AI agents are rapidly becoming the key driver behind the next wave of business automation, with organizations worldwide leveraging their power to tackle complex workflows, boost efficiency, and unlock new revenue streams. While legacy process automation delivered incremental gains, the rise of agentic AI—autonomous, adaptive software agents powered by advanced AI—marks a step-change in business transformation.
Despite this momentum, many businesses struggle to move from experimentation to impact. They need clear insight into AI agents use cases that deliver measurable value, an understanding of how agentic AI outperforms traditional automation, and guidance on how to integrate these systems safely within existing workflows.
This strategic guide serves as a playbook, defining what AI agents are, unpacking high-impact AI agents use cases across industries, comparing leading frameworks, and outlining step-by-step best practices for implementation, supported by ROI evidence and practical deployment advice.
By the end, you will have the knowledge and actionable strategies needed to evaluate, pilot, and scale AI agents for your business while staying ahead in the evolving automation landscape.
What Are AI Agents, and How Do They Work?
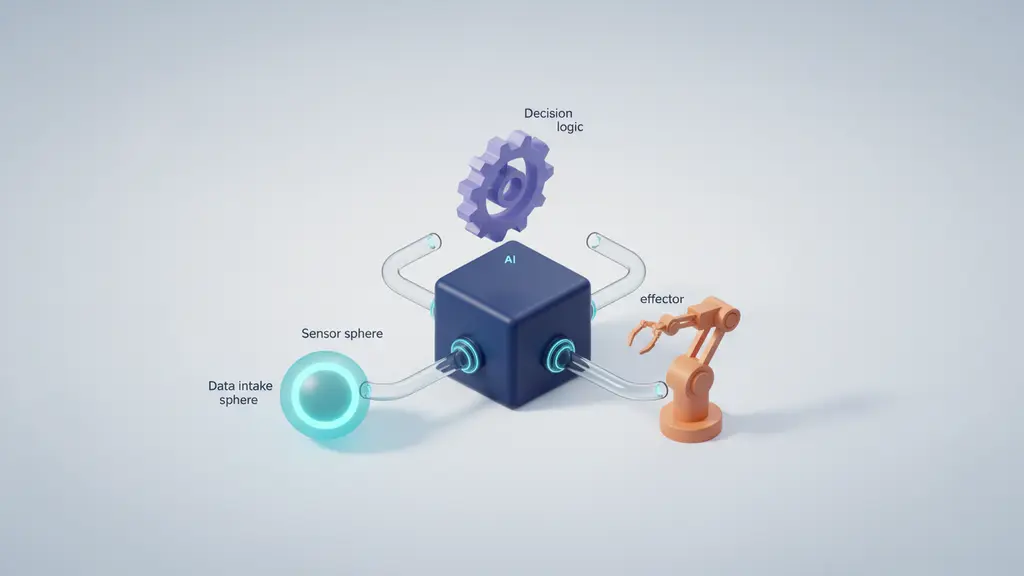
An AI agent is an autonomous, goal-driven software entity that uses AI techniques to perceive data, make decisions, and take actions to achieve objectives with minimal ongoing human oversight.
AI agents are autonomous software systems that perceive their environment, reason, and act to achieve specific goals with minimal human intervention. Unlike classic automation tools, which follow rigid rules, agentic AI solutions leverage machine learning and large language models (LLMs) to adapt, collaborate, and optimize workflows—even in dynamic or uncertain situations.
Traditional automation, like robotic process automation (RPA) or rule-based chatbots, excels at repetitive, rules-driven tasks. In contrast, AI agents can manage multi-step processes, interact across applications, respond to new data, and even cooperate with other agents or humans. They learn from outcomes, continuously improve their decisions, and handle exceptions more flexibly than earlier automation.
A typical AI agent includes sensors (data intake), a reasoning engine (decision logic), and effectors (actions). Advanced agentic AI may use a multi-agent system, where several agents collaborate—think of a virtual team of bots managing hiring, finance, or IT incidents in coordination.
