- What is Natural Language Processing (NLP)?
- How Does Natural Language Processing (NLP) Work?
- Types of Natural Language Processing (NLP) Based on Function
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) Models
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) Techniques
- Examples of NLP Techniques and Applications
- Why is Natural Language Processing (NLP) Important?
- Benefits of Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- Challenges of Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- The Evolution of Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- How To Get Started in Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- Future Scopes in Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a vital area of artificial intelligence (AI) that allows machines to understand, interpret, and generate human language. By leveraging NLP, computers can process large amounts of natural language data, from text to speech, enabling them to perform tasks like translation, sentiment analysis, and chatbot conversations.
NLP combines linguistics, computer science, and AI, making it an interdisciplinary field with diverse applications. From voice assistants like Siri and Alexa to machine translation systems like Google Translate, NLP is all around us, shaping the way we interact with technology.
In this article, we’ll dive into the core concepts of NLP, explore its techniques and applications, and discuss its evolution and future potential in the AI landscape.
What is Natural Language Processing (NLP)?
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a subfield of artificial intelligence that focuses on the interaction between computers and human language. It enables machines to understand, interpret, and generate text or speech in a way that is both meaningful and contextually relevant. NLP combines techniques from linguistics, machine learning, and computer science to process and analyze vast amounts of natural language data.
At its core, NLP involves the development of algorithms that can recognize patterns in language data, extract meaning, and make decisions based on that understanding. It encompasses a wide range of tasks, from simple functions like spell-checking to more complex applications such as translating languages or generating human-like responses in chatbots.
The ultimate goal of NLP is to enable machines to perform tasks that require human-like language comprehension. These tasks can range from understanding the sentiment of a tweet to creating an entire news article. NLP bridges the gap between human communication and machine interpretation, making it one of the most exciting and rapidly evolving fields in AI today.
How Does Natural Language Processing (NLP) Work?
NLP operates through several stages that transform raw language data into usable information for machines. These stages can vary depending on the task at hand, but they generally involve data preprocessing, feature extraction, algorithm development, and model training. Here’s a closer look at each step:
1. Data Preprocessing
The first step in NLP is to clean and prepare the text data. Since human language is often messy, containing slang, typos, and various forms of expressio,n data preprocessing helps standardize the input before analysis. This stage can involve:
- Tokenization: Breaking down text into smaller chunks, such as words or sentences, which are easier for machines to process.
- Removing stop words: Words like “and,” “the,” and “in” are often removed since they don’t add much meaning to the analysis.
- Lowercasing and normalizing: Converting all text to lowercase to avoid duplication (e.g., “AI” and “ai” being treated as the same word).
- Lemmatization and stemming: Reducing words to their root form to handle different variations (e.g., “running” becomes “run”).
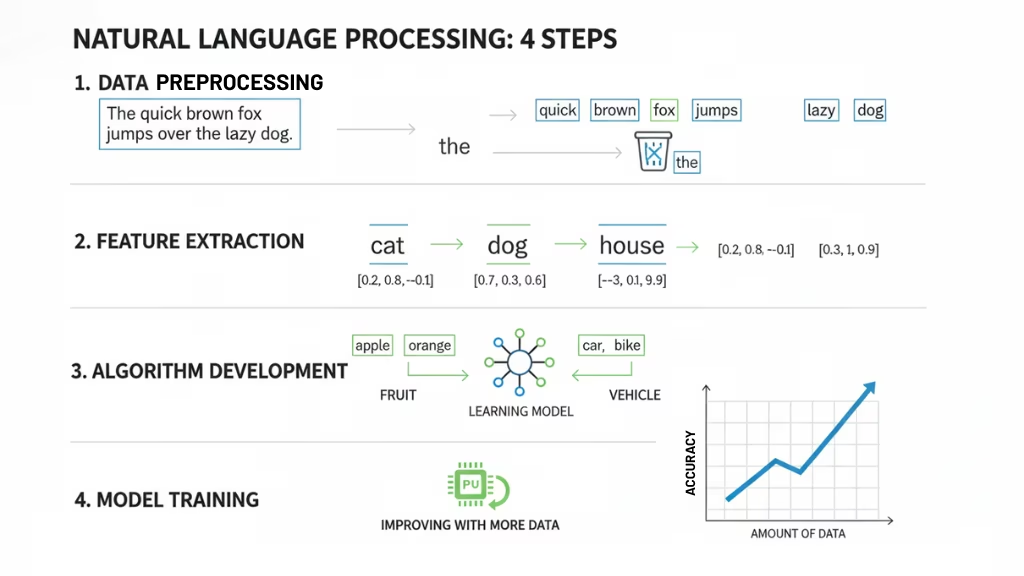
2. Feature Extraction
Once the data is cleaned, the next step is to extract features key pieces of information from the text that can be analyzed. Common feature extraction techniques include:
- Bag of Words (BoW): Representing text as a collection of words without considering the order.
- TF-IDF (Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency): A statistical measure used to evaluate how important a word is to a document in a collection.
