In the IT world, Test-Driven Development (TDD) is a widely adopted methodology. TDD involves writing software test cases before developing the actual code, ensuring that the code functions correctly from the very beginning. Let’s explore TDD.
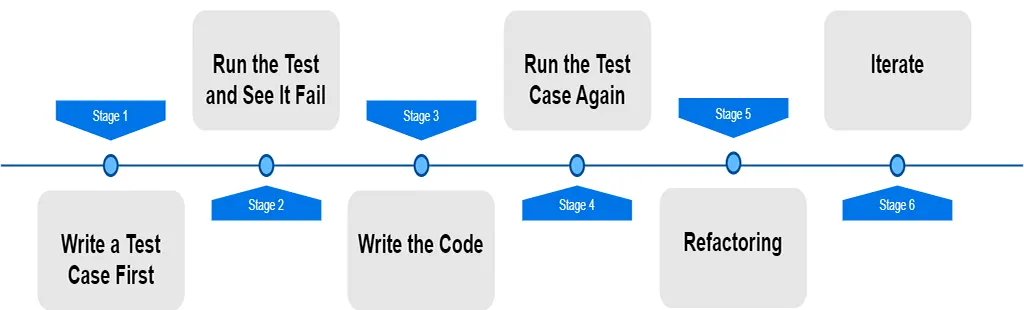
Steps of Test-Driven Development:
1. Write a Test Case First: Start by writing a test case for a small functionality. For example, we are adding two numbers. So first, we write a test to check if the function correctly adds two numbers. This test will check if 1 + 2 equals 3.
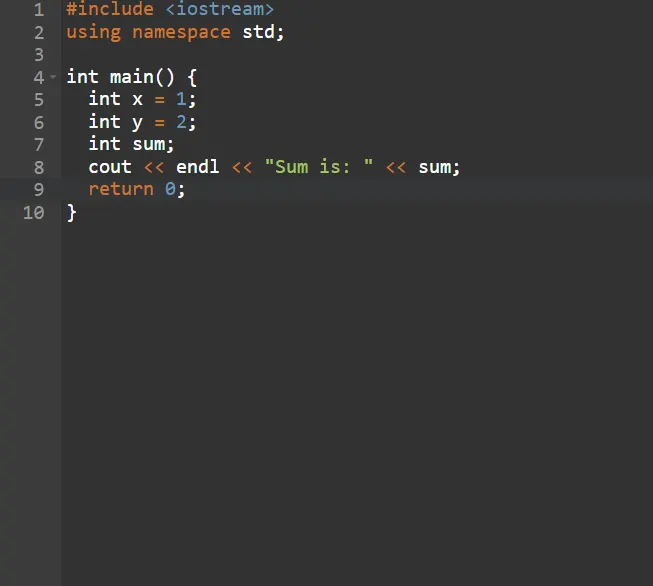
2. Run the Test and See It Fail: After writing the test case, run it. The test should fail initially since the actual code for the addition function hasn’t been written yet. Now, Compile and run the test. Since the add function has not been implemented yet, the code should fail to give the desired result.
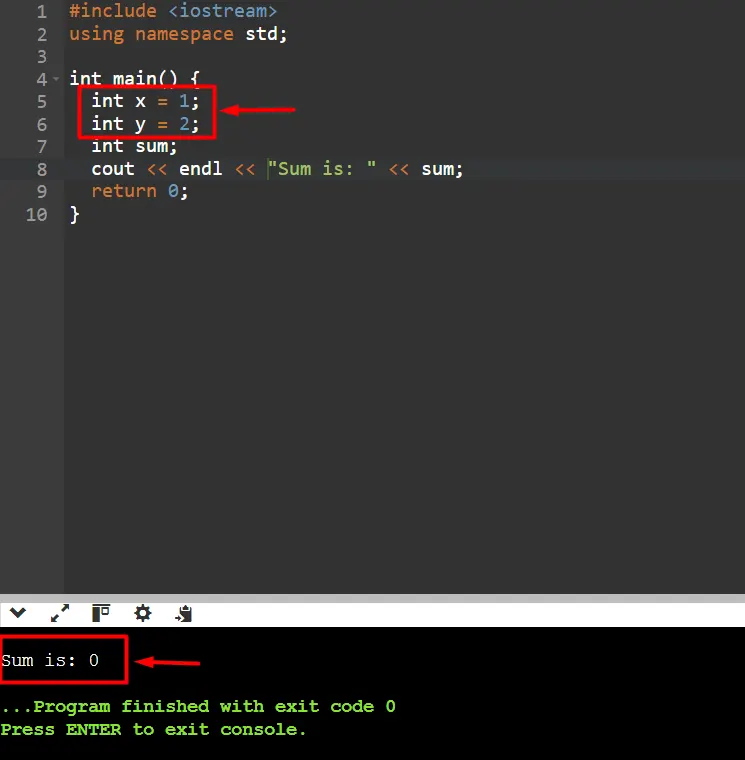
3. Write the Code: Write just enough code to pass the test. For the addition example, implement the addition function to correctly add two numbers and make sure all the libraries and environments are configured properly.