Types of AI Agents and Their Strengths
| Agent Type | Typical Application | Key Strengths | Example Industry Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reflex Agent | Rule-based, immediate action | Fast, predictable | Shop-floor inventory checks |
| Model-Based Agent | Maintains internal state/model | Contextual reasoning | Healthcare triage |
| Goal-Based Agent | Optimizes for outcomes/goals | Adaptive, flexible | Portfolio rebalancing in finance |
| Learning Agent | Learns from feedback/data | Evolves, improves over time | Personalized retail recommendations |
| Multi-Agent System | Agents collaborate on tasks | Scalability, division of labor | Supply chain optimization |
- Reflex agents act on simple rules, ideal for clear-cut repetitive work.
- Model-based agents track environment changes, useful in dynamic scenarios like patient triage.
- Goal-based agents choose actions that best achieve a defined objective, supporting complex decisioning.
- Learning agents use historical data for continuous improvement, powering personalization or anomaly detection.
- Multi-agent systems see agents delegate and collaborate, crucial for large-scale process orchestration.
AI Agents Use Cases Across Modern Business Workflows
AI agents use cases span a wide range of industries and operational functions, driven by their ability to act autonomously, adapt to changing inputs, and execute multi-step tasks with minimal human intervention. Unlike traditional automation, AI agents are not limited to predefined rules. They can reason, learn from outcomes, and coordinate across systems, making them especially effective in complex, high-volume workflows.
At a high level, AI agents use cases fall into five core categories:
Operational Automation
AI agents automate end-to-end processes such as ticket triage, invoice handling, scheduling, and incident response. These use cases deliver immediate efficiency gains by reducing manual effort and turnaround time.
Decision Support and Intelligence
In finance, healthcare, and supply chain operations, AI agents analyze large volumes of structured and unstructured data to support faster, more accurate decisions. Examples include fraud detection, risk scoring, clinical triage, and demand forecasting.
Customer and Employee Experience
Conversational and task-oriented agents handle Tier-1 customer support, employee FAQs, onboarding, and internal service requests. These AI agents use cases improve responsiveness while freeing human teams to focus on complex or high-value interactions.
Optimization and Continuous Improvement
AI agents continuously monitor systems and adjust actions in real time. Common use cases include dynamic pricing, inventory optimization, predictive maintenance, and energy load balancing.
Multi-Agent Orchestration
In advanced deployments, multiple AI agents collaborate as a coordinated system. These AI agents use cases are common in supply chain management, IT operations, and large-scale workflow orchestration, where agents divide responsibilities and optimize outcomes collectively.
By understanding these categories, organizations can more easily map AI agents use cases to real business problems, prioritize high-impact opportunities, and avoid experimenting without a clear value path.
Top 10 Real-World AI Agent Use Cases by Industry (2025)

Organizations across sectors adopt AI agents to solve high-impact, process-heavy challenges. Below is a skimmable table of the top agentic AI use cases mapped to their industries:
| Industry | AI Agent Use Case | One-Sentence Summary |
|---|---|---|
| HR | Resume Screening/Onboarding | Agents sort and match resumes, schedule interviews, and automate onboarding tasks. |
| Finance | Fraud Detection/Risk Mgmt | Agents analyze transactions and flag anomalies while automating risk assessments. |
| Healthcare | Clinical Scribing/Triage | Agents generate real-time patient notes and guide intake or triage processes. |
| Retail | Dynamic Pricing/Inventory | Agents adjust prices based on demand and forecast inventory needs seamlessly. |
| Education | Adaptive Tutoring | Intelligent agents deliver personalized learning and automate grading, support. |
| IT/DevOps | Incident Response/Code Review | Agents triage alerts, review code, and even trigger automated fixes. |
| Manufacturing | Predictive Maintenance | Agents monitor sensors, predict equipment failure, and trigger service workflows. |
| Energy | Grid Load Optimization | Multi-agent systems balance energy supply/demand and manage grid stability. |
| Legal/Compliance | Contract Review/E-Discovery | AI agents scan contracts, check compliance, and automate document discovery. |
| Customer Service | Automated Tier-1 Support | Conversational agents resolve common queries and escalate complex cases as needed. |
Tip: Jump to your sector for detailed examples and deployment tips below.