- Word embeddings: Techniques like Word2Vec or GloVe transform words into vectors, capturing their semantic meaning and relationships with other words.
3. Algorithm Development
With preprocessed data and extracted features, the next step is to develop algorithms that can process the language data and make predictions. Depending on the task, these algorithms may include:
- Supervised learning: Training a model on labeled data (e.g., categorizing emails as spam or not).
- Unsupervised learning: Analyzing data without predefined labels (e.g., topic modeling to find themes in large corpora).
- Deep learning: More advanced techniques that use neural networks to model complex patterns in language.
4. Model Training
Once the algorithm is selected, it needs to be trained using the prepared data. During training, the model adjusts its parameters to minimize errors and improve its accuracy in performing tasks like text classification, sentiment analysis, or named entity recognition (NER). The more data a model is exposed to, the better it can learn to make accurate predictions and improve its performance.
Types of Natural Language Processing (NLP) Based on Function
NLP can be categorized into two main types based on the function it serves: Natural Language Understanding (NLU) and Natural Language Generation (NLG). Each of these functions focuses on a different aspect of processing human language and is used for distinct purposes within NLP systems.
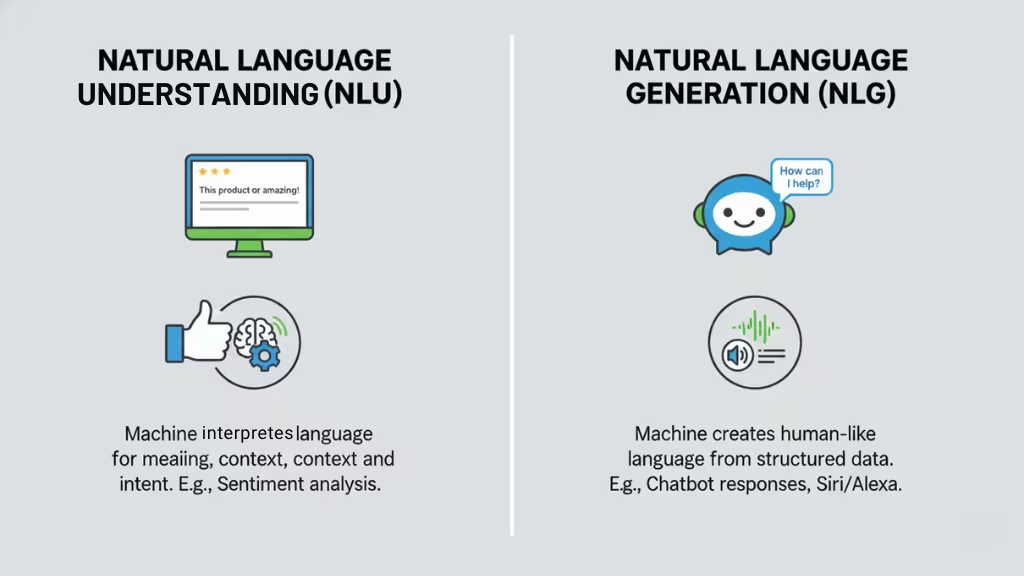
Natural Language Understanding (NLU)
Natural Language Understanding (NLU) is the process by which machines interpret and comprehend human language. The goal of NLU is to understand the meaning behind words, phrases, and sentences in a way that is contextually relevant.
NLU helps machines interpret what a text means, going beyond just the words themselves to understand context, intent, and structure. For example, when reading a review, NLU can help identify whether the review is positive or negative based on its content.
Natural Language Generation (NLG)
In contrast to NLU, Natural Language Generation (NLG) is the process by which machines create human-like language from structured data. NLG systems generate text or speech that mimics natural human language, making it useful for applications like content creation, chatbots, and automated report writing.
NLG focuses on producing language that is coherent and contextually appropriate. It enables applications that require the machine to not just understand text, but also to create meaningful responses or content based on that understanding.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) Models
NLP models are the tools that help computers understand and work with human language. Over time, these models have changed a lot. Here are the main types of NLP models:
Symbolic NLP
Symbolic NLP, also called rule-based NLP, was one of the first ways computers tried to understand language. This method uses a set of rules to process text. For example, if a computer needs to figure out if a word is a noun or a verb, it follows specific rules about how those words work in sentences.
While this approach was useful in its time, it has limitations. It can be very rigid if the text doesn’t exactly follow the rules, the system might not work well. Also, it takes a lot of time and effort to write all these rules by hand. It also struggles to understand the many different ways humans use language in everyday life.