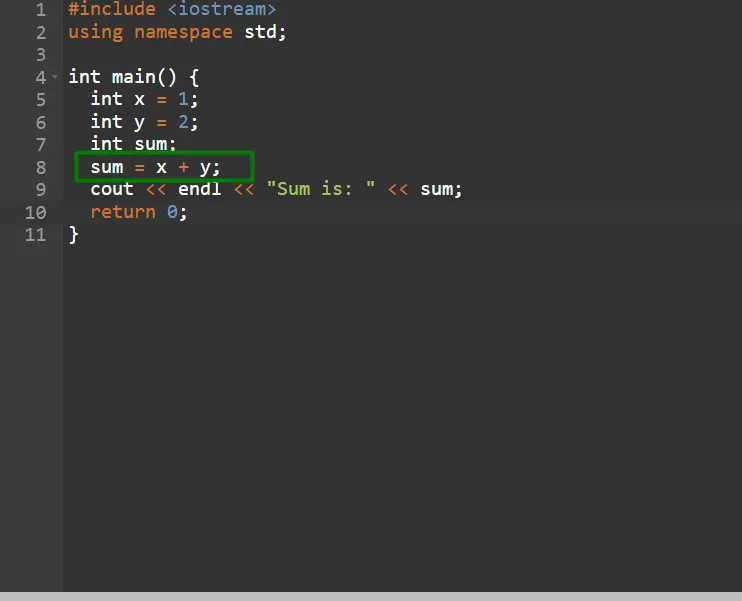
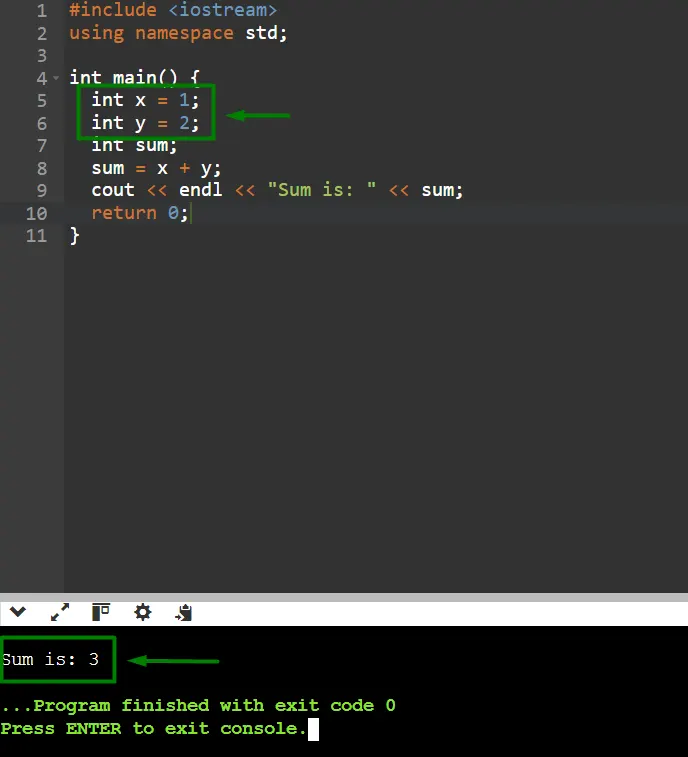
4. Run the Test Case Again: Re-run the test case. This time, the test should pass since the code now fulfills the test’s requirements. If it still fails, the code needs to be checked and corrected.
5. Refactor the Code: Once the test passes, clean up the code through refactoring. Refactoring improves code readability and maintainability without altering its behavior. In this simple case, the function might already be clear and concise, so refactoring may not be necessary.
6. Iterate: Repeat this cycle for every new feature added to the software. Continuously write test cases, run them, write code to pass the tests, and refactor.
Example Explanation:
- Test: The initial test covers the case of adding two positive numbers (1 + 2)
- Code: The Addition(+) operation is implemented to generate the sum of the two input numbers.
- Refactor: In this case, the function is straightforward, and no further refactoring is needed.
Effectiveness of Test-Driven Development:
1. Ensuring Code Quality: One of the main reasons TDD is effective is because it ensures high-quality code. When test cases are written before the code, Developers are forced to think carefully about what the code should do. So that they are less likely to make mistakes. As a result, the code has fewer bugs, and it works as expected.
2. Catching Errors Early: Errors are caught early in the development process since test cases are written first. This early detection is more efficient and cost-effective than finding errors later when the software is already in use.
3. Better Code Design: TDD encourages better code design. Because test cases are written first, they need to think about how to make the code easy to test. This usually leads to code that is more organized and easier to understand.
4. Confidence in Making Changes: With tests in place, developers can confidently modify or add new features without worrying that they will break existing functionality.
5. Continuous Feedback: TDD provides continuous feedback. Each test run gives immediate feedback on whether the code is working correctly, helping developers stay on track.
6. Easier Maintenance: Maintaining software becomes easier with TDD. It ensures that changes do not introduce new bugs, simplifying updates and keeping the software running smoothly over time.
7. Documentation: Test cases also serve as documentation, showing how the code is supposed to work. This is particularly helpful for larger teams or long-term projects.
Challenges of TDD:
While TDD has many benefits, it also has some challenges:
1. Time Investment: Writing test cases before coding can initially take extra time. However, this time is often recouped later due to fewer bugs and less rework.
2. Learning Curve: TDD can be challenging to learn, especially for developers unfamiliar with the process. It requires practice and discipline to master.
3. Discipline: Adhering to the TDD process consistently, requires discipline. The engineering team must continuously write test cases first and follow the cycle of testing and coding.
By writing their test cases, the engineering team can ensure that their code is thoroughly tested and meets the required specifications before it is considered complete. TDD has its challenges but its benefits in terms of code quality, error detection, and maintainability make it a valuable practice in software development.
This page was last edited on 28 July 2024, at 5:46 pm
Contact Us Now

Contact Us Now
Start a conversation with our team to solve complex challenges and move forward with confidence.