In-Depth: How Are AI Agents Used in Key Industries?
HR & People Operations: From Resume Screening to Onboarding
AI agents are streamlining HR from candidate sourcing to employee onboarding. They automate resume parsing, intelligent matching, and even schedule interviews—reducing manual workload and time-to-hire.
Key use cases:
- Automated resume screening: Agents quickly evaluate large talent pools based on job requirements, diversity goals, or skills needs.
- Interview and onboarding scheduling: Agents coordinate between candidates and hiring panels, minimizing back-and-forth.
- Employee FAQ agents: Always-on bots provide policy, benefits, or onboarding information 24/7.
Result: Improved HR operational efficiency, reduced bias, and better candidate experiences.
Finance & Banking: Fraud Detection, Risk & Portfolio Automation
Agentic AI delivers rapid anomaly detection and speeds up risk workflows crucial for financial services.
Core applications:
- Fraud detection agents: Scan transactions in real-time for suspicious patterns or regulatory red flags.
- Risk assessment automation: Agents gather and process diverse data points for KYC/AML or loan approvals.
- Portfolio rebalancing: Agents monitor market conditions and autonomously trigger buy/sell orders to maintain targets.
Result: Fewer false positives in fraud alerts, accelerated compliance, and more resilient portfolio management.
Healthcare: Scribing, Triage & Prior Authorization
AI agents reduce clinical burden and improve patient flow by handling complex, documentation-heavy tasks.
Sample use cases:
- Clinical note generation (scribing): Agents capture and transcribe patient encounters, letting clinicians focus more on care.
- Automated triage: Agents guide patients through intake questions, suggest next steps, or direct urgent cases appropriately.
- Prior authorization bots: Agents assemble and submit insurance paperwork, accelerating claims approval.
Result: Reduced administrative bottlenecks and better patient outcomes through real-time support.
Retail & E-Commerce: Dynamic Pricing and Personalized CX
Retailers use agentic AI to delight customers and optimize margins in real time.
Strategic use cases:
- Dynamic pricing agents: Adjust prices or discounts based on demand, inventory levels, or competitor actions.
- Inventory optimization: Predict out-of-stocks and automate replenishment using multi-agent systems.
- Shop-floor support: Conversational or logistics agents help staff and customers with queries or order status.
Result: Higher conversion rates, lower stockouts, and improved loyalty.
Education: Adaptive Tutoring Agents & Academic Workflows
EdTech firms and institutions deploy agents to personalize learning and remove friction from admin tasks.
Top applications:
- Intelligent tutoring agents: Deliver adaptive quizzes, hints, and pacing tailored to student needs.
- Grading automation: AI agents assess assignments, freeing teachers for higher-value engagement.
- Student support chatbots: Proactively answer course or scheduling questions 24/7.
Result: Improved outcomes, teacher efficiency, and student satisfaction.
IT & DevOps: Incident Response, Code Review & Automation
IT teams leverage agents to monitor, diagnose, and remediate issues with minimal human touch.
Popular workflows:
- Automated log triage: Agents classify alerts and escalate only worthy incidents.
- Code review assistants: AI agents flag bugs, code smells, and suggest improvements before merges.
- Incident response playbooks: Orchestrate diagnosis, repairs, and reporting—reducing mean time to resolution.
Result: Accelerated IT workflows, higher code quality, and less burnout for support teams.
Manufacturing & Energy: Predictive Maintenance, Grid Optimization
Operations and utilities improve uptime and sustainability with intelligent, sensor-driven agents.
Key use cases:
- Predictive maintenance: Agents ingest IoT sensor signals, forecast breakdowns, and auto-schedule repairs.
- Supply chain optimization: Multi-agent systems reroute shipments or adjust outputs in response to disruptions.
- Grid load balancing: Energy agents orchestrate supply and demand, optimize renewable integration.
Result: Cost savings, less unscheduled downtime, and greener operations.