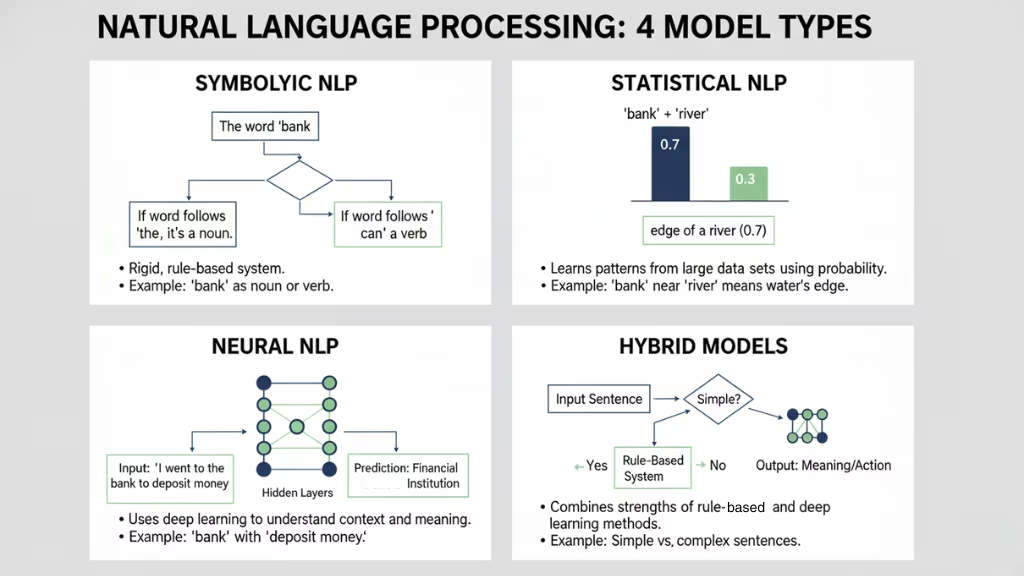
Statistical NLP
Statistical NLP is a step forward from rule-based systems. Instead of relying on rules, statistical models learn patterns from large amounts of text. These models use probability (the chance of something happening) to make decisions. For example, it might look at a huge number of sentences to figure out which words usually go together.
This approach is better than symbolic NLP because it can handle more types of language without needing so many rules. But it still doesn’t understand the deeper meaning of language. It can get the patterns right but might miss the context or true meaning of a sentence.
Neural NLP
Neural NLP is the most advanced model and is based on neural networks, which are inspired by the way the human brain works. These models are great at learning from large amounts of data and can understand language much better than earlier models.
Neural NLP uses a technique called the Transformer model, which is behind some of the most powerful language models today, like BERT and GPT. These models are good at understanding long sentences and figuring out the meaning behind words based on the context. For example, it can understand that the word “bank” means a place for money in one sentence and the edge of a river in another, just by looking at the surrounding words.
However, neural models need a lot of data and computing power to work well, so they can be expensive and slow to train.
Hybrid Models
Hybrid models mix different methods to get the best results. For example, a hybrid model might use rule-based methods for simple tasks and neural networks for more complex ones. This approach combines the strengths of all the different methods and can help solve problems more efficiently.
Hybrid models are still being developed, and researchers are working on improving them to make them even more powerful.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) Techniques
NLP techniques can be divided into two main categories: semantic techniques and syntactic techniques. These techniques are used to help computers understand, interpret, and generate human language.
Semantic Techniques
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Machine Translation | Automatically converting text or speech from one language to another. |
| Sentiment Analysis | Determining the emotional tone behind a body of text, such as positive, negative, or neutral. |
| Named Entity Recognition (NER) | Identifying entities like names, locations, or dates within text. |
| Summarization | Creating a concise version of a longer text while retaining key points. |
| Topic Modeling | Discovering abstract topics within a collection of text data. |
| Word-sense Disambiguation | Determining the meaning of a word based on its context in a sentence. |
| Chatbots | Generating responses in a conversation, such as in virtual assistants or customer support bots. |
| Information Extraction | Extracting useful information from unstructured text, like pulling data from documents. |
| Semantics | The study of meaning in language, often used to resolve ambiguities and provide context. |
| Neural NLP Feature Extraction | Using deep learning models to extract features from raw data, transforming text into usable input. |
| Information Retrieval | The process of retrieving relevant information from large datasets based on user queries. |
| Question Answering | Using NLP techniques to generate accurate answers based on text data or a knowledge base. |
| Text Classification | Classifying text into predefined categories such as spam detection or sentiment analysis. |
| Text Generation | Creating text based on a prompt, like generating a news article or completing a sentence. |
| Language Generation | Generating natural-sounding language that is contextually relevant and coherent. |
| Artificial Intelligence | A broad concept encompassing techniques and models that simulate human-like understanding and generation of text. |
Syntactic Techniques
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Parsing | Analyzing the grammatical structure of a sentence to identify the relationships between words. |
| Word Segmentation | Dividing text into individual words or meaningful units, especially in languages without spaces. |
| Morphological Segmentation | Breaking words down into their base form (e.g., ‘running’ becomes ‘run’). |
| Sentence Breaking | Identifying sentence boundaries, crucial for tasks like summarization or translation. |
| Part-of-Speech (POS) Tagging | Identifying the grammatical role of each word in a sentence (e.g., noun, verb). |
| Tokenization | Splitting text into smaller units, like words or phrases, for further analysis. |
| Lemmatization | Converting words to their base form while considering context, such as changing ‘better’ to ‘good’. |
| Stemming | Chopping off word endings to obtain a base form (e.g., ‘running’ becomes ‘run’). |
| Stop Word Removal | Removing common words (like ‘and’, ‘the’) that don’t contribute significant meaning to analysis. |
| Text Preprocessing | Cleaning and preparing text data for analysis by removing noise, formatting inconsistencies, etc. |
| Speech Recognition | Converting spoken language into written text, commonly used in voice assistants and transcription. |
Examples of NLP Techniques and Applications
Natural Language Processing (NLP) has a wide array of practical applications across different industries, significantly enhancing the way we interact with technology. Below are some of the most common NLP techniques in action:
Email Filters
NLP is widely used in email applications to filter spam. By analyzing the content of emails and detecting patterns that indicate spam (such as certain keywords, phrases, or structures), NLP can automatically classify messages as either spam or legitimate.
