is not only for better user experience issues but also for customer experience and product success.
This page was last edited on 12 September 2024, at 12:31 pm
Contact Us Now

Contact Us Now
Start a conversation with our team to solve complex challenges and move forward with confidence.