Legal, Compliance, & Governance: Contract Review and E-Discovery
Legal departments and compliance teams use agents for high-stakes, document-intensive processes.
Examples:
- Contract analysis agents: Parse agreements, flag risks, and track renewal milestones automatically.
- Regulatory compliance bots: Monitor rule changes and audit organizational adherence in real time.
- Automated e-discovery: Search and categorize documents for litigation or regulatory requests swiftly.
Result: Reduced compliance risk, faster document review, and major cost savings.
Frameworks & Tools for Building AI Agents: Comparison and Selection Guide
Organizations can choose from a growing toolkit of frameworks designed to help build, manage, or deploy agentic AI at scale. Selecting the right platform depends on technical fit, community support, and enterprise readiness.
| Framework | Core Strengths | Enterprise Readiness | Community Support | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CrewAI | Focus on workflow orchestration, open AI | High | Active | Agent collaboration, integrations |
| AutoGen | Modular design, LLM-powered agents | Moderate | Large | Natural language interface, plugins |
| Agno | Extensible, supports multi-agent systems | High | Growing | Multi-agent support, security |
- CrewAI: Leading for coordinated multi-agent workflows and business process orchestration.
- AutoGen: Favored for developer flexibility and rapid prototyping, leveraging LLMs natively.
- Agno: Strong in scenarios demanding multi-agent collaboration and customized security.
Minimal agent example:
from crewai import Agent
my_agent = Agent(
name="SupportBot",
goals=["Resolve tier-1 customer queries"],
tools=[KnowledgeBase(), ActionDispatcher()],
)
my_agent.run(input="Customer issue reported")
Tip: Assess your workflow requirements, scalability needs, and integration plans when choosing an agentic AI framework.
How to Implement and Deploy Agentic AI: Step-by-Step (Best Practices & Pitfalls)
Deploying AI agents successfully demands a structured approach that blends technical rigor with business oversight. A typical implementation workflow follows these phases:
- Identify high-value use cases
Focus on workflows with measurable bottlenecks or high volume (e.g., ticket triage, invoice processing). - Map agent architecture
Define agent roles, coordination mechanisms, and integrations with existing IT systems. - Develop and test agents incrementally
Start with a minimum viable agent, then expand to more complex automation. - Embed human-in-the-loop oversight
Enable humans to audit, override, or retrain agents—crucial for compliance and trust. - Manage deployment, monitor, and scale
Launch into production, monitor performance and error rates, and iterate for improvement.
| Step | Best Practice | Common Pitfall |
|---|---|---|
| Use case selection | Value-driven choice, not just tech-first | Automating rarely used tasks |
| Oversight | Early design of human-in-the-loop checkpoints | Overly trusting automation |
| Monitoring & tuning | Continual review of outputs and business impact | Letting agents run unchecked |
Checklist:
- Define your business/stakeholder goals up front
- Pilot with a limited, well-scoped use case
- Set up dashboards for agent decisions and exceptions
- Develop a clear process for escalation and retraining
- Regularly review legal and compliance requirements
Measuring ROI and Business Impact of AI Agents (With Real-World Data)
Quantifying the value of AI agents is essential to building a business case and sustaining executive buy-in. Organizations track both hard savings (labor reduction, error reductions) and softer gains (speed, customer experience, compliance uplift).
Common ROI performance indicators:
- Time saved: E.g., HR agents reduce screening time by up to 70%
- Cost reduction: Automated document review can cut legal costs 30–50%
- Error reduction: Agents in finance decrease compliance errors, lowering regulatory risk
- Productivity boost: AI-powered code review increases release velocity for IT teams
| Industry | Example ROI Metric | Impact Range |
|---|---|---|
| HR | Recruiting overhead reduction | 30–70% |
| Finance | Fraud false positives cut | <30% |
| Healthcare | Claims processing time reduced | 40–60% |
| Retail | Inventory write-offs lowered | 25–50% |
| IT/DevOps | Incident resolution time shortened | 35–60% |
Real-world case: A Fortune 500 manufacturer deployed predictive maintenance agents and reported over $2M annual savings from reduced unscheduled downtime.