This technique helps users save time and avoid potential security risks. Advanced spam filters also use NLP to detect phishing attempts, ensuring that users are protected from fraudulent emails.
Smart Assistants
Virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant rely heavily on NLP to process voice commands and provide relevant responses. NLP allows these assistants to understand spoken language, convert it into text, analyze the meaning, and generate appropriate actions or answers.
Whether setting reminders, playing music, or controlling smart home devices, NLP helps these systems engage in natural conversations with users.
Search Results
Search engines like Google and Bing use NLP techniques to improve the relevance of search results. Through NLP, these engines can understand the intent behind a search query, rather than just matching keywords. For example, when you search for “best restaurants near me,”
NLP helps the engine understand that you are looking for local dining options and can return the most relevant results based on location, ratings, and user preferences.
Predictive Text
Predictive text uses NLP to predict the next word or phrase while typing on your phone, making text input faster and more efficient.
Whether in emails, text messages, or social media posts, this technique analyzes previous words to suggest the most likely next word or phrase, reducing errors and speeding up the writing process.
Language Translation
Machine translation systems, such as Google Translate, use NLP to translate text from one language to another. These systems rely on NLP techniques such as statistical translation models and neural machine translation to ensure that the meaning and context of the original text are accurately conveyed in the target language.
NLP helps handle nuances, idioms, and syntax differences between languages, making real-time translation possible.
Digital Phone Calls
NLP is used in voice response systems for customer service, where the system automatically answers calls and processes queries. Techniques like speech recognition and sentiment analysis are used to understand the caller’s request and provide relevant information or transfer them to the appropriate human agent.
For example, many companies use NLP-driven automated systems to process customer support calls, providing efficient service for routine inquiries and reducing wait times.
Data Analysis
NLP is also used in data analysis to process large volumes of unstructured text data. Businesses use NLP to analyze customer feedback, social media posts, and product reviews.
This analysis can reveal valuable insights into customer sentiment, emerging trends, and potential issues. By extracting actionable data from these sources, businesses can make informed decisions and improve their products or services.
Text Analytics
Text analytics is a powerful application of NLP that involves analyzing and interpreting large amounts of text data to extract meaningful information. Businesses use text analytics to monitor social media for brand mentions, analyze customer feedback for product improvements, or even track public opinion on political issues.
NLP helps automate the extraction of insights from unstructured text data, allowing companies to react more quickly to emerging trends or customer needs.
Why is Natural Language Processing (NLP) Important?
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a key technology that helps computers understand, interpret, and generate human language. It’s important for several reasons:
Improves Human-Machine Communication
NLP makes it possible for computers to understand and respond to us in natural language the way we speak or write every day. Without NLP, we’d be limited to using structured commands or programming languages to communicate with machines. With NLP, we can interact with devices using everyday language, making technology easier and more accessible. For example, voice assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant allow us to use simple speech commands to get things done.
Boosts Automation and Efficiency
NLP helps automate routine tasks that would normally require humans to do manually. For instance, customer service chatbots powered by NLP can handle common questions, freeing up human agents to focus on more complex issues. NLP can also quickly analyze large amounts of text, such as emails or social media posts, saving time for businesses and employees. This makes operations faster and more efficient across industries like customer support, marketing, and finance.
Unlocks Insights from Big Data
Every day, massive amounts of unstructured text data are created, from social media posts to customer feedback. NLP helps us make sense of all this data by automatically analyzing it and finding meaningful patterns. With NLP, businesses can track trends, measure customer sentiment, and spot potential problems. This gives organizations the insights they need to make better decisions and respond quickly to customer needs.
Enhances Accessibility
NLP also plays a crucial role in making digital content more accessible to people with disabilities. For example, speech-to-text technology allows individuals with hearing impairments to read spoken words, while text-to-speech helps those with visual impairments understand written content. Additionally, NLP-driven machine translation breaks down language barriers, enabling people to access information in different languages and communicate more easily with others around the world.
Enables More Natural Communication
One of NLP’s greatest strengths is its ability to understand language in context. This means machines can interpret the meaning behind words and phrases, even when they have multiple meanings or are used in a specific way. For example, NLP helps determine the sentiment (positive, negative, or neutral) of text, or translate a sentence while keeping its original tone and meaning. This contextual understanding makes interactions with technology feel more natural, whether it’s through chatbots, voice assistants, or content recommendations.