Governance, Ethics, and Future Trends in Agentic AI
Adopting AI agents requires careful governance and ethical oversight to avoid risks such as automation bias, privacy breaches, and regulatory non-compliance.
Key risks and governance strategies:
- Bias and fairness: Agents must be monitored for unintended bias, especially in HR or lending scenarios.
- Transparency: Organizations need clear logs and audit trails for agent decisions.
- Human control: Maintain “human-in-the-loop” checkpoints for critical tasks.
Governance checklist:
- Audit data sources, training sets, and agent outputs regularly
- Ensure decisions can be explained to stakeholders and regulators
- Align agent roles with organizational risk policies
Frequently Asked Questions (AI Agent Use Cases)
What are AI agents and how do they work?
AI agents are autonomous software entities that perceive data, reason, and take actions to achieve goals; they use AI such as machine learning or LLMs rather than just rigid rules.
How do AI agents differ from traditional automation/RPA?
AI agents adapt and learn in dynamic environments, handling exceptions and multi-step processes, while classic RPA follows pre-set rules and fails with unexpected inputs.
What are the most common AI agent use cases in 2025?
Key use cases include resume screening in HR, fraud detection in finance, clinical note generation in healthcare, dynamic pricing in retail, and incident response in IT.
Which industries benefit most from AI agents?
Industries with high-volume, data-intensive workflows—such as HR, finance, healthcare, IT, manufacturing, and retail—see the highest ROI from adopting agentic AI.
What frameworks or tools are used to build AI agents?
Popular frameworks include CrewAI for workflow orchestration, AutoGen for LLM-powered agents, and Agno for scalable, multi-agent systems.
What does a human-in-the-loop AI agent workflow look like?
Human-in-the-loop means humans can review, approve, or override agent decisions—adding oversight for compliance, ethics, and error correction.
How can businesses measure ROI for agentic AI?
Track metrics like time saved, cost reduction, error rates, process speed, and business outcomes; compare before-and-after adoption baseline data.
What are the risks or challenges with deploying AI agents?
Challenges include managing bias, ensuring transparency, navigating compliance, and avoiding over-automation without human checks and balances.
How is “agentic AI” different from standard AI assistants or chatbots?
Agentic AI can take autonomous, multi-step actions, often coordinating across systems, while chatbots typically answer simple queries without taking broader action.
Are there open-source examples of AI agents in action?
Yes, repositories like GitHub host open-source agent frameworks and code bases, enabling organizations to experiment and build custom solutions.
Conclusion: The Business Case for Embracing AI Agents
AI agent use cases are rapidly reshaping how organizations operate, compete, and scale across industries. By enabling autonomous decision-making, continuous optimization, and coordinated workflows, agentic AI delivers tangible improvements in efficiency, accuracy, and business agility that traditional automation cannot match.
Realizing this value requires more than experimentation. Leaders must focus on selecting use cases with clear business impact, embedding ethical governance and human oversight, and choosing frameworks that support reliability, security, and long-term scalability. Successful adoption is driven by disciplined pilots, measurable outcomes, and teams equipped to manage and evolve agent-driven systems.
Organizations that approach AI agents with this strategic mindset are better positioned to move beyond incremental gains, transform core operations, and sustain competitive advantage as automation continues to evolve.
Key Takeaways
- AI agents offer adaptive, autonomous solutions far beyond traditional automation, excelling in complex, multi-step workflows.
- High-ROI use cases span HR, finance, healthcare, retail, IT, manufacturing, energy, and legal operations.
- Leading agentic AI frameworks include CrewAI, AutoGen, and Agno; pick based on scalability and business fit.
- Implementation success hinges on value-focused use case selection, robust human oversight, and clear ROI tracking.
- Governance, ethics, and transparency are essential for safe, compliant, and sustainable AI agent deployment.
This page was last edited on 4 February 2026, at 2:00 pm
Contact Us Now

Contact Us Now
Start a conversation with our team to solve complex challenges and move forward with confidence.