In short, NLP is essential for making human-machine interactions smoother, faster, and more intuitive. It’s transforming industries, from customer service to data analysis, and is a driving force behind advancements in artificial intelligence.
Benefits of Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural Language Processing (NLP) offers a wide range of benefits that are transforming industries and improving everyday experiences for individuals. Below are some of the key advantages of NLP:
1. Improved Efficiency and Productivity
NLP automates repetitive language-based tasks, saving time and increasing productivity. For example, NLP-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can handle customer queries 24/7, reducing the workload on human agents.
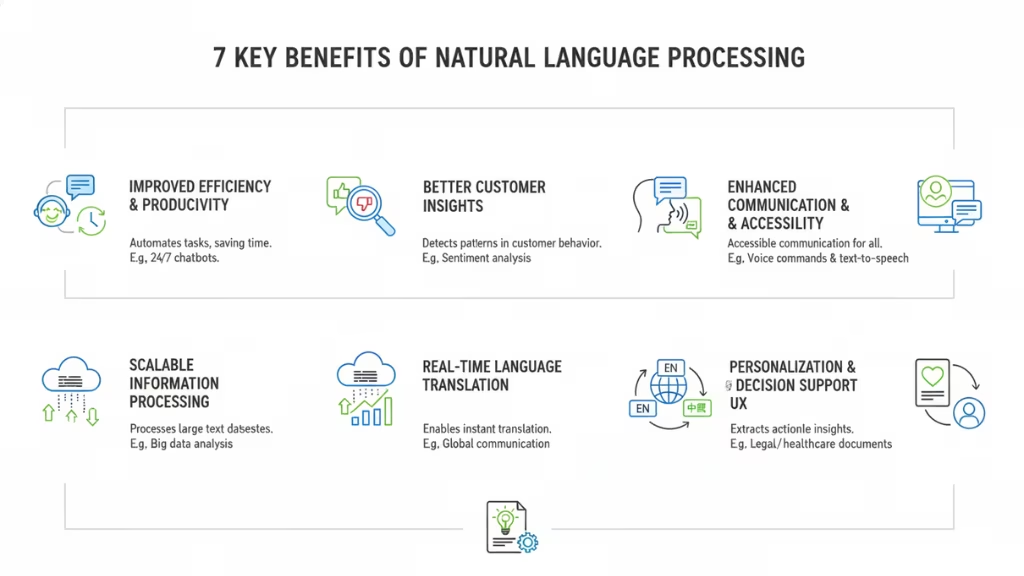
2. Better Customer Insights
NLP helps businesses gain valuable insights into customer behavior and sentiment. By analyzing large volumes of customer feedback, reviews, or social media posts, NLP tools can detect patterns and emotions, allowing businesses to understand customer preferences, identify pain points, and improve products or services.
3. Enhanced Communication and Accessibility
NLP has made communication more accessible and intuitive. Speech recognition and text-to-speech technologies allow people with disabilities to interact with devices using voice commands or to convert text into audio.
4. Scalable Information Processing
As the amount of unstructured text data continues to grow exponentially, NLP enables businesses to process and analyze this data at scale. Whether it’s analyzing customer feedback, legal documents, research papers, or social media posts, NLP algorithms can quickly process vast amounts of text to extract meaningful insights.
5. Real-Time Language Translation
Machine translation has advanced significantly thanks to NLP, allowing for real-time language translation. This is particularly useful in global business operations, where teams from different parts of the world need to collaborate or when interacting with customers in various languages.
6. Personalization and Enhanced User Experience
NLP enables systems to understand user preferences and behavior, leading to more personalized experiences. For example, recommendation systems on e-commerce platforms, video streaming services, and social media sites use NLP to analyze user interactions and make recommendations tailored to individual tastes.
7. Knowledge Extraction and Decision Support
NLP plays a significant role in knowledge extraction, where systems automatically gather useful information from unstructured data sources. This can be applied in fields like law, healthcare, and finance, where professionals need to extract critical information from vast amounts of documents.
Challenges of Natural Language Processing (NLP)
While NLP has made tremendous advancements, it still faces several challenges that limit its accuracy and effectiveness in certain contexts. Below are some of the key challenges in NLP:
1. Ambiguity and Context Understanding
One of the biggest challenges in NLP is dealing with the ambiguity of human language. Words and sentences can have multiple meanings depending on the context. For example, the word “bank” can refer to a financial institution or the side of a river.
NLP models must rely on context to understand the correct meaning, but this is not always straightforward. Even advanced models struggle with ambiguous phrases, idiomatic expressions, or words that are used differently in various regions or cultures.
2. Sarcasm and Figurative Language
Detecting sarcasm, irony, and figurative language remains a significant hurdle in NLP. Human language often involves subtle tones and meanings that aren’t always directly conveyed through the words themselves.
For instance, the phrase “Great job!” can be positive or sarcastic depending on tone and context. NLP models often fail to detect sarcasm, which can lead to misinterpretations, especially in sentiment analysis or social media monitoring, where tone plays a big role.
3. Diversity of Language and Dialects
NLP systems face difficulties when dealing with language diversity. While they can perform well in languages with large datasets (like English), they struggle with languages that have less digital presence or are less standardized. Dialects, slang, and regional variations add further complexity, making it harder to create universal models.
For instance, a model trained on British English might not perform as well when processing American English or regional English dialects, let alone languages with completely different grammatical structures like Arabic, Chinese, or Hindi.
4. Lack of Sufficient Data for Training
Modern NLP models require large datasets for training, but not all languages or applications have enough data available. For example, while English has a wealth of textual data, languages like Swahili or Maori may not have sufficient corpora to build accurate models.
This lack of data can lead to underperforming models, especially in low-resource languages or specialized domains (e.g., legal or medical text).
5. Ethical and Bias Issues
NLP systems can inherit biases present in the data they are trained on. If a model is trained on biased or unrepresentative data, it can perpetuate or even amplify those biases.
For example, models may produce skewed results in sentiment analysis or decision-making systems if the data reflects societal biases related to gender, race, or other factors. Bias detection and mitigation remain active areas of research to make NLP systems more fair and equitable.
6. Computational Resources and Cost
Training state-of-the-art NLP models, especially deep learning models, requires immense computational resources. Large models like GPT-3 or BERT require specialized hardware (such as GPUs) and substantial energy consumption to train.
These resources can be cost-prohibitive for smaller companies and organizations. Even after training, running these models at scale requires significant infrastructure, making NLP accessible primarily to large corporations or institutions with the necessary funding.
7. Evaluation and Metrics
Evaluating the performance of NLP systems can be tricky. Unlike tasks like image recognition, where success is often more straightforward (e.g., identifying objects in images), NLP tasks require a nuanced understanding of context, meaning, and intent.
Standard metrics like accuracy or F1 score may not fully capture a model’s ability to understand language in a human-like way. As a result, evaluating the success of NLP systems can be subjective and complex, especially for tasks like text generation, where output quality is harder to quantify.
8. Real-Time Processing Challenges
While NLP has made significant strides, processing text in real-time can still present challenges, especially for applications that require low-latency responses. For instance, live chatbots, customer service applications, and voice assistants must process and respond to user input instantly.
The Evolution of Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural Language Processing (NLP) has come a long way since it first began. Over the years, the way computers understand and work with human language has improved a lot. Let’s take a look at how NLP has evolved over time:
| Years | History of Natural Language Processing (NLP) |
|---|---|
| 1950s | The Beginning of NLP: In the 1950s, scientists started experimenting with making computers understand language. One of the first big projects was a machine translation system that tried to translate Russian into English, but the computers only followed basic rules and didn’t truly understand the language. |
| 1950s–1990s | Rule-Based Systems: Researchers used pre-written rules, known as symbolic NLP, to understand language. These systems worked based on grammar rules but couldn’t handle the messiness of human language like slang or words with multiple meanings. They struggled to understand context or variations in language. |
| 1990s | Statistical NLP: The approach shifted to statistical NLP, where computers learned from examples, not just rules. Computers learned language patterns from real data, like how words relate to each other in sentences, making them better at understanding language. Still, it was hard to grasp the context of words. |
| 2000–2020s | Deep Learning Revolution: Deep learning, a type of AI, improved NLP models, especially with the introduction of Transformers. Models like BERT and GPT could understand language more accurately and faster, enabling them to perform tasks like translation, answering questions, and generating human-like text. |
| 2020s | NLP Today: Advanced models like GPT-3 are now capable of generating human-like text, writing essays, and even creating code. The development of multimodal AI, which understands not just words but also images and sounds, is making computers smarter, though challenges like bias and misunderstanding sarcasm still exist. |
How To Get Started in Natural Language Processing (NLP)
If you’re interested in diving into the world of Natural Language Processing (NLP), whether as a developer, researcher, or business leader, there are several key steps to get started. While NLP can be complex, there are plenty of resources and tools available to help you learn the fundamentals and start building your own NLP applications.
1. Learn the Basics of Linguistics and Machine Learning
Understanding the foundations of language and machine learning is crucial when starting with NLP. Some of the key concepts you should familiarize yourself with include:
- Linguistics: Learn about basic linguistic concepts such as syntax (sentence structure), semantics (meaning), morphology (structure of words), and phonetics (speech sounds). This knowledge helps you understand how language works and how to process it computationally.
- Machine Learning: NLP relies heavily on machine learning, particularly supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and deep learning. Learn about basic machine learning algorithms (e.g., regression, classification, clustering) and how they are applied to NLP tasks like sentiment analysis, text classification, and clustering.
2. Get Hands-On with NLP Tools and Libraries
Once you have a basic understanding of the concepts, it’s time to start applying what you’ve learned. Several powerful libraries and tools are available for NLP tasks, many of which are open-source and easy to use for beginners.
- NLTK (Natural Language Toolkit): NLTK is one of the most widely used Python libraries for NLP. It provides easy access to linguistic resources and a suite of tools for text processing, classification, and analysis.
- spaCy: spaCy is another popular Python library designed for industrial-strength NLP. It’s fast and efficient, making it ideal for building production-level applications. spaCy also integrates with deep learning libraries like TensorFlow and PyTorch for more advanced NLP tasks.
- Hugging Face Transformers: Hugging Face has become the go-to platform for pre-trained language models like BERT, GPT-2, T5, and RoBERTa. These models can be fine-tuned for a variety of NLP tasks, from text generation to machine translation.
3. Work on Projects and Build Practical Applications
The best way to learn NLP is by working on projects. Whether you’re developing a simple chatbot, performing sentiment analysis on social media posts, or building a machine translation model, hands-on experience will solidify your knowledge and help you understand how to apply NLP in real-world scenarios.
Here are some project ideas to get started:
- Text Classification: Build a model that classifies text (e.g., spam detection in emails, sentiment analysis of product reviews).
- Chatbot Development: Create a simple chatbot using an NLP framework like Rasa or build one from scratch using a sequence-to-sequence model.
- Named Entity Recognition (NER): Develop a system that identifies entities like names, dates, and locations from news articles or business reports.
4. Dive Into Deep Learning and Pretrained Models
As you progress, you’ll encounter deep learning techniques, which have become essential in NLP. Deep learning allows models to learn from large datasets and solve complex problems, such as generating human-like text or translating languages. You’ll need to familiarize yourself with concepts like artificial neural networks, convolutional neural networks (CNNs), and recurrent neural networks (RNNs).
To make things easier, there are pretrained models available for nearly every NLP task. For instance, Hugging Face offers pretrained transformer models that you can fine-tune for your specific application. These models, like GPT-3 and BERT, have been trained on massive datasets and have already learned language patterns, allowing you to build advanced NLP systems with minimal data and computational power.
5. Join NLP Communities and Stay Updated
NLP is an ever-evolving field, with new techniques, tools, and research emerging constantly. Join communities, follow research papers, and participate in forums like Stack Overflow, GitHub, and Reddit’s NLP subreddits. Keeping up with the latest trends and engaging with others in the field will help you stay at the cutting edge of NLP advancements.
Some popular resources for staying updated include:
- ArXiv.org for NLP papers and research.
- Kaggle for NLP competitions and datasets.
- Medium for blog posts and tutorials from industry professionals.
6. Online Courses and Certifications
If you prefer a structured approach to learning, several online platforms offer in-depth courses on NLP. Many of these courses provide hands-on experience and real-world examples that are essential for building your skills. Some popular platforms include:
- Coursera: Offers courses like the NLP Specialization from DeepLearning.AI and NLP with Python.
- Udemy: Features a variety of NLP courses, ranging from beginner to advanced levels.
- edX: Provides courses on NLP from institutions like MIT and Harvard.
- Fast.ai: Offers practical deep learning courses, including NLP applications using deep learning.
By following these steps and continually practicing, you can develop a strong foundation in NLP and apply your knowledge to build innovative projects and solutions.
Future Scopes in Natural Language Processing (NLP)
The field of Natural Language Processing (NLP) is rapidly advancing, with new research, technologies, and applications constantly emerging. As NLP continues to evolve, it will have an even greater impact on a variety of industries and create new opportunities for both businesses and individuals. Below are some of the most exciting future directions for NLP:
1. Multimodal NLP
While current NLP systems primarily process text, the future of NLP is shifting towards multimodal models that combine multiple forms of input data, such as text, images, and even sound. These models can process not only written language but also visual and auditory information, enabling more dynamic and sophisticated interactions. For example, a multimodal system could analyze a photo, understand the objects within it, and describe the scene in natural language.
This opens up new possibilities for applications in areas like autonomous driving, assistive technologies, and robotics, where multiple types of data must be integrated to understand the context fully.
2. Language Models as General AI
Large pre-trained language models like GPT-3 and BERT have already demonstrated remarkable capabilities in a wide range of tasks, from language generation to machine translation. As these models continue to improve, we may see them evolve into more generalized systems that can handle even broader AI tasks, such as reasoning, decision-making, and problem-solving across multiple domains.
In the future, these models could become the foundation of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) systems that can perform any intellectual task that a human can.
3. Real-Time NLP Applications
With advancements in computational power and model efficiency, real-time NLP systems will become more prevalent. Currently, applications like voice assistants or real-time translation still face challenges in delivering responses instantly while maintaining high accuracy.
However, as technology improves, we can expect more seamless real-time communication in various languages, improved virtual assistants, and more responsive chatbots that can engage in complex, live conversations. Real-time sentiment analysis could also be used for customer service or market research, providing immediate feedback from customers or social media interactions.
4. Enhanced Multilingual NLP
While NLP models currently perform well in languages like English, significant progress is needed to improve NLP for low-resource languages. The future of NLP will see more accurate and accessible models for languages that are not well-represented in digital spaces.
Multilingual models that can efficiently handle multiple languages in a single framework (e.g., mBERT and XLM-R) will become more sophisticated, enabling broader global communication and interaction. These advancements will help bridge language barriers and improve services in regions with diverse linguistic needs.
5. Ethical NLP and Bias Mitigation
One of the most pressing issues in the future of NLP is addressing bias and fairness. As NLP systems are trained on data that reflects societal biases, there is a growing concern about models perpetuating harmful stereotypes or discriminatory behavior.
Future research will focus on developing fairer, more transparent NLP models that actively mitigate bias in language generation, sentiment analysis, and other tasks. This will be crucial in ensuring that NLP applications are equitable and ethical, particularly as they are adopted in sensitive areas like hiring, criminal justice, and healthcare.
6. NLP for Healthcare
In healthcare, NLP is poised to revolutionize the way we interact with medical records, research papers, and patient data. The future of NLP in healthcare includes automated medical diagnosis, where NLP models analyze patient records to suggest diagnoses or identify potential health risks.
NLP will also play a critical role in drug discovery by helping researchers quickly analyze vast amounts of scientific literature and medical journals to uncover new treatments. Additionally, clinical decision support systems powered by NLP will help doctors make more informed decisions based on patient data, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
7. Human-AI Collaboration
NLP will increasingly facilitate collaborations between humans and AI. Rather than replacing jobs, NLP systems will augment human capabilities by handling repetitive, language-based tasks and allowing humans to focus on more creative or complex work.
For example, in content creation, NLP can assist by generating drafts, analyzing trends, or performing research, while humans focus on refining the content and making strategic decisions. In the education sector, NLP-powered tools can support personalized learning experiences by understanding student queries and offering tailored content recommendations.
8. NLP for Legal and Financial Applications
The legal and financial sectors are already benefiting from NLP, but the future holds even more potential. NLP will be increasingly used to analyze legal contracts, financial documents, and regulatory filings, automating tasks like contract review and compliance checks.
In law, NLP can help lawyers find relevant precedents more efficiently, while in finance, it can help detect fraudulent activity or predict market trends based on textual data from news reports, financial statements, and social media.
Conclusion
Natural Language Processing (NLP) has become an essential part of artificial intelligence, enabling machines to understand, interpret, and generate human language in ways that were once thought impossible. From early rule-based systems to the advanced neural models of today, NLP has evolved significantly, and its applications are far-reaching, touching industries such as healthcare, finance, customer service, and beyond.
As NLP technology continues to advance, we can expect even more sophisticated models that are capable of understanding and interacting with human language in deeper, more meaningful ways. The rise of multimodal models, real-time applications, and more ethical NLP systems promises to revolutionize the field further and bring us closer to achieving true human-AI collaboration.
FAQs
What is Natural Language Processing (NLP)?
NLP is a subfield of artificial intelligence that focuses on the interaction between computers and human language. It enables machines to understand, interpret, and generate text or speech in a way that is both meaningful and contextually relevant.
What are the main types of NLP?
The two main types of NLP are Natural Language Understanding (NLU), which focuses on interpreting and comprehending human language, and Natural Language Generation (NLG), which focuses on generating human-like language from structured data.
How does NLP work?
NLP works through stages like data preprocessing, feature extraction, algorithm development, and model training. It uses linguistic and statistical techniques to analyze text data and learn patterns that can be applied to various language-related tasks.
What are some popular NLP tools?
Popular NLP tools and libraries include NLTK, spaCy, Hugging Face Transformers, and Gensim. These tools help with tasks like tokenization, sentiment analysis, named entity recognition, and text generation.
What are the challenges in NLP?
Some of the challenges in NLP include ambiguity, understanding context, handling multiple languages and dialects, addressing bias in models, and managing the computational resources required to train complex models.
What is an NLP model, and how does it differ from regular programming?
An NLP model is a machine learning model trained to understand and generate human language. Unlike traditional programming, where outputs are predefined by the programmer, NLP models are trained on data and adapt to new, unseen inputs, allowing them to generate or classify language based on learned patterns.
Can NLP systems really understand or read text like a human?
While NLP systems are very good at processing language, they do not “understand” text like humans do. They can identify patterns and context but lack the nuanced understanding that human cognition brings. However, as models evolve, they’re becoming increasingly capable of mimicking human-like language processing.
What are the hot topics in NLP right now?
Trending topics in NLP include multimodal models, where text is combined with image/audio processing. Knowledge graphs, prompt engineering, and models for low-resource languages are also gaining attention. Keep an eye on ethical NLP for fairness and transparency in machine learning.
What project should I build to start working with NLP?
Choose a practical problem to work on, such as email classification (spam or not), sentiment analysis for customer feedback, or even a simple chatbot. Start with pre‑trained models for easier implementation, then gradually incorporate more complex features as you progress.
This page was last edited on 2 December 2025, at 5:32 pm
Contact Us Now

Contact Us Now
Start a conversation with our team to solve complex challenges and move forward with confidence.










